Methods modulating immunoregulatory effect of stem cells
A technology of mesenchymal stem cells and cytokines, which is applied in the field of enhancing the immunosuppressive activity or immunostimulatory activity of mesenchymal stem cells, and can solve the problems of unclear basic mechanism in vivo
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0094] Materials and Methods
[0095] mice. Male C57BL / 6, C3H / HeJCr and F1 (C57BL / 6xC3H) mice aged 6-8 weeks were from the National Cancer Institute (Frederick, Md.). IFNγ-R1 - / - Mice and iNOS - / - Mice were from Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, Me.). Mice were maintained in the Robert Wood Johnson Medical School Vivarium. In each experiment, animals were matched according to age and sex, and all experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
[0096] reagent. Recombinant mouse IFNγ and TNFα, IL-1α, IL-1β monoclonal antibodies against mouse TNFα, IL-1α, IL-1β and CCR5, FITC-conjugated anti-mouse CD11b and PE-conjugated anti-mouse antibodies F4 / 80 was from eBiosciences (La Jolla, Calif.). Antibodies against IL-10 and TGF-β and recombinant mouse M-CSF were from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, Minn.). Anti-IFNγ was from Harlan (Indianapolis, Ind.). Anti-CXCR3 was from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, Calif.). Indomethacin, 1-methyl-DL-tryptophan (1-MT) and N...
Embodiment 2
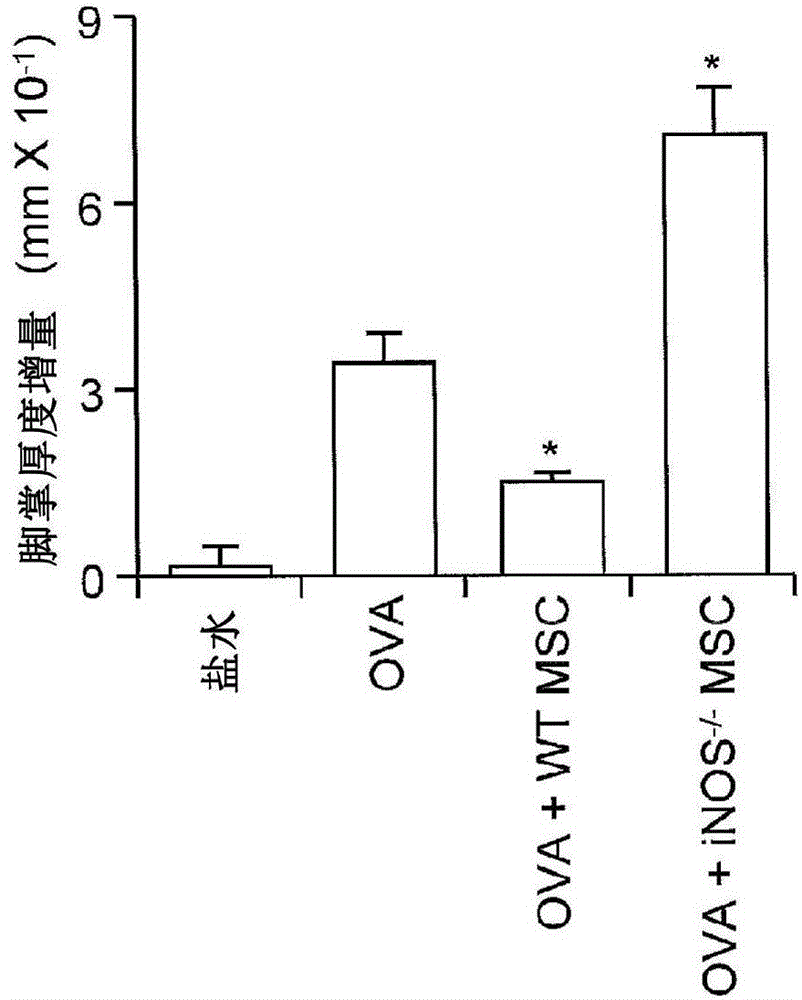
[0108] The immunosuppressive function of MSCs is induced by pro-inflammatory cytokines.
[0109] To identify underlying mechanisms, clones of mouse MSCs were employed. The stem cell properties of these clones are defined by their ability to differentiate into adipocytes or osteoblasts and their surface markers CD34; CD11b; CD11c; CD45; MHC class II; CD44 + ;Sca-1 + ; MHC class Il ow expression to limit. All results presented herein were replicated using at least three different MSC clones.
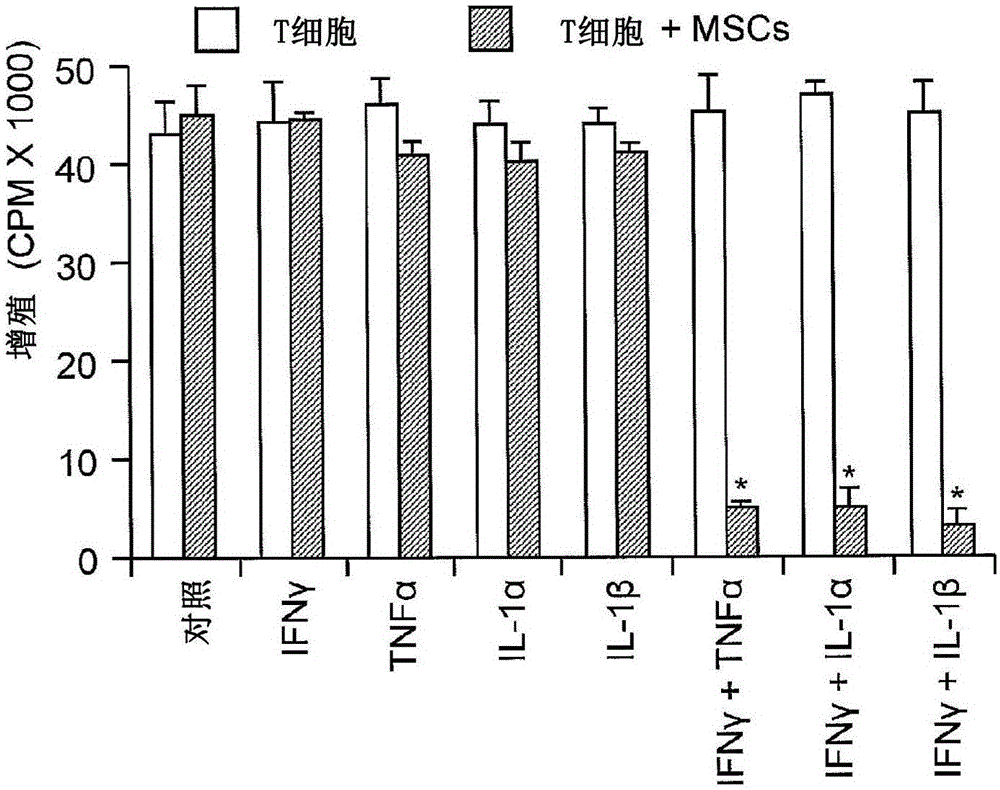
[0110] Since most of the reported studies of MSC-induced immunosuppression were based on their effects on T cell proliferation and cytokine production, the effect of MSCs on IL-2-driven proliferation of T cell blasts was first examined. fresh CD4 + T cell blasts are generated from splenocytes by activation with anti-CD3 followed by expansion with IL-2 for several days (Devadas et al. (2006) Immunity 25:237-247; Radvanyi et al. (1996) Cell Immunol. 170:260- 273). T cell blasts were a...
Embodiment 3
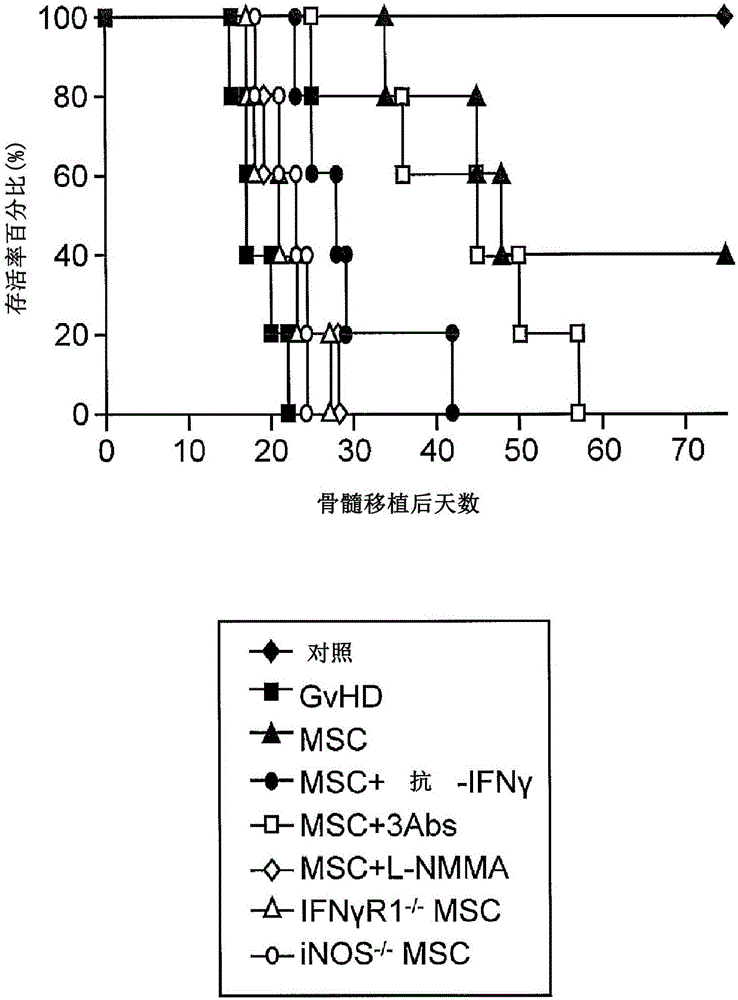
[0118] Nitric oxide is required for MSC-induced immunosuppression
[0119]To identify the mechanisms by which immunosuppression induced by cytokine-exposed MSCs is affected, the anti-CD3-activated splenocytes (1:20, MSC:splenocytes) co-cultured with MSCs in the TRANSWELL system were examined in various designs. reaction. When the two chambers of the pores were separated by a permeable membrane (0.4 μm pore membrane), MSCs had little effect on T cell proliferation, suggesting that membrane-associated proteins or other local acting factors are critical for T cell proliferation induced by cytokine-primed MSCs. Inhibition of cell proliferation is critical. Although it was recently reported (Sato et al. (2007) supra) that PGE-2, but not IDO, was required, PGE-2 was found not to be involved. Indeed, it was found that indomethacin (10 μM, a PGE-2 blocker), anti-IL-10 (20 μg / ml), anti-TGFβ (20 μg / ml) or 1-methyl-DL-tryptophan ( 1-MT, 1 mM, an IDO inhibitor) had no effect on MSC-ind...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com