Method for sorting transient severe faults of power system
A serious fault, power system technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, circuit devices, AC network circuits, etc., can solve the problem of automatic screening and setting of multiple faults without substantial solutions, without considering the stability of the post-inertia transient phase, and unsatisfactory The requirements for the development of power grid scale and other issues can achieve the effect of accurate and reliable generation of serious faults, ensure data reusability, and improve the scope of indicators.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
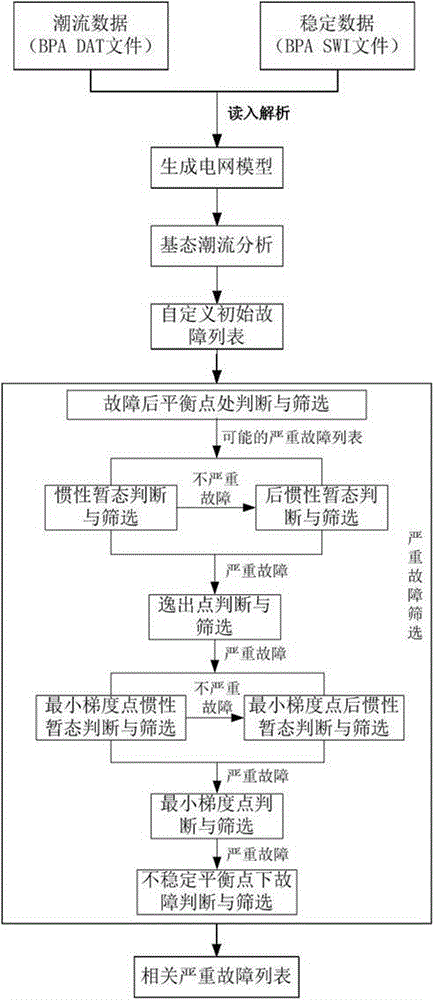
[0033]This embodiment provides a method for screening severe transient faults in power systems, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0034] Step S1: power flow data and stability calculation data;
[0035] Step S2: read and analyze the data in the step S1 to generate a grid model;
[0036] Step S3: Carry out the ground state power flow analysis according to the power grid model generated in step S2, and ensure the convergence of the power flow analysis calculation;
[0037] Step S4: forming an initial predefined fault;
[0038] Step S5: Judging and screening at the balance point after the fault;
[0039] Step S6: performing inertial transient judgment and screening on the faults judged and screened in step S5;
[0040] Step S7: Judging and screening the remaining faults in step S6 to perform post-inertia transient judgment and s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com