Method for calculating work load based on beam surface strain values measured by optical fiber sensors
A fiber optic sensor and workload technology, which is applied in the field of fiber optic sensing, can solve the problems of time-consuming, labor-intensive, and high-cost sensors, and achieve the effects of reducing complexity, light weight, and high computing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
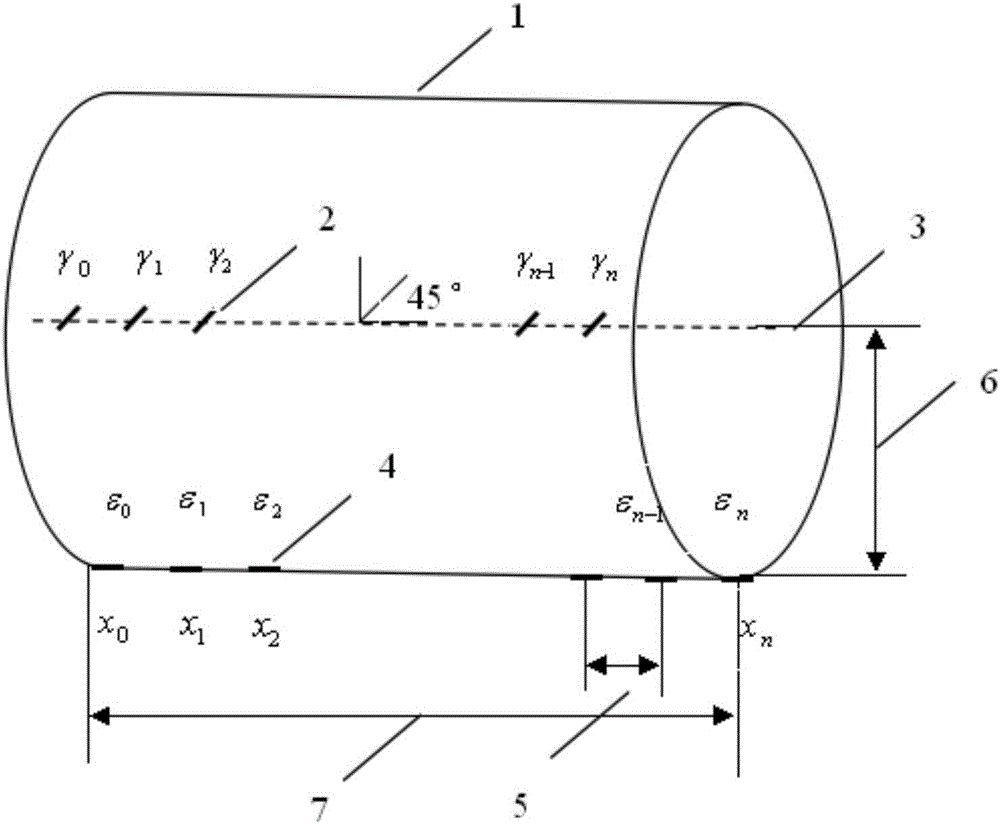
[0024] The implementation object is as figure 1 The cantilever beam structure shown is fixed at the left end and the free end of the beam at the right end. figure 1 Middle, 1-beam; 2-FBG sensor (to measure torsional strain); 3-axis of beam; 4-FBG sensor (to measure bending strain); 5-sensor interval △l; 6-c (sensor to neutral axis or center The distance of the surface); 7-the length l of the beam. The bending strain optical fiber sensor is mounted along the axial direction of the beam, and the torsional strain optical fiber sensor is mounted along the axial direction of the beam at an angle of 45° to the axial direction.
[0025] The present invention is specifically realized as follows:
[0026] (1) Install multiple optical fiber sensors on the beam structure. When measuring the bending load, stick it along the axial direction of the beam; when measuring the torsional load, the optical fiber sensor should be at 45° to the axis of the beam;
[0027] (2) After the fiber opti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com