Knotting method of vanadium iron ingot mold
An ingot mold and ferrovanadium technology, which is applied in the field of knotting technology, can solve the problems such as the great influence on the smelting yield and the difficulty of cleaning the alloy layer of vanadium discus, so as to improve the quality of knotting, reduce the processing cost and increase the recovery rate Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
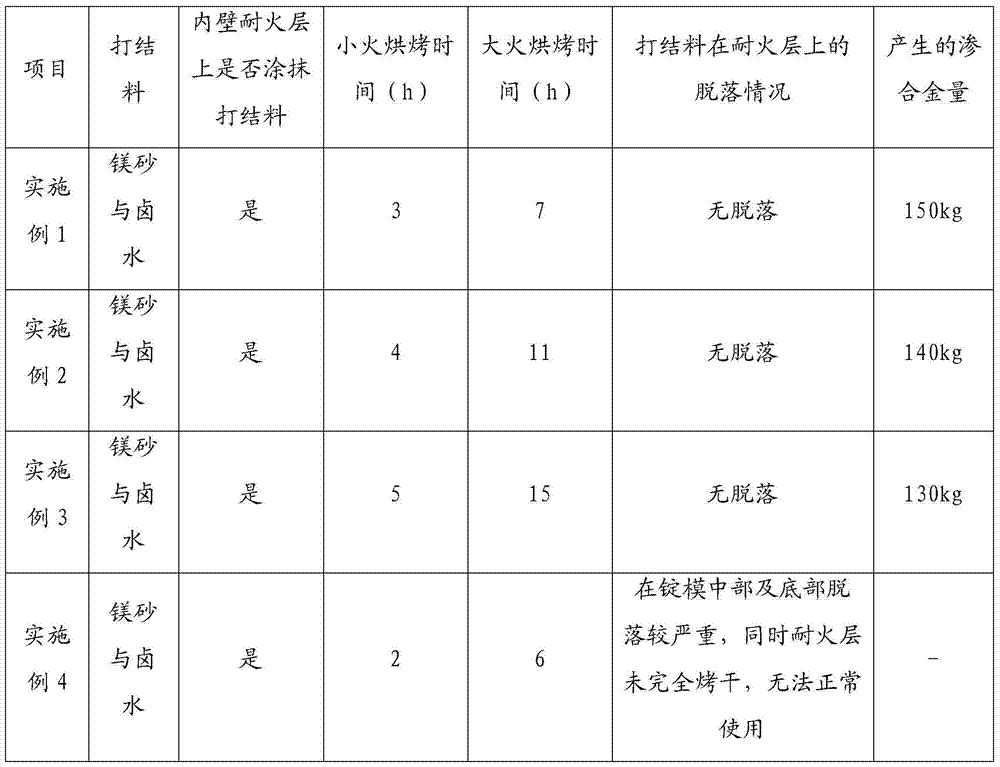
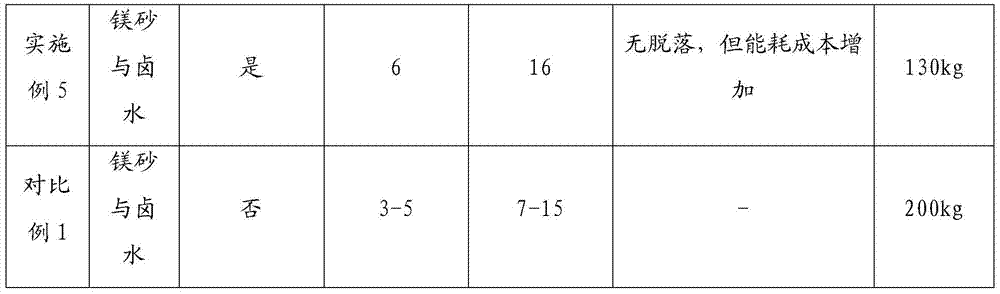
[0025] 1. First use the knotting material composed of magnesia and brine to knot a refractory layer with a thickness of 120-160mm on the inner wall of the ingot mold.
[0026] 2. After the refractory layer is knotted, use magnesium fire mud brine slurry to brush the entire inner wall of the ingot mold, and the coating thickness is 3-5mm.
[0027] 3. After painting, use gas to bake, first use a small fire with a temperature of 250°C to 300°C for 3 hours, and then bake with a temperature of 800°C to 850°C for 7 hours.
Embodiment 2
[0029] 1. First use the knotting material composed of magnesia and brine to knot a refractory layer with a thickness of 120-160mm on the inner wall of the ingot mold.
[0030] 2. After the refractory layer is knotted, use magnesium fire mud brine slurry to brush the entire inner wall of the ingot mold, and the coating thickness is 3-5mm.
[0031] 3. After painting, use gas to bake, first use a low fire at 250°C to 300°C for 4 hours, and then bake at a temperature of 800°C to 850°C for 11 hours.
Embodiment 3
[0033] 1. First use the knotting material composed of magnesia and brine to knot a refractory layer with a thickness of 120-160mm on the inner wall of the ingot mold.
[0034] 2. After the refractory layer is knotted, use magnesium fire mud brine slurry to brush the entire inner wall of the ingot mold, and the coating thickness is 3-5mm.
[0035] 3. After painting, use coal gas to bake, first use a low fire with a temperature of 250°C to 300°C for 5 hours, and then bake with a temperature of 800°C to 850°C for 15 hours.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com