Robust broadband self-adaptive beamforming method used for ultrasound imaging
An adaptive beam and ultrasonic imaging technology, applied in radio wave measurement systems, instruments, etc., can solve problems affecting the robustness of the method, phase distortion, and limited performance improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0053] The technical solutions of the present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
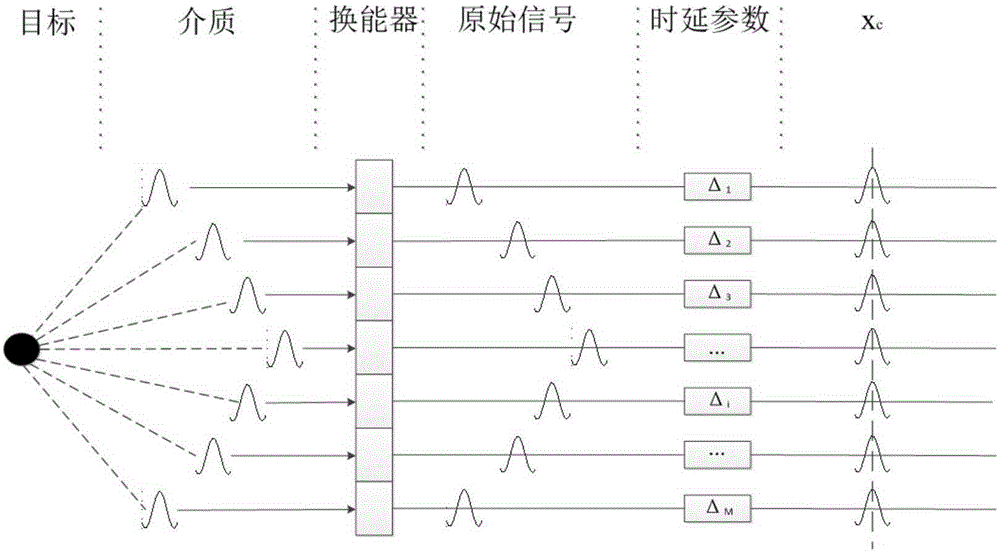
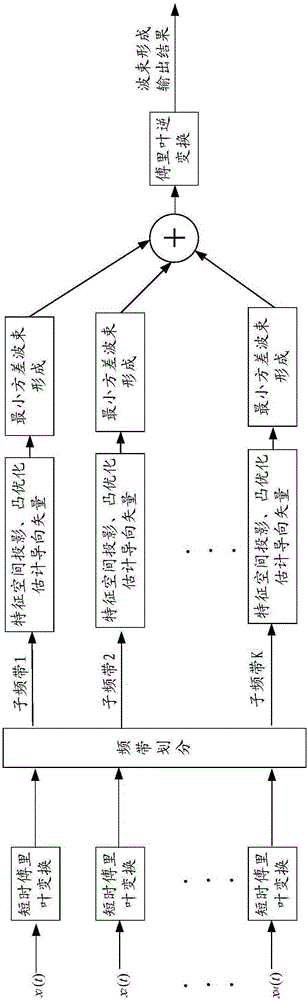
[0054] figure 1It is a schematic flowchart of an adaptive beamforming method provided by an embodiment of the present invention, and the embodiment of the present invention is applied to ultrasound imaging in B mode. The ultrasonic transducer array with M array elements at equal intervals works in the B-mode imaging linear scanning mode, and performs beamforming processing on the received echo data, and each scan line corresponds to the received signal of M array elements (that is, M is the number of array elements), and the number of samples of each array element is N, and the echo data received by all array elements corresponding to each scan line under B-mode ultrasonic imaging can be described by an M*N matrix . It should be noted that these echo data in the time domain have been preprocessed with time delay, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com