Photoconductive detector
A detector and photoconductive technology, which is applied in the field of detectors, can solve the problems of complex electrode structure, weakening of current signal, and decrease of detector quantum efficiency, so as to improve energy spectrum resolution, signal-to-noise ratio, and enhance carrier The effect of collecting performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
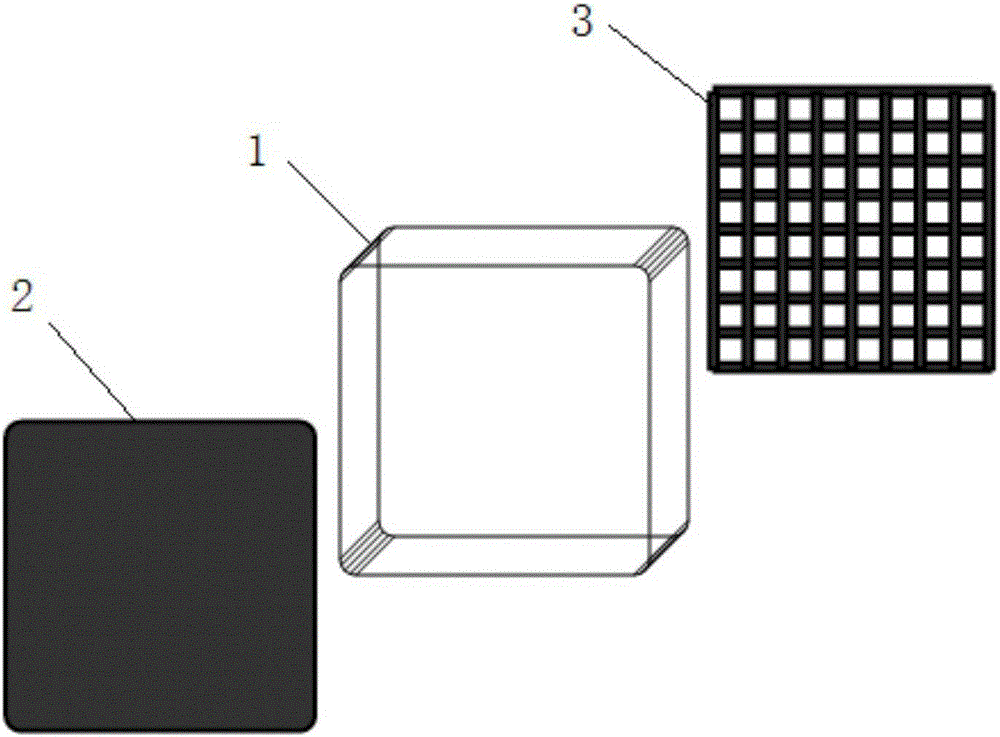
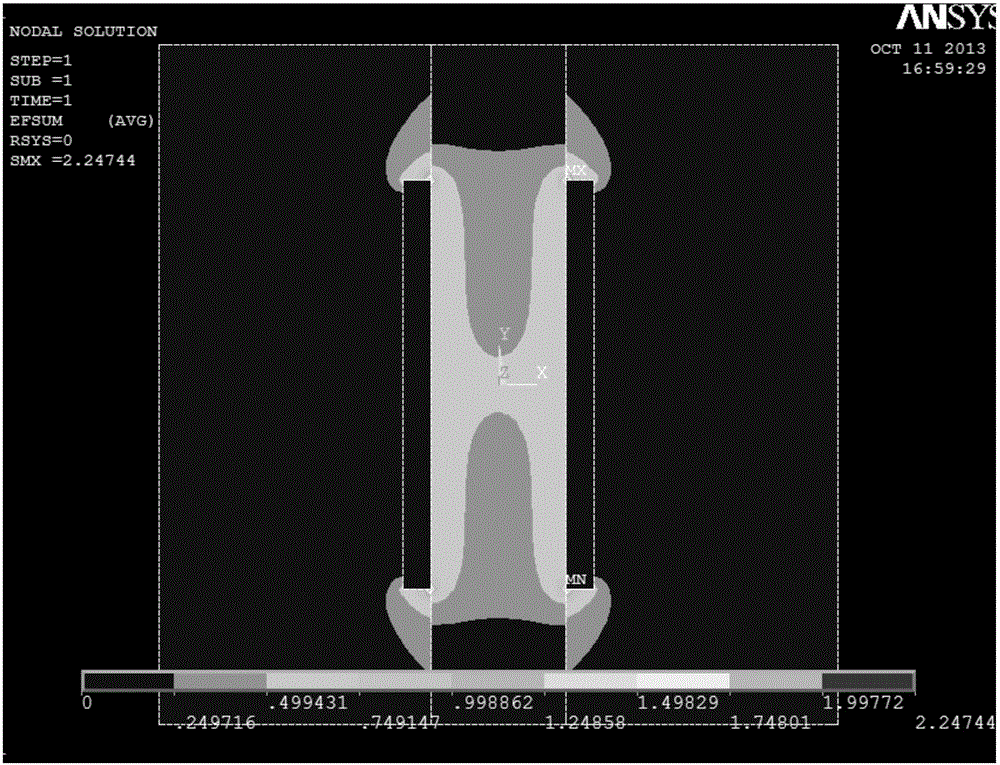
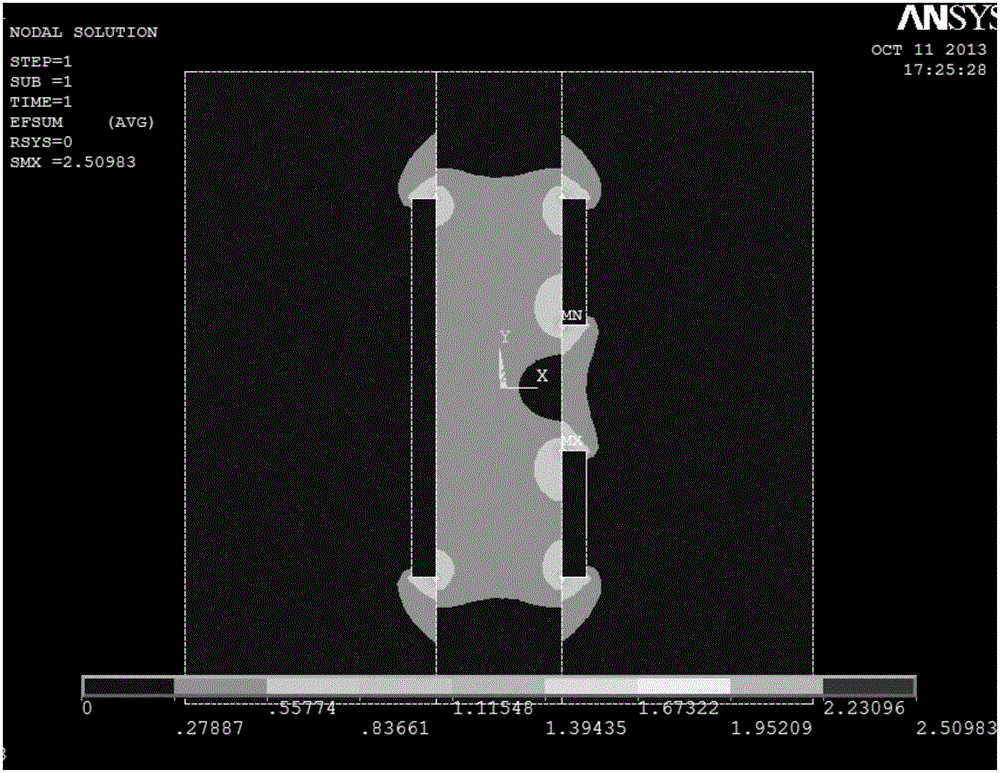
[0027] A photoconductive detector, such as figure 1 As shown, it includes a semiconductor 1 and two electrodes located on both sides of the semiconductor 1, the cathode 2 is a flat plate in the prior art, and the anode 3 is different from the cathode 2 in that it has a plurality of through holes uniformly distributed along the longitudinal direction of the detector electric field , so that the anode 3 is a network-like or mesh-shaped electrode plate, thereby reducing the effective area of the anode 3, and enhancing the electric field near the anode 3, so that the electric field inside the detector tends to be uniform in the lateral direction, and the anode The weight field near 3 has been strengthened. The electric field distribution of the detector is as figure 2 and image 3 as shown, figure 2 is the electric field distribution of detectors us...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com