Active power distribution network frame planning method on the basis of bi-level planning
A technology of active distribution network and two-layer planning, applied in the direction of instruments, data processing applications, information technology support systems, etc., can solve problems such as limiting the scope of application of the model and the uncertainty of upper-level planning problems.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0044] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
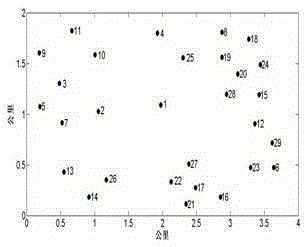
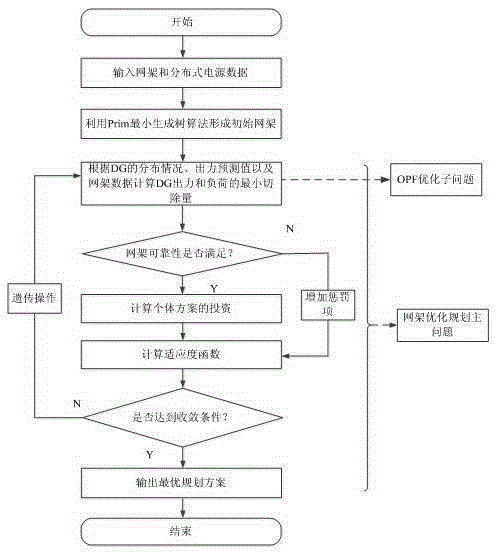
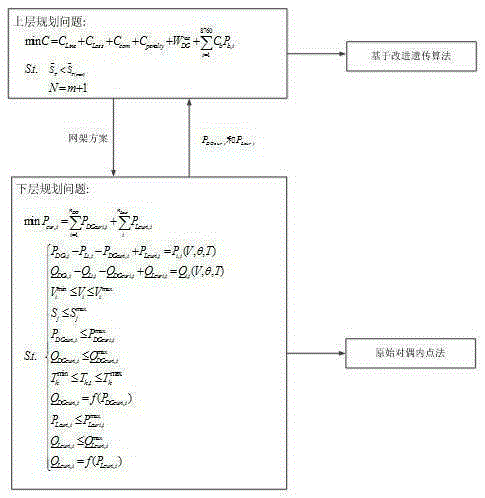
[0045] A two-level planning-based active distribution network grid planning method is used in the research of active distribution network grid planning. Taking the 29-node test system as an example, such as figure 1 shown, combined with figure 2 The flowchart shown in detail is as follows:
[0046] Since the boundary condition of the grid planning problem of the active distribution network is the known scheme of distributed power distribution and fixed capacity, the grid is constructed from scratch. Therefore, an initial plan for forming a network frame is required. Based on this, in order to make the genetic algorithm have better performance in solving the planning model of the active distribution network structure, the settings of the initial gene coding and initial scheme formation are improved. The specific solution steps are as follows:
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com