Method for judging and positioning distributed traveling wave fault of power transmission line
A technique for traveling wave faults, transmission lines, applied to fault location, fault detection by conductor type, measurement of electricity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0041] Below in conjunction with the drawings, preferred embodiments of the present invention are given and described in detail.
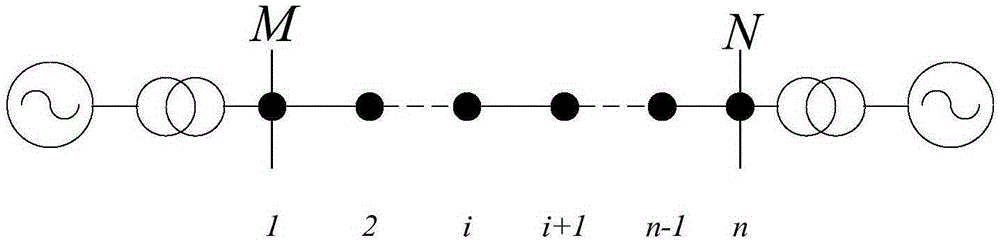
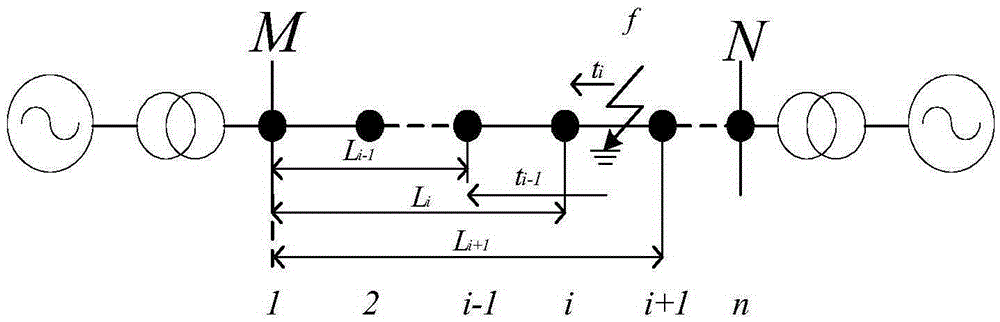
[0042] like Figure 4 As shown, taking the ground fault of phase A as an example, the total length of the transmission line is 120km, and 4 sets of detection devices are installed on it, and each set of detection devices is separated by 30km. Faults occurred when the closing angle was 0° (the voltage crossed zero) and 10° (the voltage did not cross zero), and the sampling frequency was 1MHz.
[0043] Step 1: Detect and read the fault current information of 4 sets of detection devices.
[0044] Step 2: Use the T matrix to perform phase-mode transformation on the fault data.
[0045] Step 3: Select 2 1 The scaled wavelet performs zero-crossing detection on the fault data, and K is selected according to the line parameters w =0.07, K=0.05. The identification results of different fault points are shown in Table 1.
[0046] Step 4: Select the cubi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com