Low area full adder with shared transistors
A transistor and full adder technology, applied in the field of full adders, can solve problems such as power reduction of full adders
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
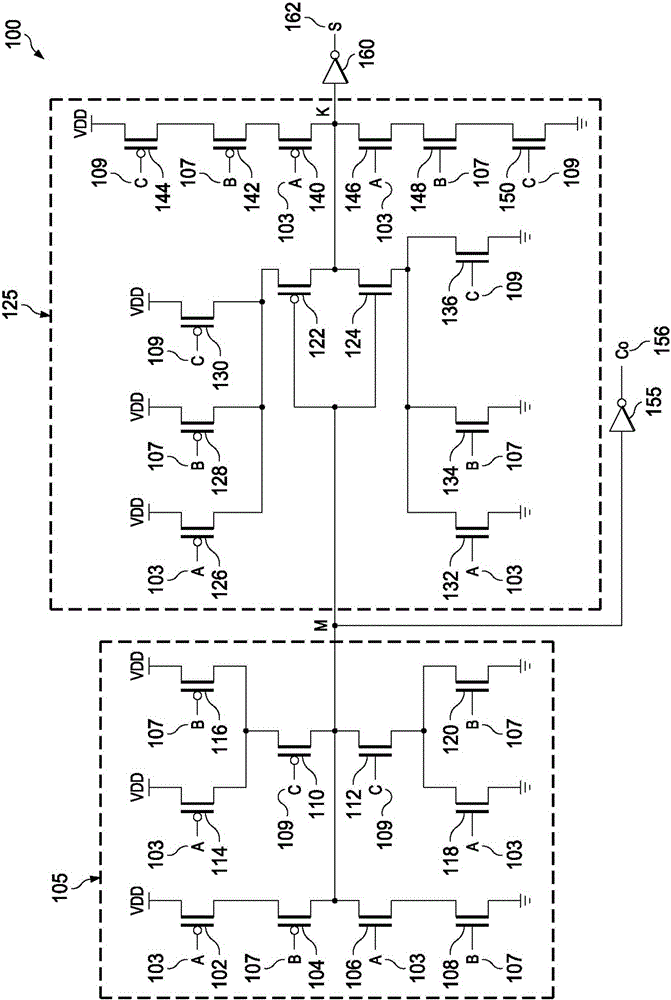
[0012] FIG. 1 shows a conventional full adder 100 . The conventional full adder 100 includes a carry generating circuit 105 , a sum generating circuit 125 , a first inverter 155 and a second inverter 160 . The carry generating circuit 105 is now explained. The carry generating circuit 105 comprises a first PMOS transistor 102 having a gate terminal receiving a first input A103 and a source terminal being coupled to a power supply terminal VDD. The drain terminal of the first PMOS transistor 102 is coupled to the source terminal of the second PMOS transistor 104 . The gate terminal of the second PMOS transistor 104 receives a second input B107.
[0013] The drain terminal of the second PMOS transistor 104 is coupled to the first node M. As shown in FIG. The carry generating circuit 105 further comprises a first NMOS transistor 106 having a gate terminal receiving the first input A103 and a drain terminal being coupled to the first node M . The source terminal of the first N...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com