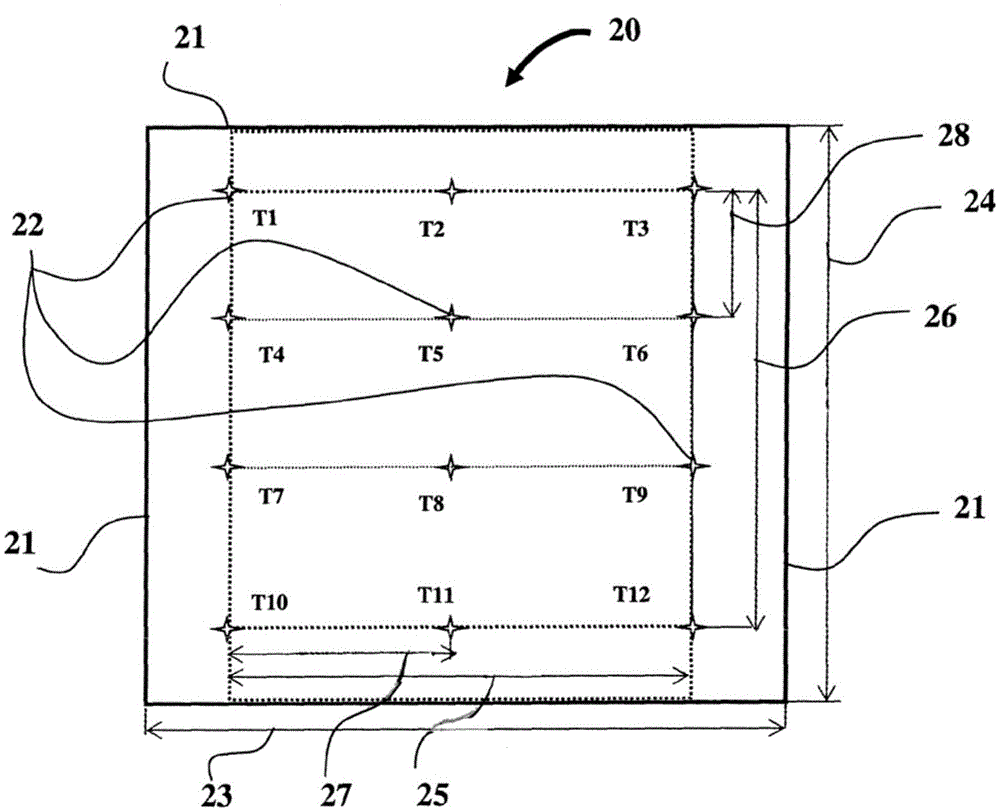
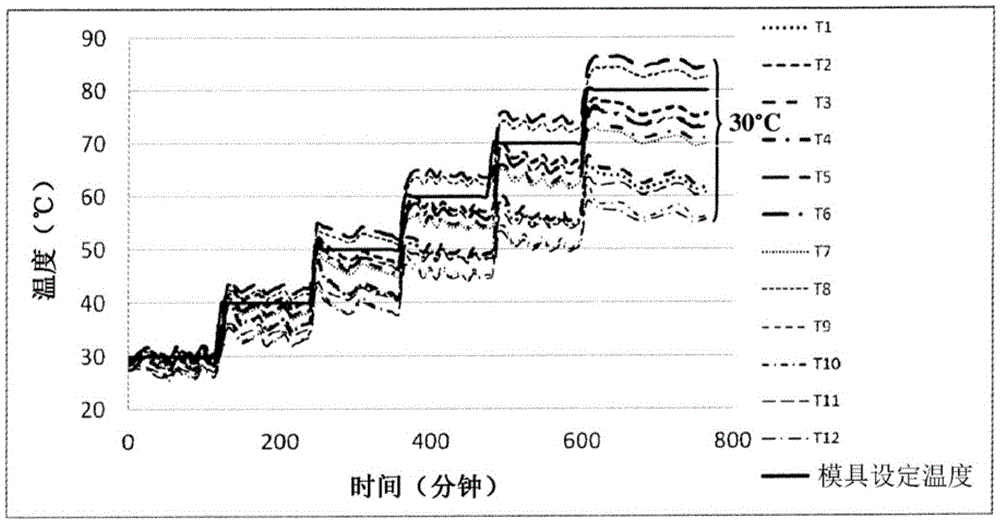
Method for producing non-metal self-heatable molds
A metal heat and mold technology, applied in the direction of coating, etc., can solve the problems of early degradation of metal layer due to chemical erosion heat loss, unsuitable for products with holes, complex manufacturing process, etc., to achieve good mold surface temperature uniformity, chemical erosion prevention , the effect of reducing heat loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0044] The preparation of the curable formulation and / or any of its steps may be a batch or continuous process. The mixing equipment used in this method can be any vessel and auxiliary equipment known to those skilled in the art.
[0045]The method of curing the curable composition can be performed by a conventional method well known to those skilled in the art. For example, in one embodiment curing may be performed at a predetermined temperature, typically from about 10°C to about 300°C; in another embodiment at a temperature from about 10°C to about 200°C; and in yet another embodiment Examples are carried out at temperatures from about 25°C to about 150°C. In one embodiment, curing may be performed for a predetermined period of time, such as typically from about 1 minute to about 1 week, in another embodiment from about 10 minutes to about 2 days, and in yet another embodiment about 1 hour to about 24 hours. For periods of less than about 1 minute, the time may be too sh...
example 1 and comparative example A
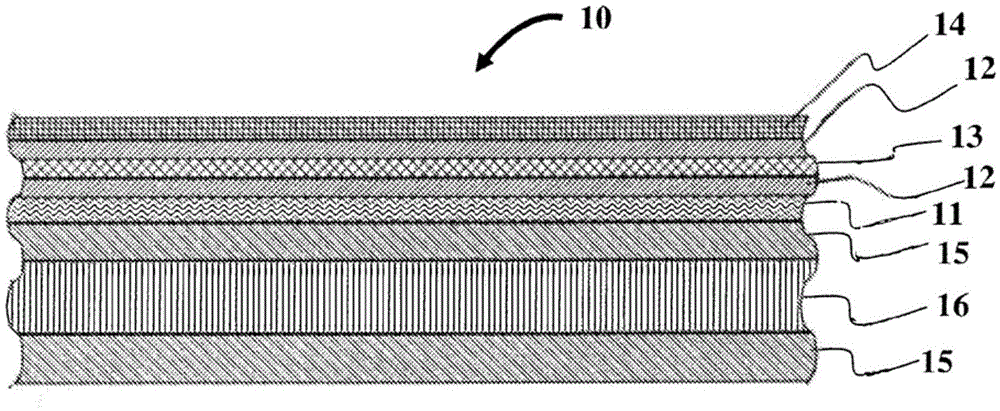
[0095] The first multilayer mold structure was prepared by the following general method:
[0096] (1) Applying one or more composite surface layers 2 mm thick into the master mold via injection molding;
[0097] (2) applying one or more thermally conductive adhesive layers adjacent to one or more layers of step (1) with a spatula;
[0098] (3) Manually stacking one or more 1mm thick aluminum sheet layers adjacent to one or more layers of step (2);
[0099] (4) Manually stacking one or more fabric layers adjacent to one or more layers of step (3);
[0100] (5) manually stacking one or more nonwoven fiber mat layers adjacent to one or more layers of step (4);
[0101] (6) manually stacking one or more heating layers with holes adjacent to one or more layers of step (5);
[0102] (7) Manually stacking one or more fabric layers adjacent to one or more layers of step (6);
[0103] (8) Manually stacking one or more porous foam core material layers adjacent to one or more layers ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com