Method for parallel shooting and bouncing rays based on dynamic load balancing technology
A dynamic load and bouncing ray technology, applied in resource allocation, program control design, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as low parallel efficiency, unclear subtask division methods, and inability to meet computing needs, so as to improve parallel efficiency and achieve good results. Scalability, the effect of good load balancing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
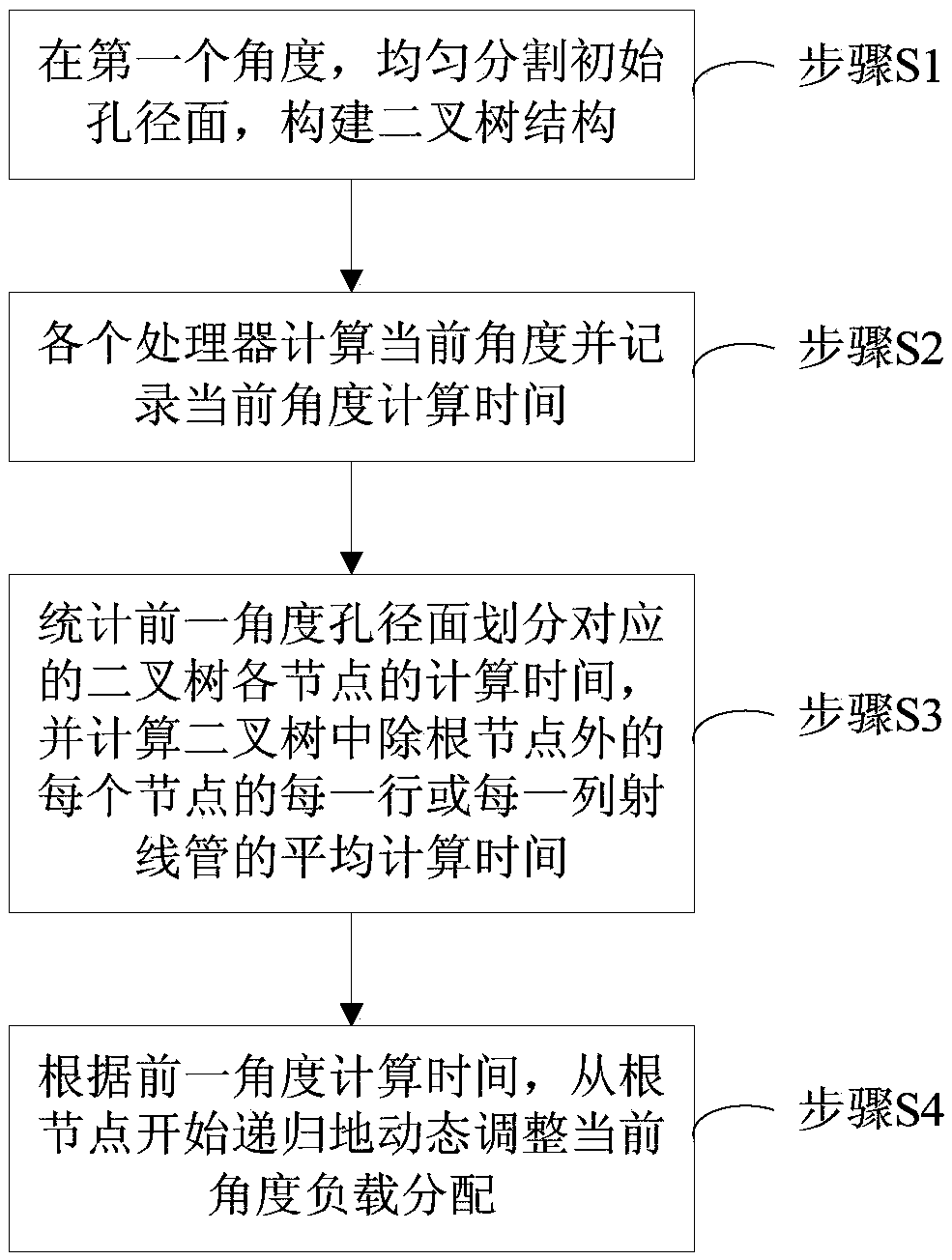
[0083] A parallel bouncing ray method based on dynamic load balancing technology, comprising the following steps:
[0084] Step S1, at the first incident angle, according to the number N of processors participating in the calculation, the initial aperture surface is evenly divided into N sub-aperture surfaces with the same area and the same number of ray tubes;
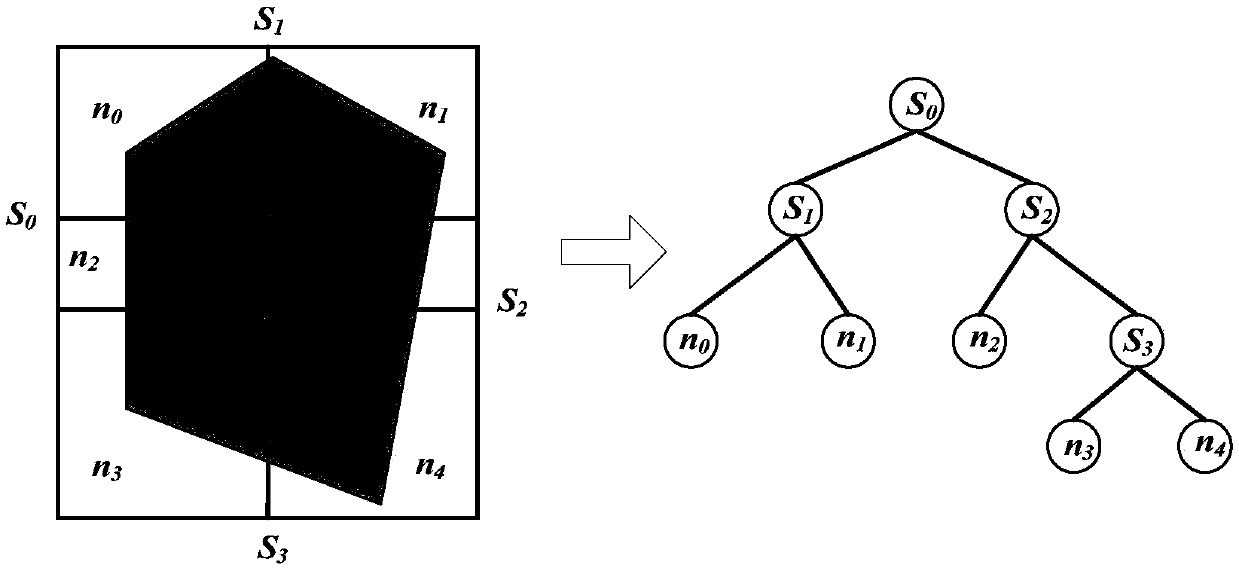
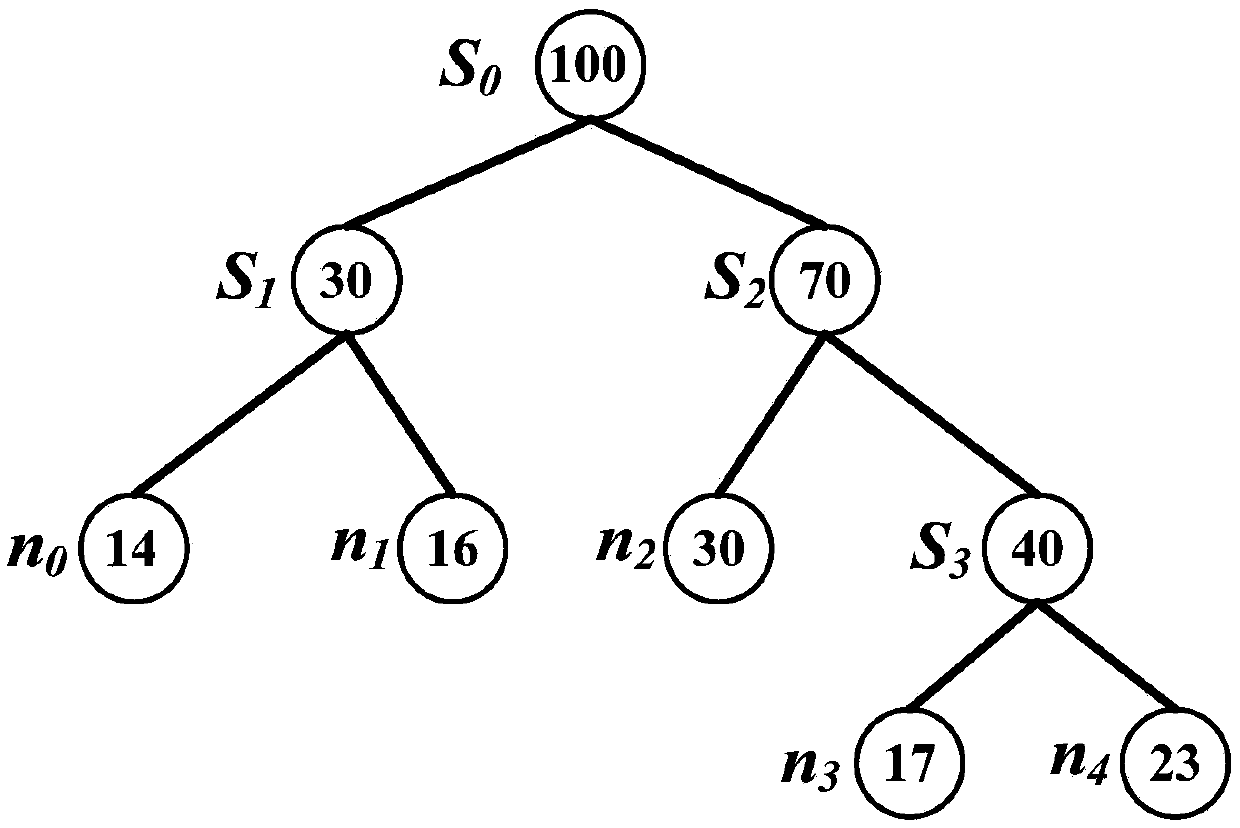
[0085] According to formula (1), the aperture surface is first divided into two sub-aperture surfaces along the longer side of the aperture surface, and one sub-aperture surface is assigned A processor calculates, another sub-aperture surface distributes The two sub-aperture surfaces will be recursively divided and allocated to processors, until the number of processors N=1 for calculating the sub-aperture surfaces, the division of the sub-aperture surfaces is terminated;
[0086] Such as figure 2 As shown, the division process of the aperture surface is shown. This process also builds a binary tree. The division...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com