Patents
Literature
231 results about "Rectangular aperture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Rectangular Apertures can be used to define the boundaries of an optical path or to mask out specific areas in an optical system, for example on a test target, monochromator, CCD or a detector.
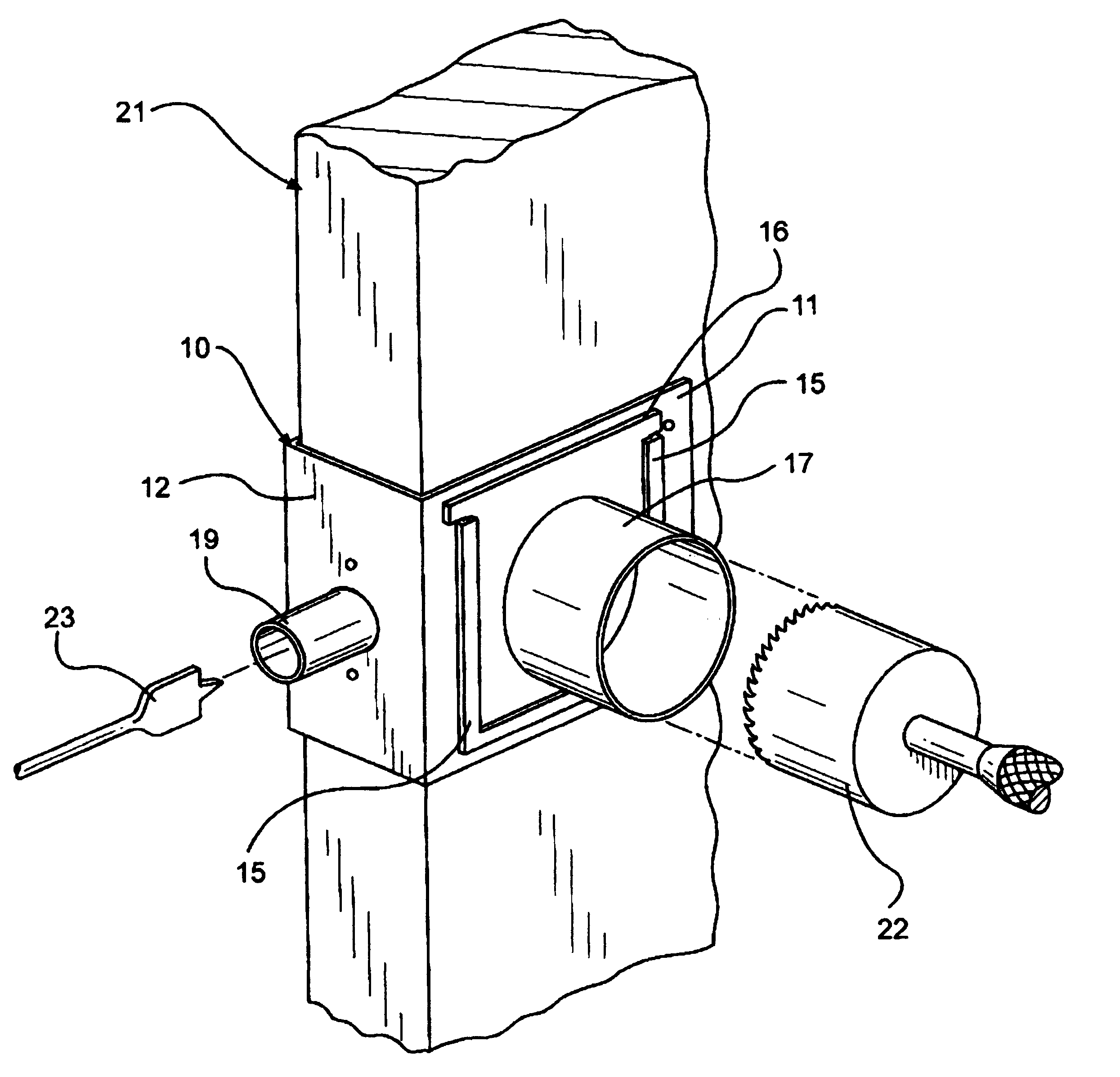
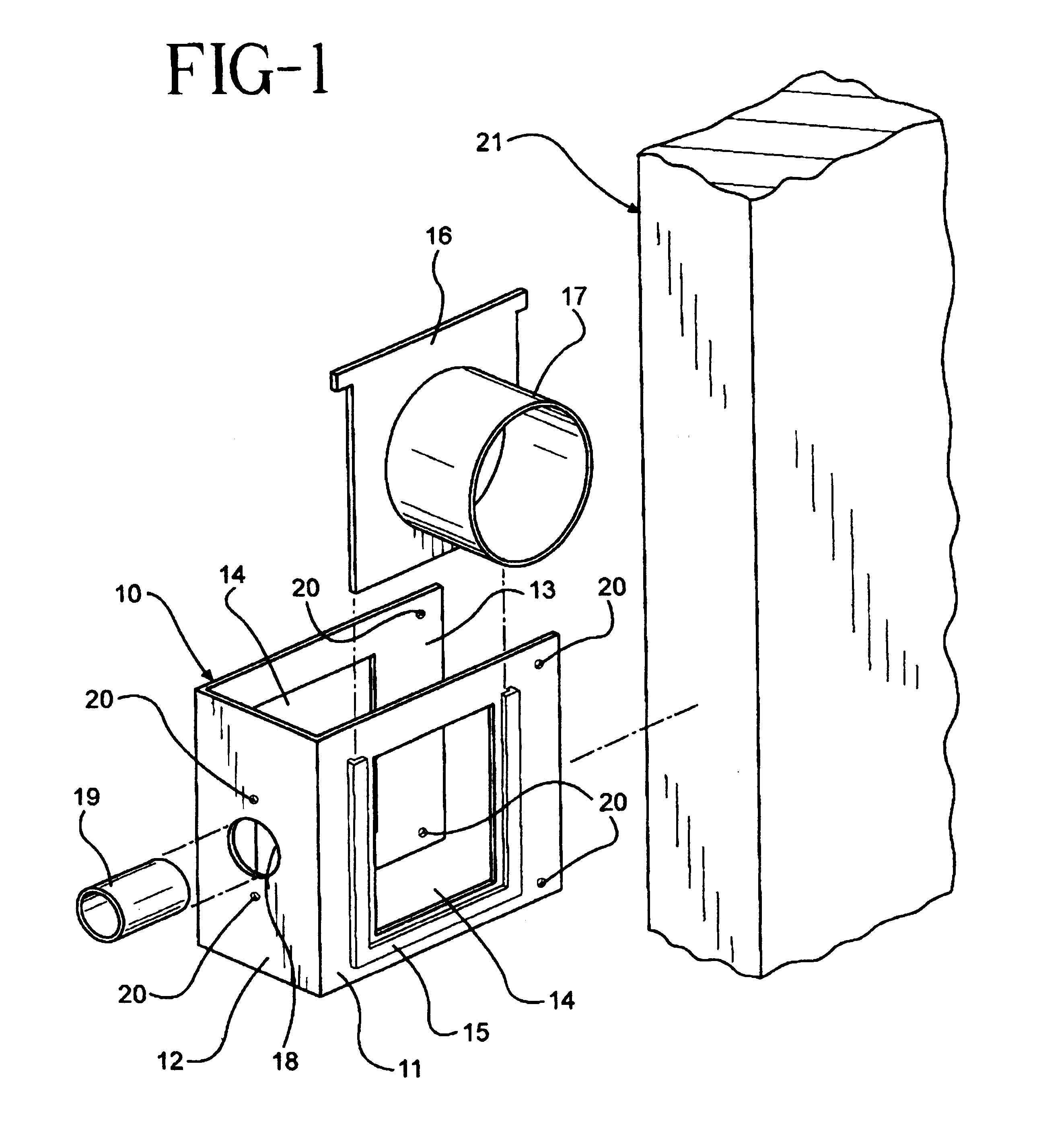
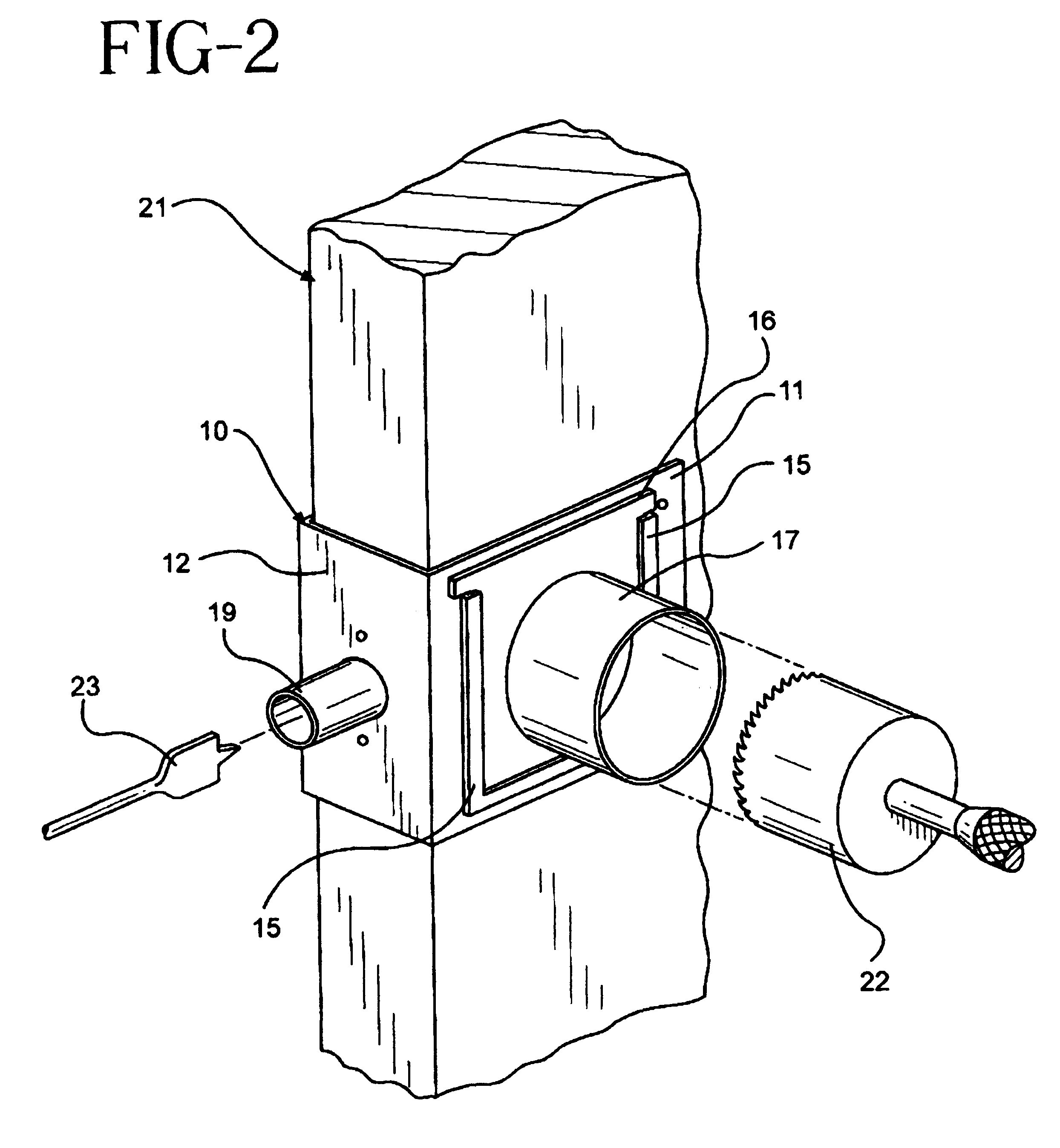
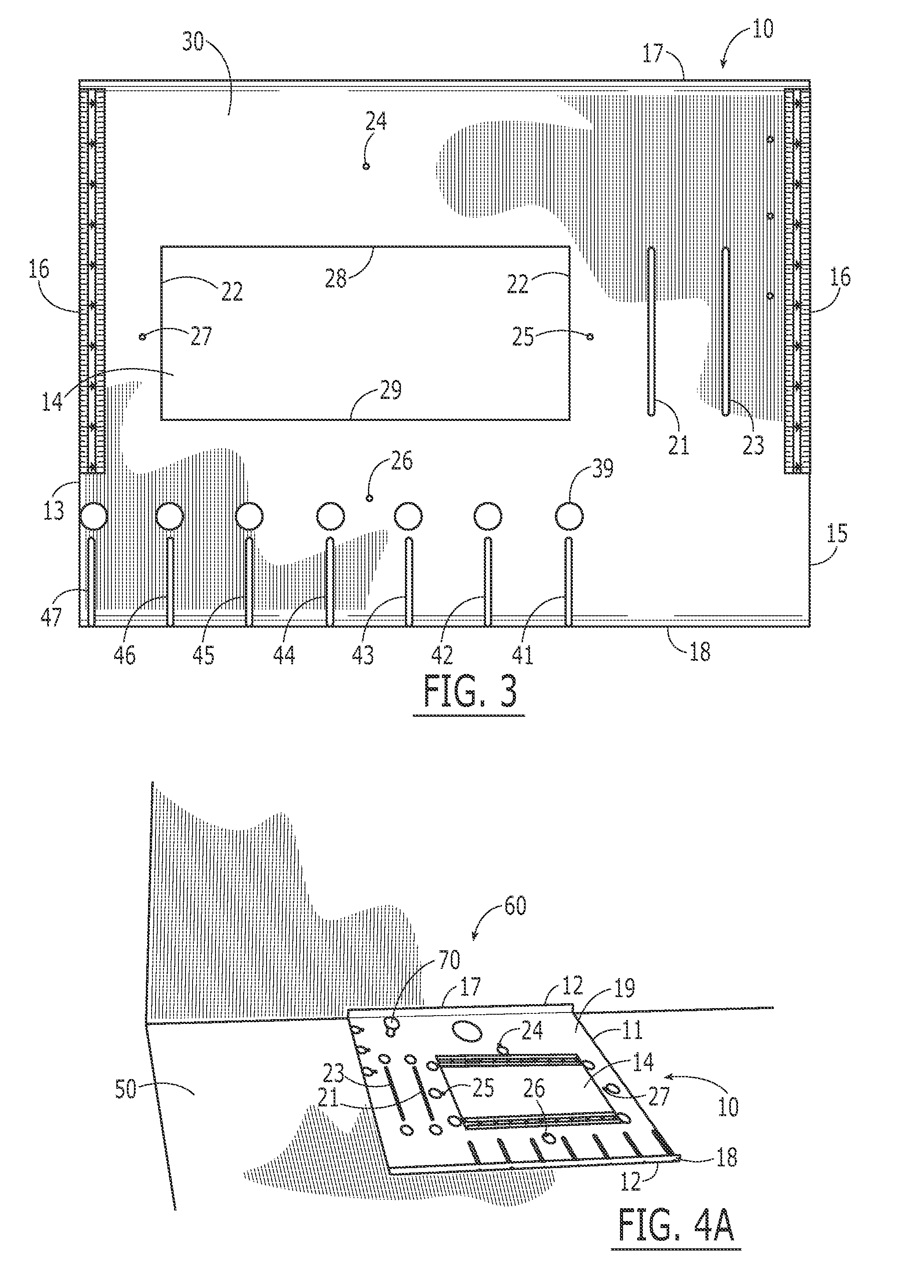
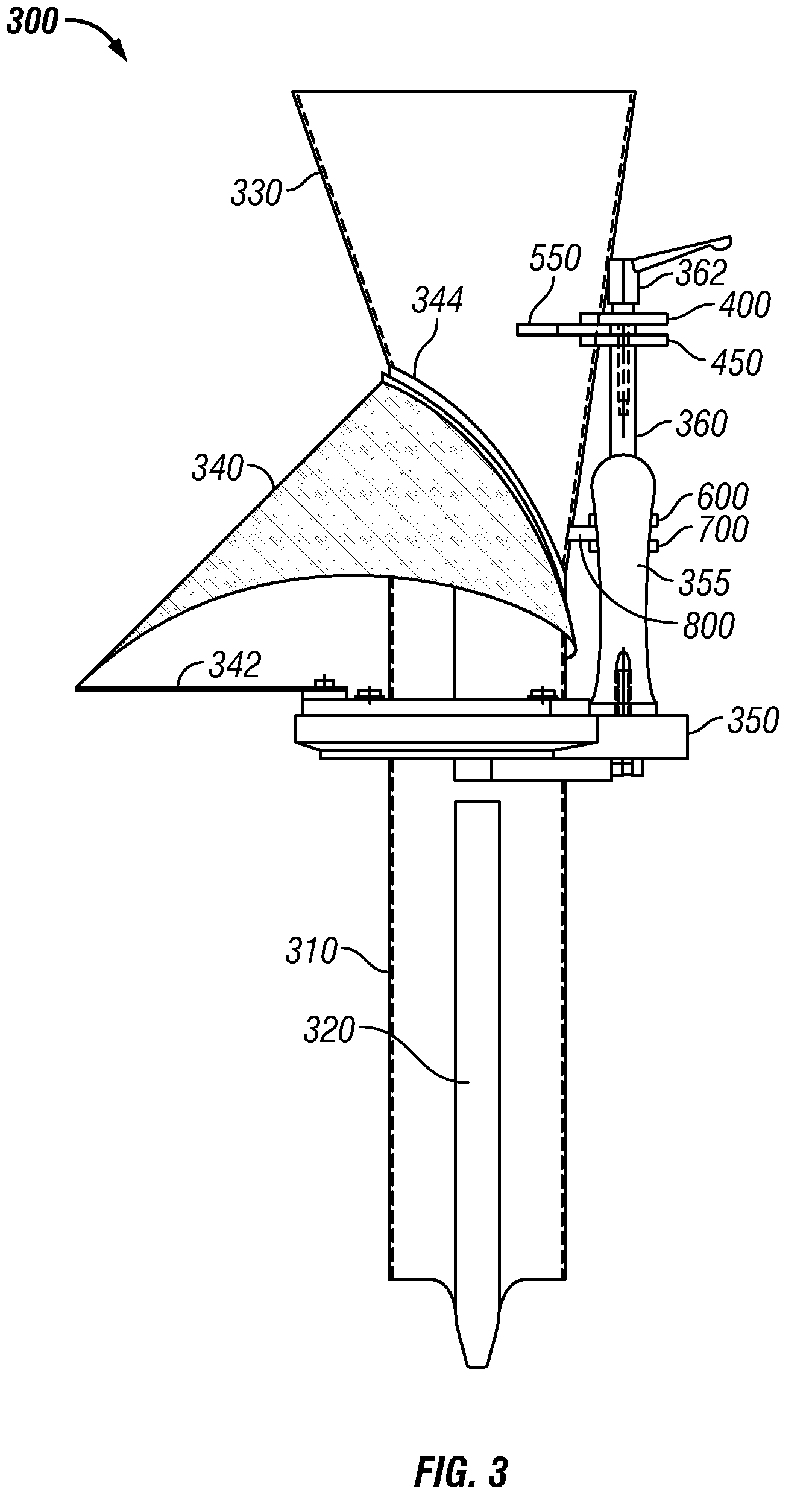
Bracket drill template
InactiveUS6193449B1Losing accuracySimple taskDrilling/boring measurement devicesThread cutting machinesRectangular apertureEngineering
A 3 sided bracket shaped template for accurately drilling door knob and lock holes in doors comprising a template plate a at right angle to a lock plate again at a right angle to a reverse plate. The template plate and reverse plate each contain rectangular apertures for drill passage, and the template plate further has zee bracket sleeves on the bottom and both sides of the rectangular aperture for slidably mounting removable plate guides each with different perpendicular cylindrical extension guide for drills of varying sizes. The lock plate also has a centered circular hole with a tubular drill guide perpendicular to the lock plate.
Owner:DIAZ ALBERTO
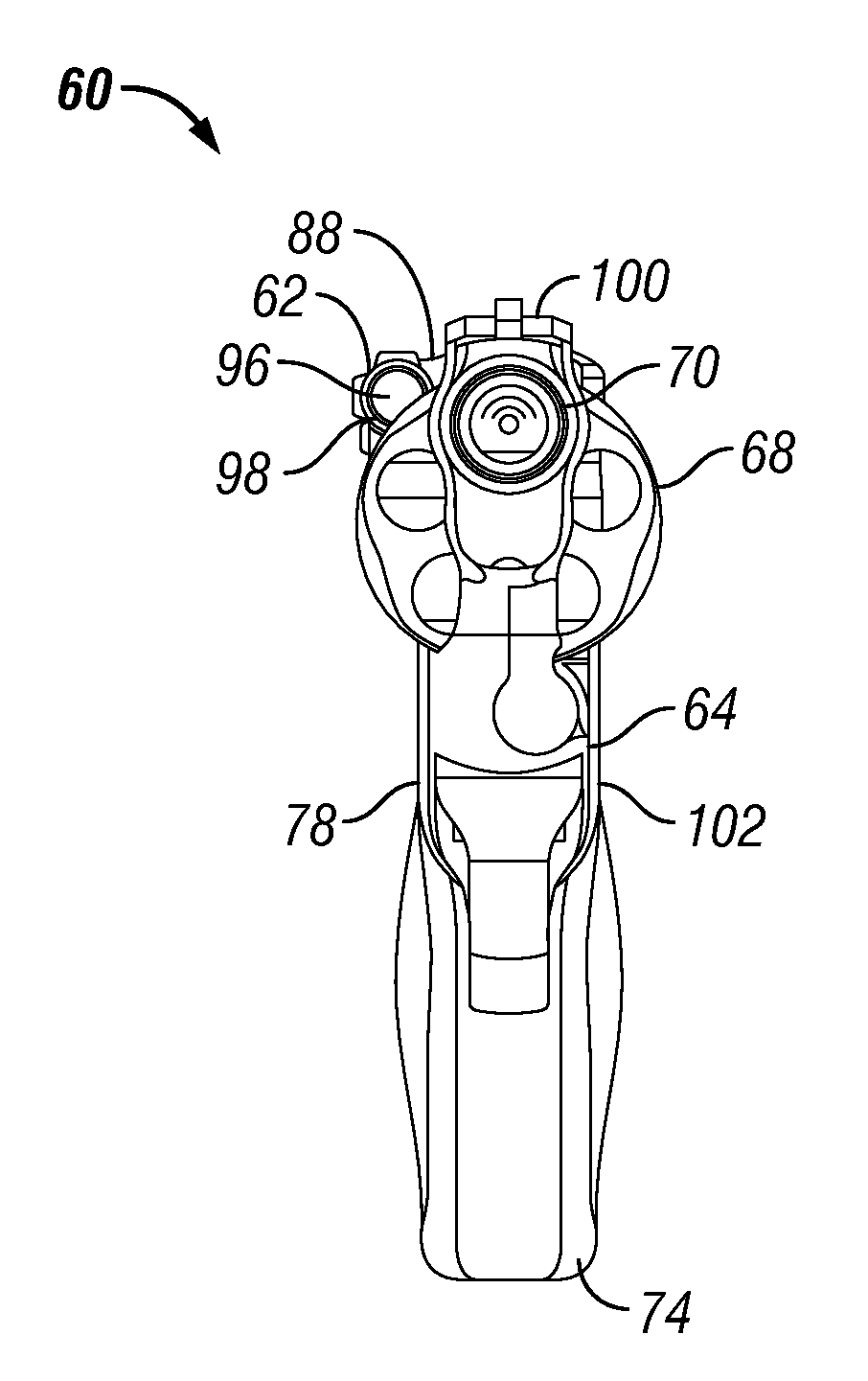
Frame-mounted laser aiming device
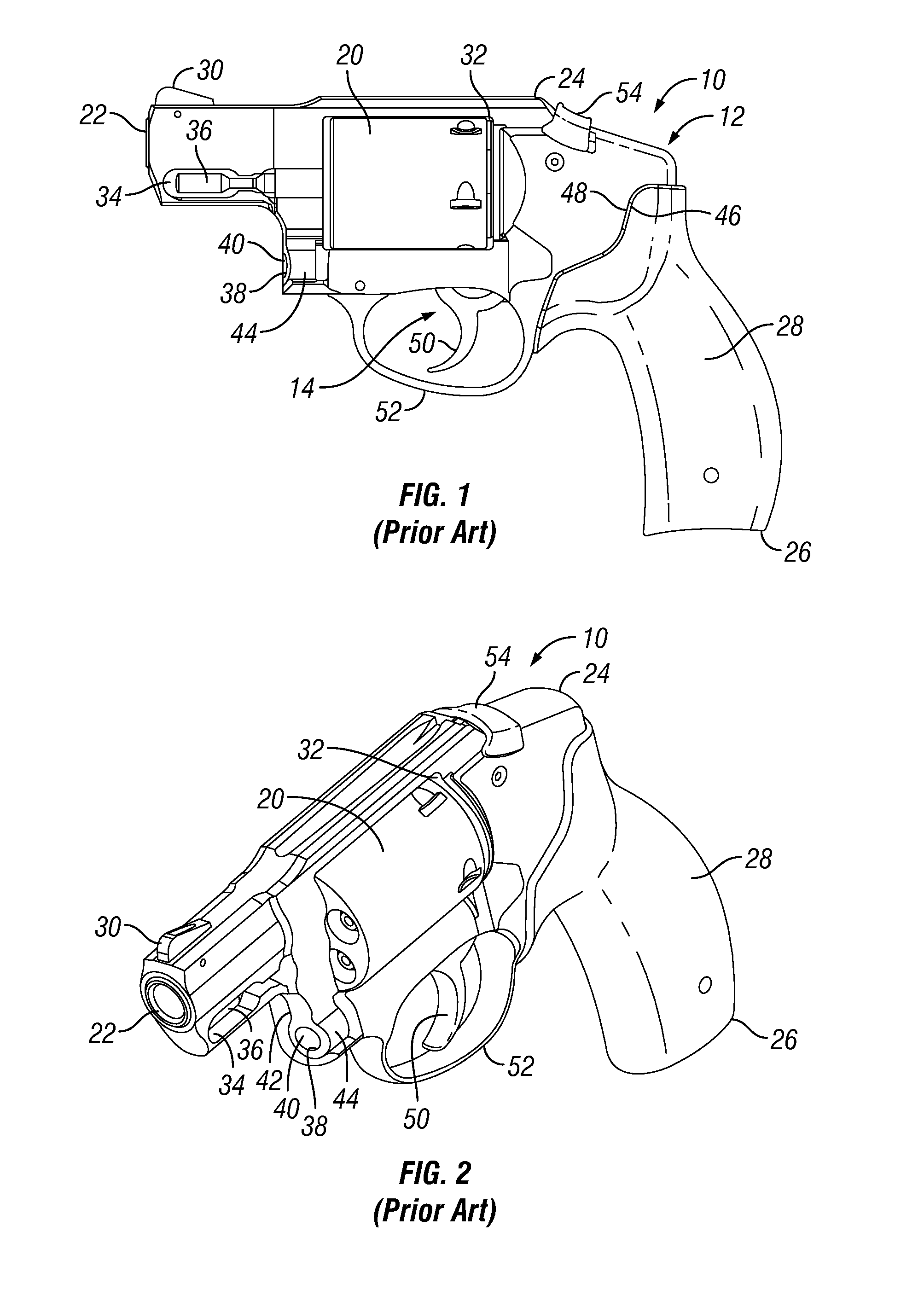
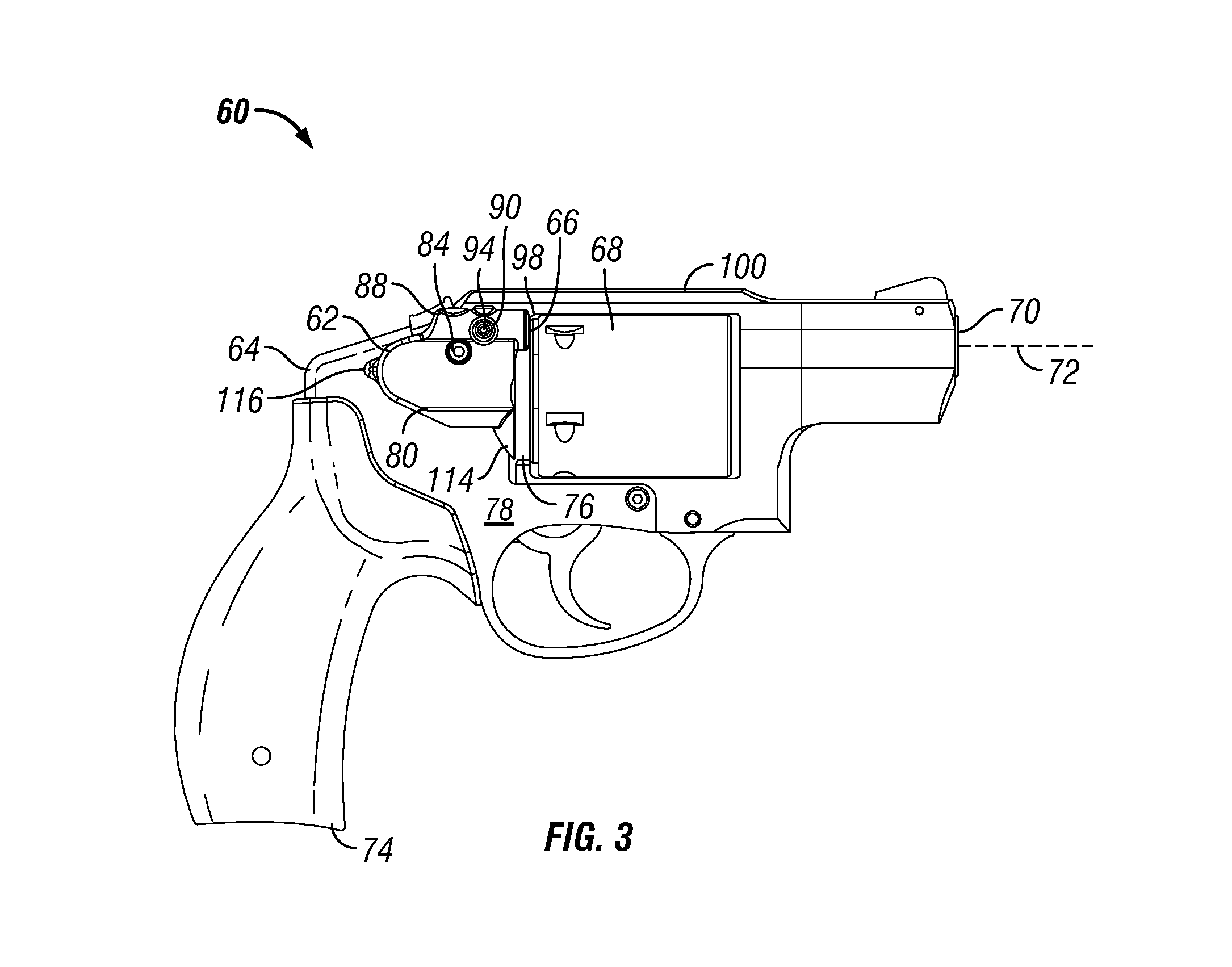
InactiveUS20120047787A1Easy to installEasily interchangeableSighting devicesRectangular apertureOptoelectronics
A revolver having a frame that defines a rectangular aperture to which a cylinder is mounted, and a laser aiming device that is mounted to the frame, rearward of the rectangular aperture. The laser aiming device is secured to the frame by a fastener that is inserted through an opening defined in a central position of the laser aiming device and into a corresponding hole formed in the frame. The alignment axis of the laser aiming device is proximate the firing axis of the revolver. The laser aiming device is light weight and lies substantially flush against the revolver, between the frame and the cylinder.
Owner:SMITH & WESSON
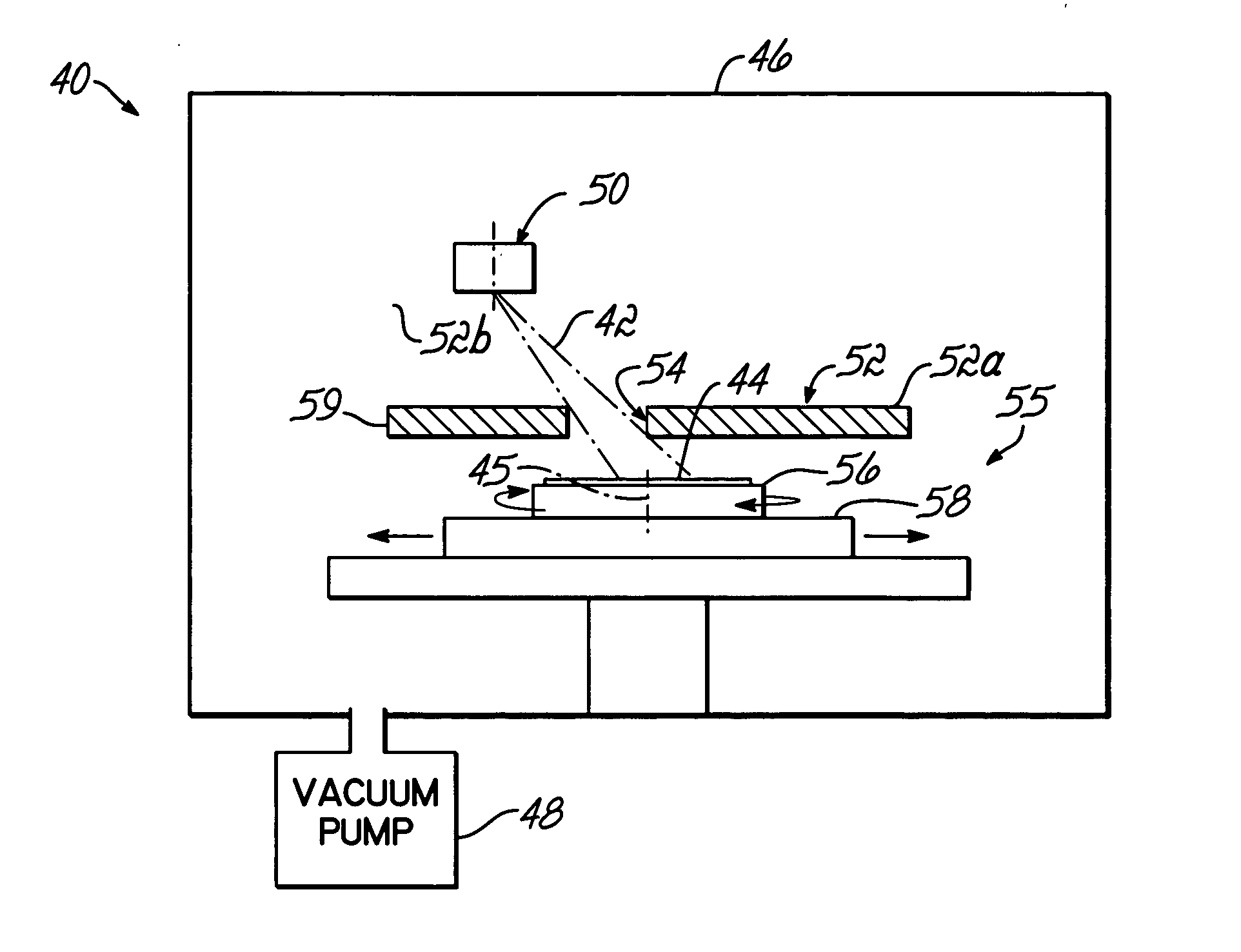
Method and apparatus for surface processing of a substrate
Method and apparatus for processing a substrate with a beam of energetic particles. The beam is directed from a source through a rectangular aperture in a shield positioned between the source and substrate to a treatment zone in a plane of substrate movement. Features on the substrate are aligned parallel to a major dimension of the rectangular aperture and the substrate is moved orthogonally to the aperture's major dimension. The beam impinges the substrate through the aperture during movement. The substrate may be periodically rotated by approximately 180° to reorient the features relative to the major dimension of the rectangular aperture. The resulting treatment profile is symmetrical about the sides of the features oriented toward the major dimension of the rectangular aperture.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
Ultra-wideband (UWB) antenna
InactiveUS7646341B1Reduce areaEasy to liftSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsUltra-widebandRectangular aperture
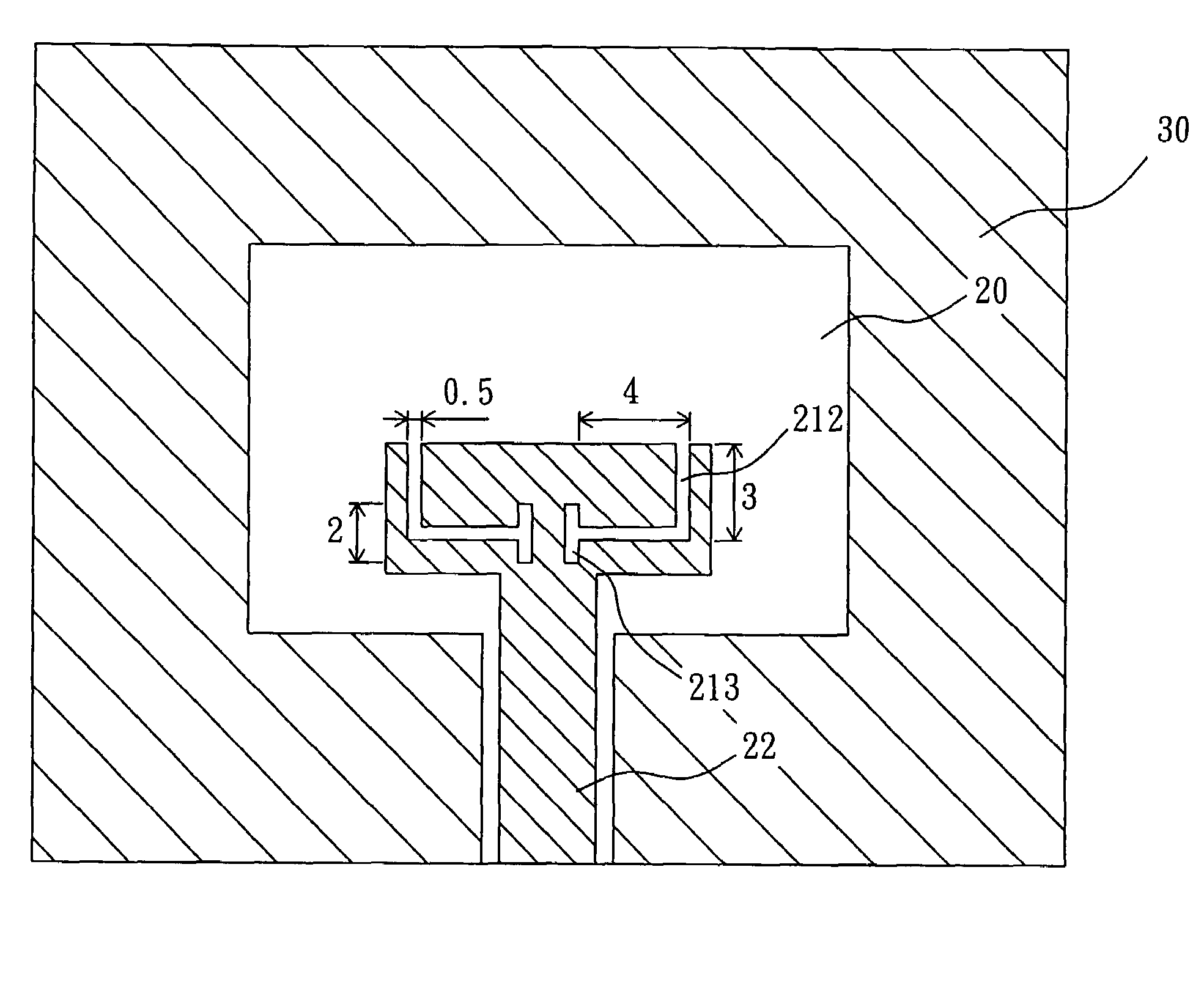
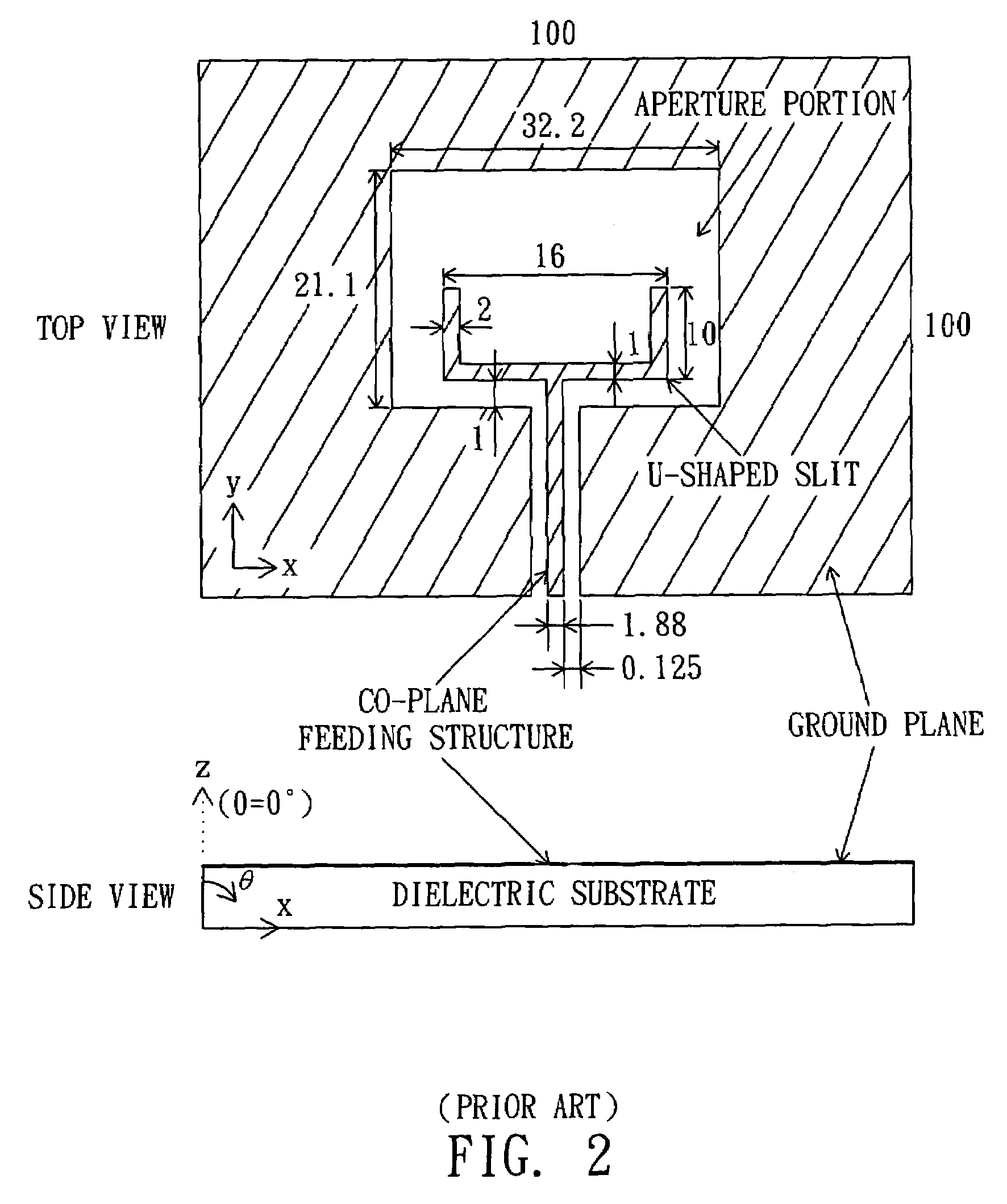
The present invention relates to an ultra-wideband (UWB) antenna, which comprises: a rectangular aperture portion, formed from a ground plane of a printed circuit board and having an aperture; and a co-plane feeding structure, having a horizontal portion and a vertical portion, wherein the vertical portion is perpendicular to the horizontal portion, and the vertical portion is disposed in the aperture and connected with an external terminal. The ultra-wideband (UWB) antenna of the present invention can receive the wireless signal with 3.1˜10.6 GHz band, and have a very compact area (13 mm×23 mm) and is easy to be mass produced. Furthermore, a parasitism element can be added into the co-plane feeding structure, so as to reject the in-band interferences from the existing systems like 5˜6 GHz signals of wireless LAN.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Light emitting device and method of manufacturing light emitting device
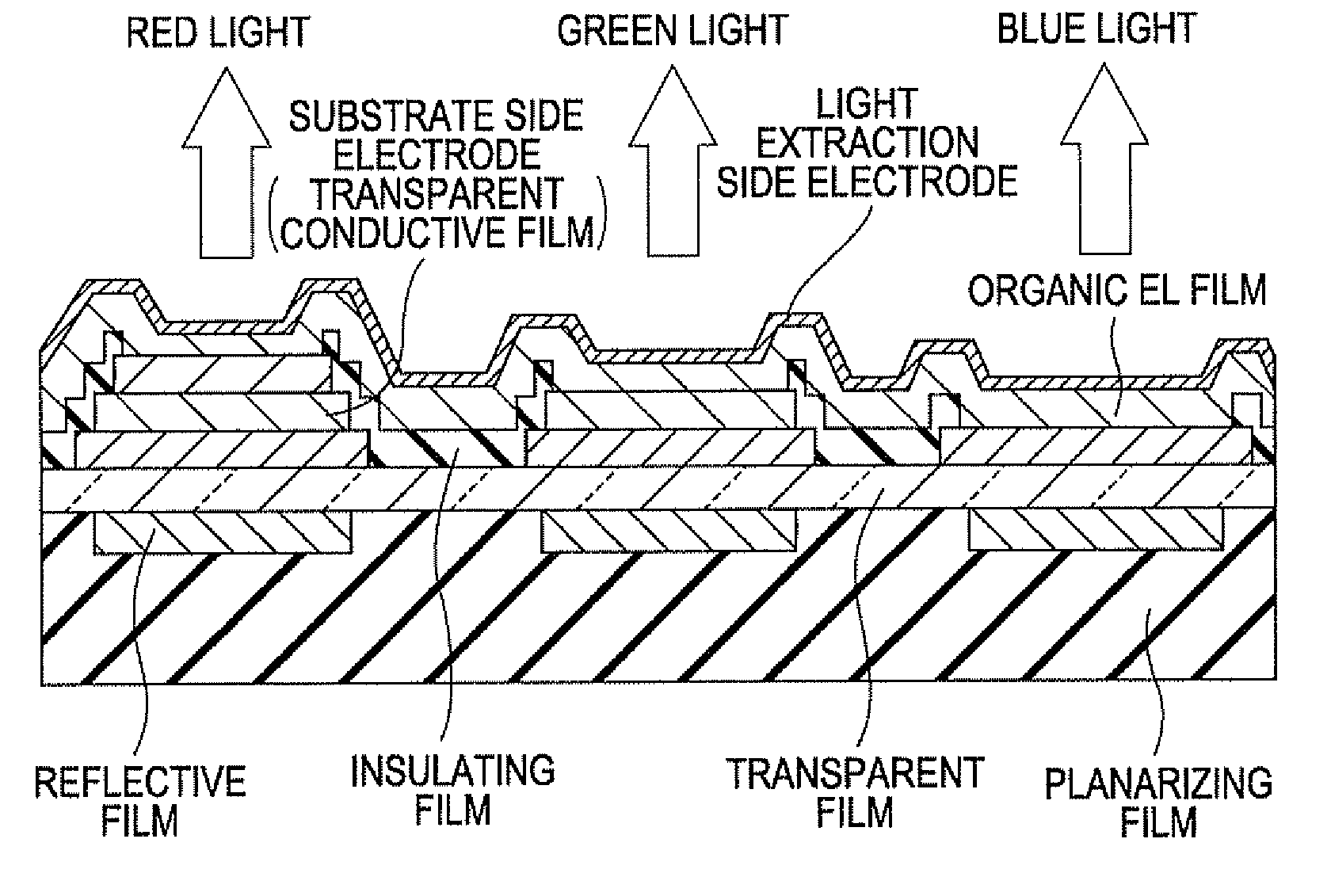
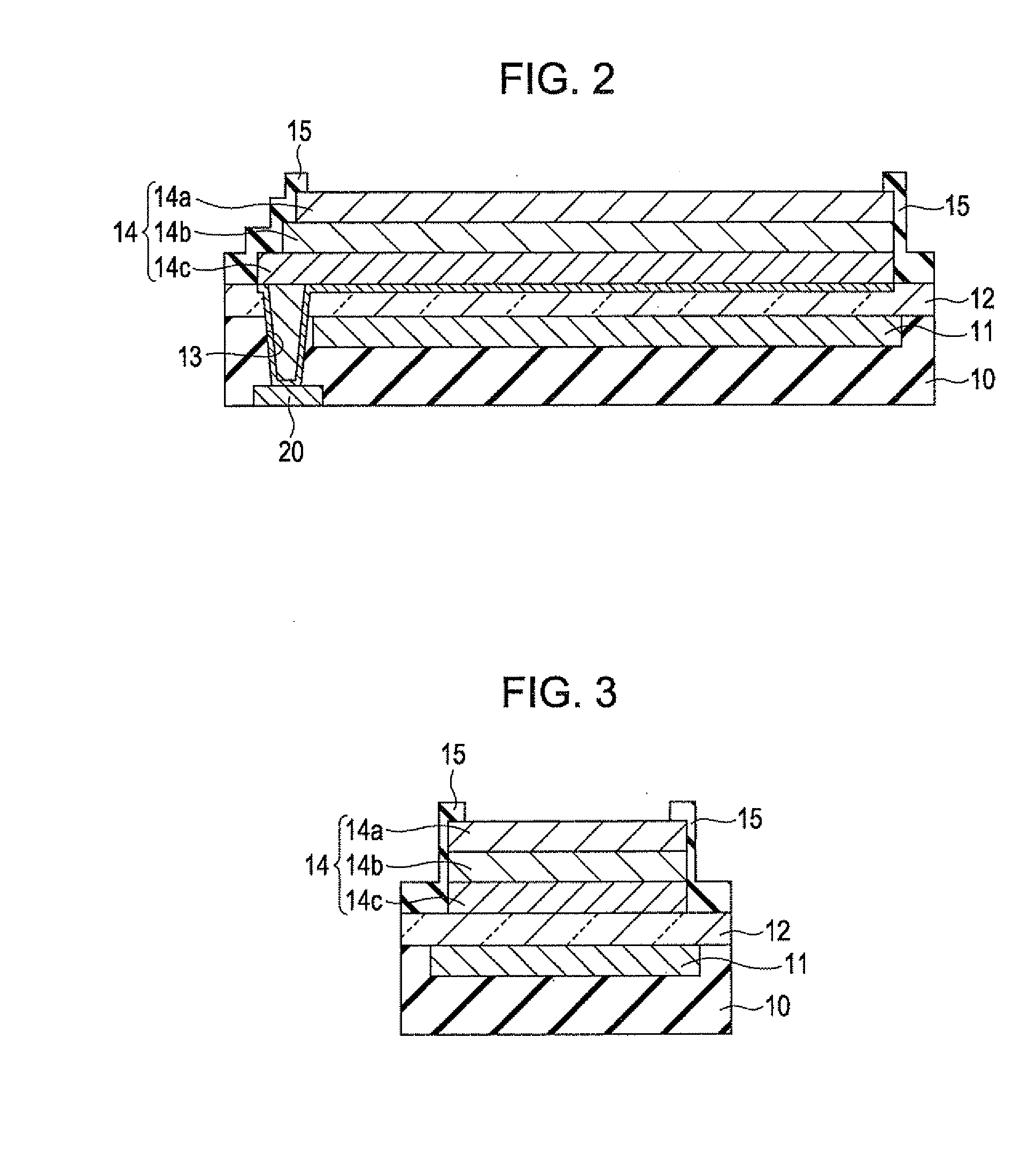
ActiveUS20120229014A1Reduce areaPrevent excessive flowDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsRectangular apertureTransparent conducting film
On one short side of a rectangular aperture area, transparent conductive films are patterned by being deviated in a stepwise shape. On another side, an end surface of the transparent conductive films is patterned to be aligned. The end surface of the transparent conductive films is covered with an insulating film.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Connector including circular bladder constriction and associated methods
InactiveUS7364448B2Easy to manufactureImprove carrying capacityCoupling device detailsOptical light guidesRectangular apertureMechanical engineering
A connector may include first and second connector portions being movable between unmated and mated positions. First and second bladders may be in respective first and second connector portions and cooperate therewith so that opposing ends of the first and second bladders are urged together and moved from a closed to an open position as the first and second connector portions are moved from the unmated to the mated position. At least one of the first and second connector portions may define a circular constriction for closing an end of a respective bladder into a circular peripheral shape when the first and second connector portions are in the unmated position. One or both of the bladder ends may define a generally rectangular aperture when in the open position.
Owner:TELEDYNE INSTR INC
Template for positioning vents or boots for an HVAC system
InactiveUS7086171B2Improve efficiencyLow costMechanical clearance measurementsStraightedgesRectangular apertureEngineering
A template for locating the placement of the vents for an HVAC system is provided. The template includes a body defining a first set of parallel edges. Further, the body defines longitudinal and latitudinal walls of a rectangular aperture. The longitudinal walls run parallel to the first set of parallel edges and the latitudinal walls run perpendicular to the first set of parallel edges. The rectangular aperture is useable to define a location of a vent for an HVAC system on at least one of a floor or wall. At least one adjustment aperture is defined by the body beside at least one of the latitudinal or longitudinal walls to accommodate the defining of a location for a vent having at least one of different width or length than provided by the rectangular aperture.
Owner:LAWSON MARK
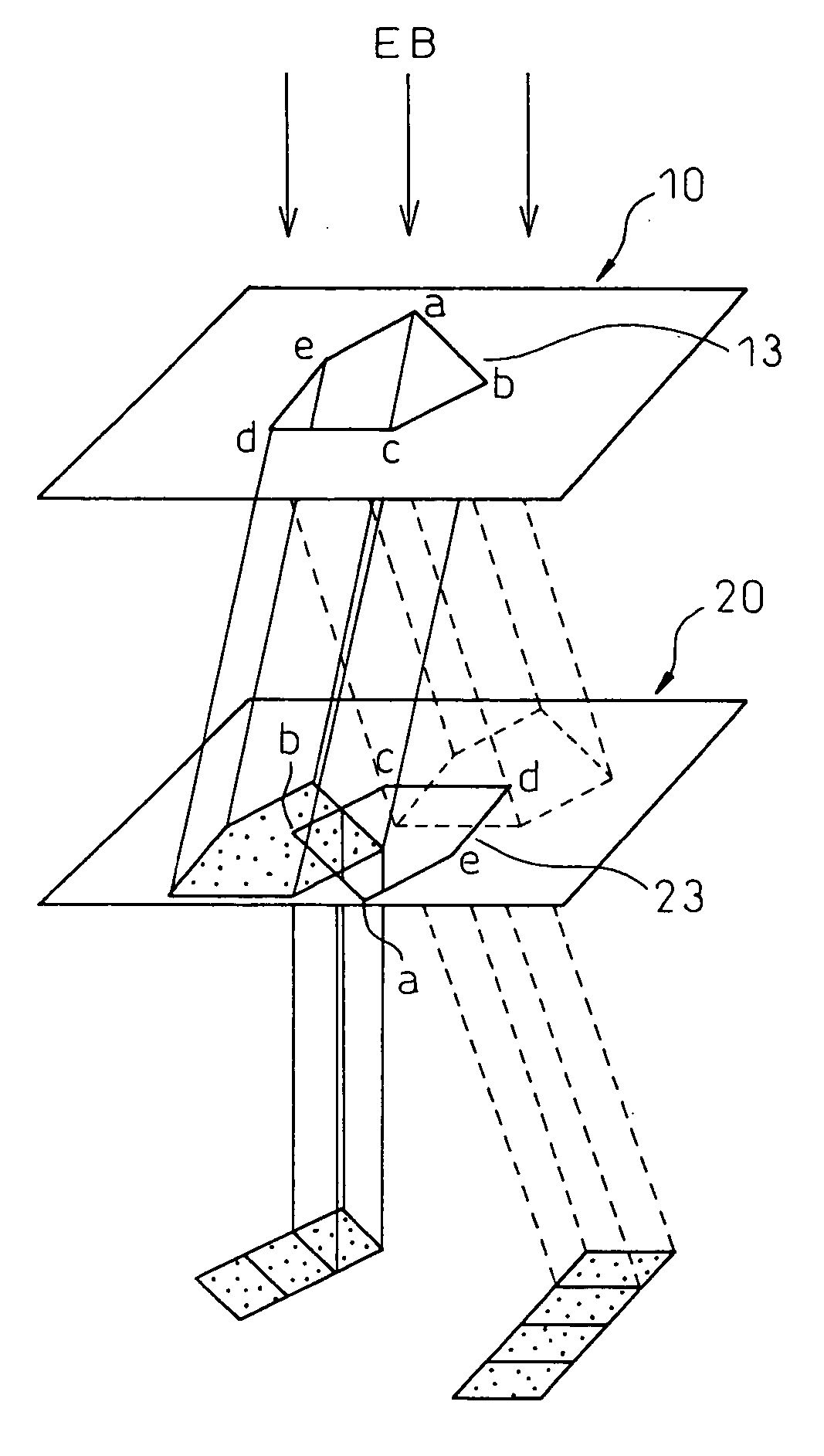
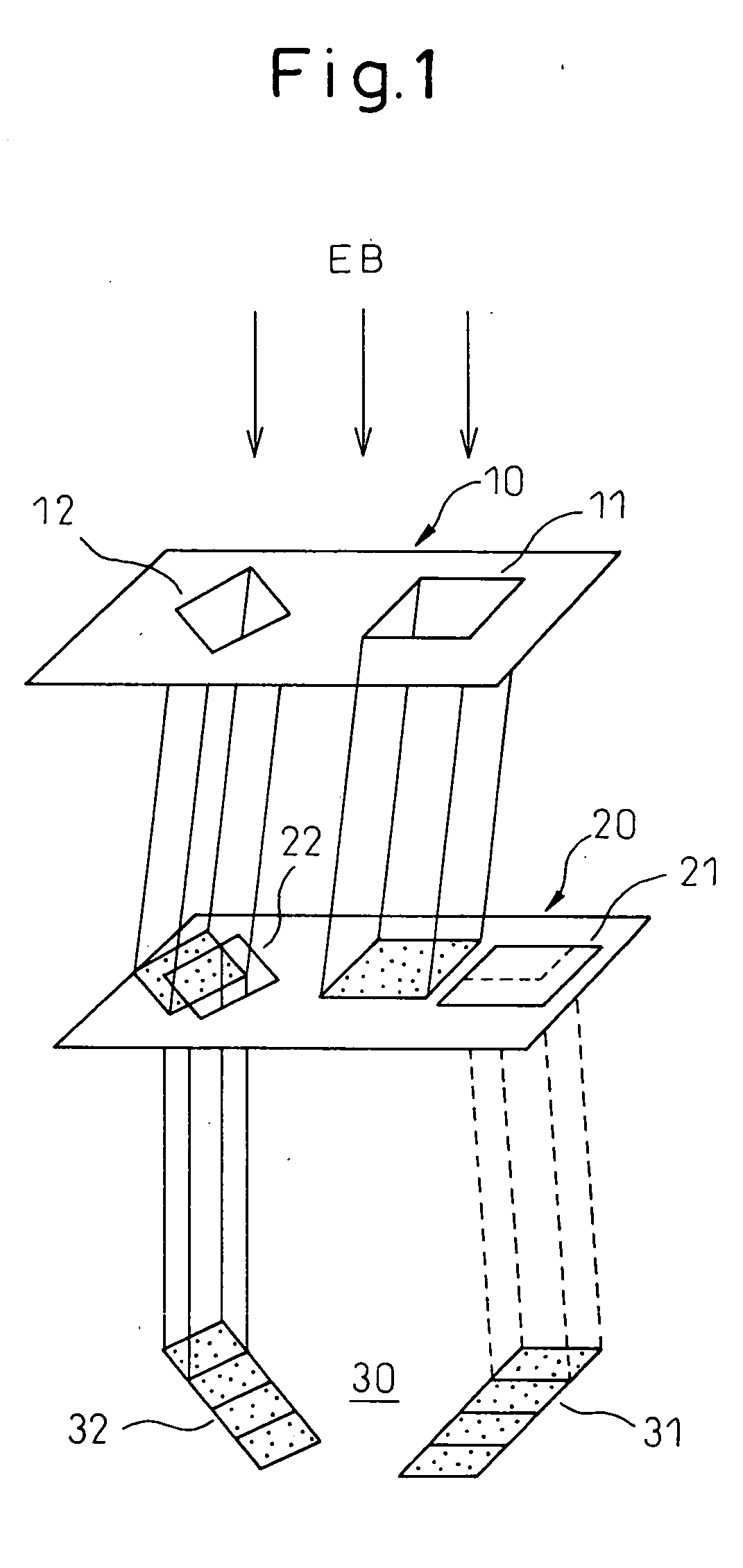
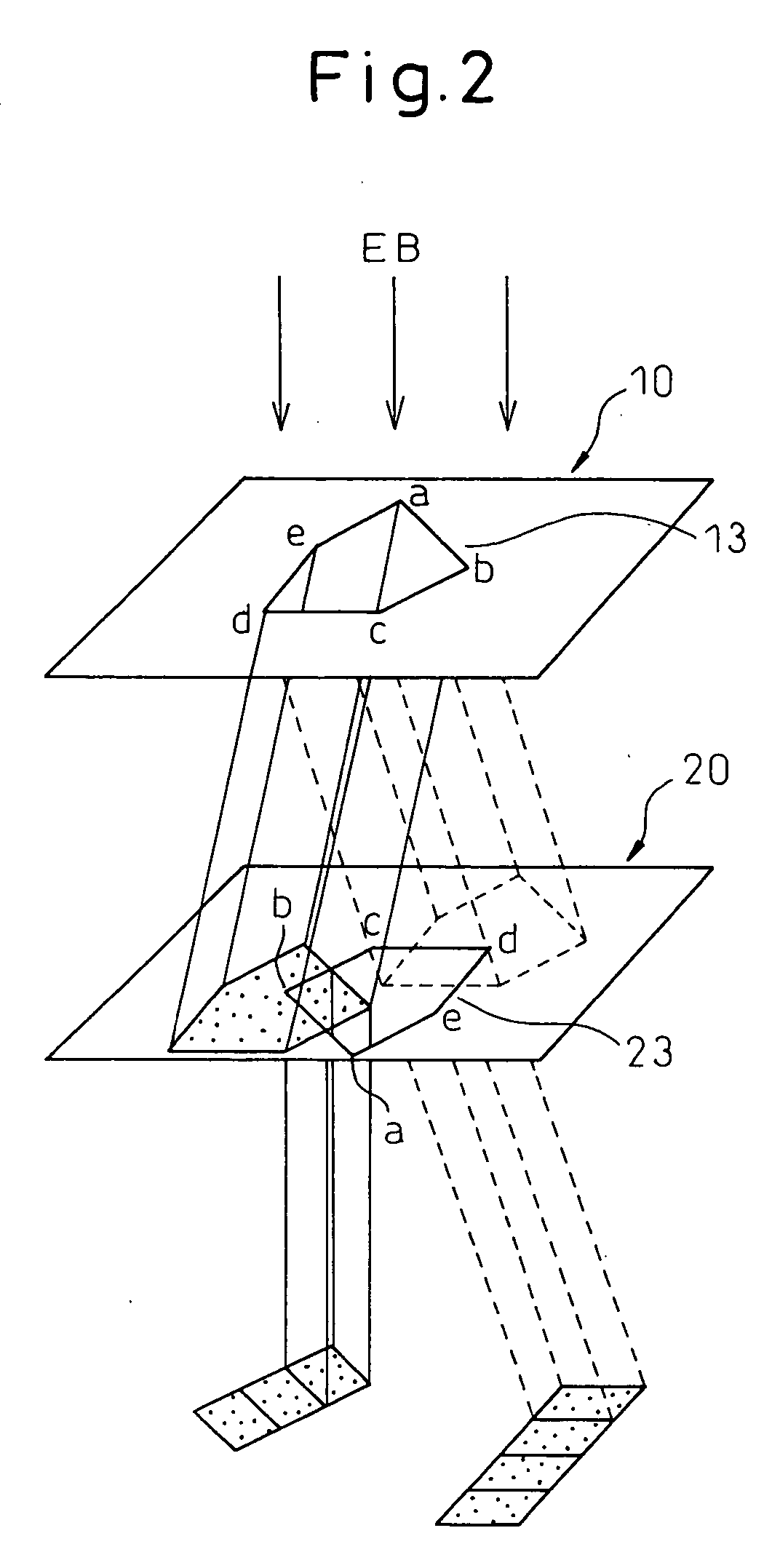
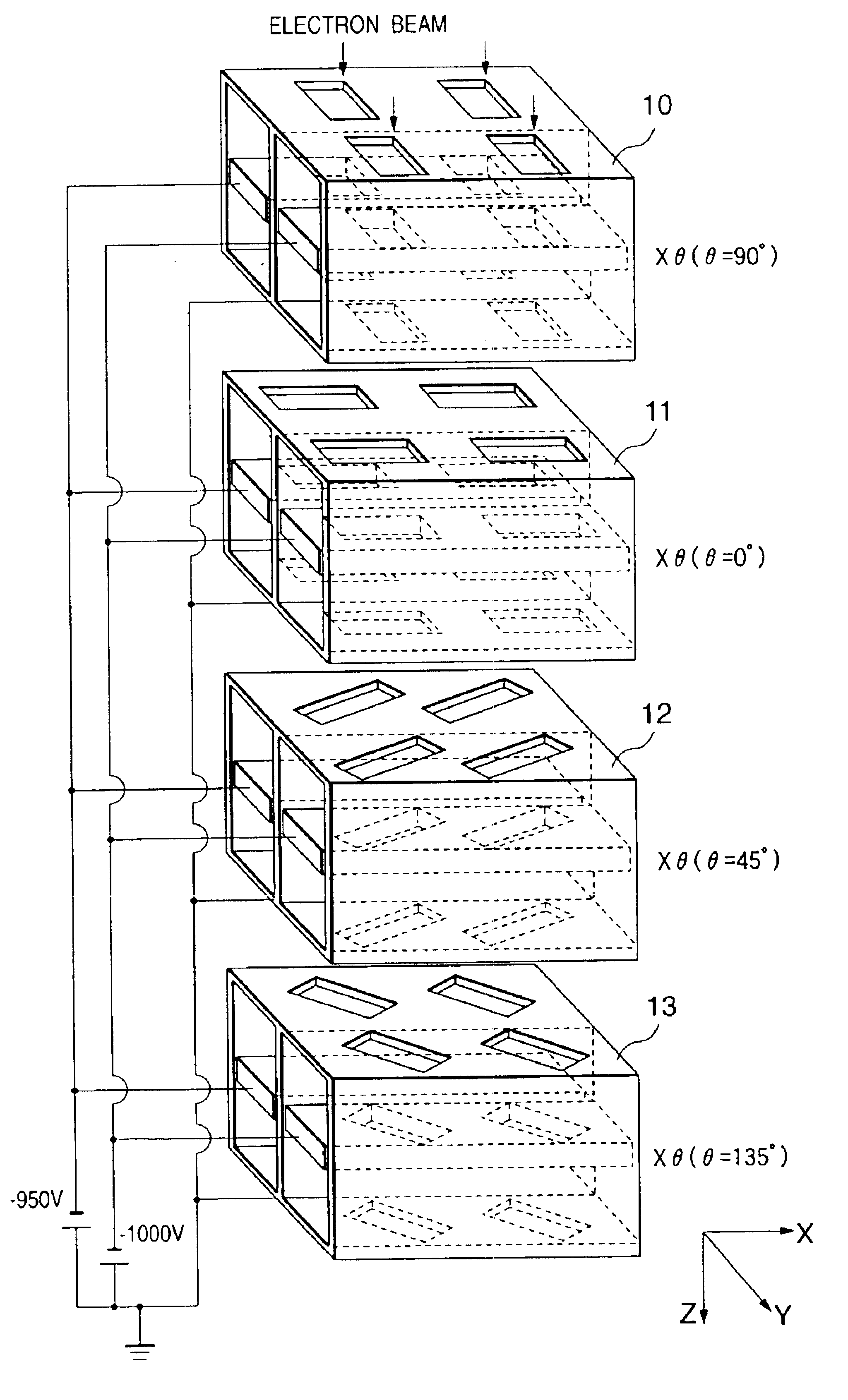
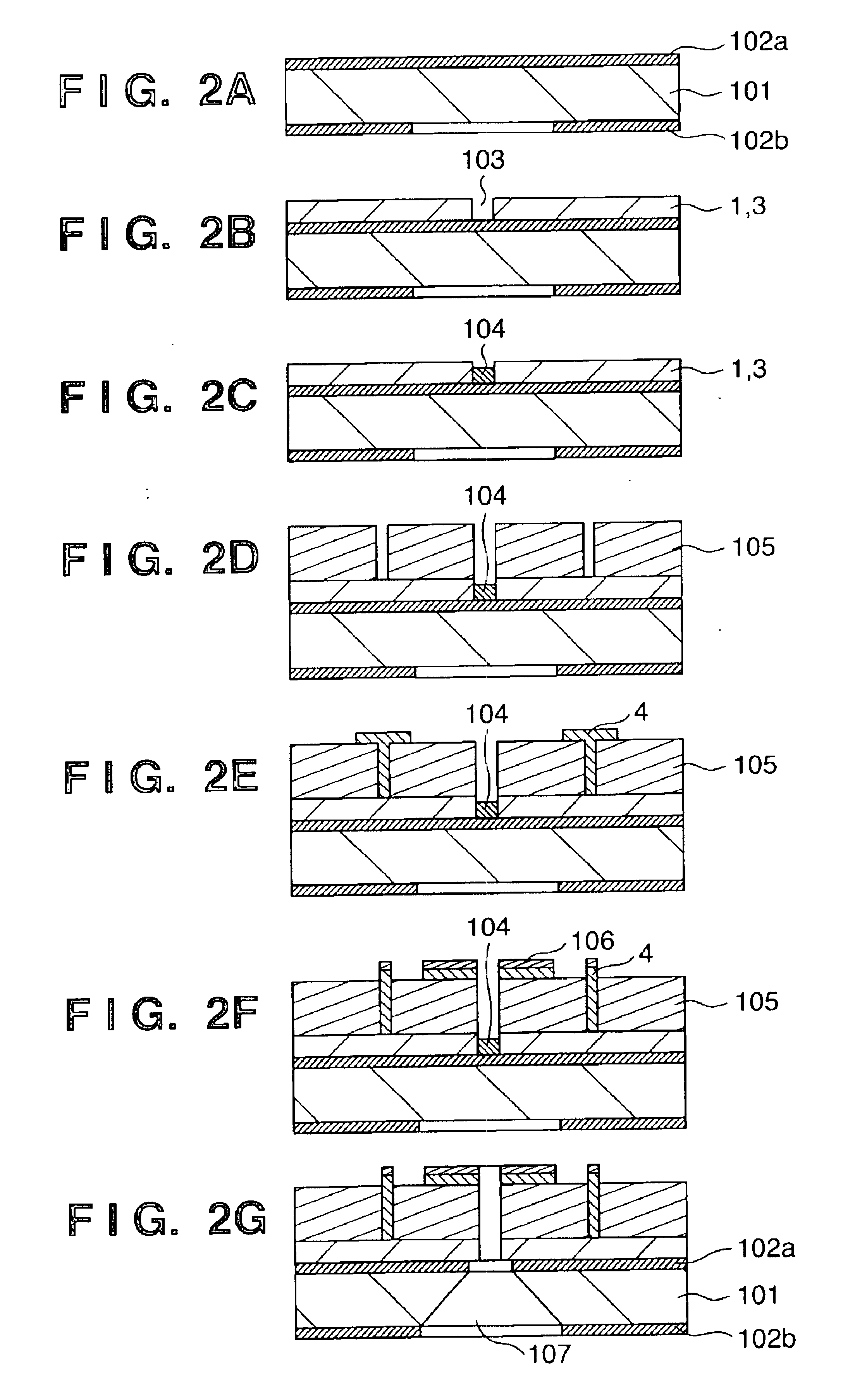
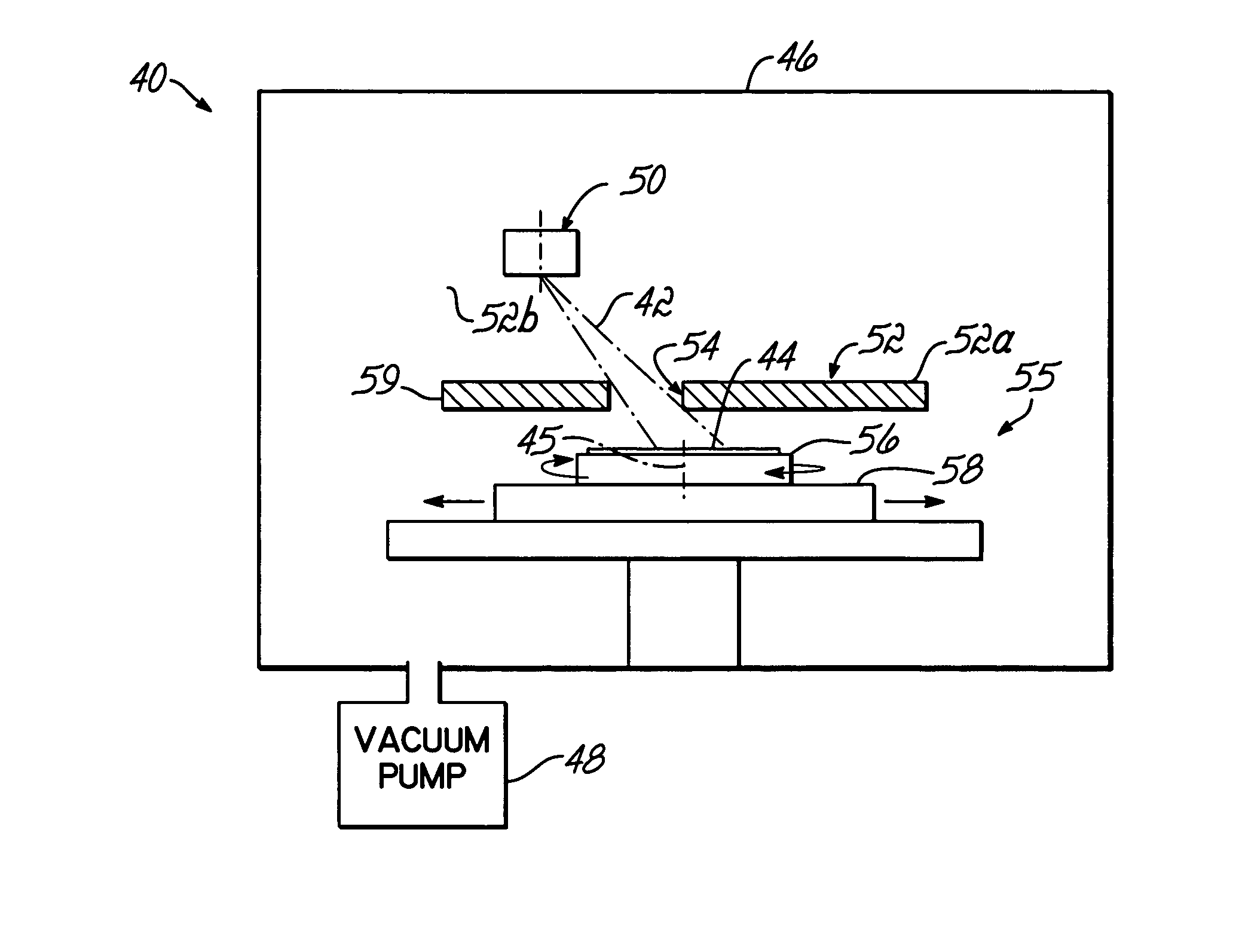
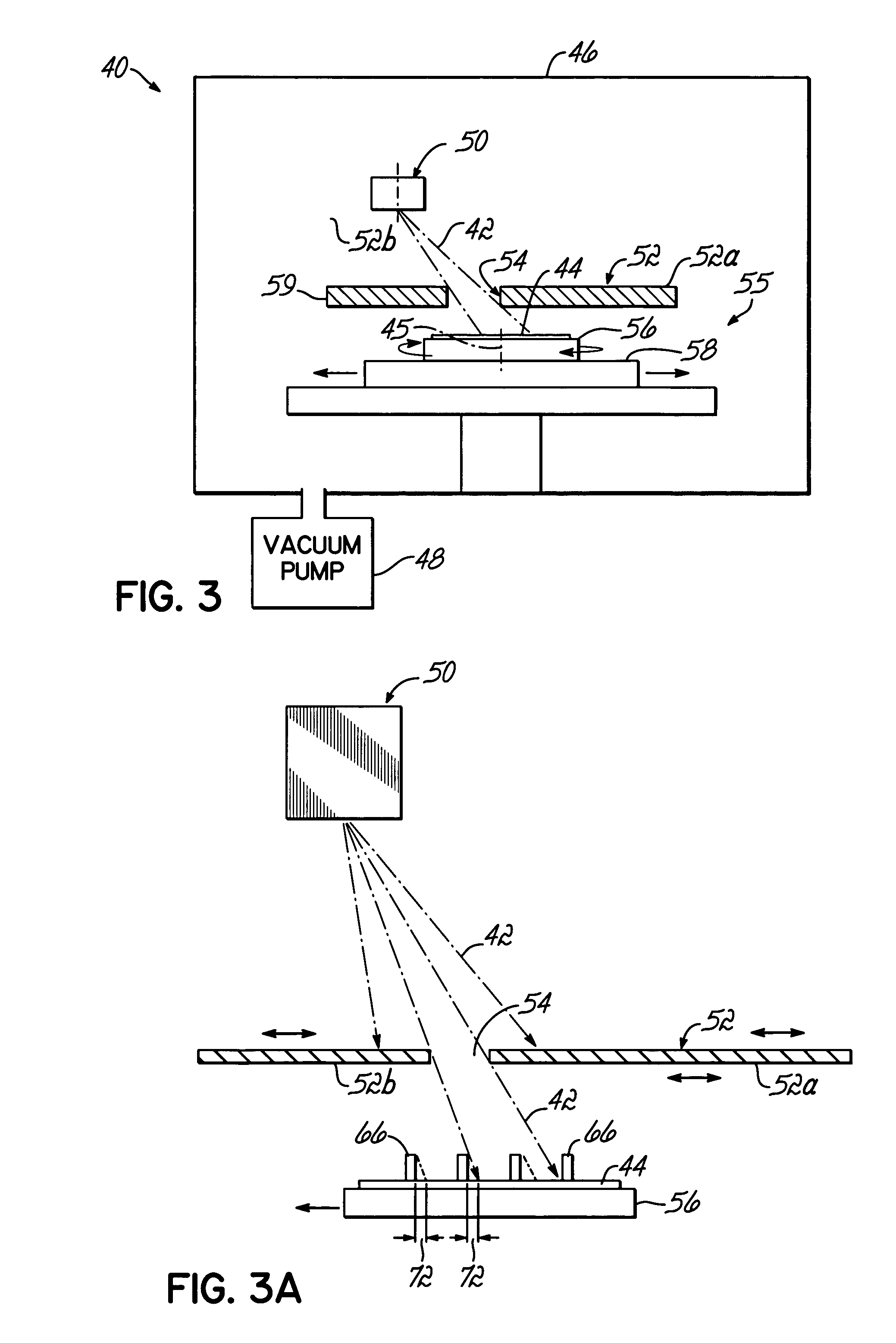
Variable rectangle-type electron beam exposure apparatus and pattern exposure-formation method
InactiveUS20060169925A1Low accuracyInhibit swellingElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsRectangular apertureElectron
A variable rectangle-type electron beam exposure apparatus for forming rectangular beams of different angles which is capable of highly finely conducting exposure with respect to a predetermined fine line pattern having an arbitrary angle in the pattern region. The apparatus includes a first slit member (10) in which a plurality of rectangular apertures (11, 12) are respectively arranged by different angles; a second slit member (20) in which a plurality of rectangular apertures (21, 22) which are respectively positioned in parallel with the corresponding rectangular apertures of the first slit member, are arranged; and a deflecting unit (40) for deflecting an electron beam, which has been transmitted through a plurality of apertures of the first slit member, so that, when the electron beam transmitted through the first aperture of the first slit member is transmitted through the corresponding first aperture of the second slit member, the electron beam transmitted through the apertures except for the first aperture of the first slit can be intercepted by the second slit member.
Owner:FUJITSU MICROELECTRONICS LTD
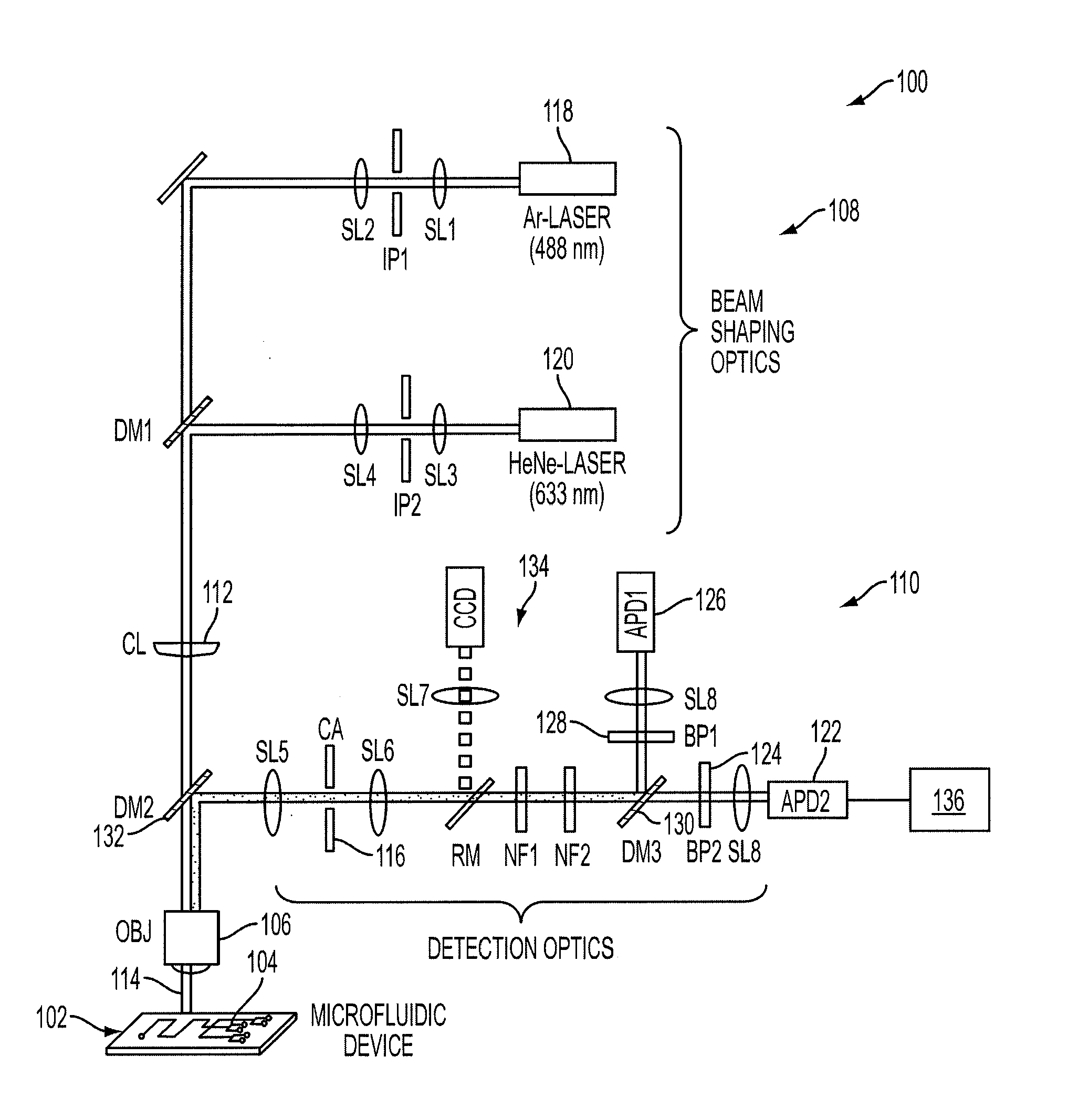
Cylindrical illumination confocal spectroscopy system
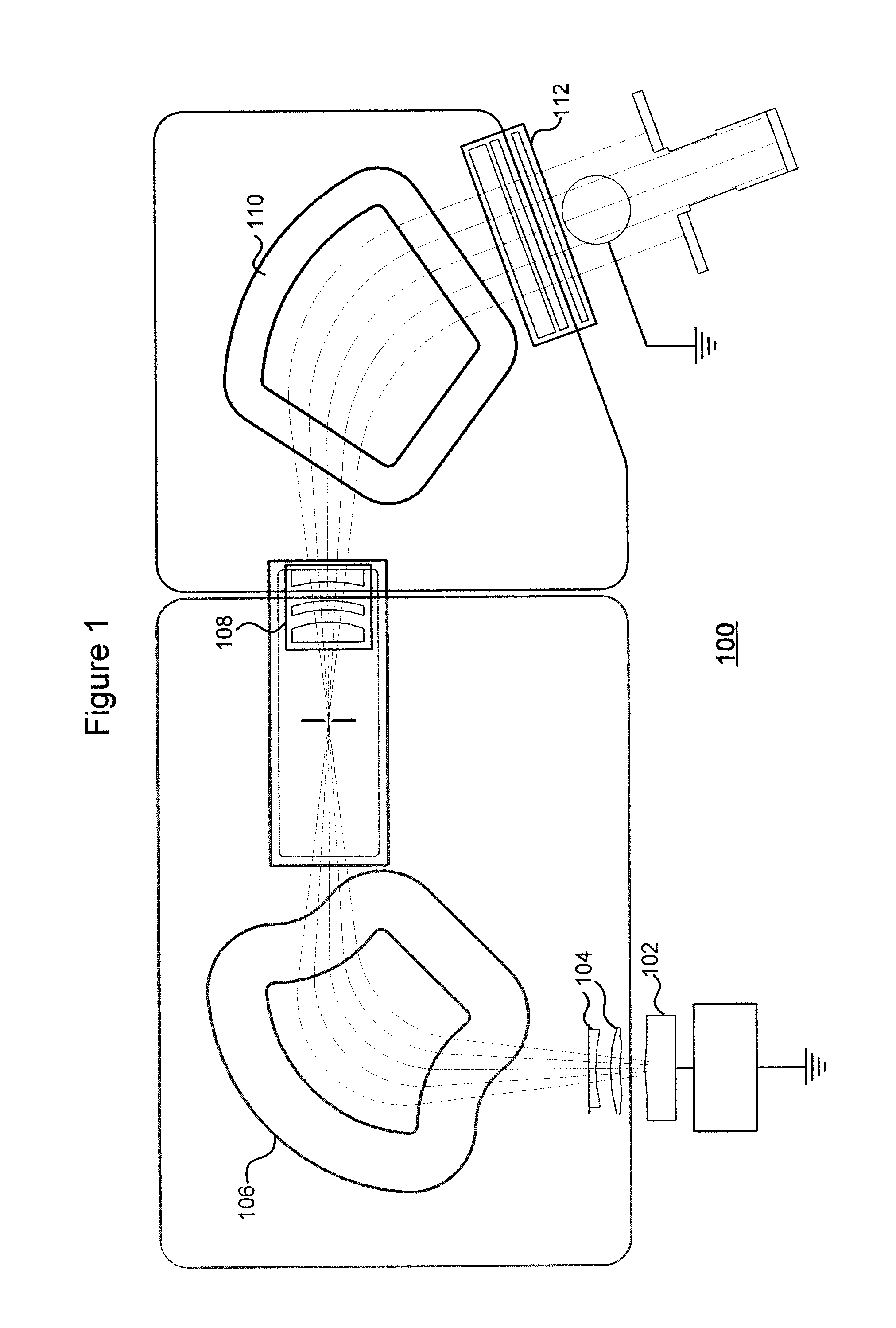
A cylindrical illumination confocal spectroscopy system has a fluidic device having a fluid channel defined therein, an objective lens unit arranged proximate the fluidic device, an illumination system in optical communication with the objective lens unit to provide light to illuminate a sample through the objective lens unit, and a detection system in optical communication with the objective lens unit to receive at least a portion of light that passes through the objective lens unit from the sample. The illumination system includes a beam-shaping lens unit constructed and arranged to provide a substantially planar illumination beam that subtends across, and is longer than, a lateral dimension of the fluid channel, the substantially planar illumination beam having a diffraction limited thickness in a direction substantially orthogonal to the lateral dimension of the fluid channel. The substantially planar illumination beam incident upon the fluidic device has a width that is substantially longer than the lateral dimension of the fluid channel such that the substantially planar illumination beam has an illumination intensity that is uniform across the lateral dimension of the fluid channel to within ±10%. The detection system comprises an aperture stop defining a substantially rectangular aperture having a longitudinal dimension and a transverse dimension. The aperture stop is arranged so that the substantially rectangular aperture is confocal with an illuminated portion of the fluid channel such that the transverse dimension of the substantially rectangular aperture substantially subtends the lateral dimension of the fluid channel without extending substantially beyond the fluid channel and allows light to pass from only a uniform excitation region while occluding light from outside the uniform excitation region, and the lateral dimension of the substantially rectangular aperture substantially matches the diffraction limited thickness of the planar illumination beam.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
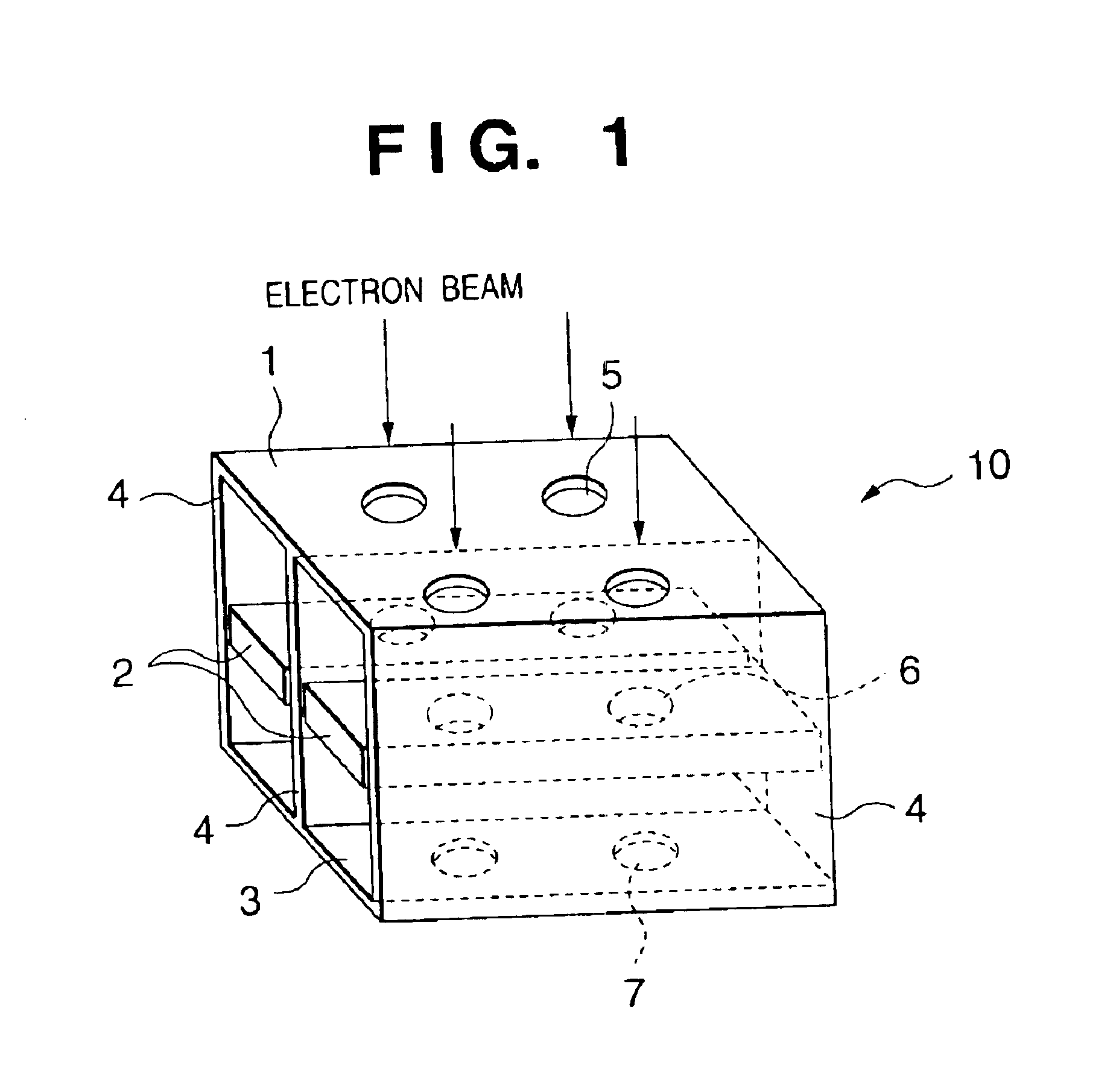
Electron optical system, charged-particle beam exposure apparatus using the same, and device manufacturing method
InactiveUS6903345B2Improve accuracyReduce crosstalkThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersRectangular apertureOptical axis
An electron optical system has a plurality of electron lenses. The system includes a first electron optical system array having electrodes with a plurality of rectangular apertures, and a second electron optical system array having electrodes with a plurality of rectangular apertures. The first and second electron optical system arrays are arranged along an optical axis in which a long side of each aperture of the first electron optical system array is perpendicular to a long side of each aperture of the second electron optical system array.
Owner:CANON KK
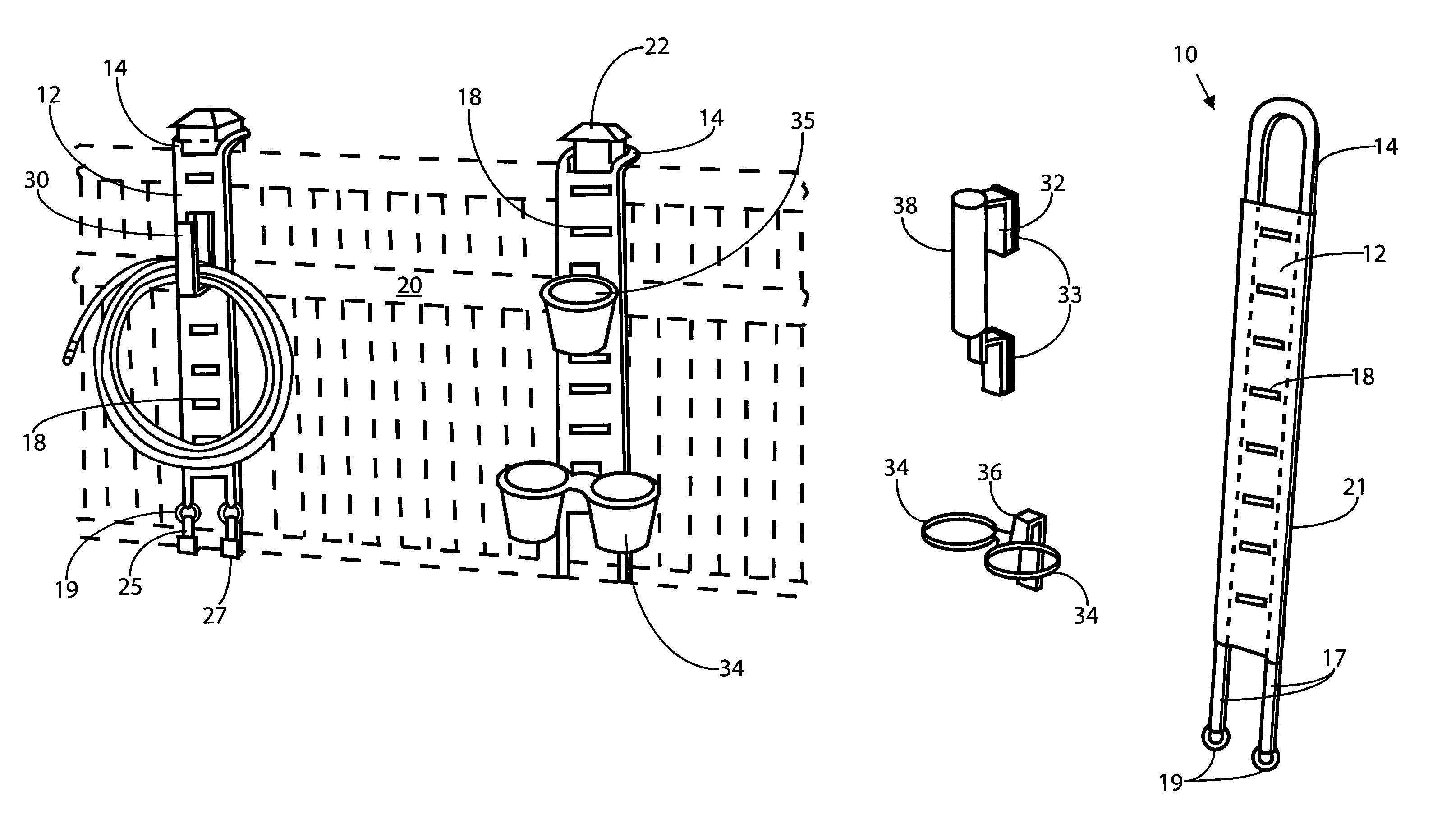
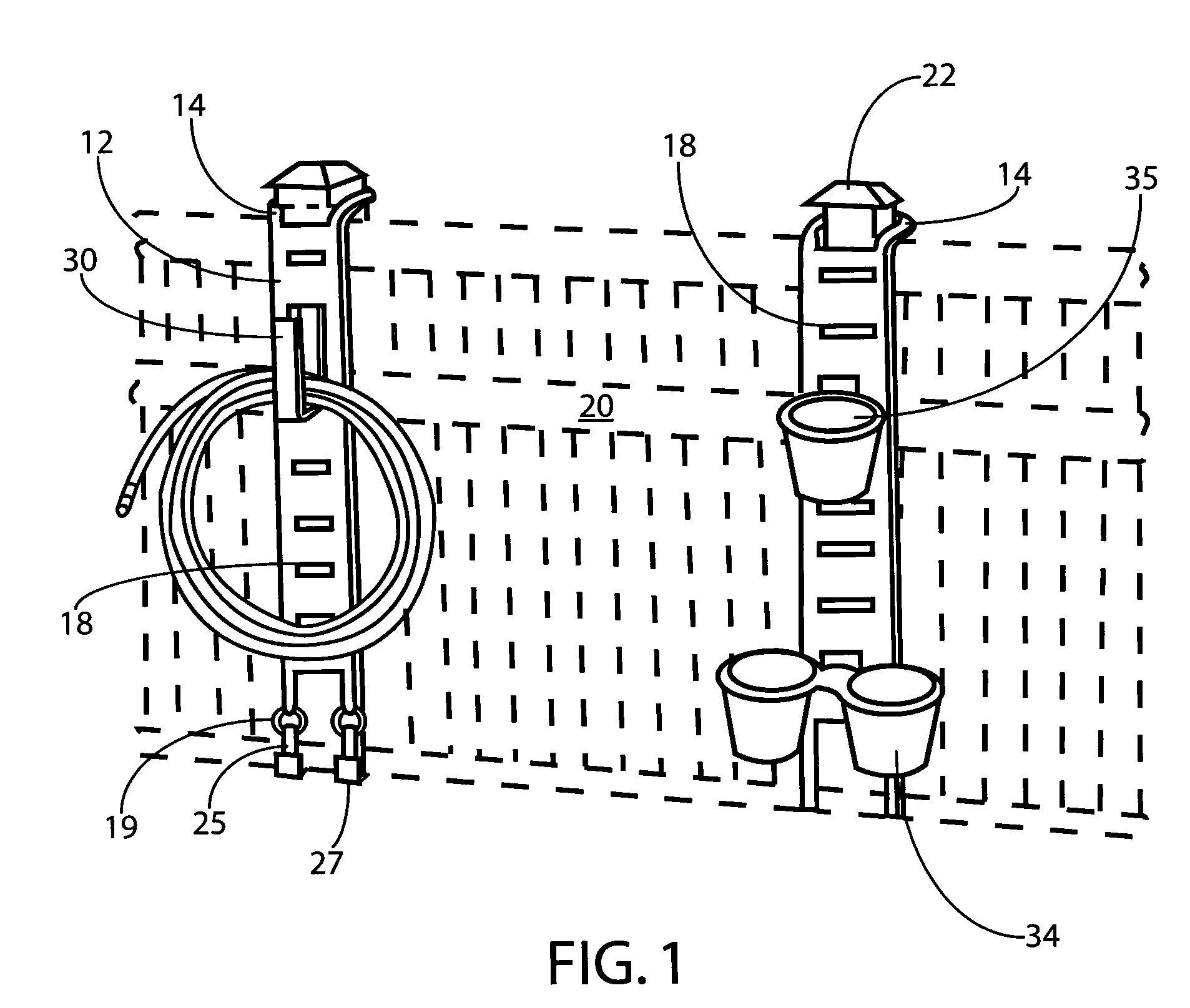
Protective fence hanger
ActiveUS7845604B2Potential damageEasy to installCandle holdersLighting support devicesRectangular apertureEngineering
Owner:CONNOR JR ROBERT T
Etching device and etching method for any apodised fiber bragg grating
ActiveCN102621609ASimple structureEasy to implementDiffraction gratingsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusFiberGrating
The invention provides an etching device and an etching method for any apodised fiber bragg grating. The device comprises a laser, a rectangular aperture, a programmable spatial light modulator, a function generator, a cylindrical lens, phase mask fixtures and three-dimensional adjusting racks. The device has the advantages of simple structure, economy, practicality, high repeatability and high flexibility and is easy to realize; and the limitations in a traditional apodised fiber bragg grating manufacturing process that a high coherent light source needs to be used or two conjugated amplitude templates need to be processed, and only a single apodised fiber bragg grating can be manufactured are overcome.
Owner:南京聚科光电技术有限公司
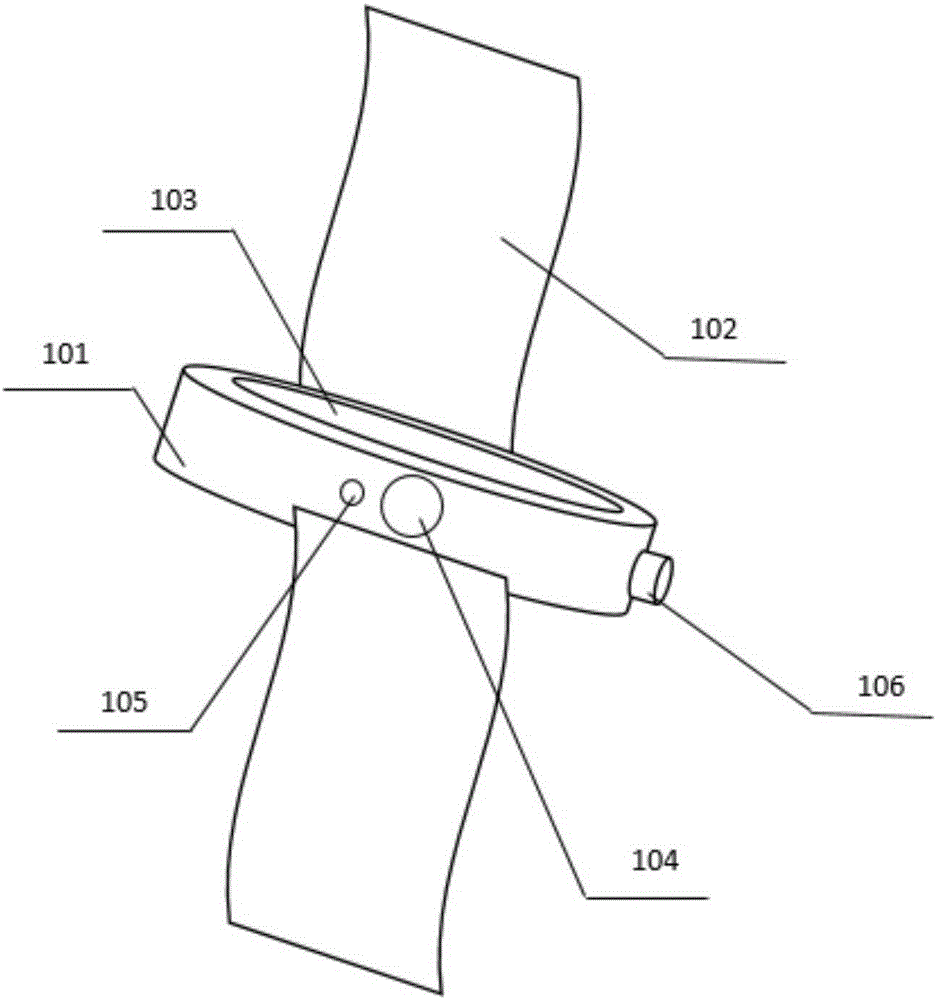
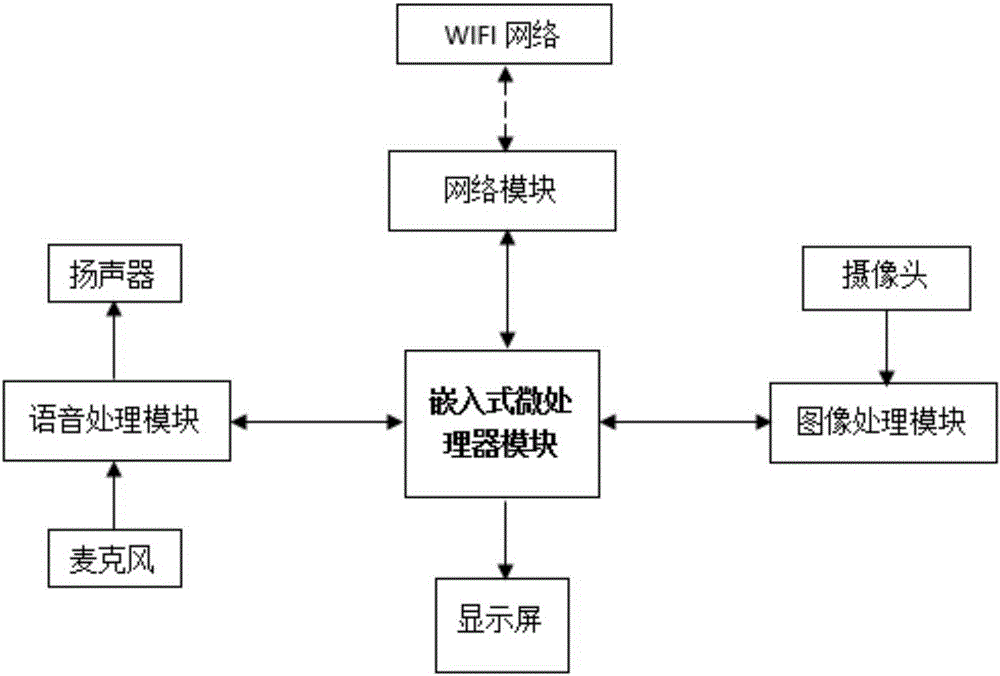
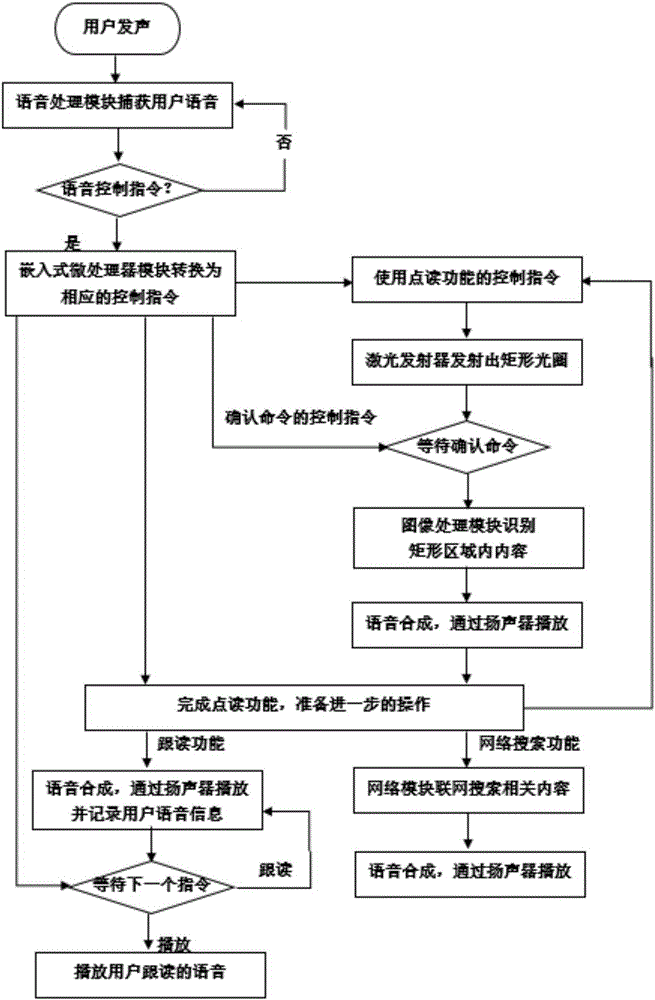
Voice control based point-and-read watch and point-and-read method thereof
ActiveCN105224073AExpand your learningMeet learning needsInput/output for user-computer interactionSpeech recognitionRectangular apertureImaging processing
The present invention discloses a voice control based point-and-read watch, comprising a watch body and a watch band. The present invention further discloses a point-and-read method applied to the voice control based point-and-read watch, wherein the method comprises the following steps: (1) sending, by a user, a voice control command and performing a point-and-read operation; (2) moving, by the user, the watch to enable an aperture to surround content that needs point-and-read; (3) performing, by an image processing module, intelligent identification on an area surrounded by the rectangular aperture, to generate a text; (4) performing, by a voice processing module, TTS voice synthesis according to the text, playing corresponding point-and-read content; and (5) performing, by the user, a further operation on the point-and-read content. The present invention has the advantages of meeting a requirement of the user for any book, and enabling the user to perform a point-and-read operation more conveniently during the study.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
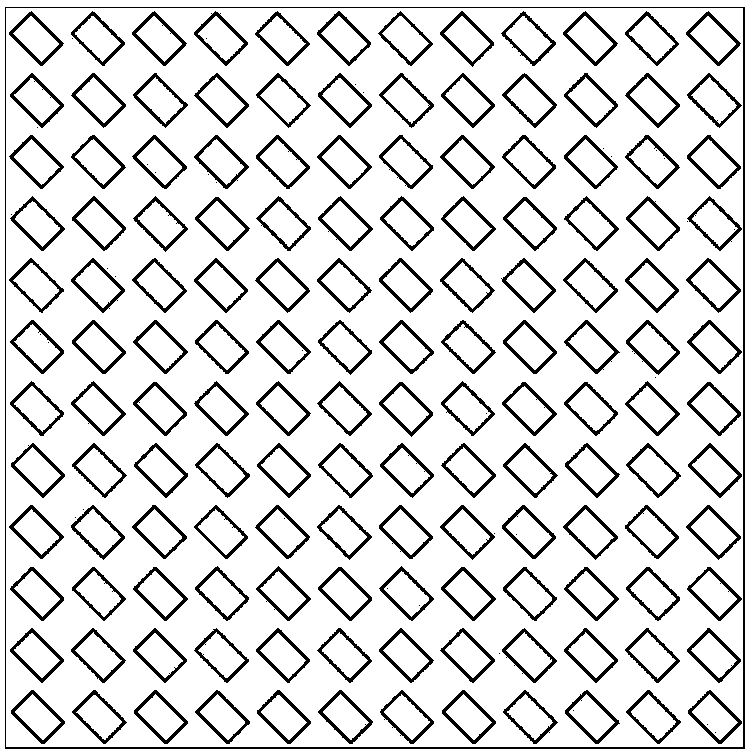
Rectangular-hole single-stage diffraction grating
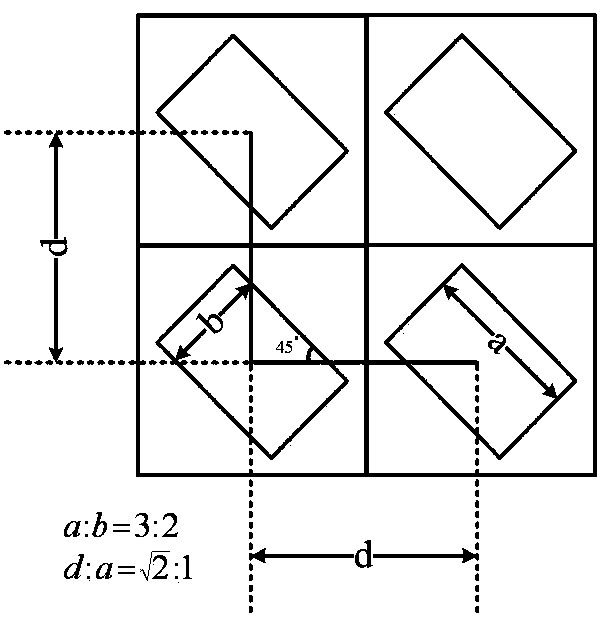
ActiveCN103901519ASelf-supportingImprove efficiencyDiffraction gratingsRectangular apertureMaterials science
The invention provides a rectangular-hole single-stage diffraction grating. The grating is formed by repeatedly arranging regular light-pervious rectangular hole modules on a light-impervious substrate periodically in the two-dimensional direction, the length-width ratio of each module rectangular hole of the grating is 3:2, the long edge of each rectangular hole and the one-dimensional axis direction form an included angle of 45 degrees, and the proportion of the distance between diagonal line intersection points of every two adjacent rectangular holes in the same dimension to the length of the long edge of each rectangular hole is shown in the instruction. Compared with an existing grating, the single-stage diffraction grating can effectively inhibit high-level diffraction, 2n-level and 3n-level diffraction can be eliminated, n is an integer except zero, and five-level and higher-level diffraction can be inhibited to be 0.16% or lower than 0.16% of first-level diffraction. The single-stage diffraction grating can achieve self-supporting, has higher diffraction efficiency and has a binaryzation feature; the regular rectangular hole modules are arranged in order, and accordingly the grating is easy to manufacture and popularize and use in practice.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
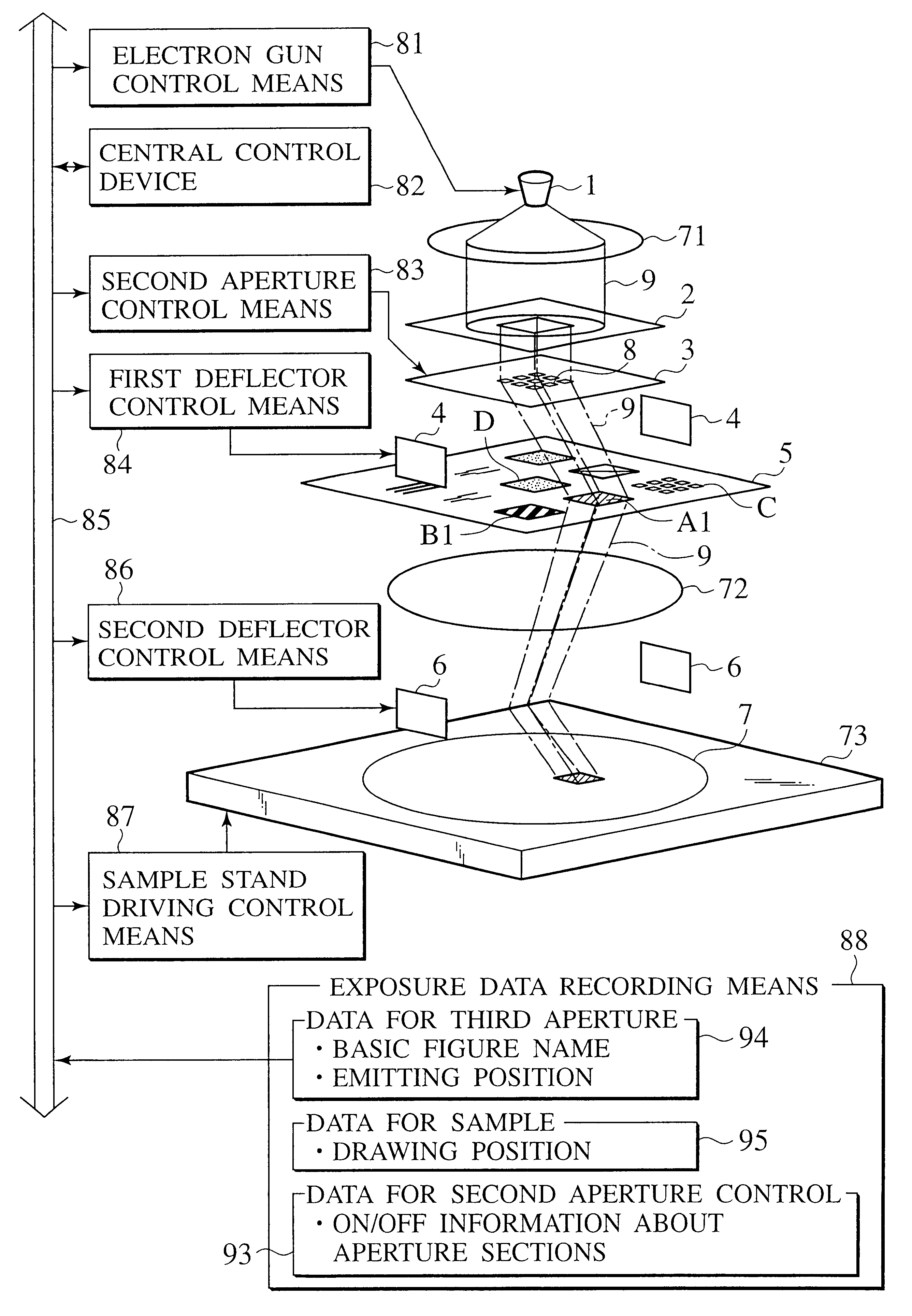
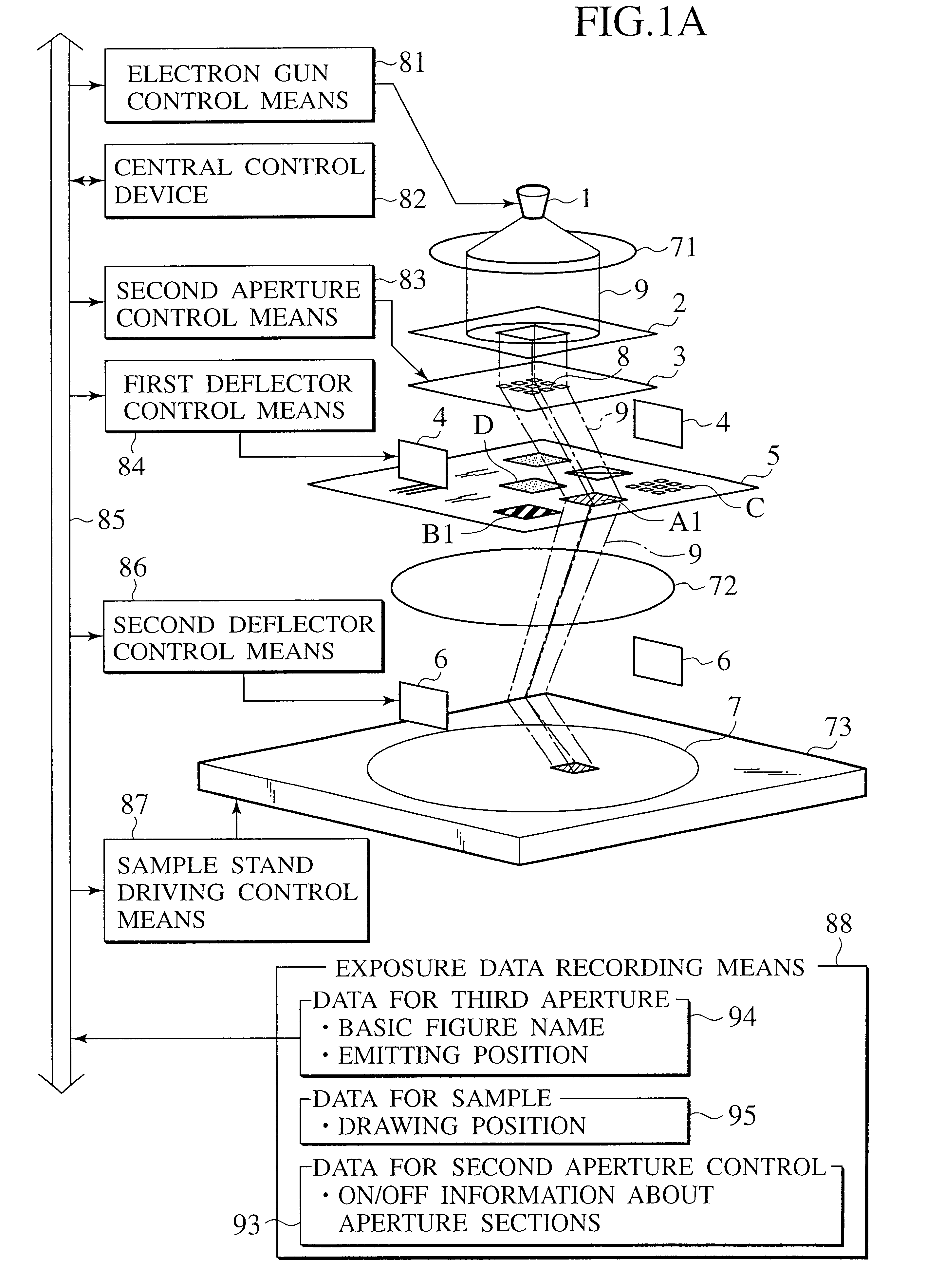
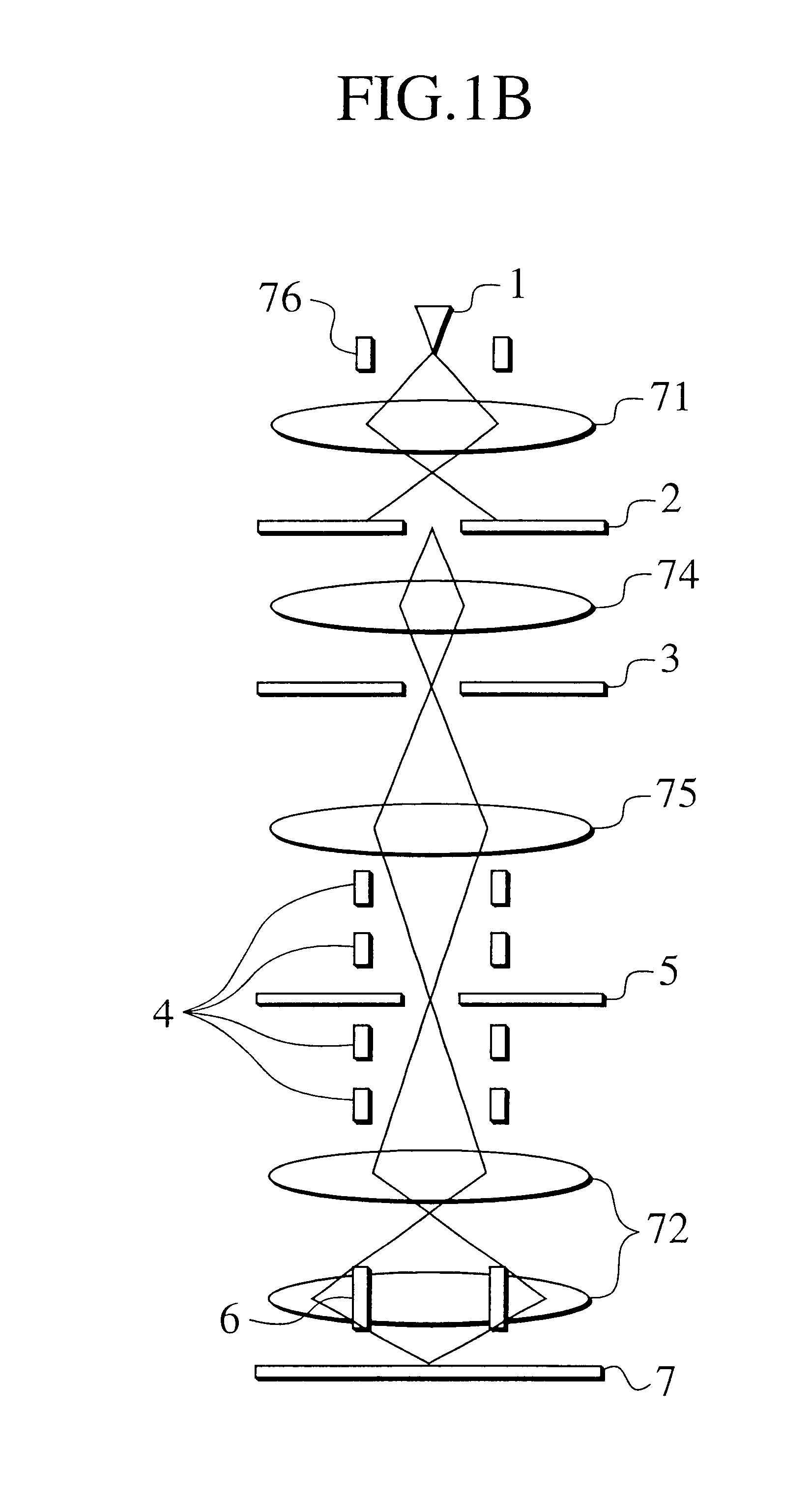
Charged beam exposure apparatus having blanking aperture and basic figure aperture
InactiveUS6703629B2Particle separator tubesRadiation/particle handlingRectangular apertureLight beam
Two or more-staged masks are prepared for a charged beam generating source. One mask has first aperture sections having rectangular apertures arranged into a lattice form, and electrodes which deflects a beam at respective first aperture sections. The other mask has a second aperture section having basic figure apertures for shaping the beam which passes or passed through the first aperture sections. Layout data of a semiconductor apparatus are divided into sizes of the basic figures which take reduction in exposure into consideration so as to be classified according to the basic figures. The beam which is shaped into a form of an overlapped portion of the divided layouts and the classified basic figure is emitted onto a sample.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
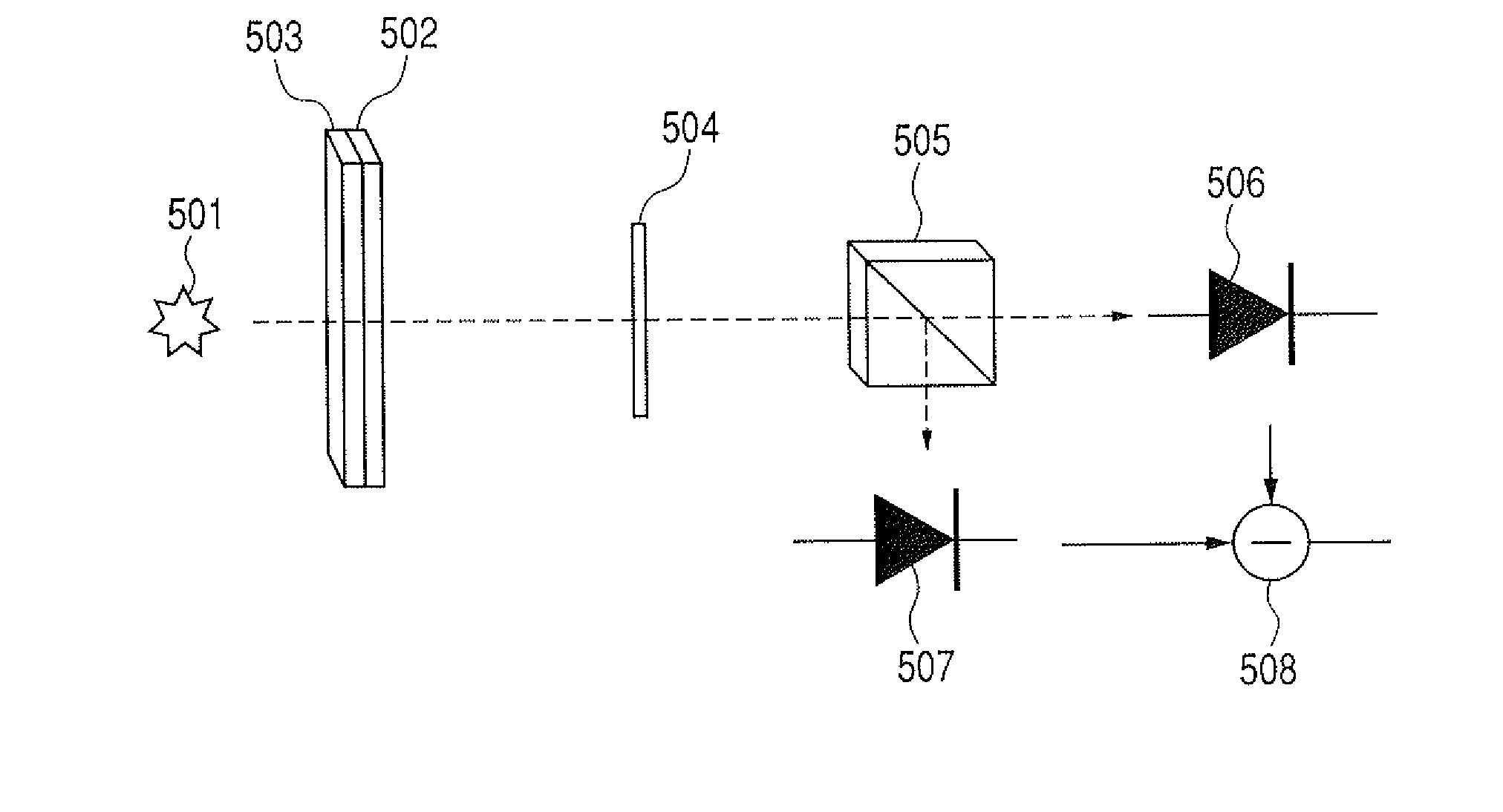
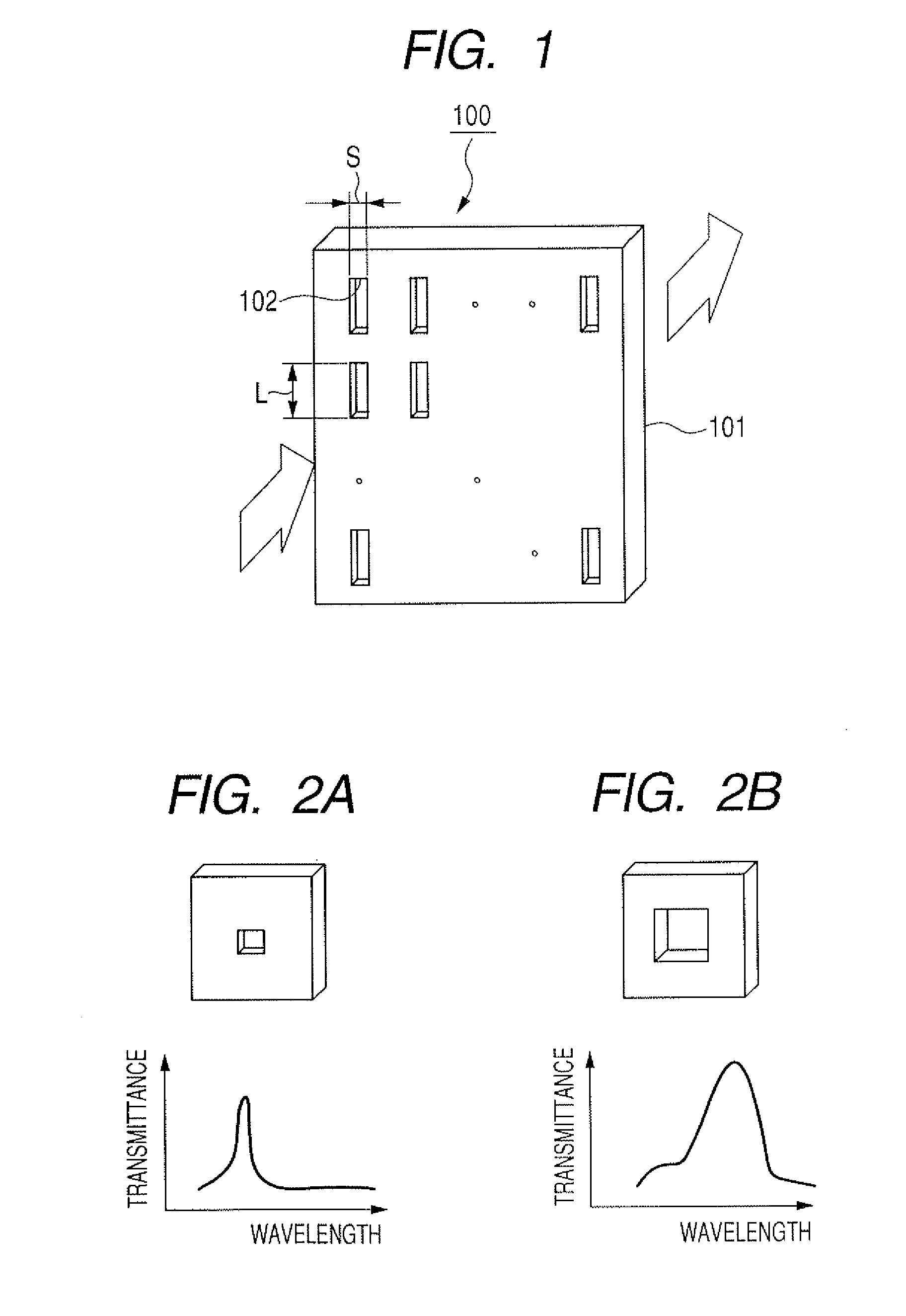
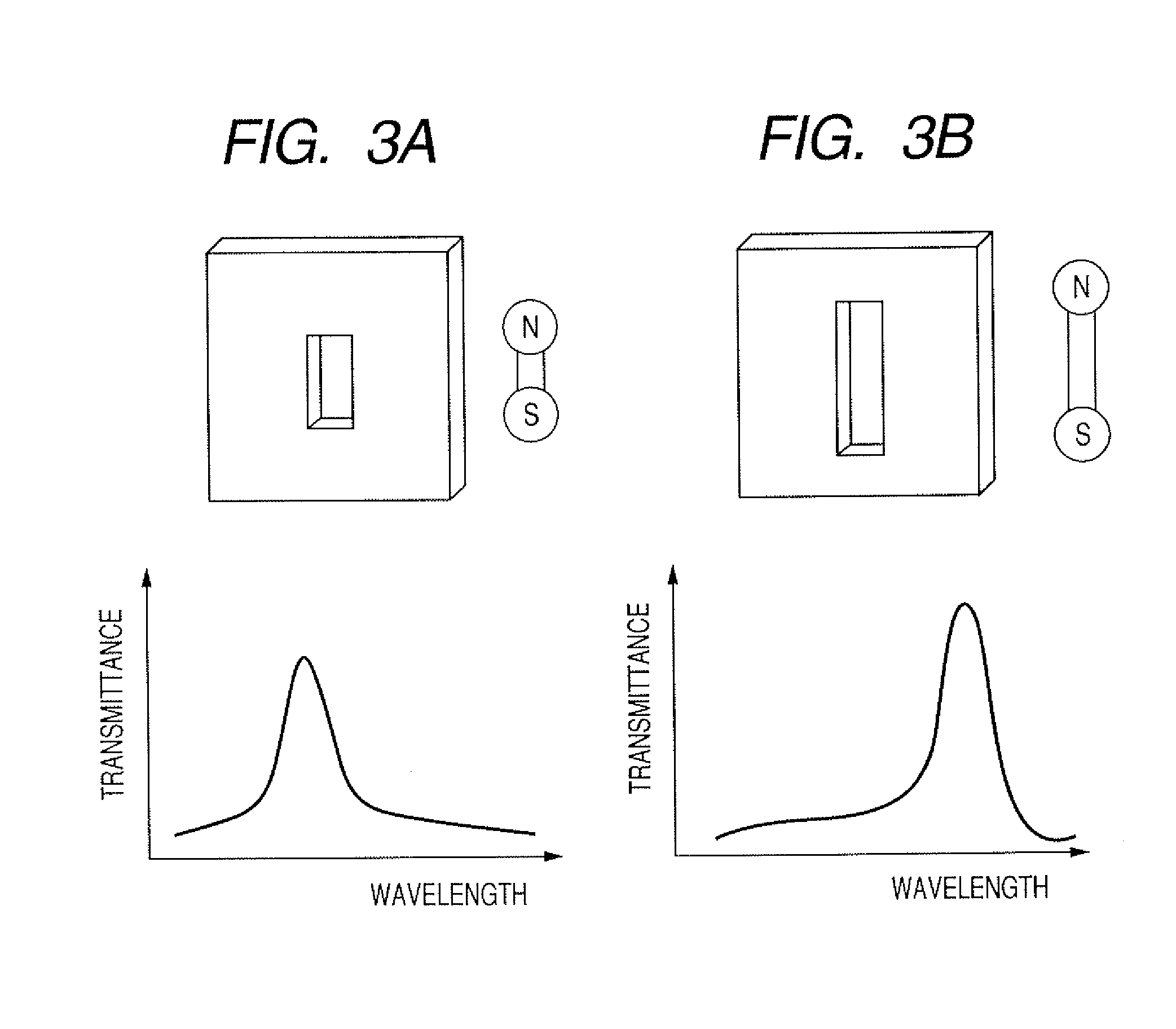
Method for designing light transmission device, optical element and sensor
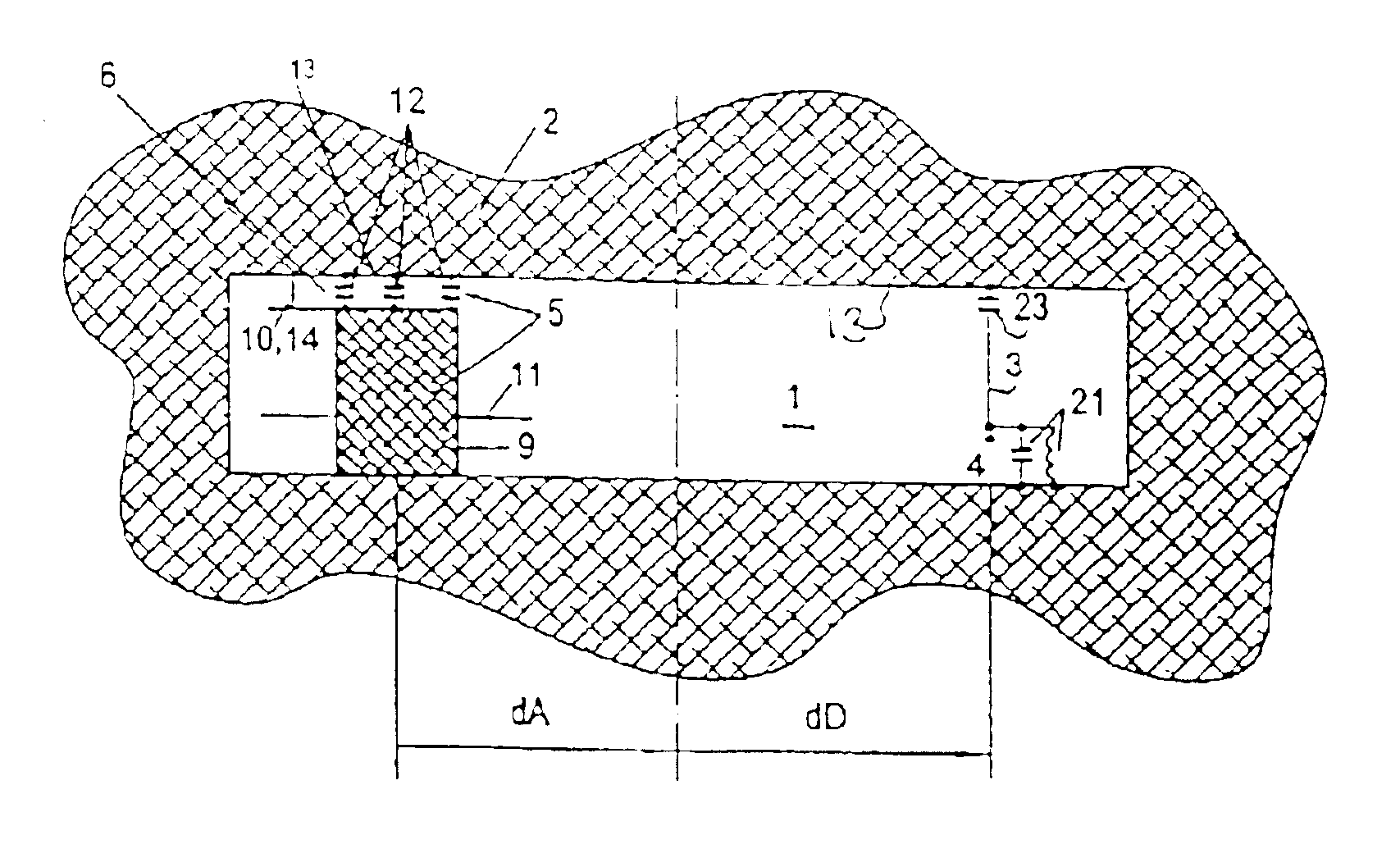
The present invention provides a method for designing a light transmission device, which adjusts a wavelength region of a spectrum of transmitted light without expanding a width of a transmission spectrum and without lowering the transmittance. The method for designing a light transmission device having a metal thin film, and a rectangular aperture which is formed in a plane of the metal thin film, has a long side and a short side and makes light pass therethrough, wherein the short side has a dimension smaller than a wavelength of incident light, and the long side is determined to have such a dimension that a peak wavelength at which the transmittance of light passing through the rectangular aperture is maximal can be a predetermined value.
Owner:CANON KK
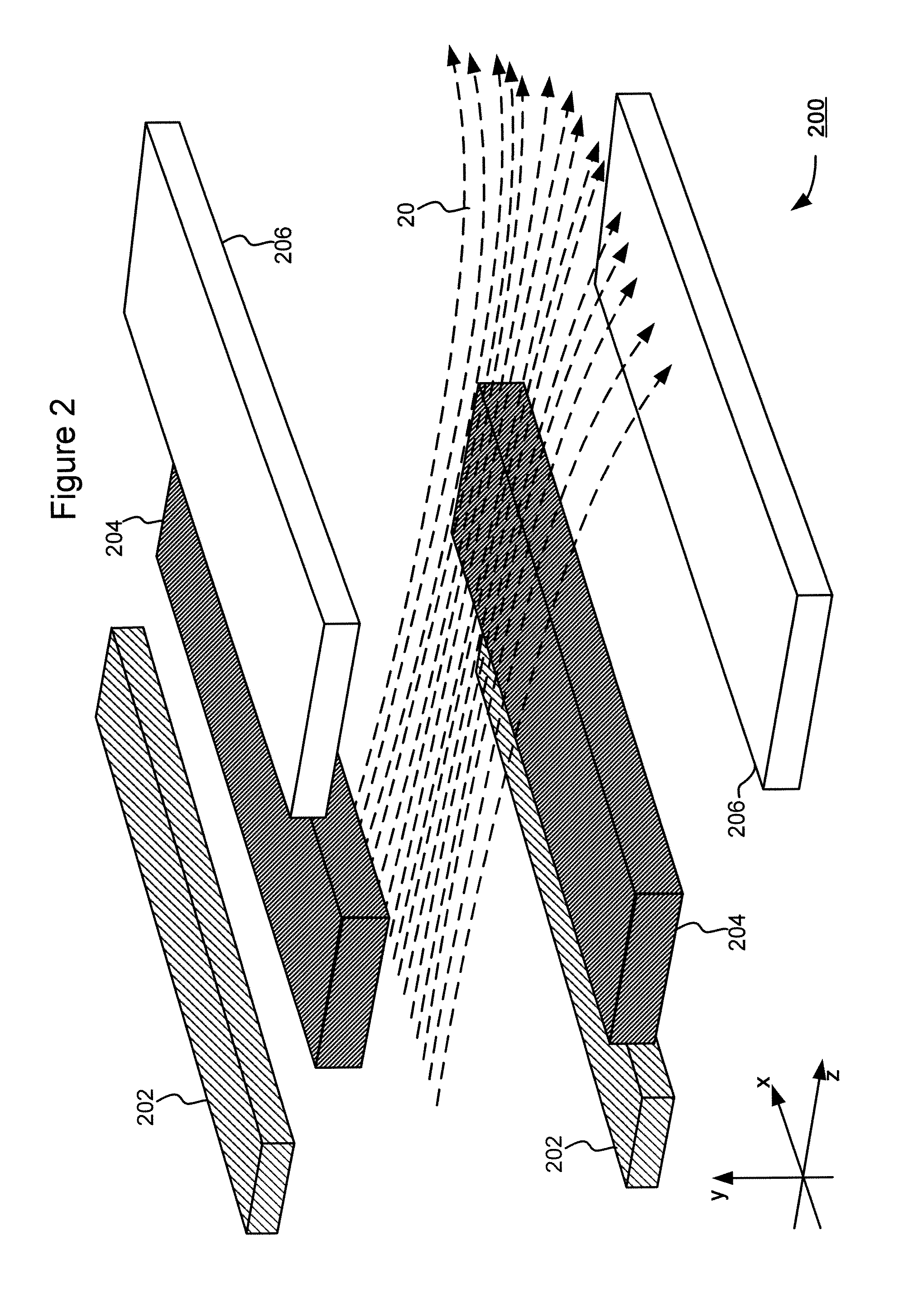
Technique for Shaping a Ribbon-Shaped Ion Beam
A technique for shaping a ribbon-shaped ion beam is disclosed. In one particular exemplary embodiment, the technique may be realized as an apparatus for shaping a ribbon-shaped ion beam. The apparatus may comprise an electrostatic lens having a substantially rectangular aperture for a ribbon-shaped ion beam to pass through, wherein a plurality of focusing elements are positioned along short edges of the aperture, and wherein each focusing element is separately biased and oriented to shape the ribbon-shaped ion beam.
Owner:VARIAN SEMICON EQUIP ASSOC INC
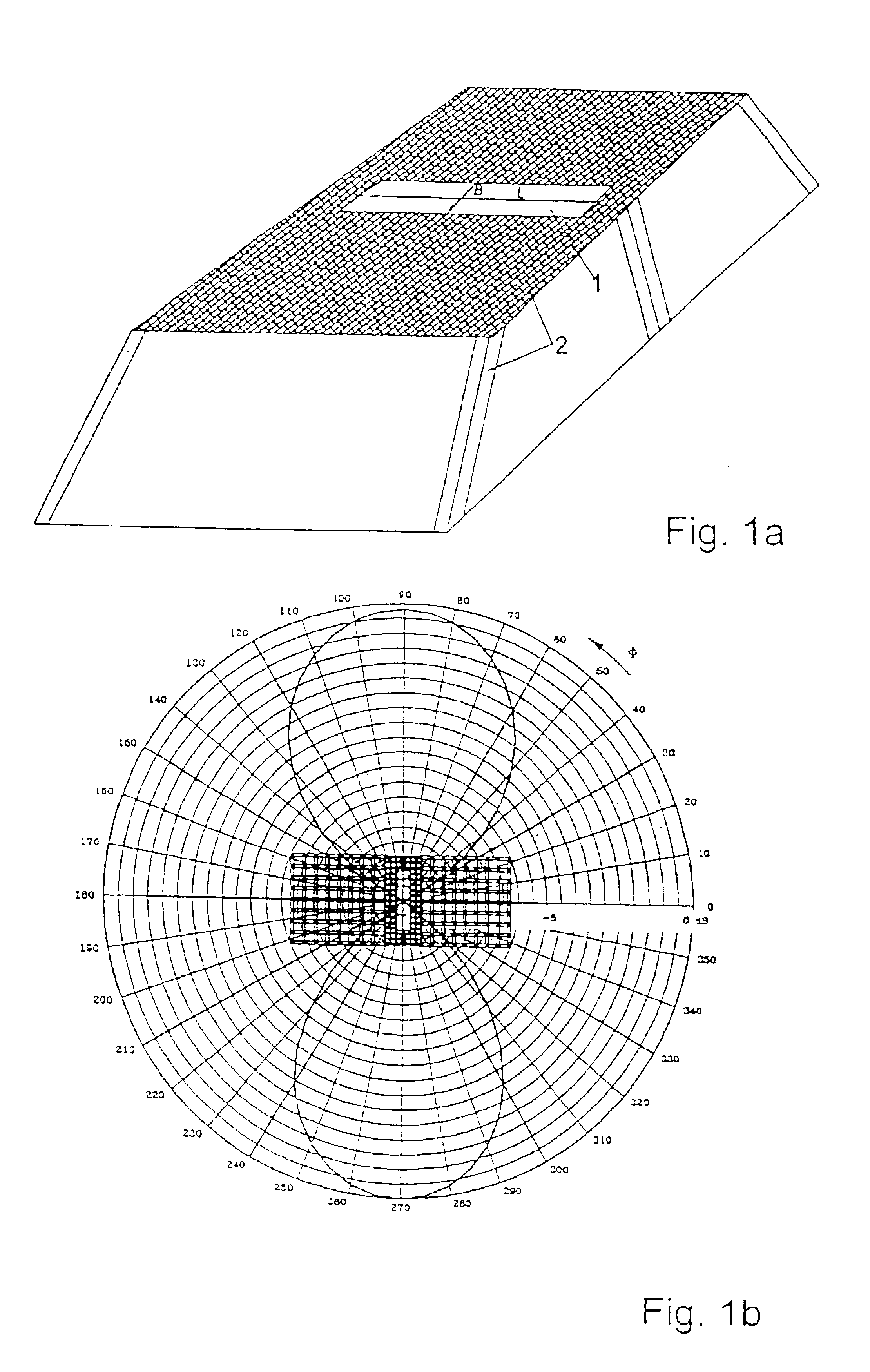
Antenna arrangement in the aperture of an electrically conductive vehicle chassis
InactiveUS6927735B2Avoid disadvantagesReduce inductanceAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesSlot antennasCapacitanceLow inductance
A radio antenna arrangement disposed in the conductive surface of a vehicle consisting of a substantially rectangular aperture having aperture length L and width B, wherein said aperture length L is sufficiently small so that the self-resonant frequency of the aperture is greater than the center frequency of the operating frequency range. There is a capacitive tuning element disposed in the aperture for tuning the aperture to a resonant frequency to approximately the center frequency of the operating frequency range. The capacitive tuning element serves as capacitive connection between the edges of the aperture, and is formed as a low-inductance element, so that due to the residual inductive effect, the remaining magnetic reactive power is as small as possible relative to the magnetically generated reactive power from the magnetic fields in the aperture. An input coupling element is also disposed in the aperture for coupling the antenna connection point to the resonance like high electromagnetic fields.
Owner:DELPHI DELCO ELECTRONICS EUROPE GMBH
Device capable of generating uniform linear laser beams based on high-numerical aperture cylindrical lens focusing
The invention relates to a device capable of generating uniform linear laser beams based on high-numerical aperture cylindrical lens focusing. The device is composed of a linear polarization laser light source, a spherical lens assembly, a rectangular aperture, a 1 / 2 wave plate, a discontinuous wave plate and a high-numerical aperture cylindrical lens. Light beams generated by the linear polarization laser light source are subjected to beam expansion and collimation which are performed by the spherical lens assembly, and then, rectangular linearly polarized light which is almost uniform and is arranged at the center of a light spot selectively passes through the rectangular aperture; the rectangular linearly polarized light emitted by the rectangular aperture passes through the 1 / 2 wave plate, and then, passes through or does not pass through the discontinuous wave plate; and after that, the rectangular linearly polarized light is focused by the high-numerical aperture cylindrical lens, and the uniform linear laser beams are generated at a focal plane. With the device which is of structural simplicity adopted, under the situations that the discontinuous wave plate is used or not used, the uniform linear laser beams of which the center is flat-topped can be obtained at the focal plane through simply rotating the 1 / 2 wave plate and changing the numerical aperture of the high-numerical aperture cylindrical lens, wherein the uniform linear laser beams can be used for linear scanning microscopic imaging, and micro-nano materials processing and detection.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Drink insulator with bottle opener
InactiveUS7685908B1Inexpensive and simple to manufactureInexpensive and simple to and distributeBottle/container closurePower operated devicesRectangular apertureEngineering
A combination device for insulating a beverage vessel and removing a bottle cap is disclosed. This device includes a generally cylindrically-shaped insulating sleeve, a substantially planar and disk-shaped metal insert with a rectangular aperture that pries off a bottle cap, and a ring-shaped structure that stabilizes the insert within the insulating sleeve.
Owner:DESIGNFLUENCE
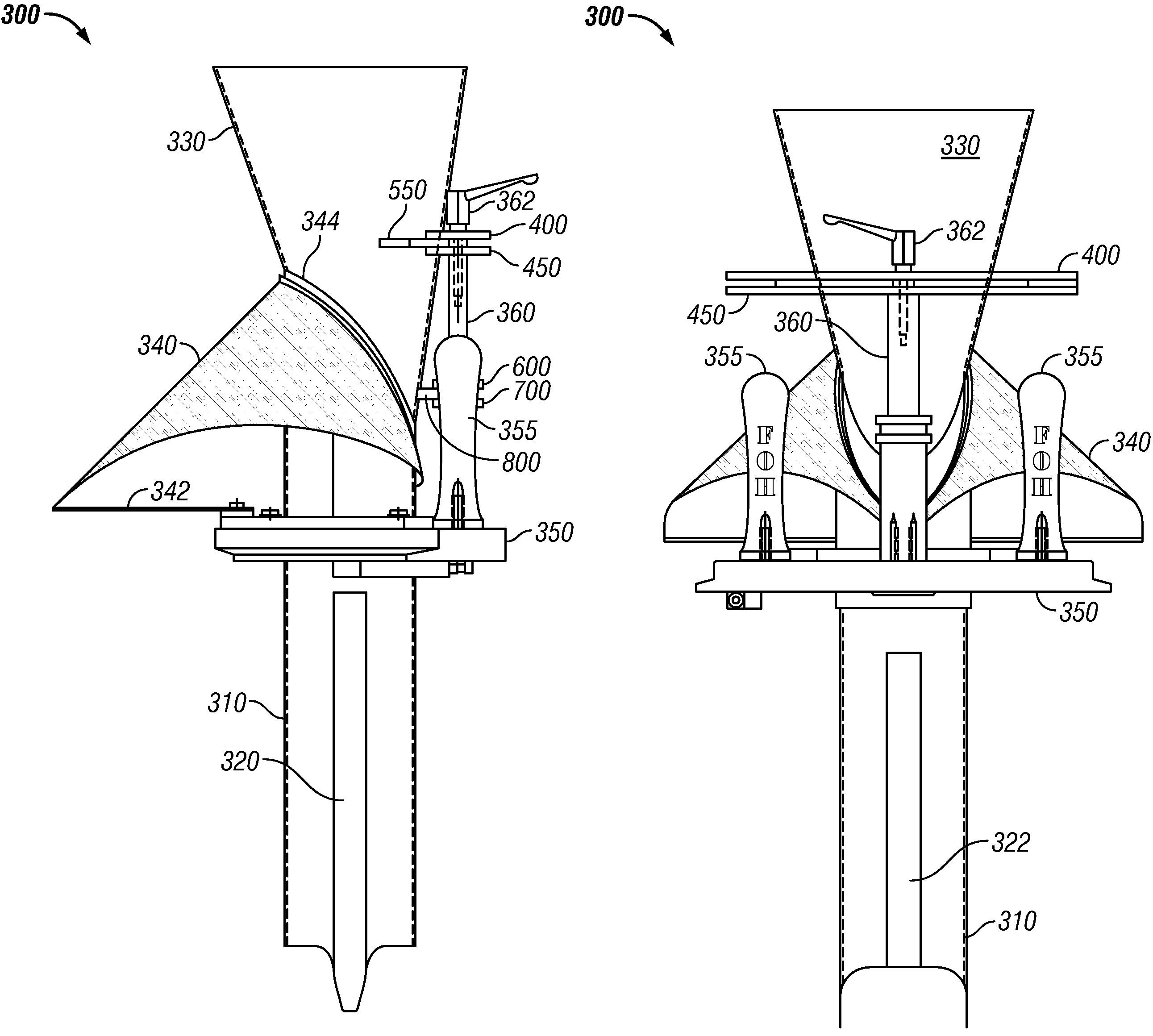
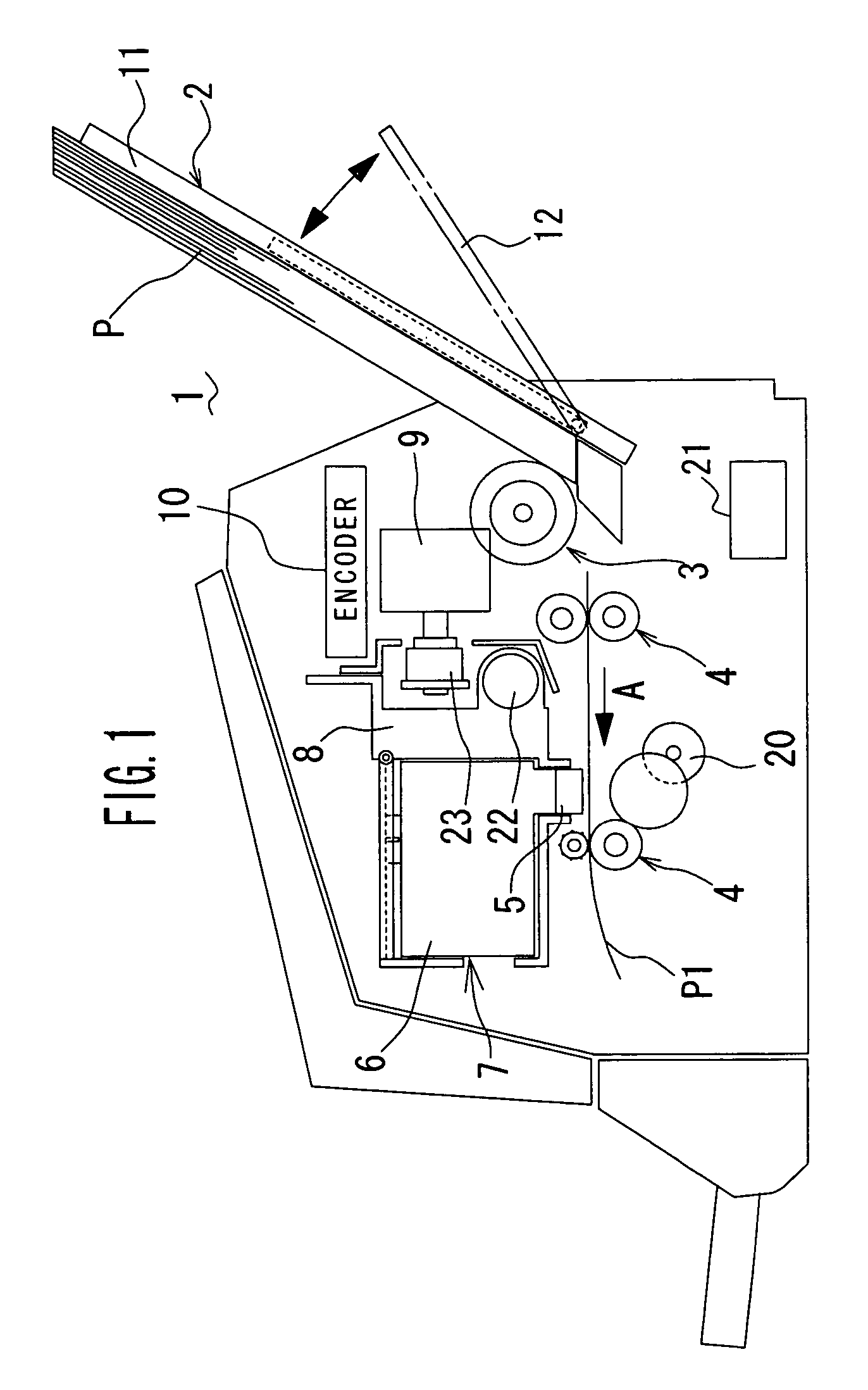
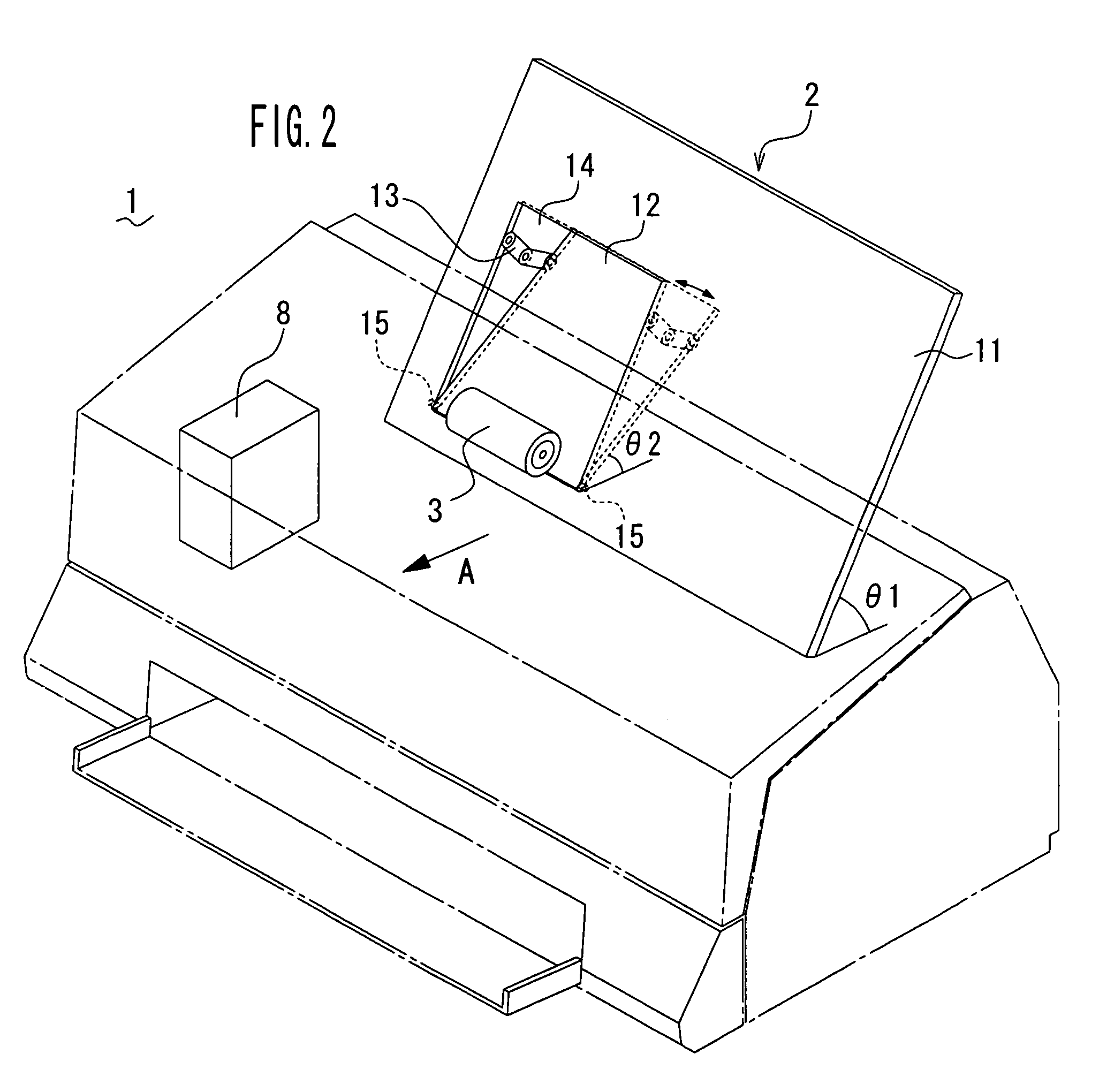
Apparatus and method for mounting a bag former
InactiveUS7523597B2Avoid relative motionPrevent rotationPaper/cardboard wound articlesSuccessive articlesRectangular apertureEngineering
A self-aligning former assembly has a single-point mount for attachment to an automated form / fill / seal packaging machine. Substantially rectangular apertures in a plurality of mounting brackets are configured to fit snugly on corresponding substantially rectangular shoulders formed on a mounting post. The configuration inhibits pivoting motion of the former on the mounting post. In an illustrated embodiment, the mounting post is attached to a base plate with a plurality of spaced-apart fasteners which prevent rotational movement of the mounting post relative to the base plate. Radial attachments are used in the illustrated embodiment to secure the funnel portion of a product feed tube to the mounting apparatus. Paired upper and lower mounting brackets permit precise alignment of the device prior to affixing the radial attachments to the mounting brackets. The disclosed mounting system obviates the need for subsequent adjustment of the former on the packaging system to align the former assembly with the pull-down belts and the longitudinal seal former.
Owner:J & F BUSINESS
Method and apparatus for surface processing of a substrate
Method and apparatus for processing a substrate with a beam of energetic particles. The beam is directed from a source through a rectangular aperture in a shield positioned between the source and substrate to a treatment zone in a plane of substrate movement. Features on the substrate are aligned parallel to a major dimension of the rectangular aperture and the substrate is moved orthogonally to the aperture's major dimension. The beam impinges the substrate through the aperture during movement. The substrate may be periodically rotated by approximately 180° to reorient the features relative to the major dimension of the rectangular aperture. The resulting treatment profile is symmetrical about the sides of the features oriented toward the major dimension of the rectangular aperture.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
Security device for media case and method
InactiveUS7526931B2Less-costly to manufactureEasy to useClothing locksLocks for portable objectsRectangular apertureEngineering
The present invention provides a security device and method for securing a media case. The security device may include a hinged pair of closure members, which when closed define a substantially rectangular aperture for receiving a media case to be secured with a close fit. The closure members include an internal protrusion that extends within a portion of the substantially rectangular aperture that coincides with a finger cavity portion of a media case. The closure members include a latch opposite the side including the internal protrusion.
Owner:AUTRONIC PLASTICS
Color cathode ray tube
InactiveUS6124668AHigh color purityElectrode and associated part arrangementsRectangular apertureEffective surface
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 03994 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 2, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 2, 1998 PCT Filed Oct. 31, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 20514 PCT Pub. Date May 14, 1998A shadow mask disposed to face a phosphor screen of a cathode ray tube includes a substantially rectangular effective surface on which a number of substantially rectangular apertures are formed. The effective surface has horizontal and vertical axes which perpendicularly cross in the center thereof and diagonal axes passing through the center. The apertures are arranged to form a plurality of vertical rows of apertures extending in the direction of the vertical axis. Each of the vertical rows of apertures includes a plurality of apertures arranged in the direction of the vertical axis with a bridge portion being interposed between two adjacent apertures, and those vertical rows of apertures are arranged in the direction of the horizontal axis at a predetermined pitch. The width W of the apertures in the direction of the horizontal axis is formed so as to gradually increase from that of the aperture located at the center of the effective surface to that of the apertures located at the peripheries of the effective surface in the direction of the horizontal axis. The width of each of corner apertures located in the vicinity of the ends of the diagonal axes is larger than the width of the aperture located on the horizontal axis in the same vertical row of apertures to which the corner aperture belongs.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Transmission type self-focusing single-stage diffraction grating
ActiveCN104777540AHigh purityAchieving Linear MeasurementsDiffraction gratingsRectangular apertureSelf-focusing
The invention provides a transmission type self-focusing single-stage diffraction grating which comprises two primitives: namely, rectangular holes and long rectangular strips, wherein the two primitives have the same width and different lengths; each long rectangular strip is tens to hundreds of times as long as each rectangular hole; in the diffraction direction perpendicular to the grating, the adjacent rectangular holes and the adjacent long rectangular strips are tightly stacked together; in the diffraction direction, the rectangular holes and the long rectangular strips are randomly arranged on the surface of a grating substrate according to respective distribution rules; in a stacked region of the rectangular holes and the long rectangular strips, the multiplicative relationship of two-dimensional transmission functions of the two is met. The transmission type self-focusing single-stage diffraction grating only comprises 0 and + / -1 stage diffractions so as to effectively eliminate the influence of higher harmonics on the spectrum, has a focal plane perpendicular to the grating plane, for focusing photons with different energies, integrates the light splitting, focusing, high-harmonic restraining and other characteristics, has the diffraction modes different from an ordinary grating, and is a composite optical element.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Image forming apparatus
InactiveUS7510278B2Low costFeed thick recording paper sheetsOther printing apparatusElevation angleRectangular aperture
In an image forming apparatus such as an inkjet printer, deformation of a thick recording paper sheet such as a postcard in the conveyance thereof is prevented by a simple and inexpensive structure. A rectangular aperture corresponding to a size of the postcard is formed on a first tray portion, and a second tray portion is attached to the rectangular aperture. The second tray portion is rotatably borne at a front end thereof on the first tray portion, and linked with the first tray portion at a rear end by link members so that the rotation angle of the second tray portion with respect to the first tray portion is restricted. When the second tray portion is opened, the second tray portion is held with an elevation angle with respect to a paper conveying path gentler than that of the first-tray portion, so that the postcard can be inserted into the paper conveying path with a gentle elevation angle. Consequently, the deformation of the postcard can be prevented.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Self-Aligning Former Assembly
InactiveUS20080229712A1Avoid relative motionPrevent rotationPaper/cardboard wound articlesSuccessive articlesRectangular apertureFeeding tube
A self-aligning former assembly has a single-point mount for attachment to an automated form / fill / seal packaging machine. Substantially rectangular apertures in a plurality of mounting brackets are configured to fit snugly on corresponding substantially rectangular shoulders formed on a mounting post. The configuration inhibits pivoting motion of the former on the mounting post. In an illustrated embodiment, the mounting post is attached to a base plate with a plurality of spaced-apart fasteners which prevent rotational movement of the mounting post relative to the base plate. Radial attachments are used in the illustrated embodiment to secure the funnel portion of a product feed tube to the mounting apparatus. Paired upper and lower mounting brackets permit precise alignment of the device prior to affixing the radial attachments to the mounting brackets. The disclosed mounting system obviates the need for subsequent adjustment of the former on the packaging system to align the former assembly with the pull-down belts and the longitudinal seal former.
Owner:J & F BUSINESS
Protective fence hanger
ActiveUS20080245937A1Easy to installEasy to relocateCandle holdersLighting support devicesRectangular apertureEngineering
Owner:CONNOR JR ROBERT T
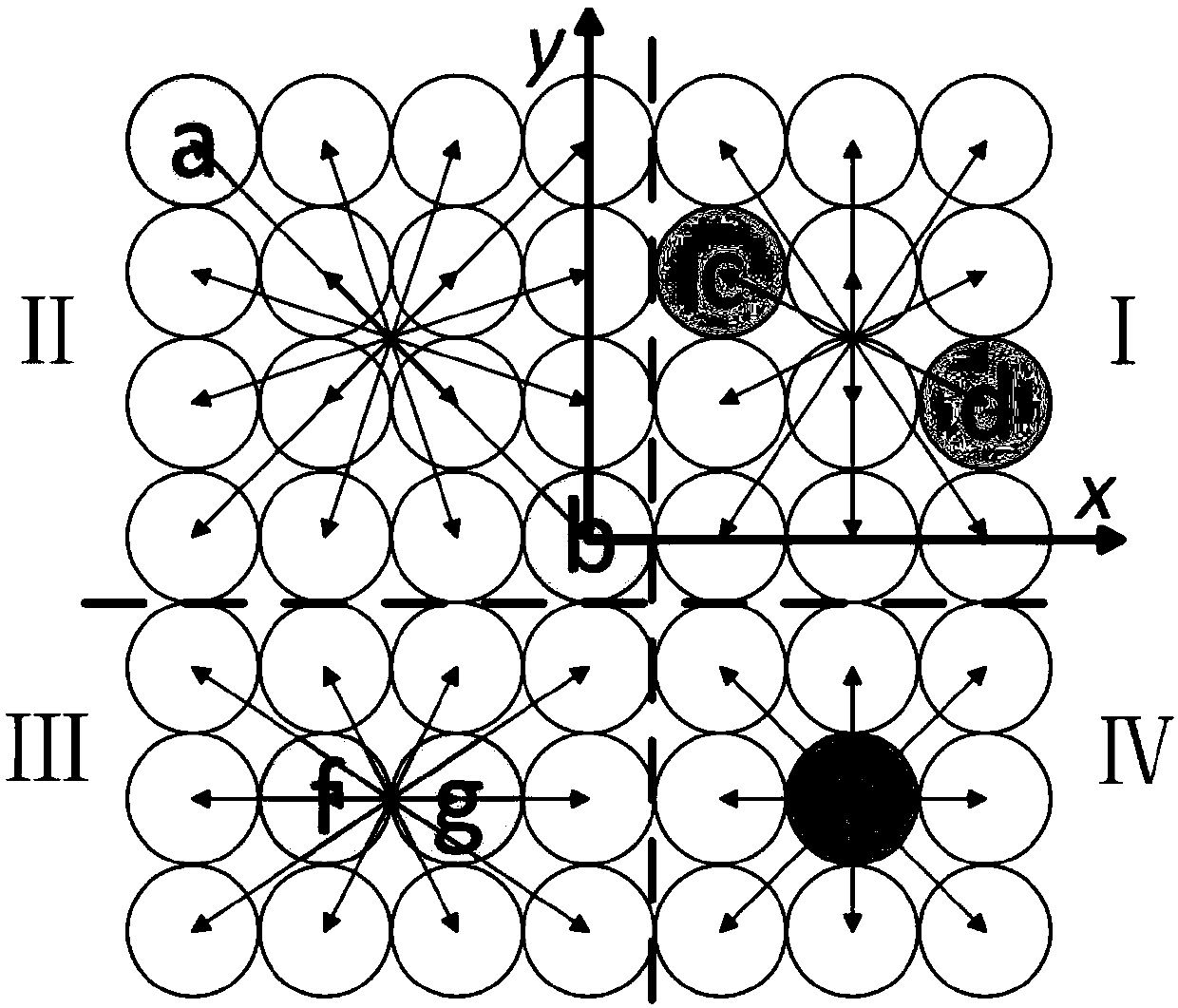
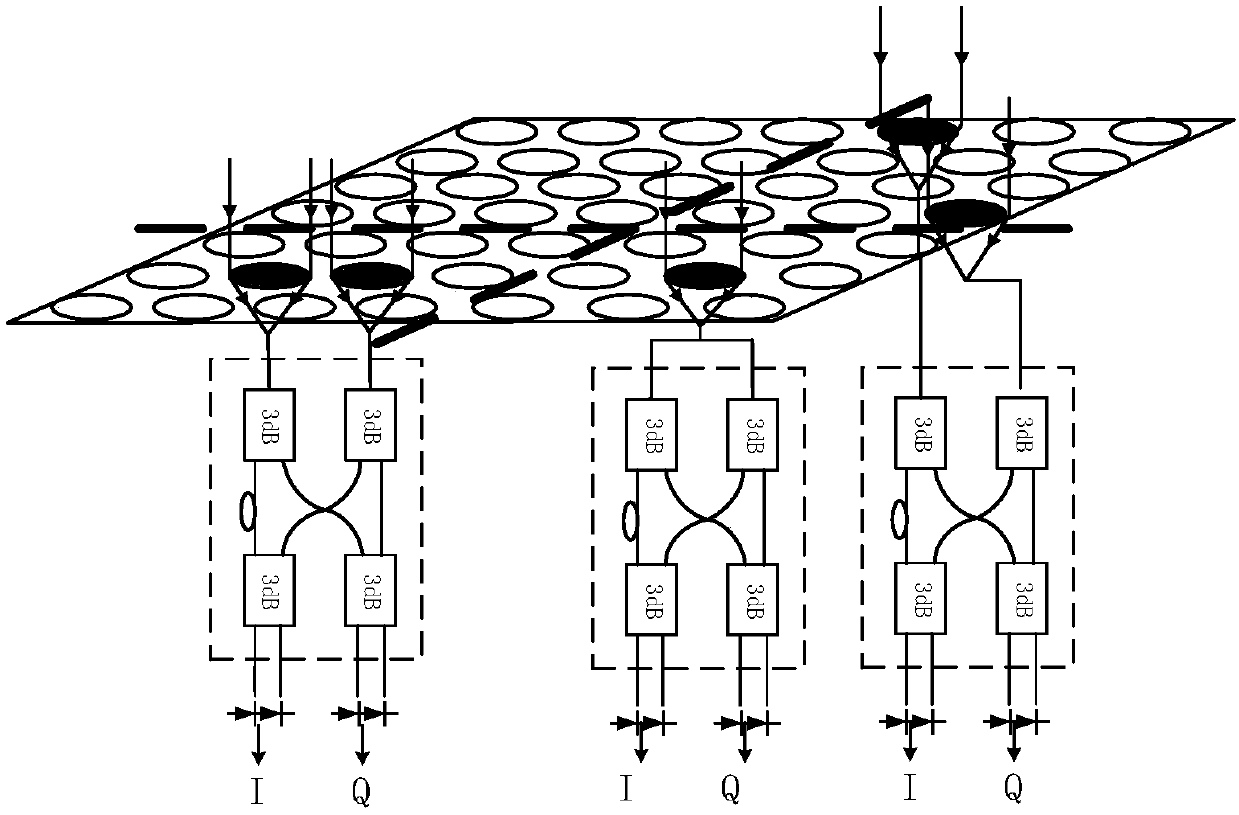
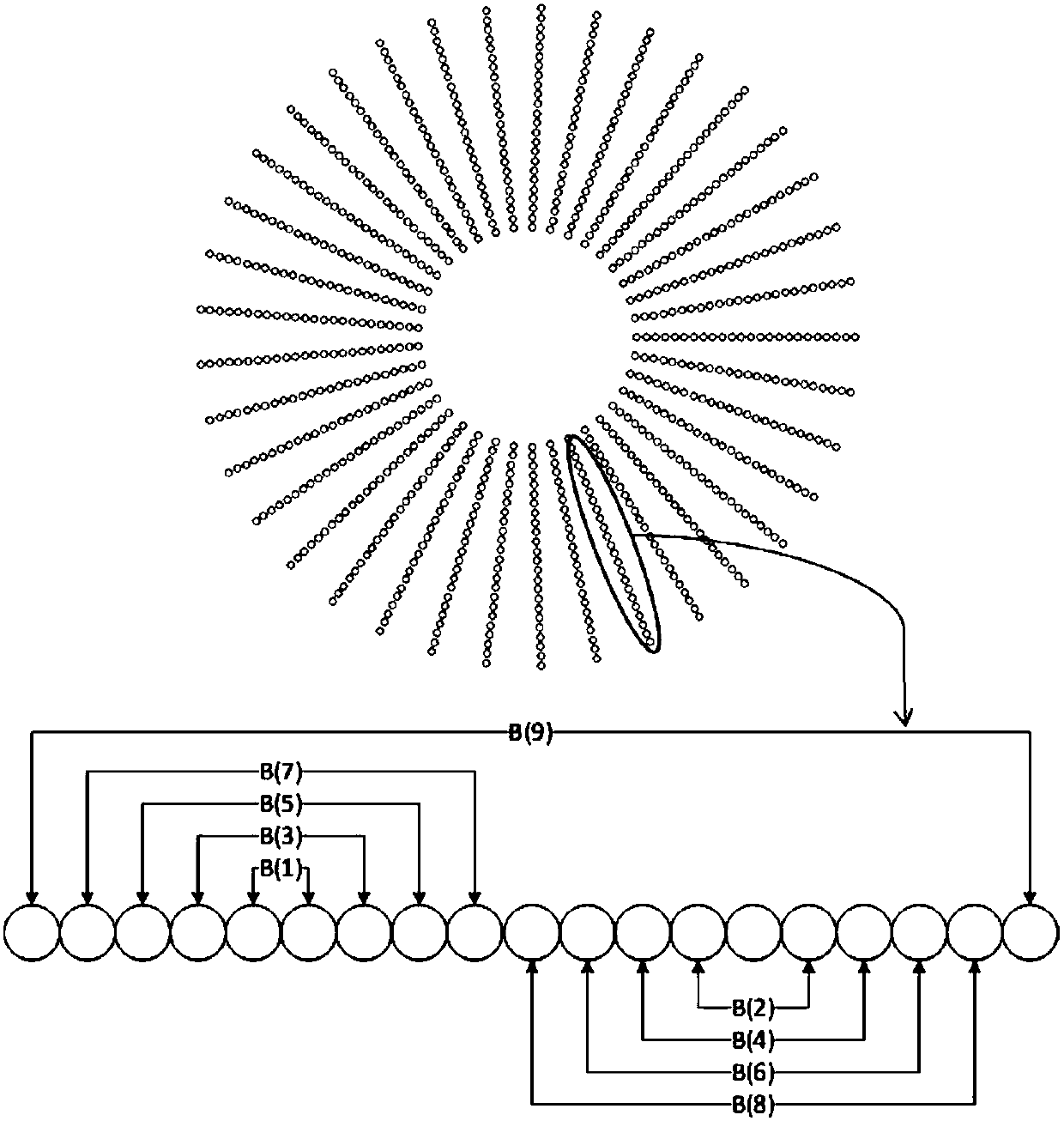
Compact rectangular aperture configuration structure and sampling method of target space frequency
PendingCN107748397AEfficient use ofApertures are tightly arrangedOptical detectionFrequency coverageRectangular aperture
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
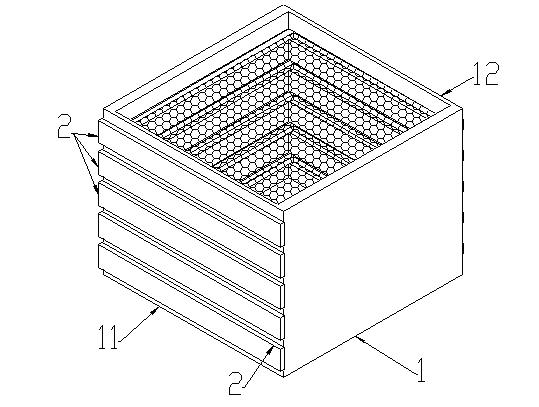
Filter box capable of adjusting filtration stage number and precision
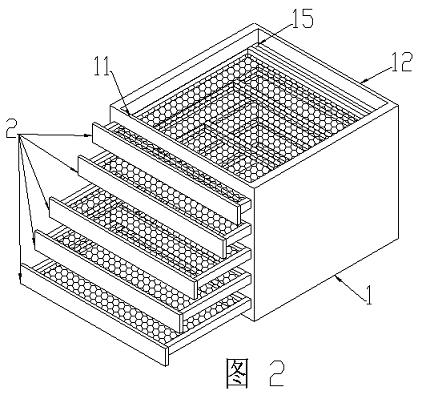
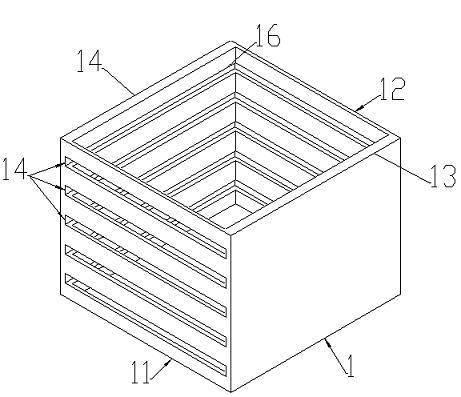
InactiveCN102366689AAdjustable filterabilityAdjustable filter precisionDispersed particle filtrationRectangular apertureFiltration
The invention discloses a filter box capable of adjusting filtration stage number and precision, which comprises a box body (1) and a filter plate (2), a filter screen (23) is arranged on the filter plate (2), the filter box comprises one or more filter plates (2), the corresponding positions of a front panel (11) and a rear panel (12) of the box body are provided with one or more rectangular apertures (15), the size of the rectangular aperture (15) is matched with size of the filter plate (2). The invention uses the multistage filter plate (2) capable of changing, the users can install the filter plates (2) with different numbers according to the requirement, so that the different filtration precision is achieved, the filter box capable of adjusting filtration stage number and precision has strong adaptability in the workplace environment.
Owner:林秀云
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com