An emission imaging device with a polyhedral cavity structure
An imaging device, a polyhedron technology, which is used in radiation detection devices, clinical applications of radiological diagnosis, instruments for radiological diagnosis, etc. The effect of increasing the axial distance and increasing the solid angle of space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
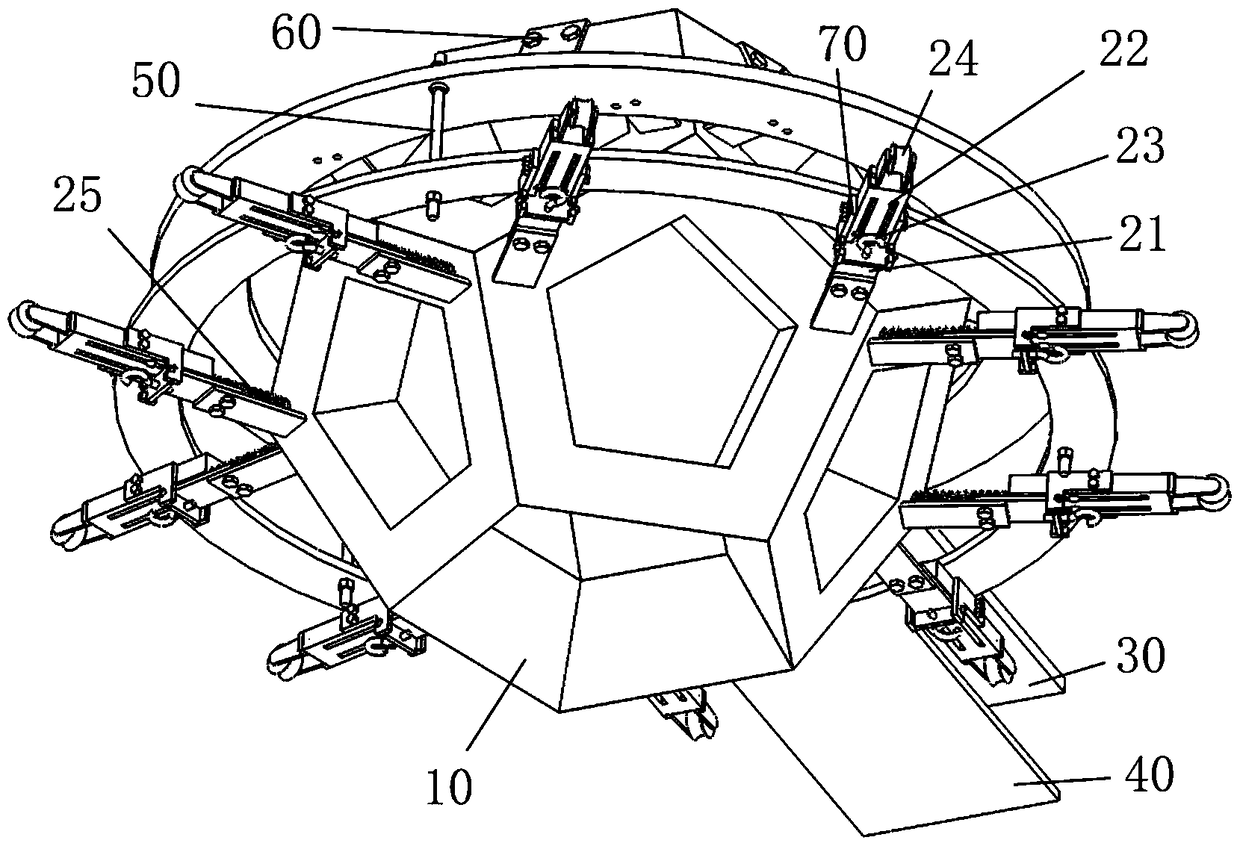
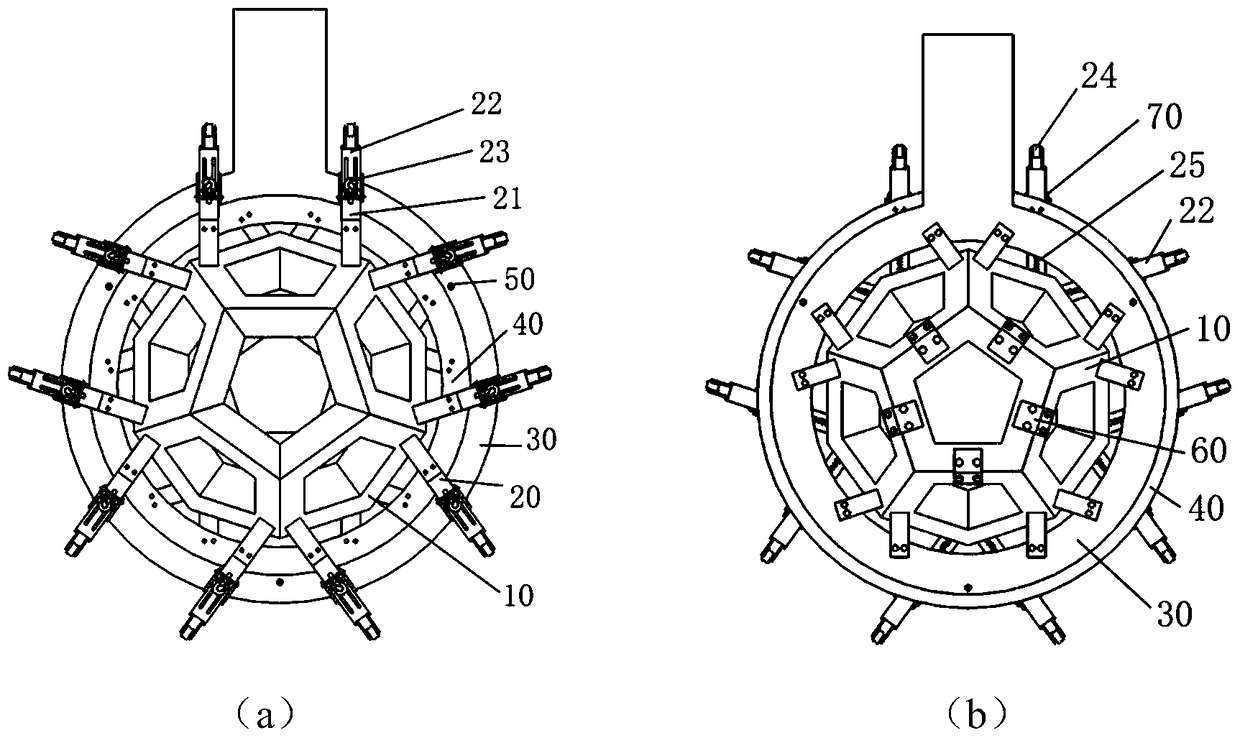
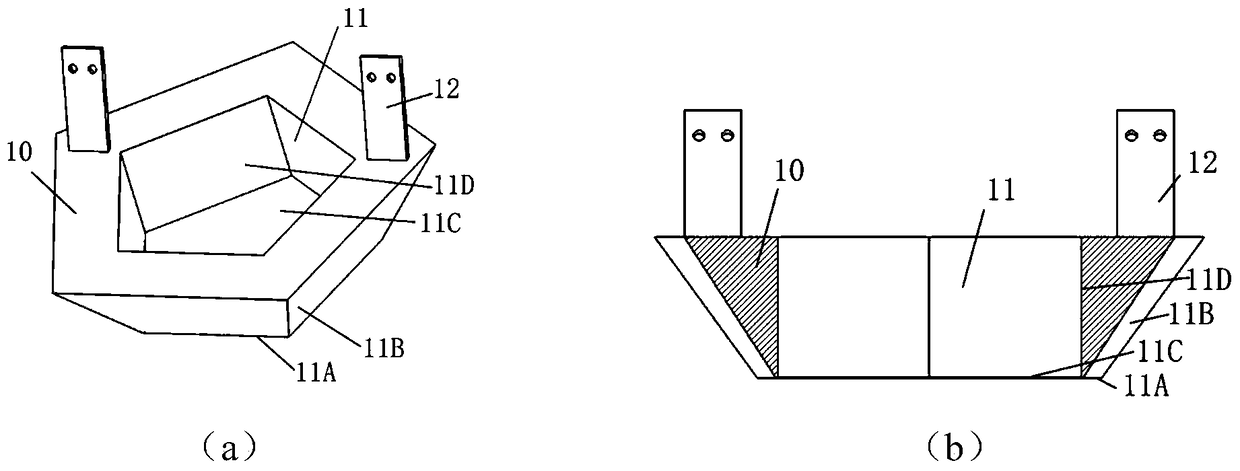
[0042] Such as figure 1 As shown, in this embodiment, the cavity structures 11 of the polygonal modules 10 are all regular pentagons, and detection elements such as crystal arrays and optical sensors are installed in the cavity structures 11, and the outer surfaces 11B of the eleven polygonal modules 10 are arranged in pairs. Splicing together to form a regular dodecahedron with a gap, forming a regular dodecahedron cavity;
[0043] There is a vacancy of a polygonal module 10 at the bottom of the dodecahedron structure, which is used to allow the detected object to enter the cavity of the dodecahedron. The polygonal modules 10 around the vacancy are installed on their own independent sliding systems 20, and then installed on the lower support frame 40, forming the lower half of the dodecahedron structure, the polygonal modules 10 adjacent to the lower half are directly installed on the upper support frame 30, and fixed with the remaining polygonal modules 10 through obtuse ang...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Such as Figure 9 As shown in (a) and (b), the structure and composition of the imaging device in this embodiment are basically the same as in Embodiment 1, the only difference is that the cavity structures 11 of the polygonal module 10 are not all regular pentagons, which include regular Pentagons and regular hexagons, twelve regular pentagons and nineteen regular hexagons together form a truncated icosahedron with a gap; the angle of the obtuse connecting block 60 is 138.19 ° or 142.623 °, with For connecting two hexagons and pentagons and hexagons.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com