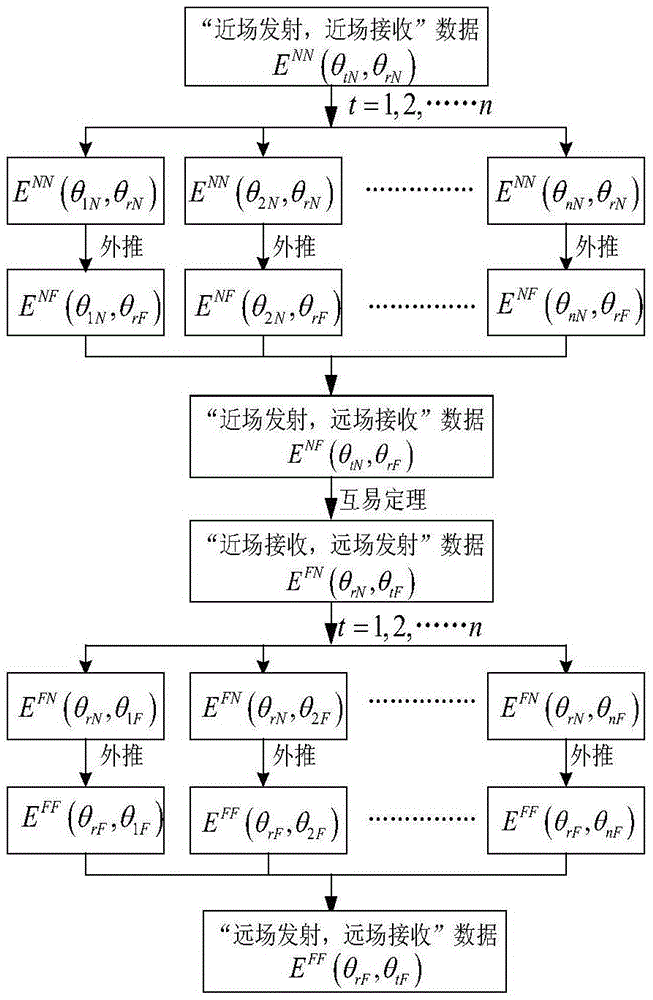
Method of using extrapolation to acquire far field RCS possessing multiple scattering objects
A technology of multiple scattering and pushing method, applied in radio wave measurement systems, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as performance degradation and large errors, and achieve high-precision results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
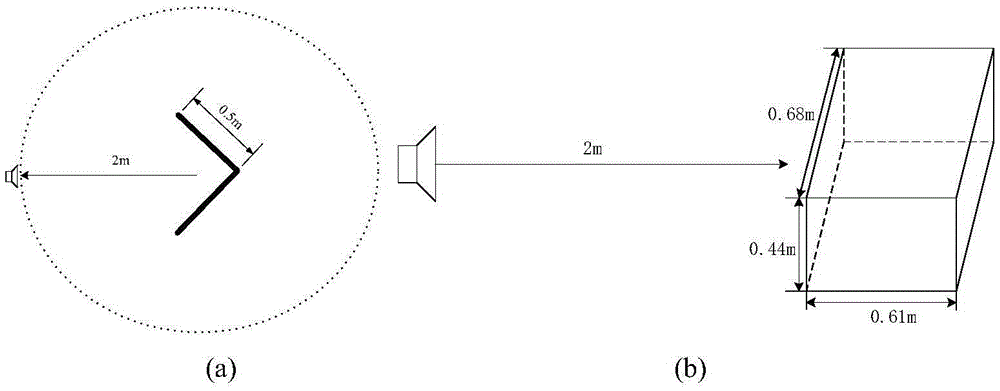
[0027] refer to figure 2 -a Select a straight dihedral structure model with a side length of 0.5m, the test frequency is 1.645GHz, and the wavelength is 0.1824m. According to the near-field measurement condition R≤2D 2 / λ=5.5m, where is the maximum size of the target, so the near-field distance is selected as R=2m during the simulation. Specific steps are as follows:
[0028] 1) Use the electromagnetic simulation software FEKO to model and simulate the straight dihedral angle model, and collect near-field bistatic scattering data on the azimuth plane at a distance of R=2m from the target to be measured. The antenna transmits at a certain point while receiving at intervals of 1° on the circumference far from the target R. By analogy, the antenna performs "single transmission and multiple collection" collection point by point on the circumference in turn, so as to obtain complete near-field dual-station data, denoted as E NN (θ tN ,θ rN ).
[0029] 2) The near-field da...
example 2
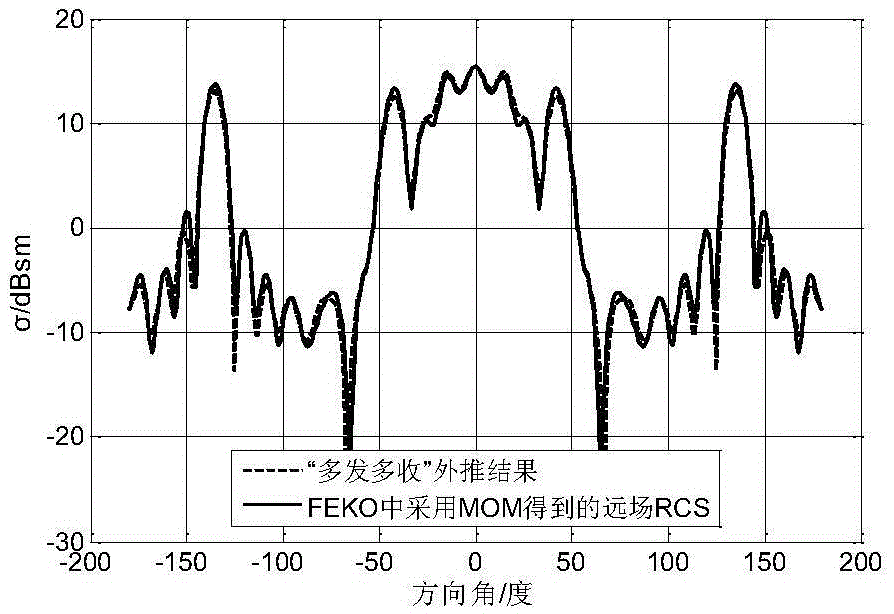
[0036] refer to figure 2 -b Choose a straight cavity structure model with a length of 0.68m, a width of 0.61m, and a height of 0.44m. The test frequency is 1.5GHz and the wavelength is 0.2m. According to the near-field measurement condition R≤2D 2 / λ=4.6m, where D=0.68m is the maximum size of the target, and the near-field distance is selected as R=2m during simulation. Carry out the simulation according to the same steps in Example 1, and the obtained extrapolation results refer to Figure 4 , compared with the far-field RCS of the cavity, the coincidence degree of the two is also very high, and the average error in the coupling area is 0.38dB. The effectiveness of the method is verified.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com