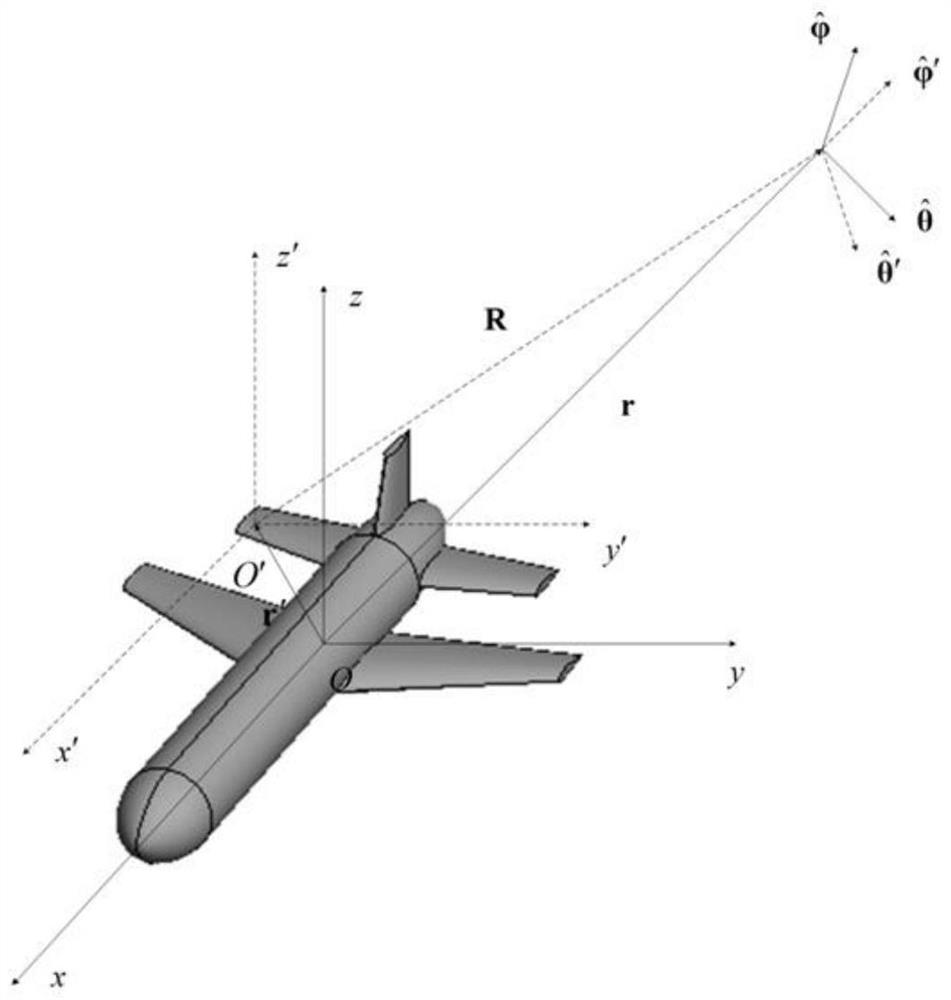
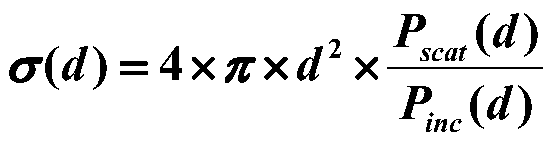Patents
Literature
49 results about "Near field scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
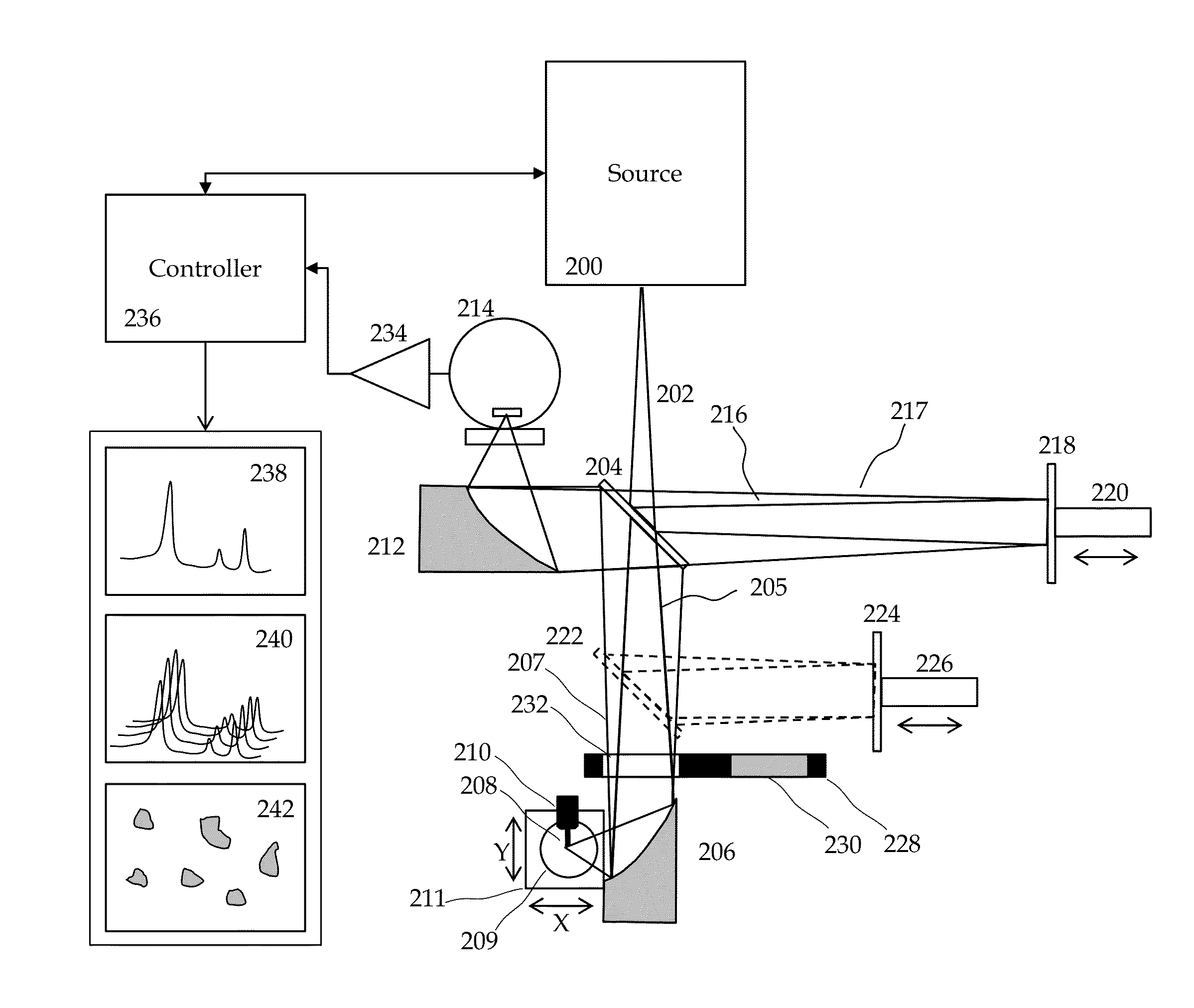
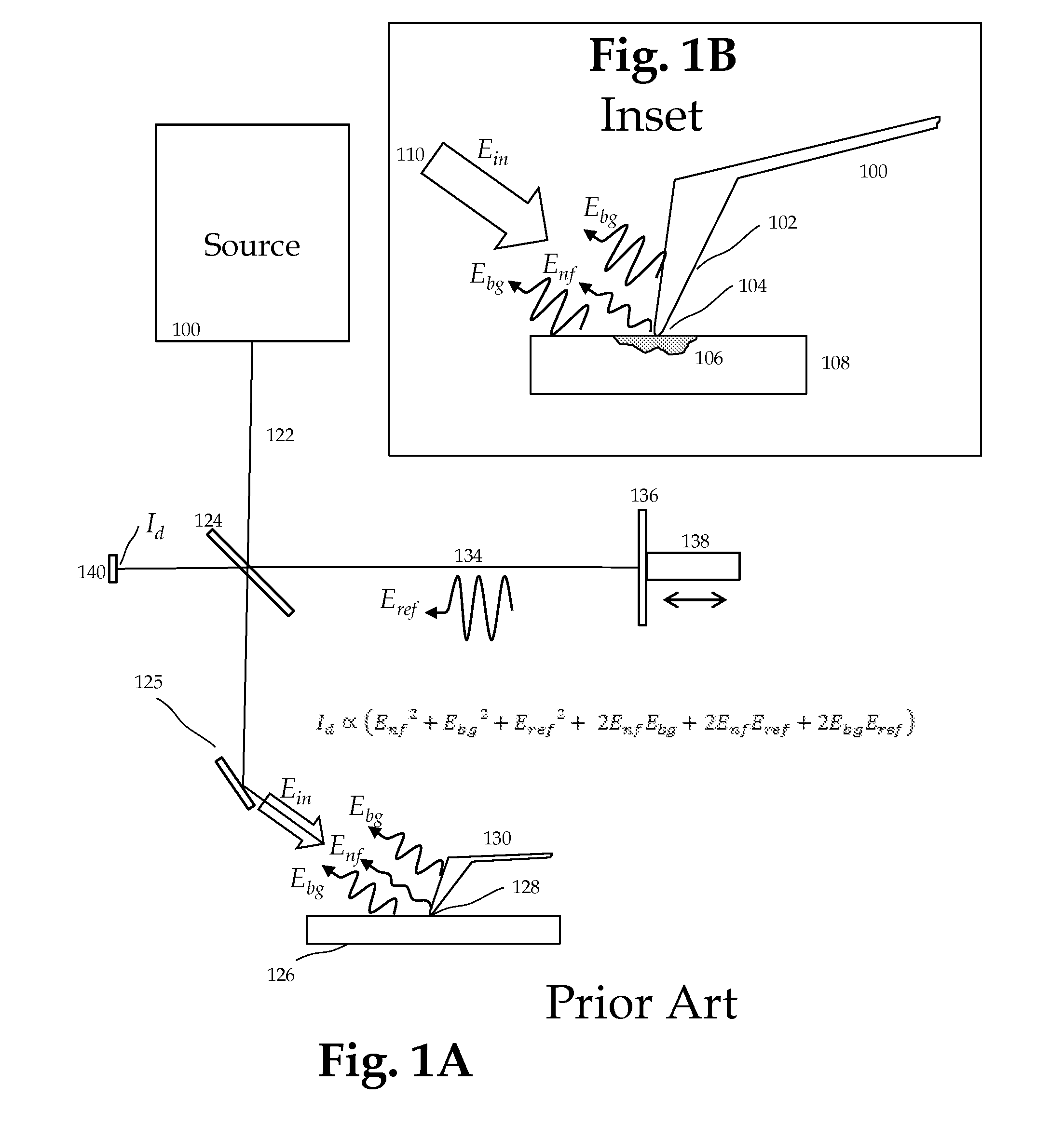
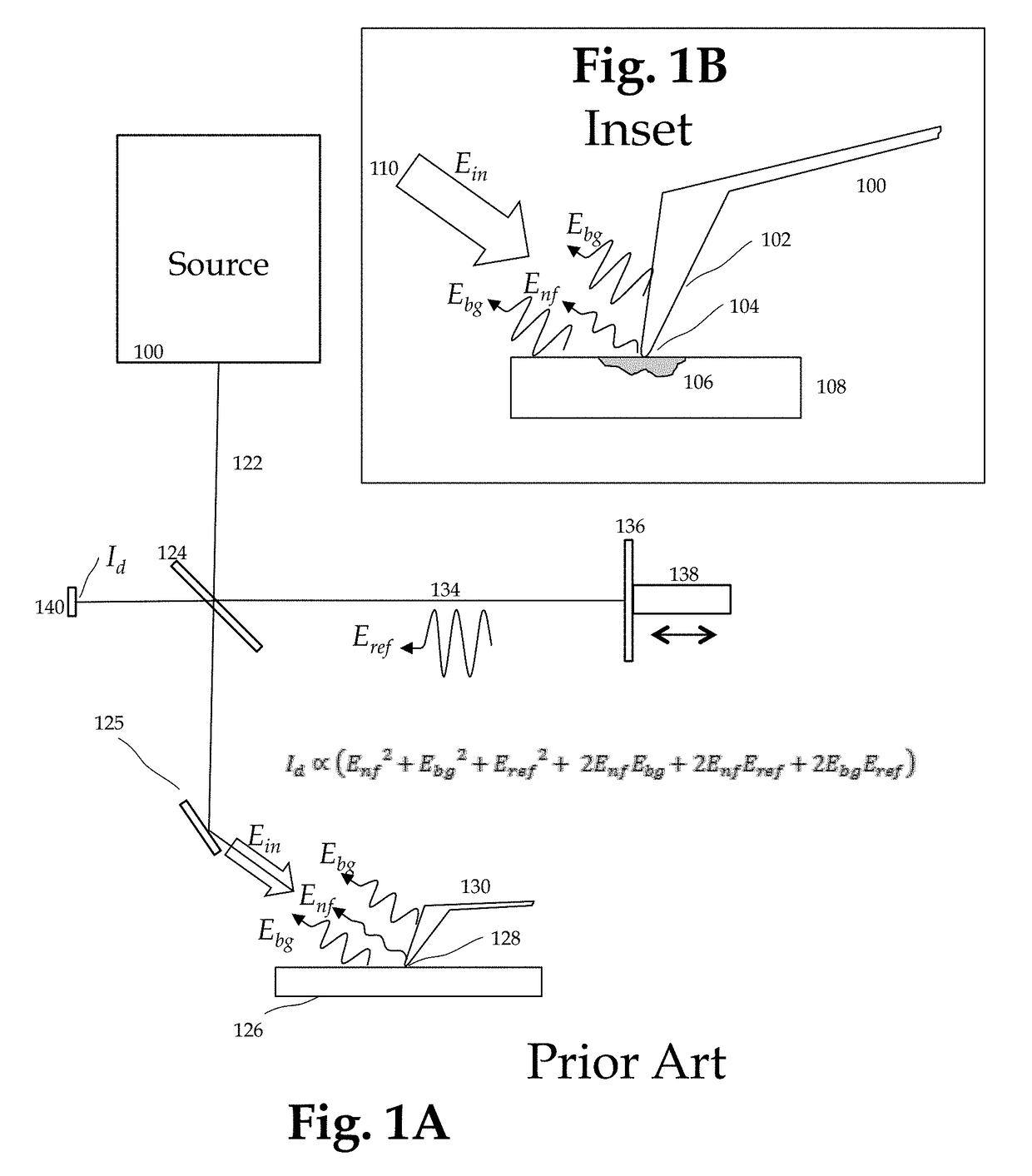
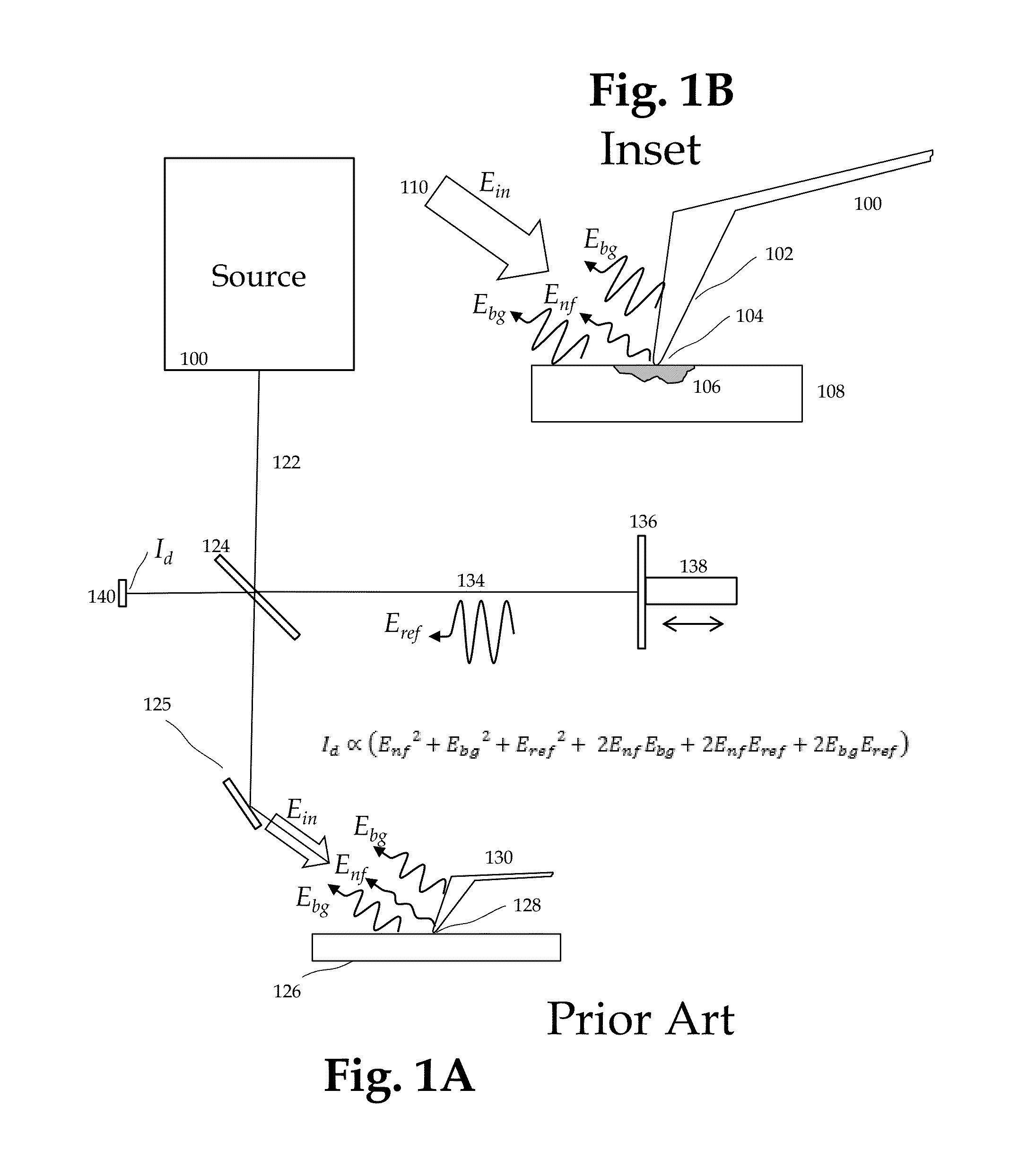
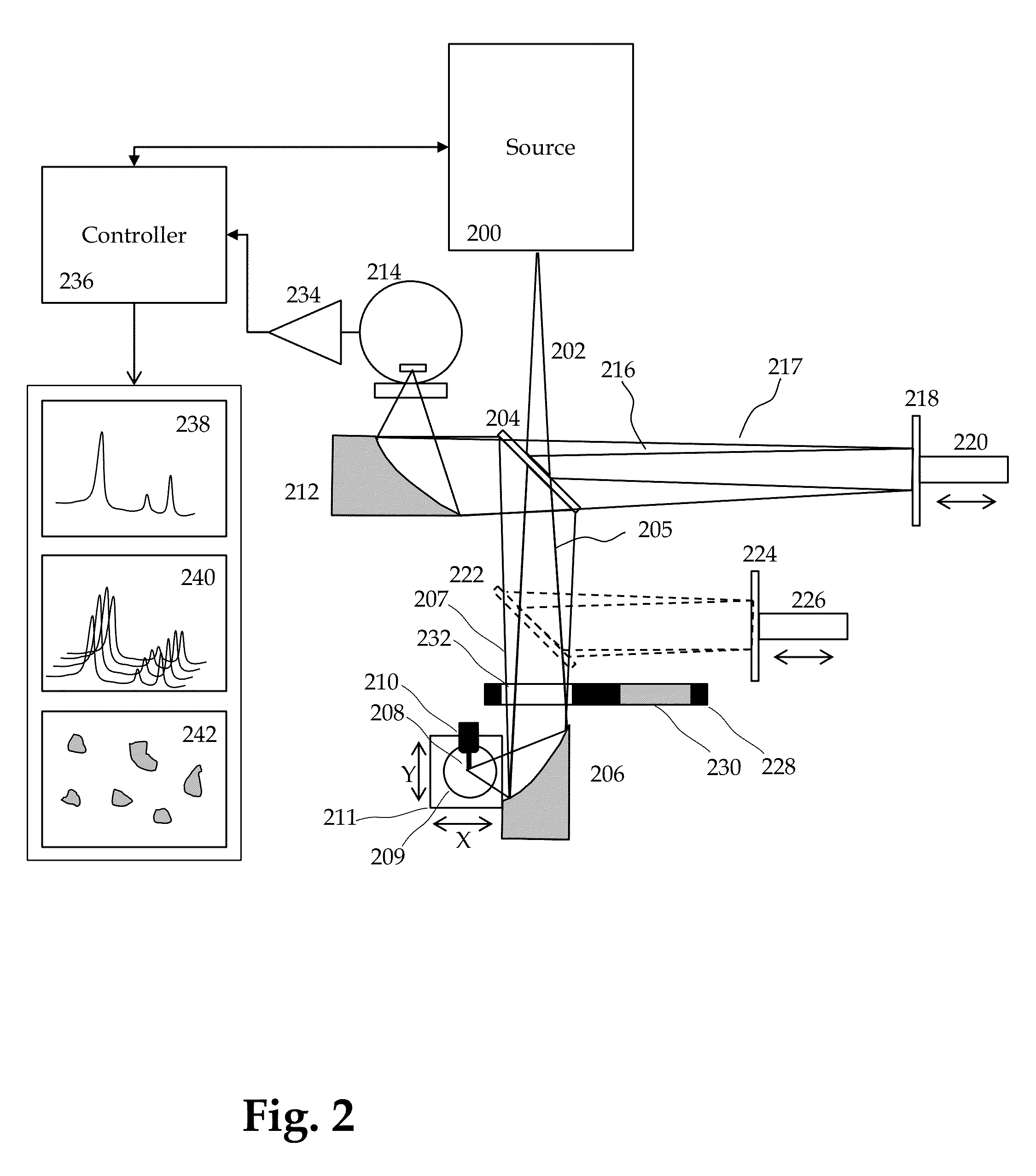
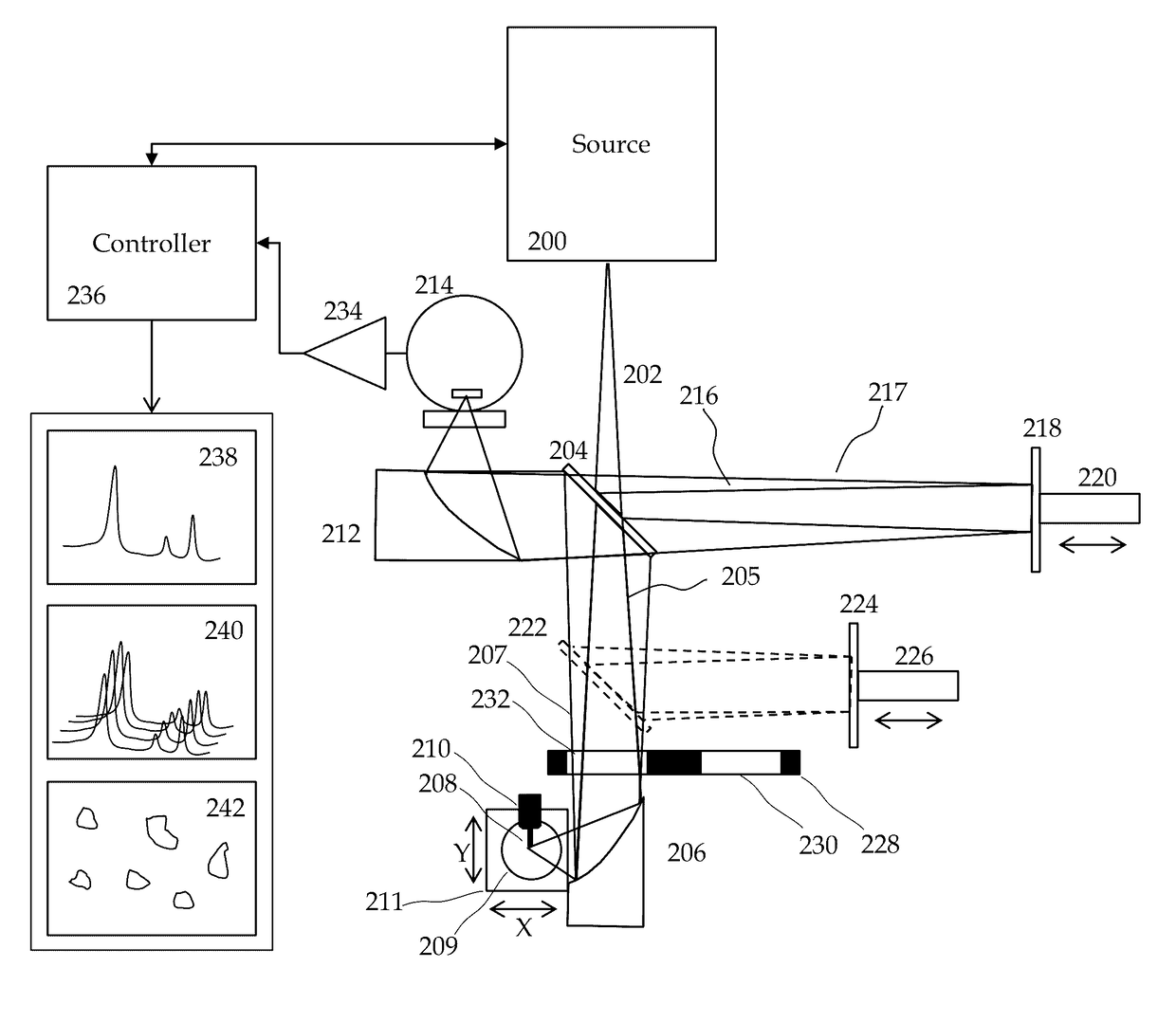
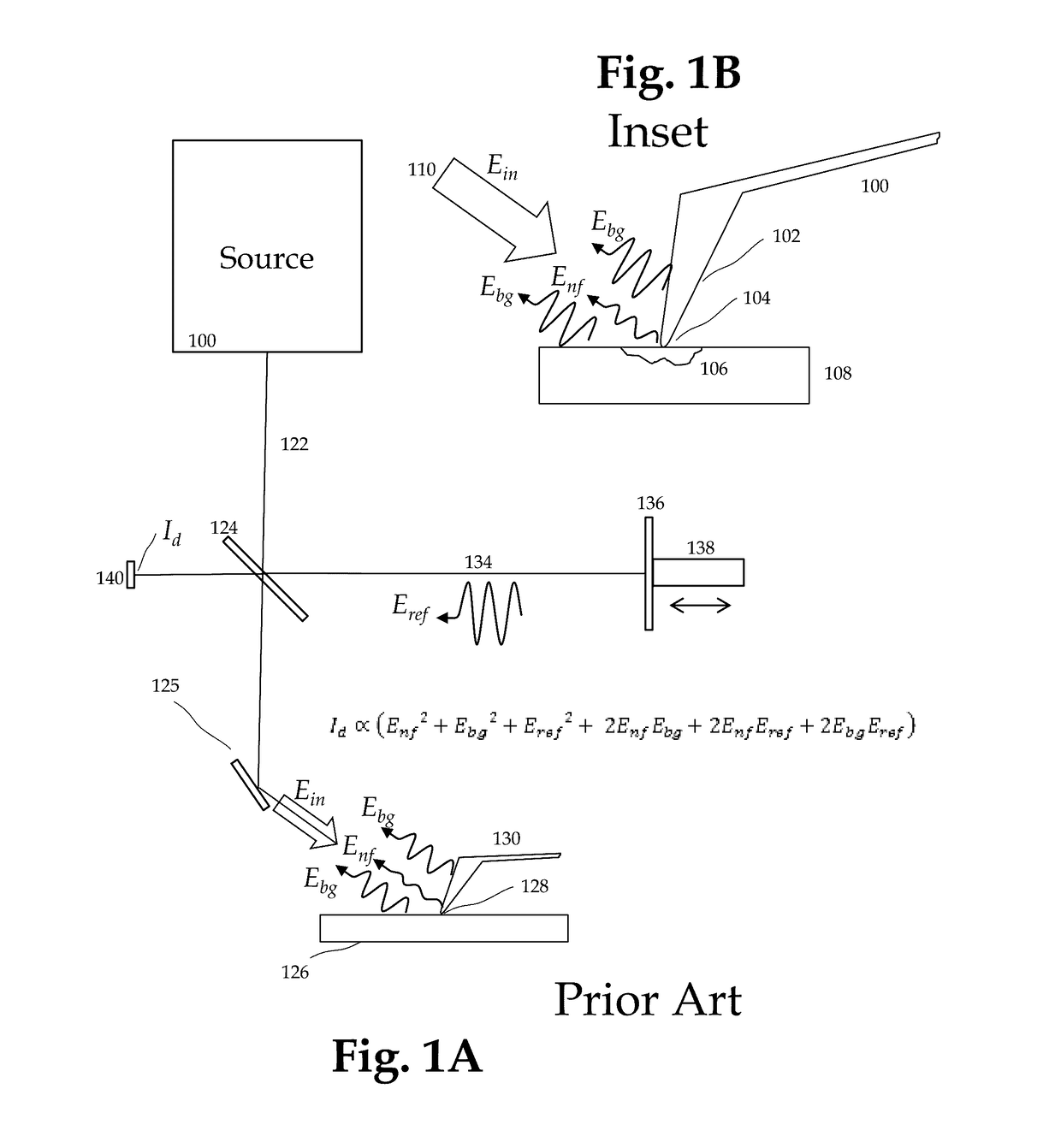
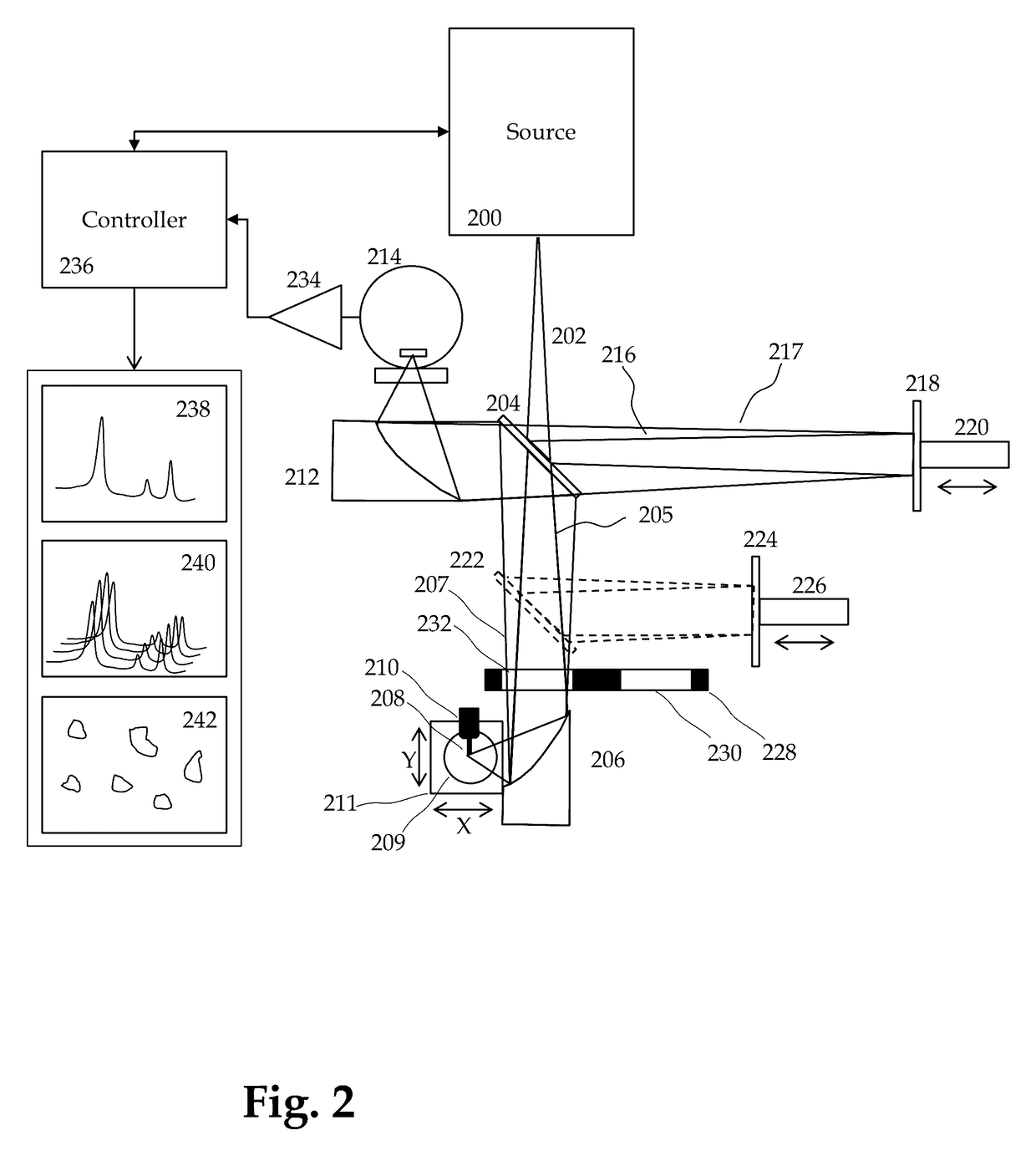
Method and apparatus for infrared scattering scanning near-field optical microscopy
ActiveUS8793811B1Increase speedRapid and accurate calculationNanoopticsScanning probe microscopySignal-to-quantization-noise ratioNear field optical microscope
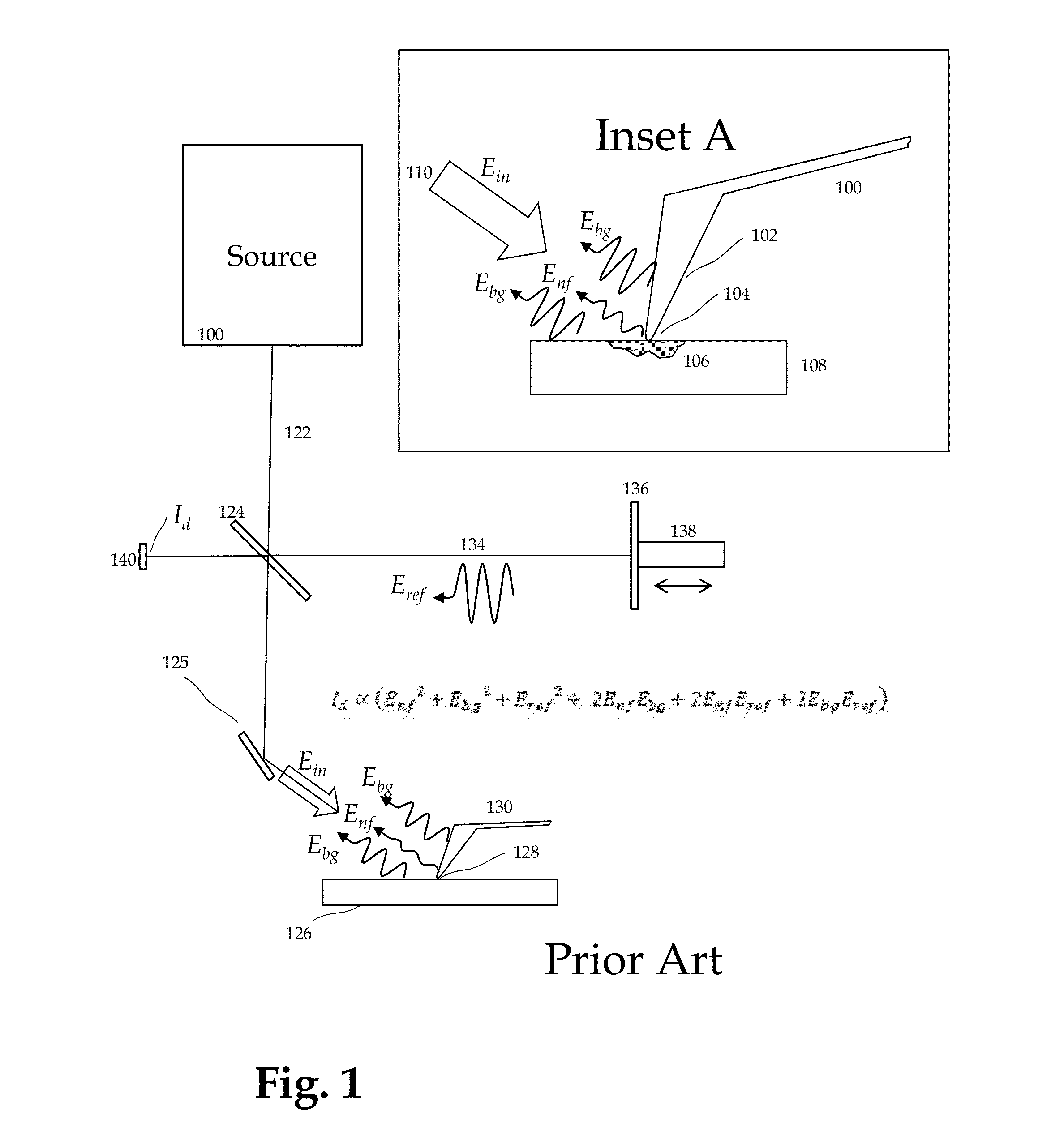
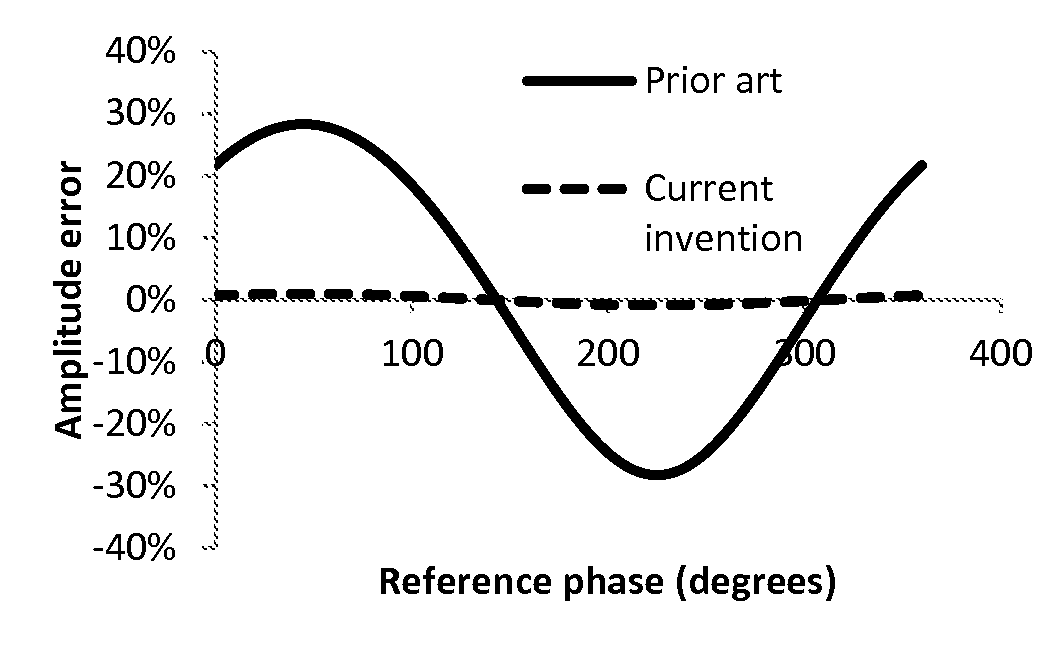
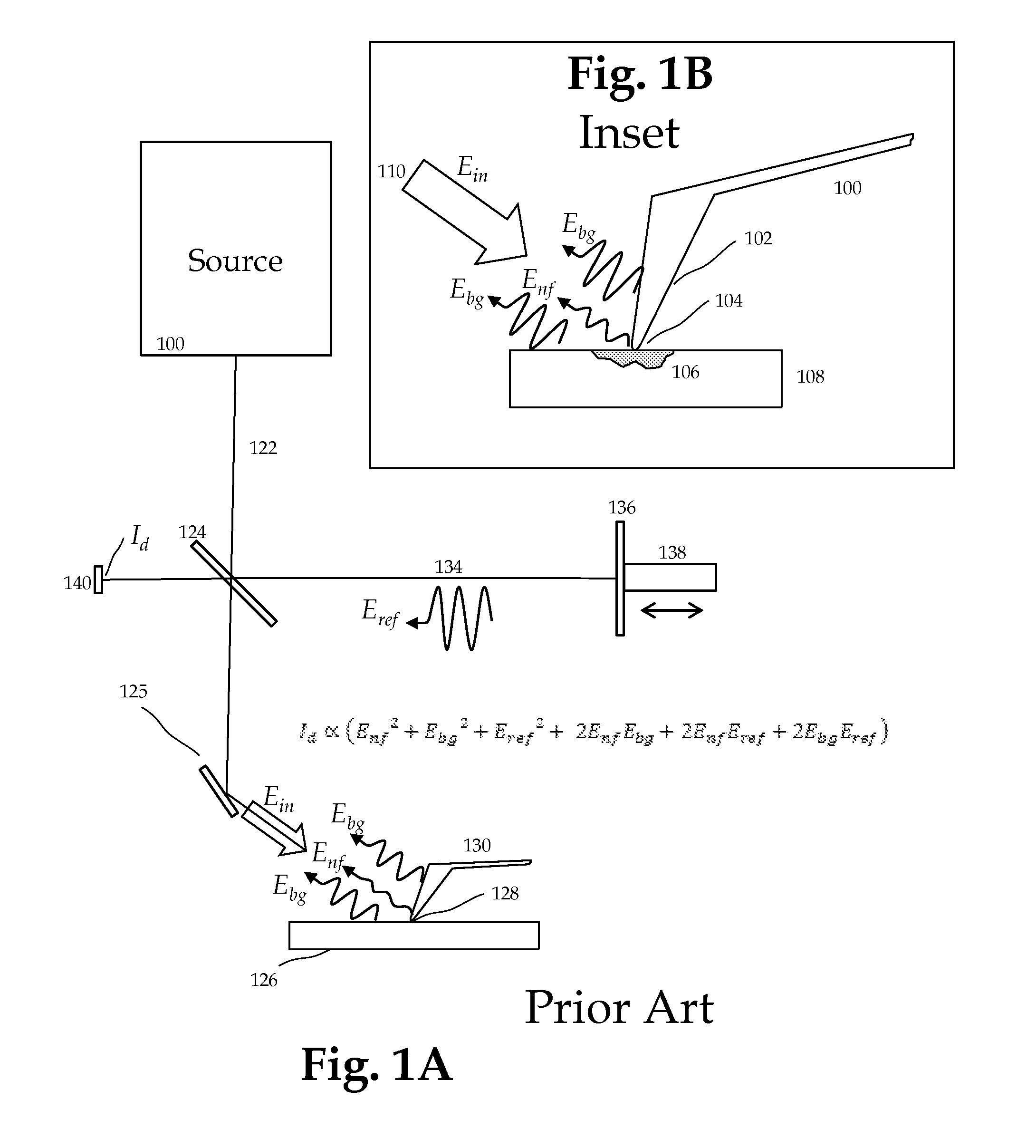
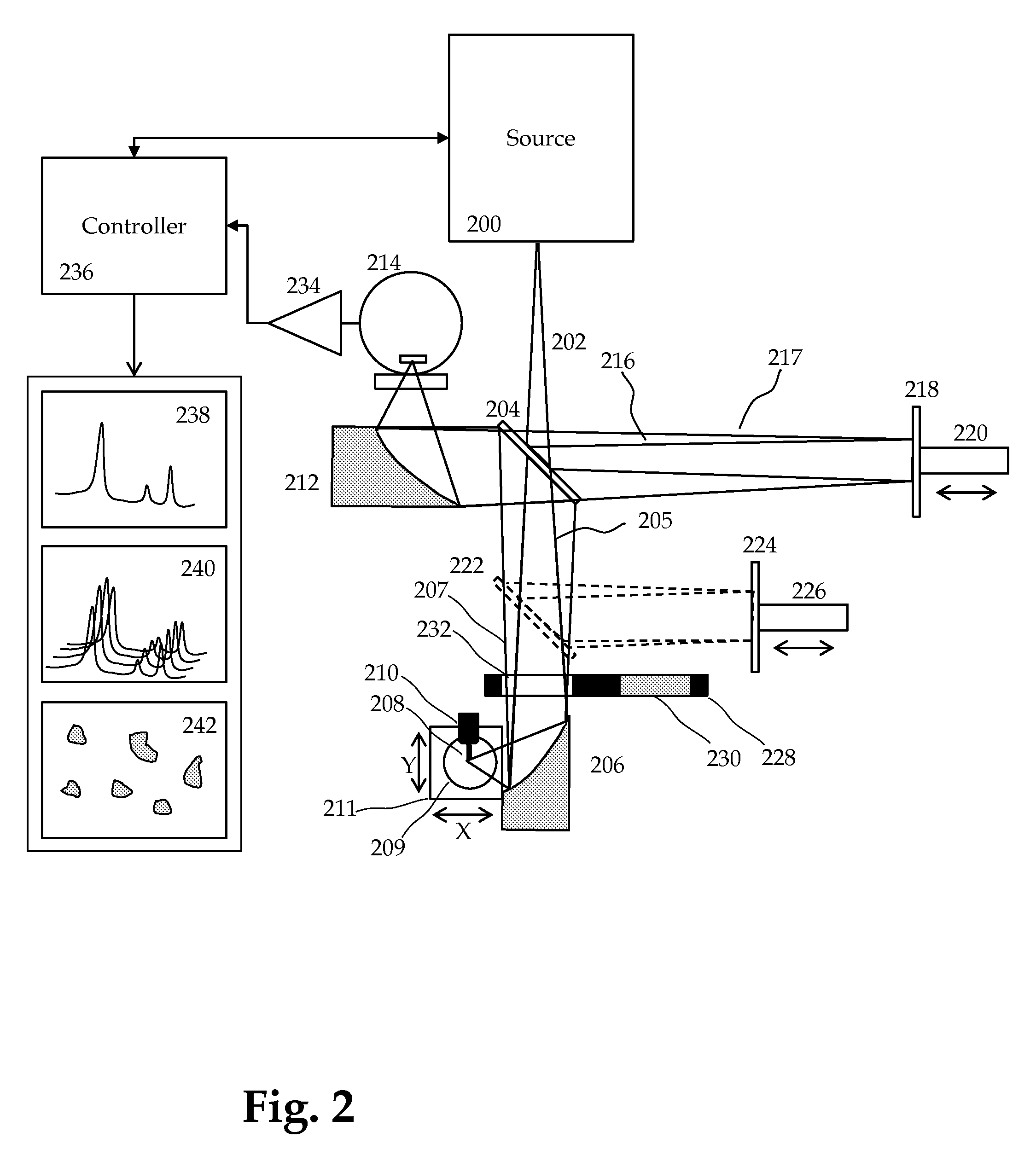
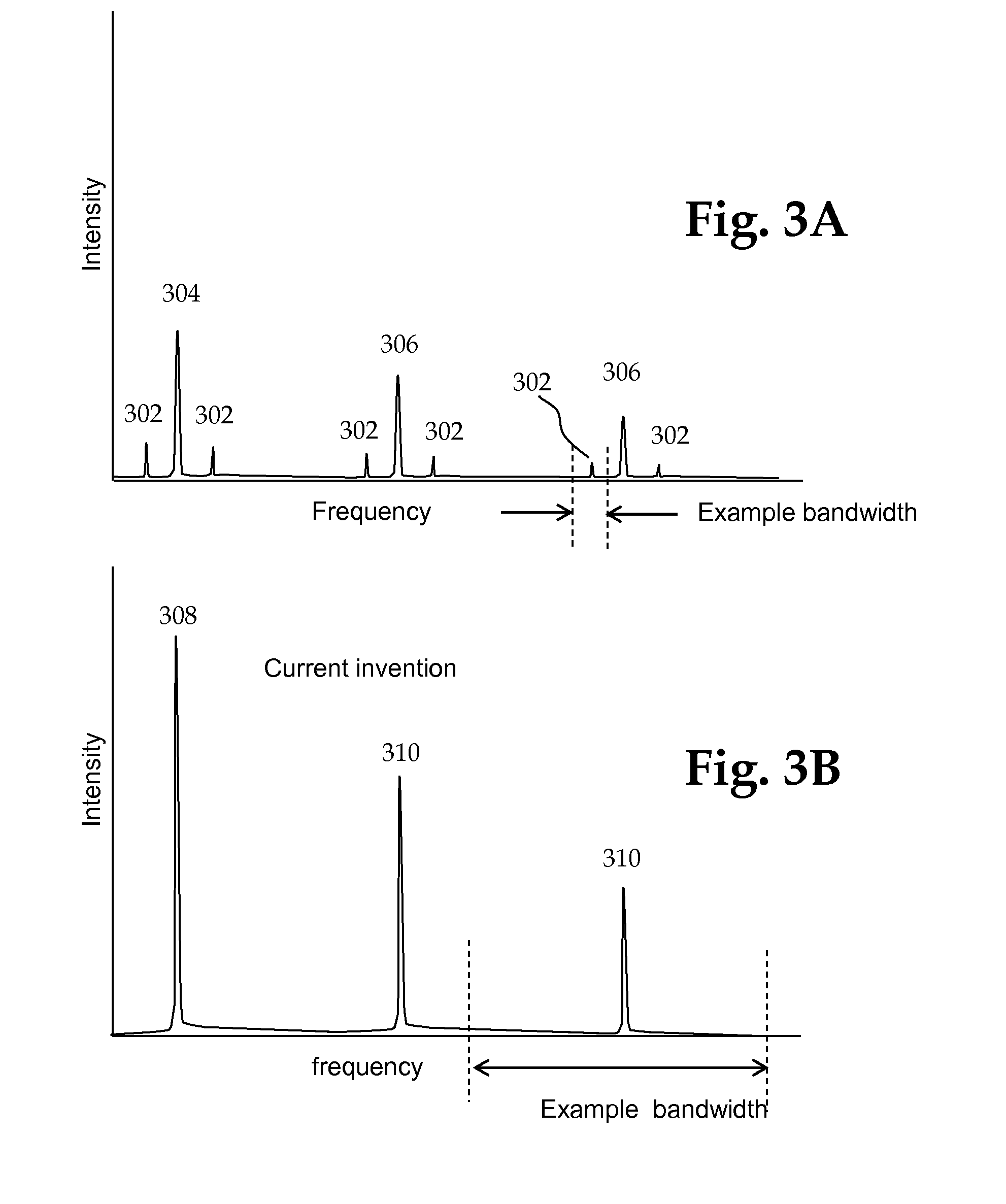
This invention involves measurement of optical properties of materials with sub-micron spatial resolution through infrared scattering scanning near field optical microscopy (s-SNOM). Specifically, the current invention provides substantial improvements over the prior art by achieving high signal to noise, high measurement speed and high accuracy of optical amplitude and phase. Additionally, it eliminates the need for an in situ reference to calculate wavelength dependent spectra of optical phase, or absorption spectra. These goals are achieved via improved asymmetric interferometry where the near field scattered light is interfered with a reference beam in an interferometer. The invention achieves dramatic improvements in background rejection by arranging a reference beam that is much more intense than the background scattered radiation. Combined with frequency selective demodulation techniques, the near-field scattered light can be efficiently and accurately discriminated from background scattered light. These goals are achieved via a range of improvements including a large dynamic range detector, careful control of relative beam intensities, and high bandwidth demodulation techniques.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
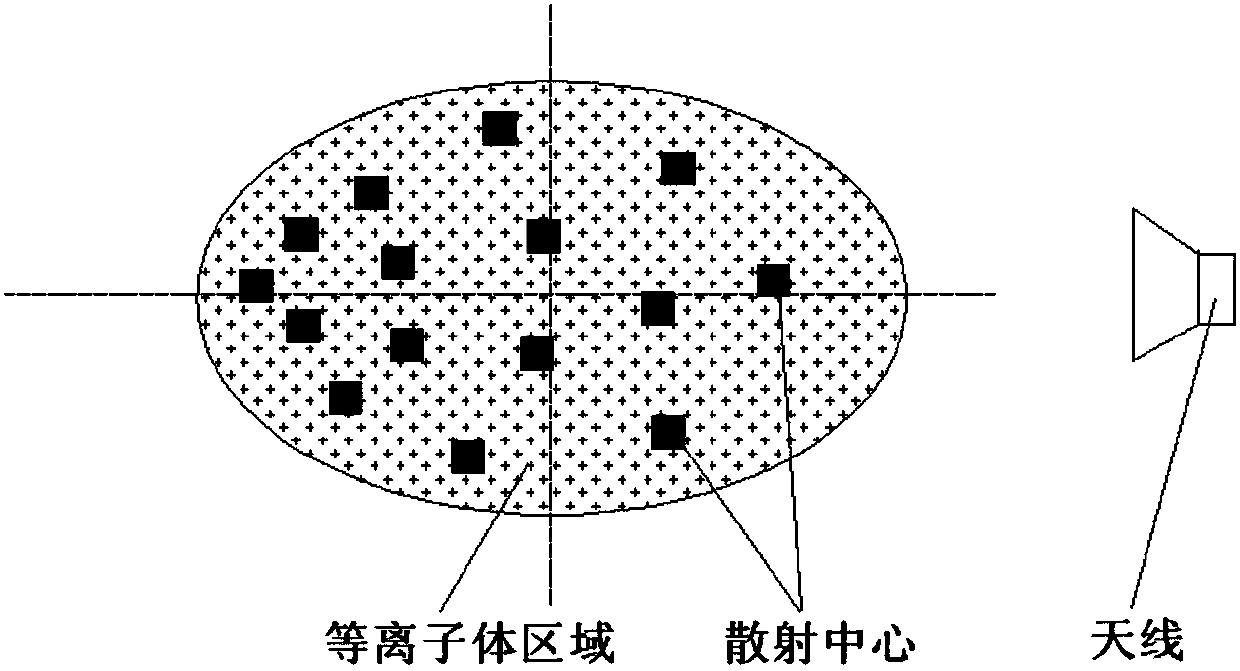
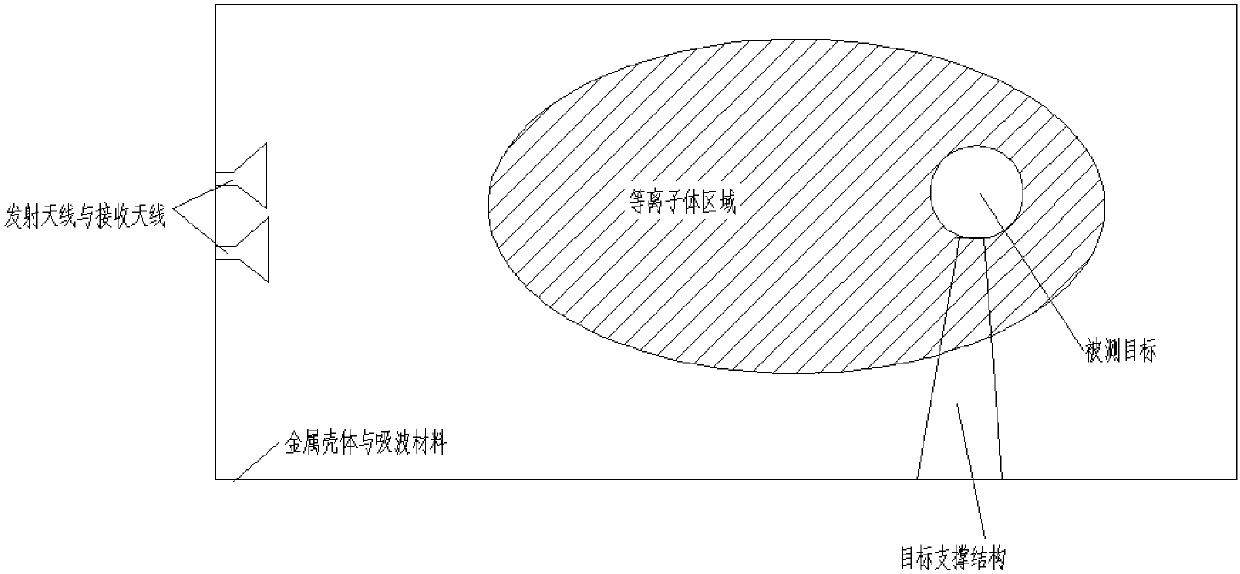
Method and system for extracting radar scattering feature data based on plasma near-field testing
ActiveCN107942330ARealize generationImplementing Scattering Cross Section Performance TestingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionScattering cross-sectionTechnology research
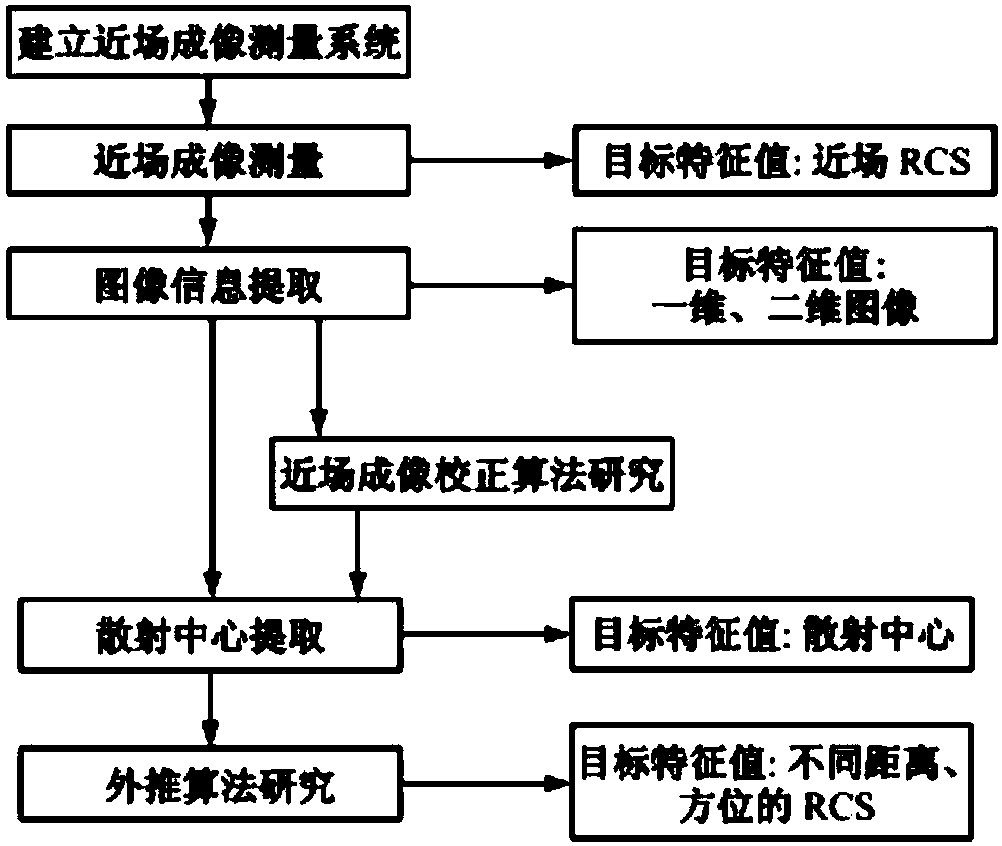
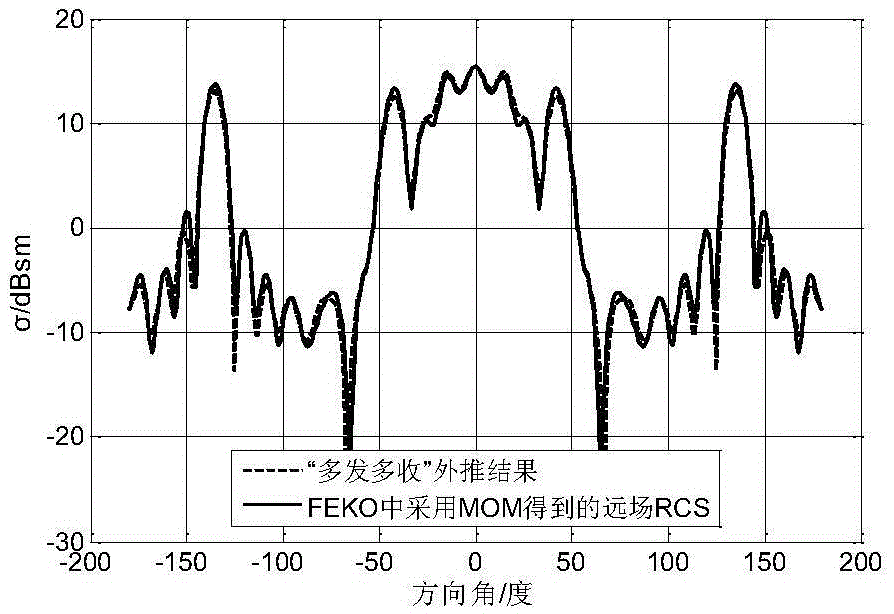
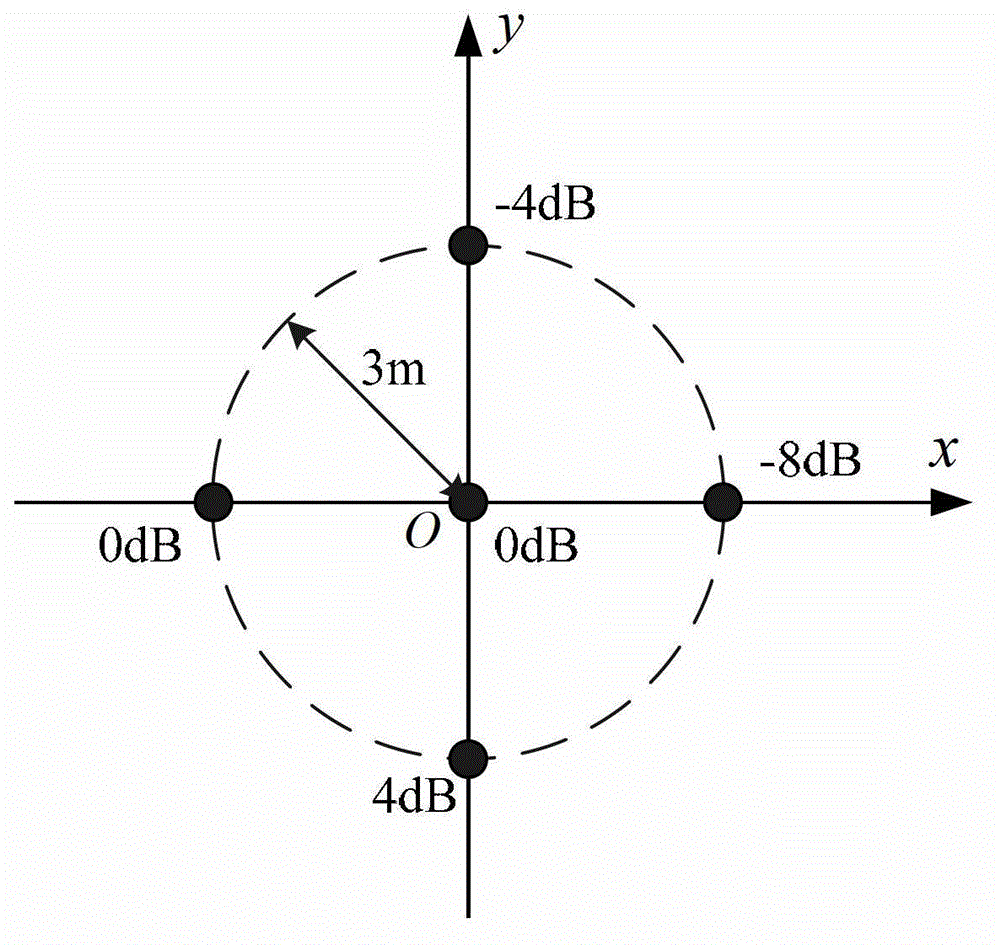
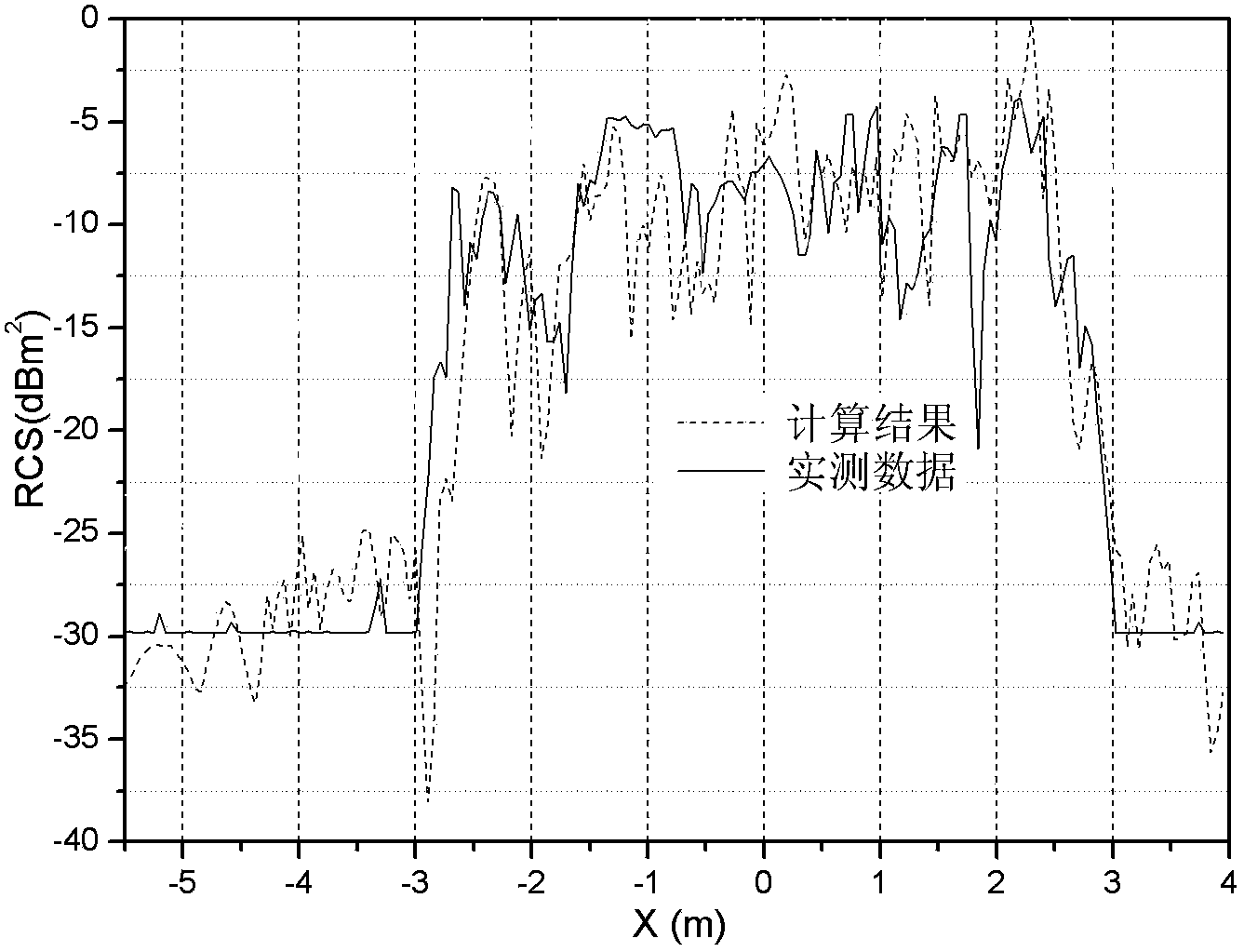
A method and system for extracting radar scattering feature data based on plasma near-field testing are disclosed. An ISAR imaging principle is adopted in a microwave anechoic chamber simulating vacuum environment, and a one-dimensional scanning near-field test method is employed to test scattering performance of a tested target. A near-field scattering 2D image of the tested target is obtained, and near-field correction techniques are used to correct errors of influence error exerted by spherical waves on RCS performance tests. A scattering center is adopted to achieve far-field RCS extrapolation of the tested target, and radar scattering cross section far field data of the test target is obtained. Via the test and the data extraction method, overall target radar cross section data of a plasma-coated aircraft can be provided for a special environment that generates plasma clouds and for peculiar diffusion and ionization characteristics of plasma. A test angle covers a wide angle rangeof -30 degrees to 30 degrees, test accuracy is higher than 2dB, and therefore a test method is provided for plasma stealth technology research and stealth performance evaluation.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE INST OF THE LONG MARCH VEHICLE +1
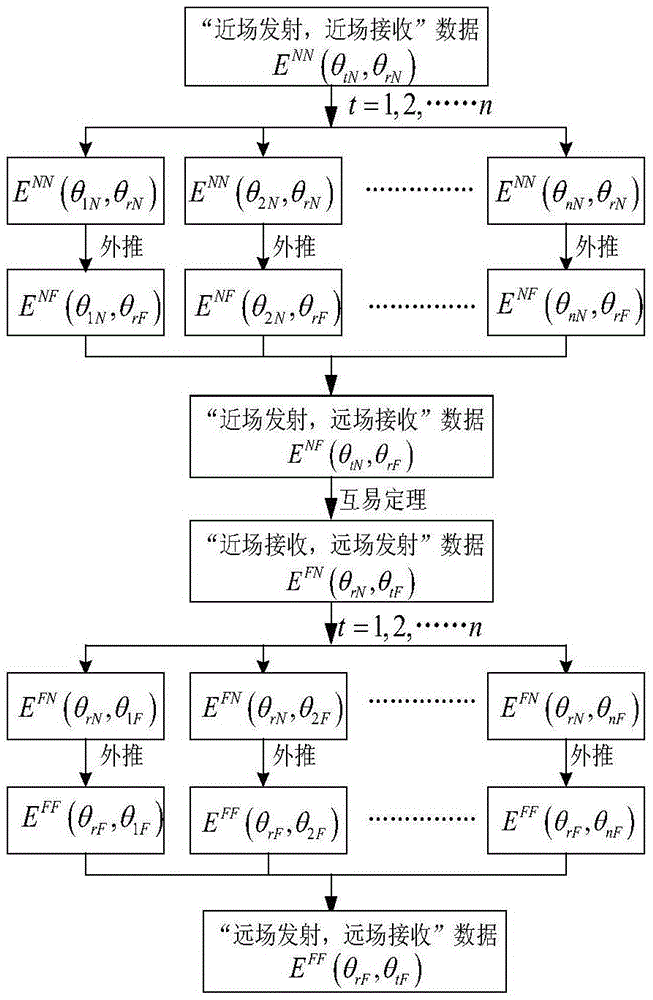
Method of using extrapolation to acquire far field RCS possessing multiple scattering objects
InactiveCN105572652AFit closelyHigh precisionWave based measurement systemsDiagonalNear field scattering
The invention provides a near field scattering extrapolation method based on near-field complete double station information. The method is characterized that extrapolation processing is performed on near field scattering data collected under each angle after near-field double station scattering information of an object full angle domain is acquired; then according to a reciprocal theory, extrapolated data is equivalent to ''far field emission and near field receiving'' data; and then extrapolation is performed on the data so that the data satisfies a ''far field emission and far field receiving'' condition; and finally, an element on a diagonal line is removed and a far field RCS of each angle is acquired.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
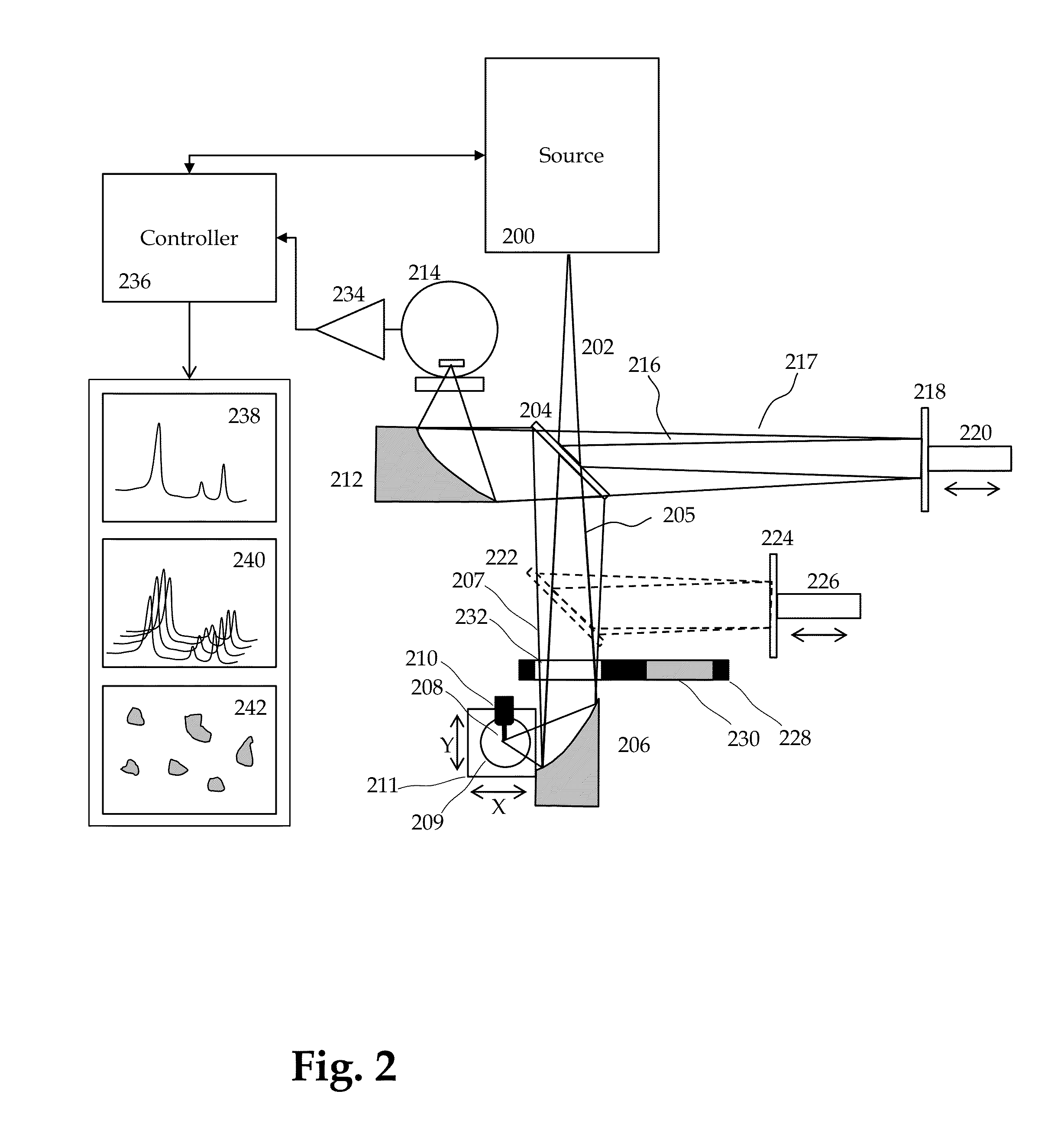
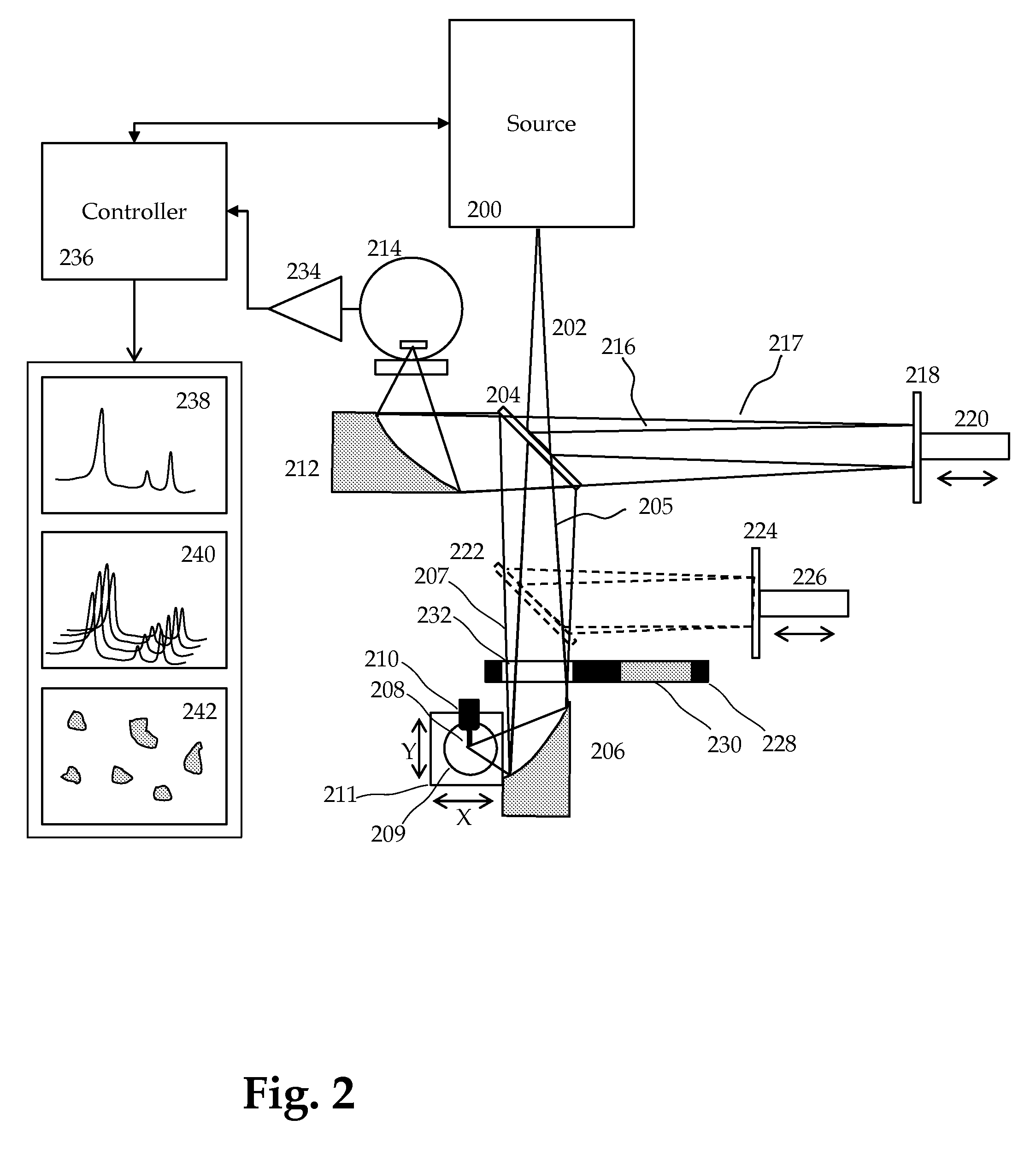
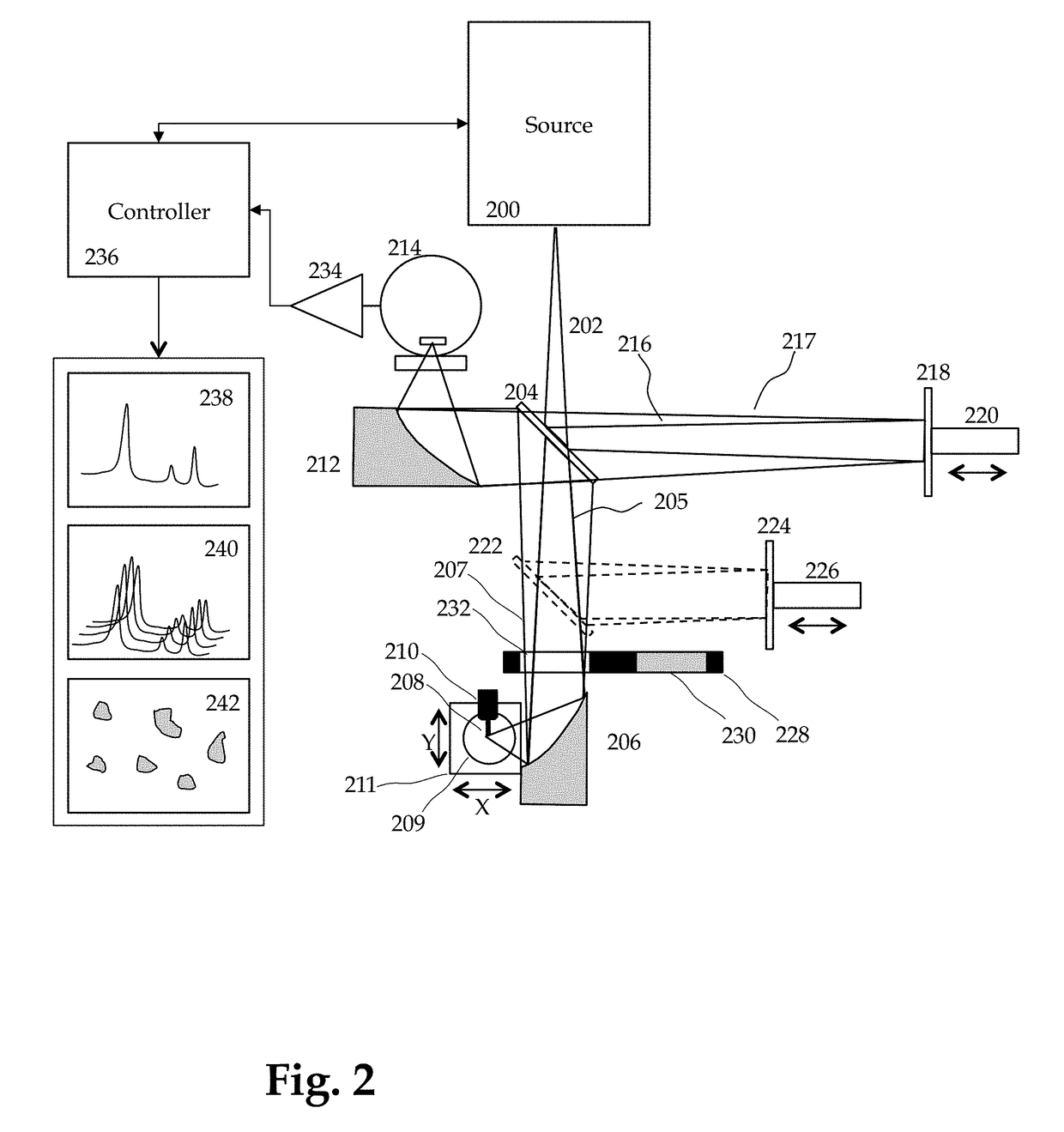
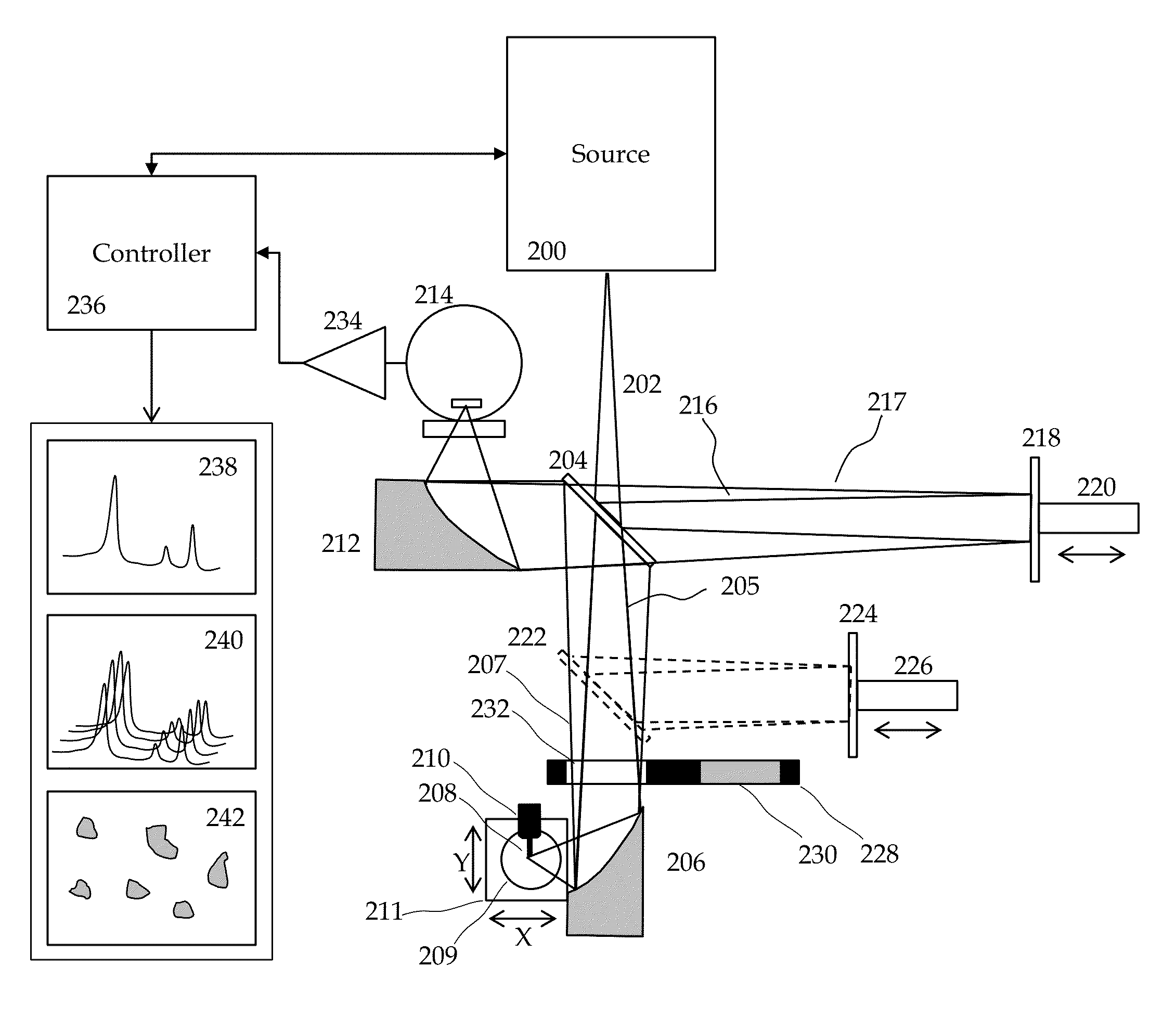
Method and Apparatus for Infrared Scattering Scanning Near-field Optical Microscopy
ActiveUS20160003868A1Rapid and accurate calculationEasy to measureScattering properties measurementsScanning probe microscopyNear field optical microscopeScattering radiation
This invention involves measurement of optical properties of materials with sub-micron spatial resolution through infrared scattering scanning near field optical microscopy (s-SNOM). Specifically, the current invention provides substantial improvements over the prior art by achieving high signal to noise, high measurement speed and high accuracy of optical amplitude and phase. Additionally, it some embodiments, it eliminates the need for an in situ reference to calculate wavelength dependent spectra of optical phase, or absorption spectra. These goals are achieved via improved asymmetric interferometry where the near-field scattered light is interfered with a reference beam in an interferometer. The invention achieves dramatic improvements in background rejection by arranging a reference beam that is much more intense than the background scattered radiation. Combined with frequency selective demodulation techniques, the near-field scattered light can be efficiently and accurately discriminated from background scattered light. These goals are achieved via a range of improvements including a large dynamic range detector, careful control of relative beam intensities, and high bandwidth demodulation techniques. In other embodiments, phase and amplitude stability are improved with a novel s-SNOM configuration.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
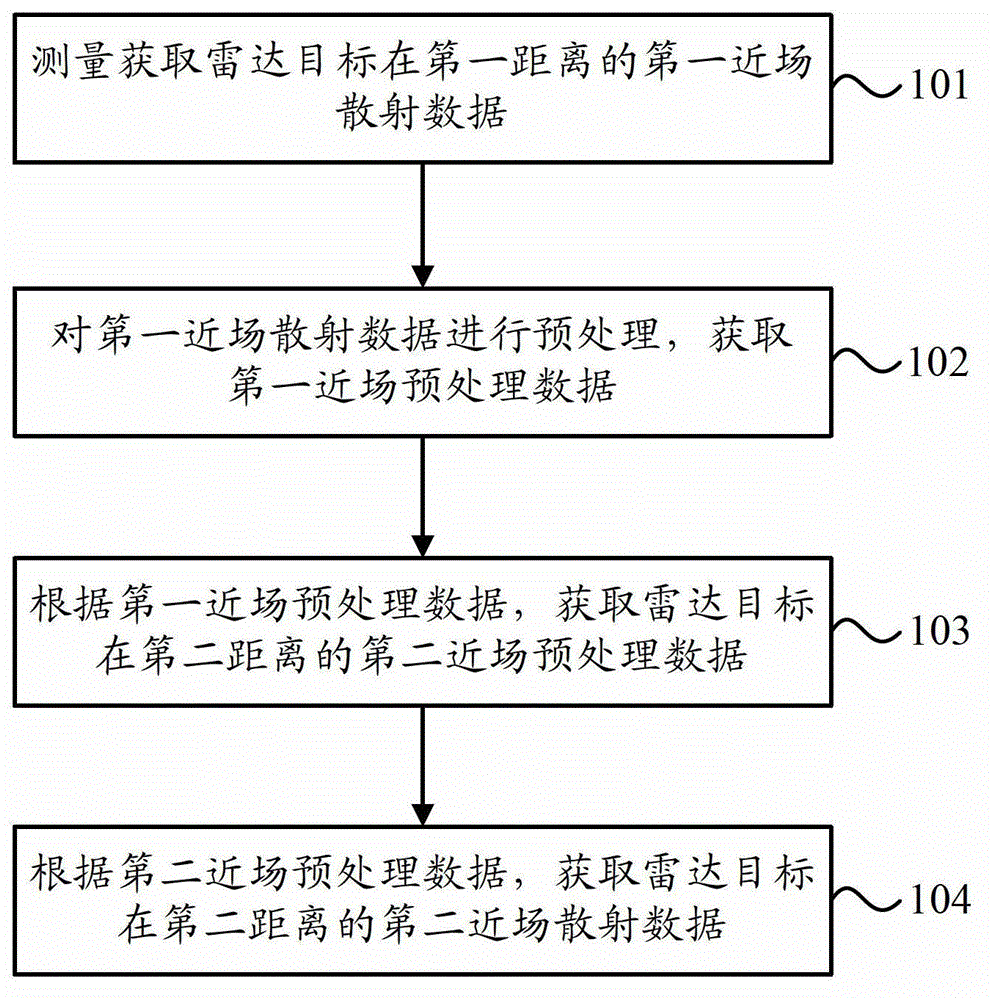
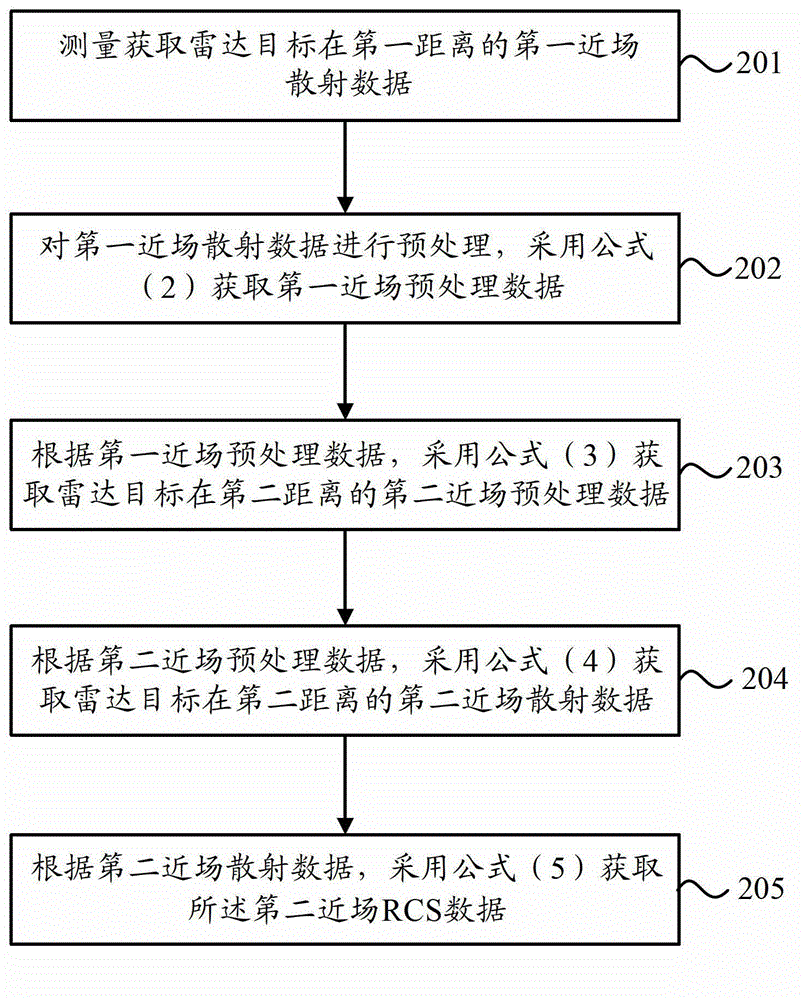
Near field-to-near field transformation method of radar scattering cross section
ActiveCN102944872AConvenient researchReduce testing costsWave based measurement systemsScattering cross-sectionField transformation
The invention provides a near field-to-near field transformation method of a radar scattering cross section. The near field-to-near field transformation method comprises the steps of performing measurement to obtain first near field scattering data at a first distance of a radar target; preprocessing the first near field scattering data to obtain first near field preprocessed data; according to the first near field preprocessed data, obtaining second near field preprocessed data at a second distance of the radar target; and according to the second near field preprocessed data, obtaining second near field scattering data at the second distance of the radar target, wherein scattering data at any distance within the range of the near field of the target can be obtained through the measured near field scattering data at a certain distance, and accordingly, radar cross section (RCS) data at any distance within the range of the near field of the target can be obtained. By means of the near field-to-near field transformation method, testing cost is reduced, and changes of scattering properties of the target to be tested along with the distance can be conveniently researched.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Near field backward RCS measuring system and method based on chain relation formula
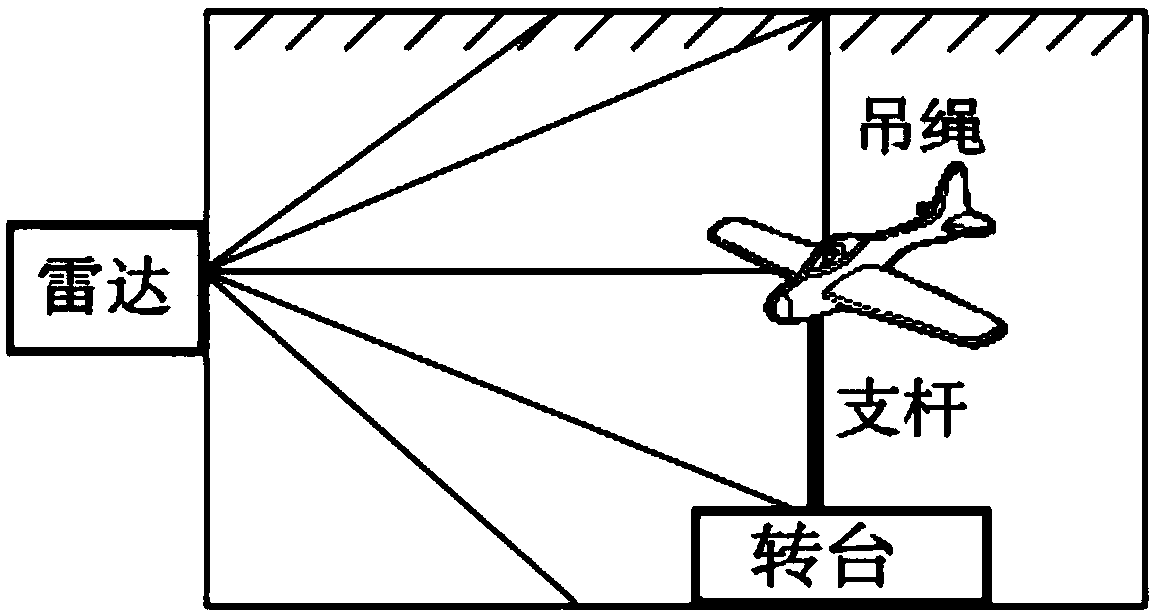
ActiveCN107783092AReduce the level of interference clutterImprove conversion efficiencyWave based measurement systemsRadar systemsField conditions
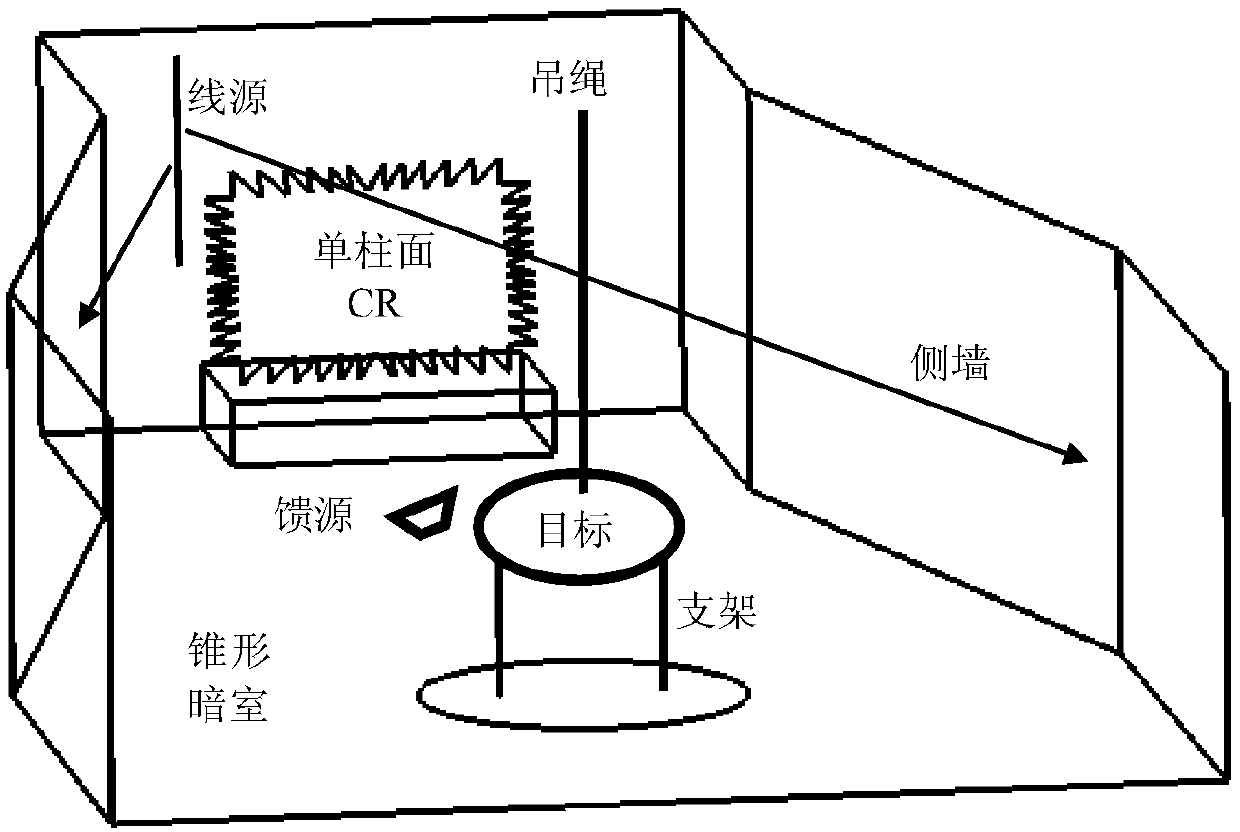
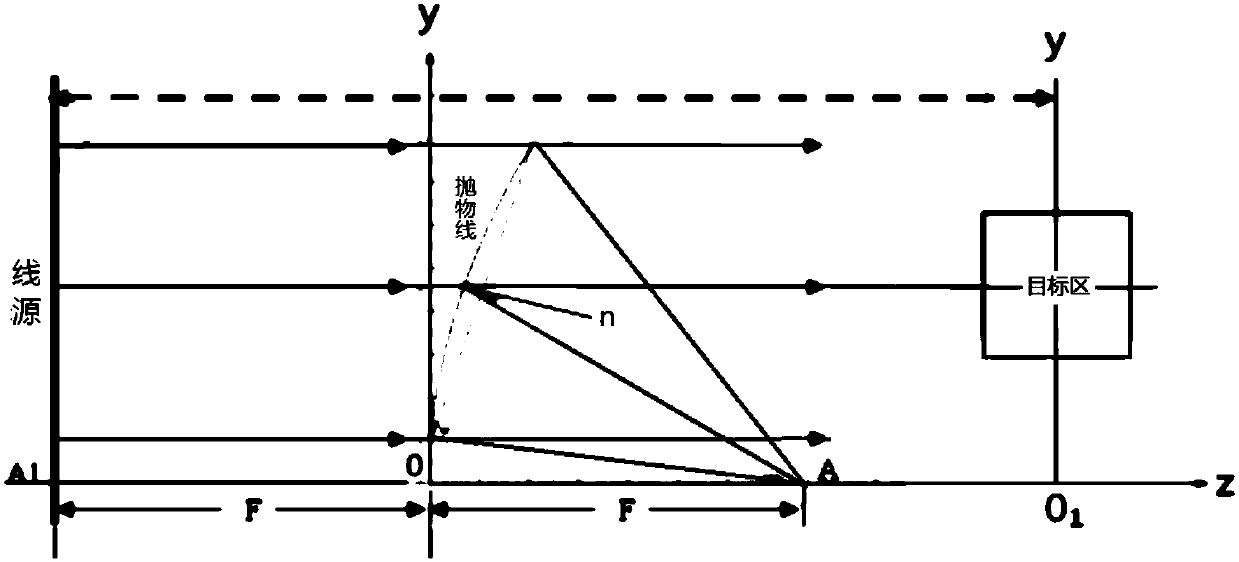
The invention discloses a near field backward RCS measuring system and method based on a chain relation formula; the method uses a line source vertical to the ground to form cylindrical waves, and a cylindrical surface field satisfies far field conditions only in the height direction; in order to reduce side wall interference clutters, a conical microwave darkroom is designed; the cylindrical surface field rear wall echo level is smaller than a compact field by 10dB, thus setting the darkroom door in the rear wall, and facilitating target transport. The invention provides a near field RCS measuring radar system comprising a target and environment portion, a microwave amplitude and phase measuring portion, and a NFFFT and high resolution imaging portion; the invention also provides a near field RCS measuring method comprising the following steps: support and environment vector background cancellation, measuring near field scattering coefficient FN scaling, and secondary scaling of the NFFFT and in a NFFFT process. The advantages are that 1, NFFFT transformation is simplified from two-dimension into one-dimension; 2, multi-diffraction in the horizontal direction of the target will cause errors; 3, interference clutters caused on the darkroom ground, roof slits and steps can be reduced.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A method for accurately acquiring near field echo
ActiveCN103675781ASolve the distance problemAccurate near-field echo dataWave based measurement systemsEcho intensityPolarization scattering matrix
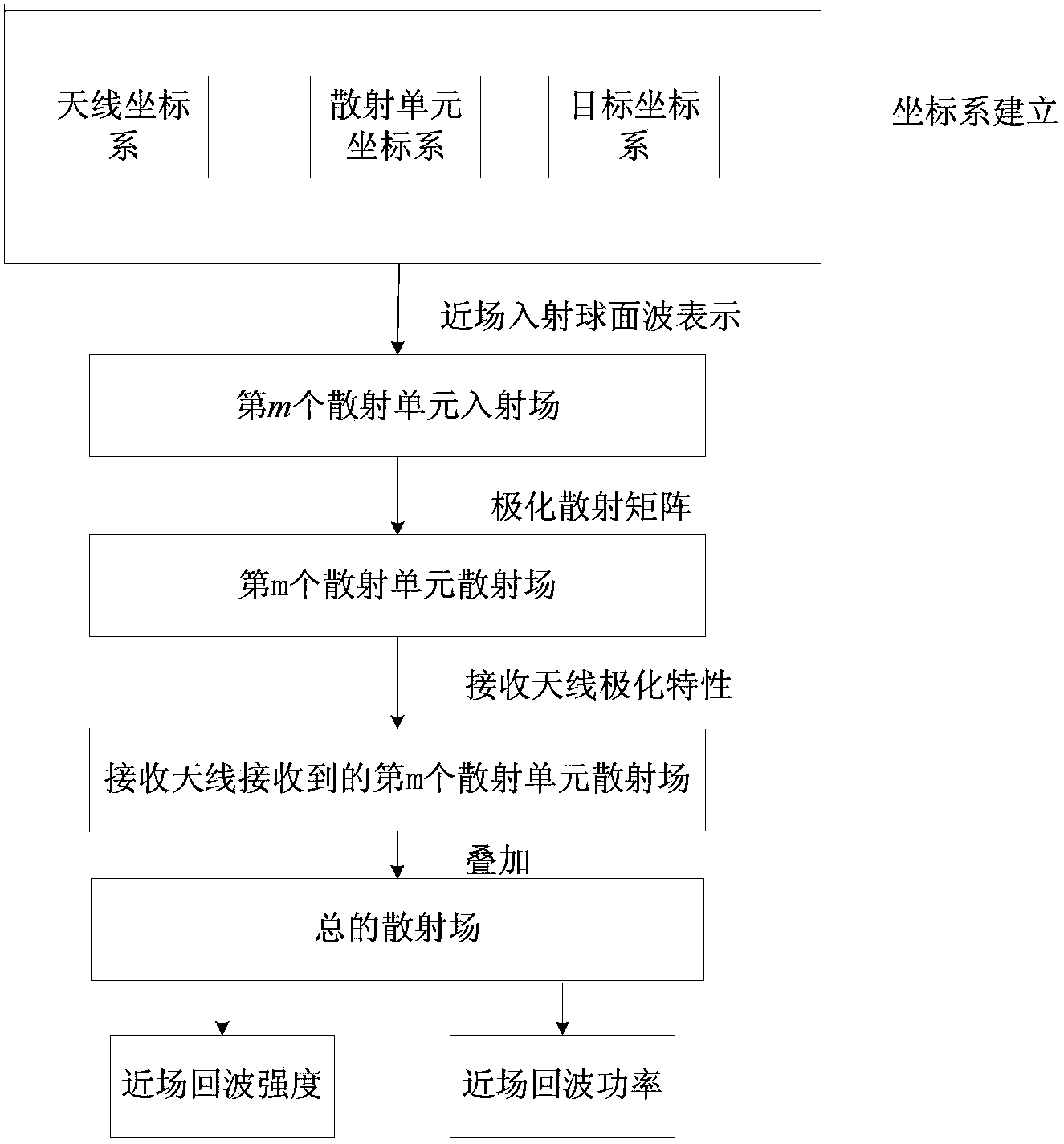
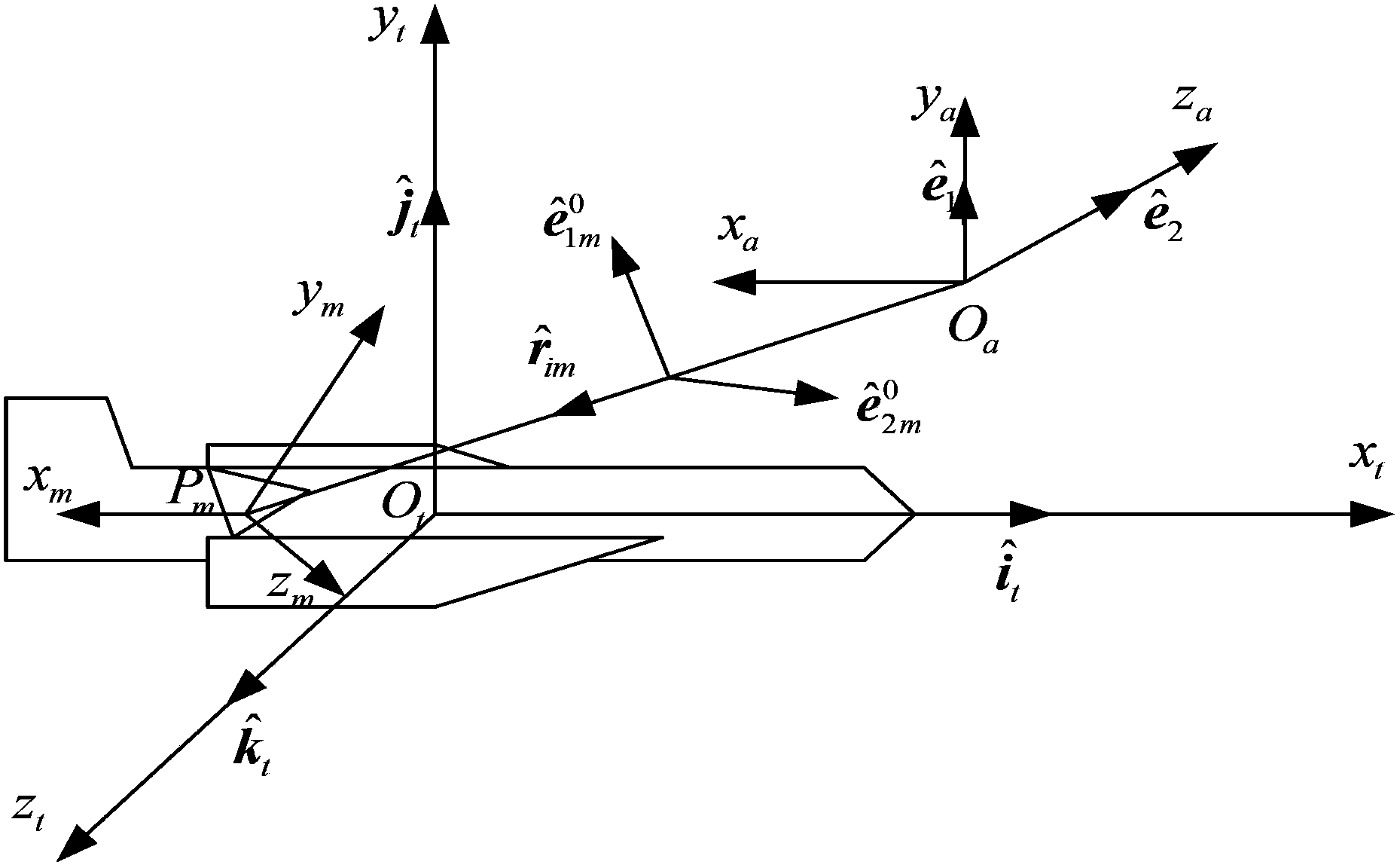
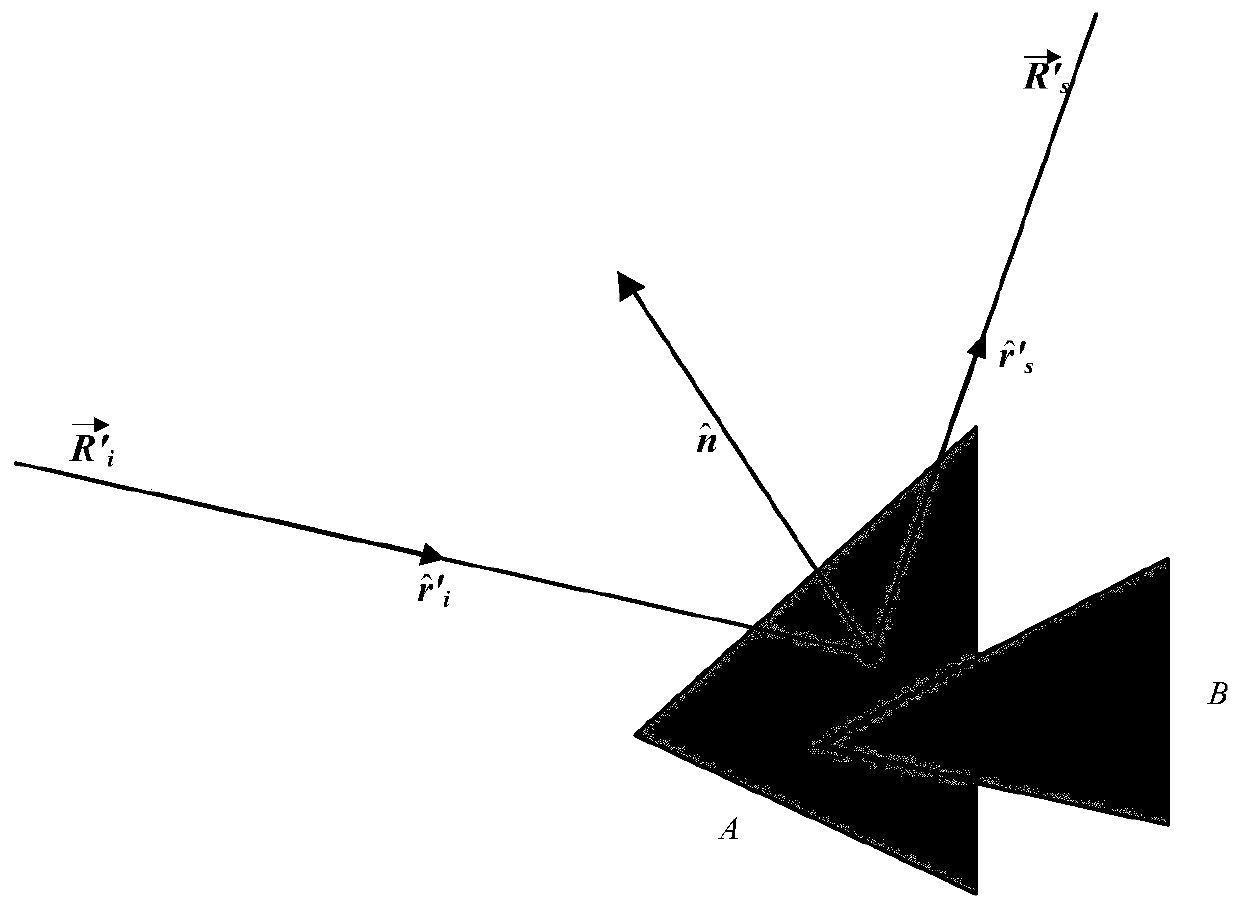
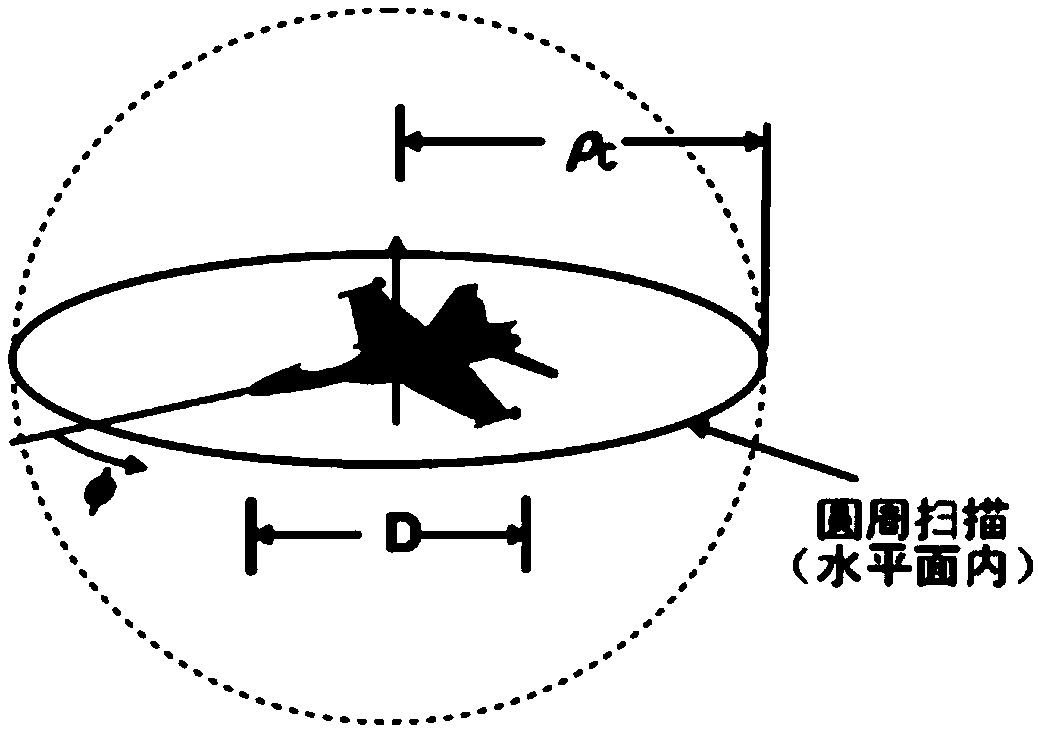
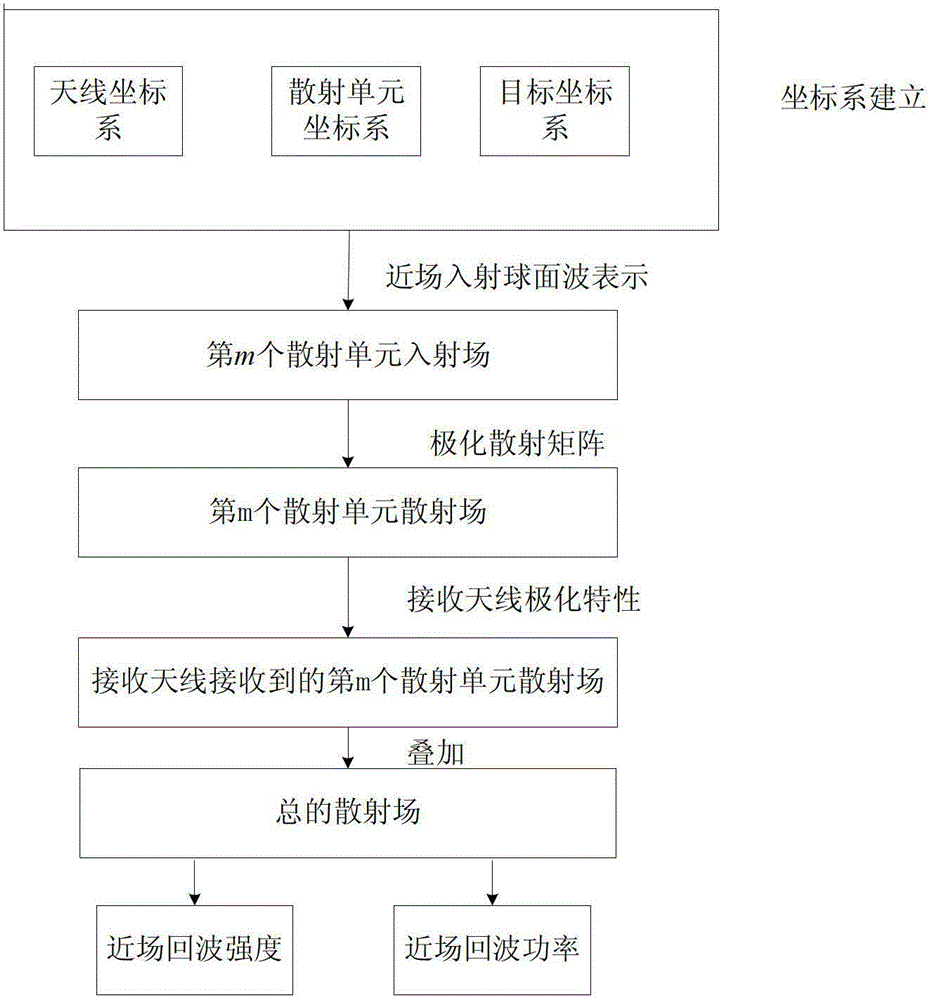
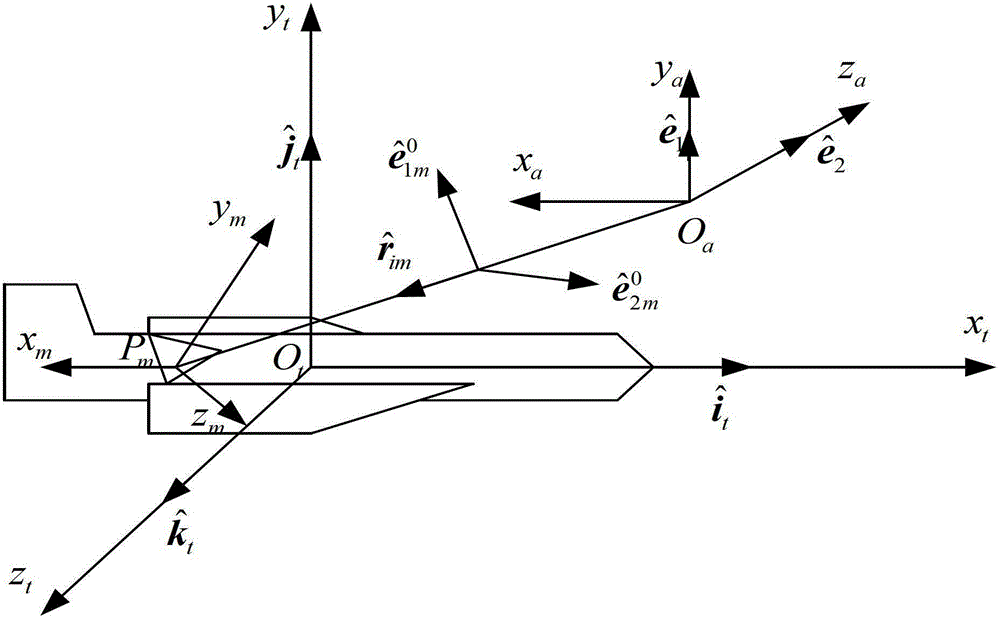
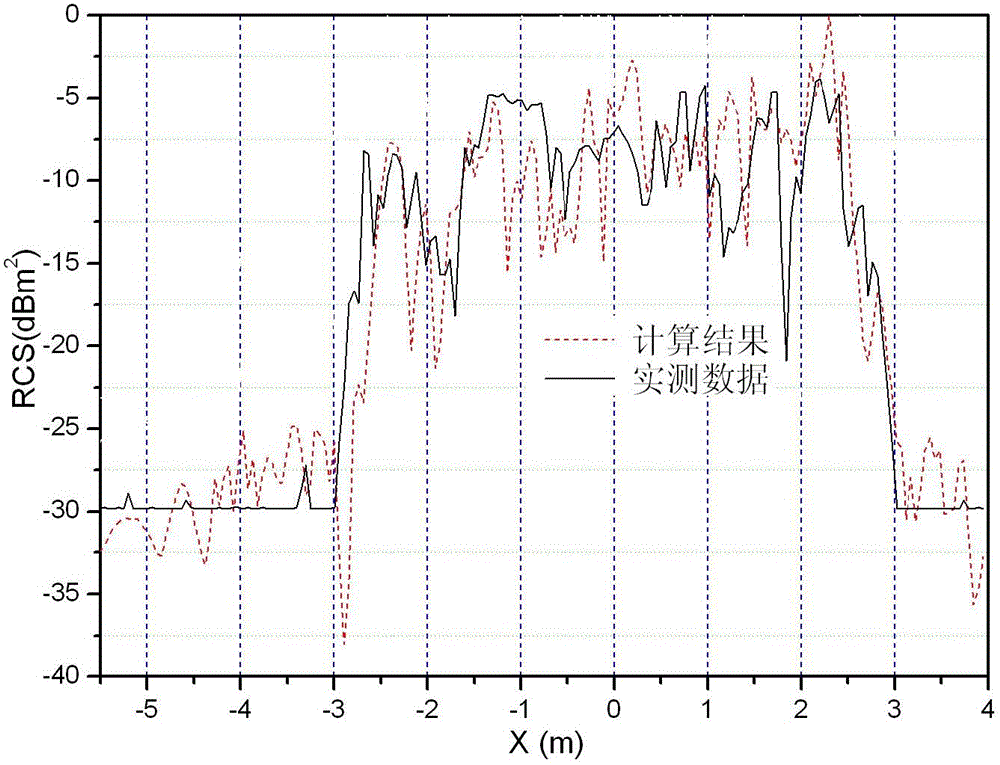
The invention belongs to technical field of signal characteristic control and specifically relates to a method for accurately acquiring near field echo. The method comprises following steps of: a step 1, establishing a target coordinate system O-XtYtZt, an antenna coordinate system O-XaYaZa, and a scattering unit coordinate system O-XmYmZm; a step 2, acquiring a field incident on a mth scattering unit from the surface of a scattering body; a step 3, acquiring scattered fields of the scattering units; a step 4, acquiring a scattered field of the mth scattering unit received by a receiving antenna; a step 5, superposing the scattered fields of each scattering unit received by the receiving antenna in order to acquire a total scattered field; and a step 6, calculating the total scattered field so as to acquire near field echo intensity and power characteristics. The method establishes a complex target near field scattering model with a PO+PTD+GP method and introduces a concept of near field polarization scattering matrix so as to express scattering properties with different mechanisms by using a unified expression, thereby simplifying a calculating process.
Owner:中国航天科工集团第二研究院二〇七所
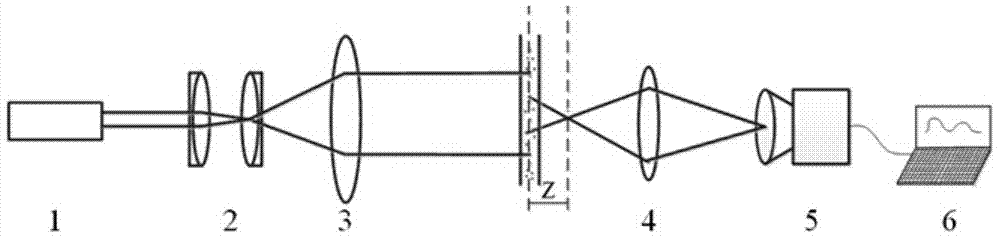
Flow two dimension velocity field measurement device and method based on near field scattering
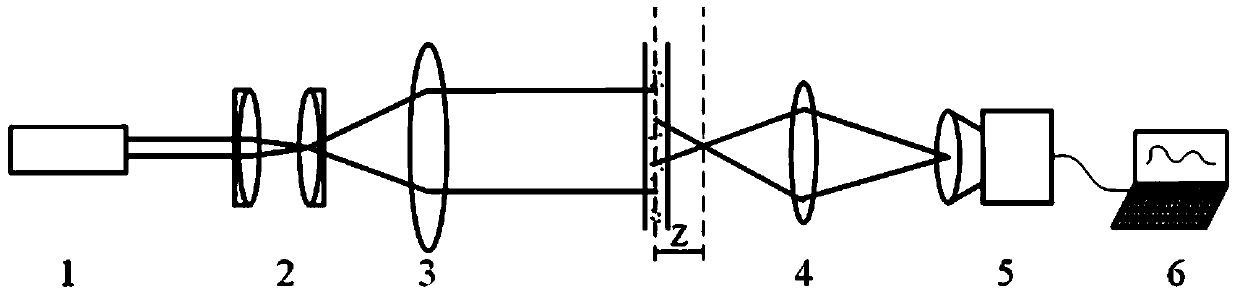
ActiveCN104698219AReduce alignment requirementsIncrease concentrationFluid speed measurementMeasurement deviceCcd camera
The invention discloses a flow two dimension velocity field measurement method and a flow two dimension velocity field measurement device based on near field scattering. The flow two dimension velocity field measurement device based on the near field scattering comprises a laser, a space filter, a collimating lens, a lens group, a CCD (charge coupled device) camera and a computer. Compared with the prior art, the flow two dimension velocity field measurement device based on the near field scattering has the advantages of being pretty simple in structure, low in demand for light path centering, and capable of achieving the purpose of effectively removing stray light under the circumstance that a complex device for eliminating central light strength is not needed. The particle diameter of tracer particles needed by a measurement technology used in the flow two dimension velocity field measurement method based on the near field scattering can be less than the wavelength of incident light emitted from the laser, and concentration of the tracer particles is high, and therefore the measurement technology can be used in measurement of a nanometer fluid flow two dimension velocity field. The measurement technology is simple and quick in data analysis, can achieve online measurement, and guarantees that accuracy and linearity of the flow two dimension velocity field measurement method based on the near field scattering are not limited by the particle diameter and the concentration of the tracer particles by using a differential processing method.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
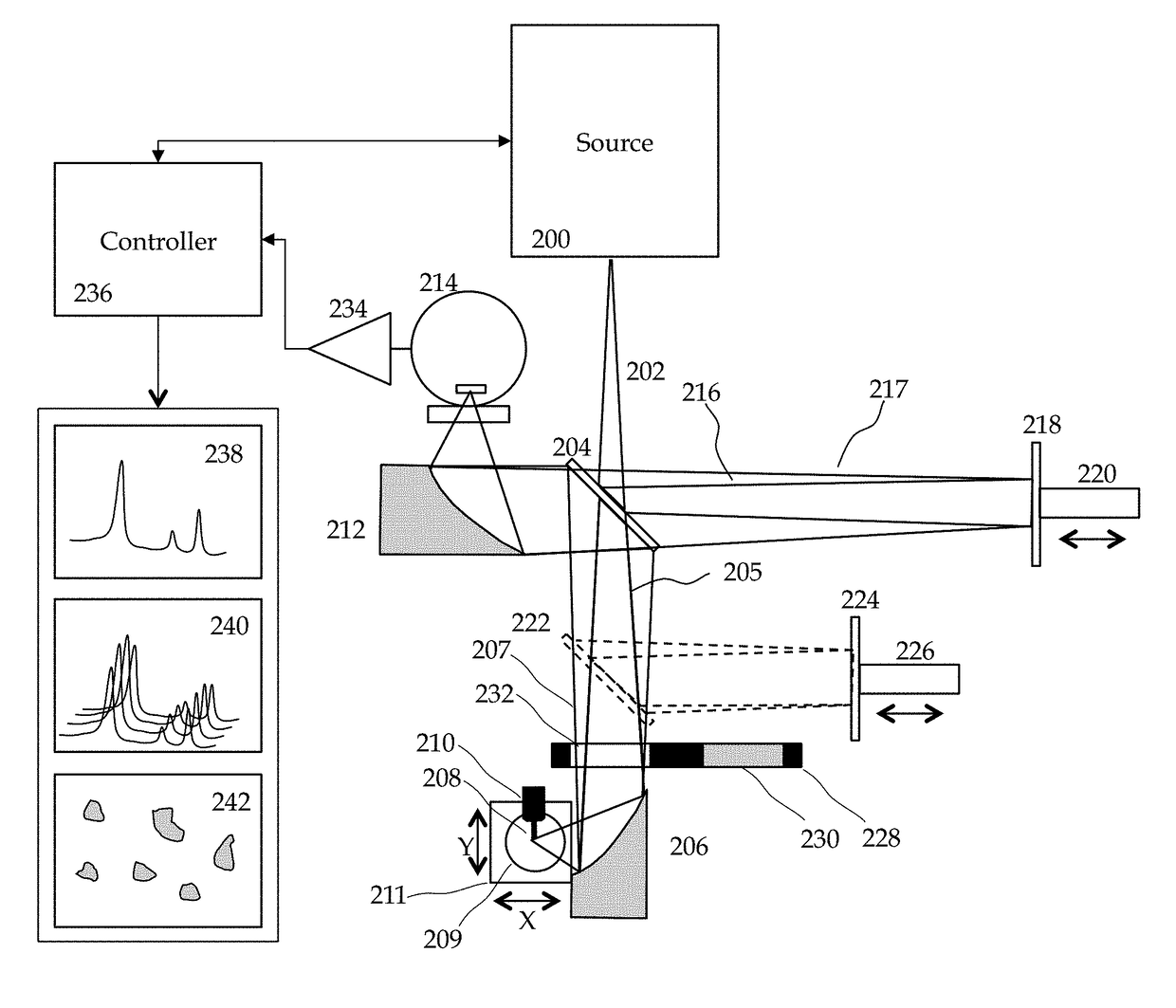
Method and Apparatus for Infrared Scattering Scanning Near-field Optical Microscopy with High Speed Point Spectroscopy
ActiveUS20170003316A1Increase speedRapid and accurate calculationScattering properties measurementsScanning probe microscopySpectroscopyNear field optical microscope
This invention involves measurement of optical properties of materials with sub-micron spatial resolution through infrared scattering scanning near field optical microscopy (s-SNOM). Specifically, the current invention provides substantial improvements over the prior art by achieving high signal to noise, high measurement speed and high accuracy of optical amplitude and phase. Additionally, it some embodiments, it eliminates the need for an in situ reference to calculate wavelength dependent spectra of optical phase, or absorption spectra. These goals are achieved via improved asymmetric interferometry where the near-field scattered light is interfered with a reference beam in an interferometer. The invention achieves dramatic improvements in background rejection by arranging a reference beam that is much more intense than the background scattered radiation. Combined with frequency selective demodulation techniques, the near-field scattered light can be efficiently and accurately discriminated from background scattered light. These goals are achieved via a range of improvements including a large dynamic range detector, careful control of relative beam intensities, and high bandwidth demodulation techniques. In other embodiments, phase and amplitude stability are improved with a novel s-SNOM configuration. In other embodiments an absorption spectrum may be obtained directly by comparing properties from a known and unknown region of a sample as a function of illumination center wavelength.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Method and Apparatus for Infrared Scattering Scanning Near-field Optical Microscopy with High Speed Point Spectroscopy
ActiveUS20170219622A1Increase speedRapid and accurate calculationRadiation pyrometryScattering properties measurementsSpectroscopySignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
This invention involves measurement of optical properties of materials with sub-micron spatial resolution through infrared scattering scanning near field optical microscopy (s-SNOM). Specifically, the current invention provides substantial improvements over the prior art by achieving high signal to noise, high measurement speed and high accuracy of optical amplitude and phase. Additionally, it some embodiments, it eliminates the need for an in situ reference to calculate wavelength dependent spectra of optical phase, or absorption spectra. These goals are achieved via improved asymmetric interferometry where the near-field scattered light is interfered with a reference beam in an interferometer. The invention achieves dramatic improvements in background rejection by arranging a reference beam that is much more intense than the background scattered radiation. Combined with frequency selective demodulation techniques, the near-field scattered light can be efficiently and accurately discriminated from background scattered light. These goals are achieved via a range of improvements including a large dynamic range detector, careful control of relative beam intensities, and high bandwidth demodulation techniques. In other embodiments, phase and amplitude stability are improved with a novel s-SNOM configuration. In other embodiments an absorption spectrum may be obtained directly by comparing properties from a known and unknown region of a sample as a function of illumination center wavelength.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Method and apparatus for infrared scattering scanning near-field optical microscopy
ActiveUS9372154B2Rapid and accurate calculationEasy to measureScattering properties measurementsScanning probe microscopySignal-to-quantization-noise ratioNear field optical microscope
This invention involves measurement of optical properties of materials with sub-micron spatial resolution through infrared scattering scanning near field optical microscopy (s-SNOM). Specifically, the current invention provides substantial improvements over the prior art by achieving high signal to noise, high measurement speed and high accuracy of optical amplitude and phase. Additionally, it some embodiments, it eliminates the need for an in situ reference to calculate wavelength dependent spectra of optical phase, or absorption spectra. These goals are achieved via improved asymmetric interferometry where the near-field scattered light is interfered with a reference beam in an interferometer. The invention achieves dramatic improvements in background rejection by arranging a reference beam that is much more intense than the background scattered radiation. Combined with frequency selective demodulation techniques, the near-field scattered light can be efficiently and accurately discriminated from background scattered light. These goals are achieved via a range of improvements including a large dynamic range detector, careful control of relative beam intensities, and high bandwidth demodulation techniques. In other embodiments, phase and amplitude stability are improved with a novel s-SNOM configuration.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Method and apparatus for infrared scattering scanning near-field optical microscopy with high speed point spectroscopy
ActiveUS9658247B2Rapid and accurate calculationFast wayScattering properties measurementsScanning probe microscopySpectroscopySignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
This invention involves measurement of optical properties of materials with sub-micron spatial resolution through infrared scattering scanning near field optical microscopy (s-SNOM). Specifically, the current invention provides substantial improvements over the prior art by achieving high signal to noise, high measurement speed and high accuracy of optical amplitude and phase. Additionally, it some embodiments, it eliminates the need for an in situ reference to calculate wavelength dependent spectra of optical phase, or absorption spectra. These goals are achieved via improved asymmetric interferometry where the near-field scattered light is interfered with a reference beam in an interferometer. The invention achieves dramatic improvements in background rejection by arranging a reference beam that is much more intense than the background scattered radiation. Combined with frequency selective demodulation techniques, the near-field scattered light can be efficiently and accurately discriminated from background scattered light. These goals are achieved via a range of improvements including a large dynamic range detector, careful control of relative beam intensities, and high bandwidth demodulation techniques. In other embodiments, phase and amplitude stability are improved with a novel s-SNOM configuration. In other embodiments an absorption spectrum may be obtained directly by comparing properties from a known and unknown region of a sample as a function of illumination center wavelength.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
ISAR imaging simulation method based on time domain shooting bouncing ray quick near-field calculation
ActiveCN106556833ACalculation speedImprove calculation accuracyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPatch modelDelay calculation
The invention relates to an ISAR imaging simulation method based on time domain shooting bouncing ray-method quick near-field calculation. The method comprises steps of (S1) setting a target triangular patch model and transient incident field capable of being any time domain waveform, (S2) employing a time domain shooting bouncing ray quick near-field calculation method to calculate a transient near-field scattering echo illuminated on the target triangular patch model by time domain plane waves, (S3) unifying the target transient near-field scattering echo in a frequency domain according to an incident signal, and (S4) repeatedly executing step 2 and 3 according to angle width and sampling density required by ISAR imaging definition to achieve echo data of a selected angle sample, and then conducting azimuth focusing to achieve a target ISAR image. Real narrow pulse broadband radar close range imaging detection can be simulated; quick calculation speed, high calculation precision and wide application range can be achieved; and pre-estimating data can be provided for target near-field scattering image diagnosis, so cost can be reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
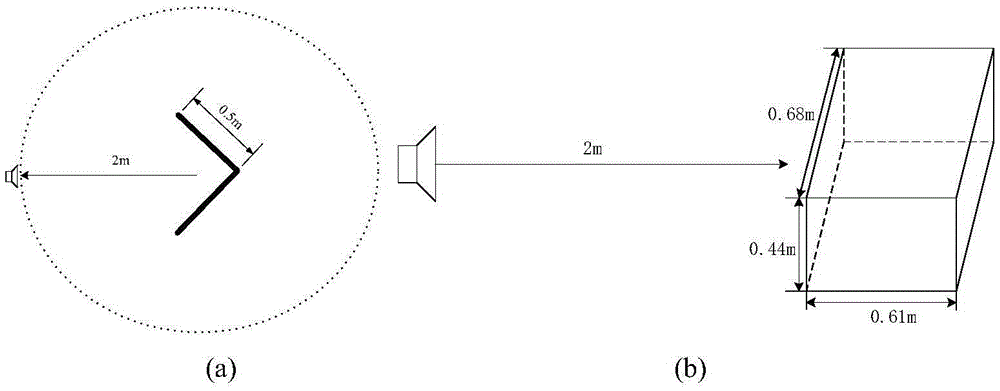
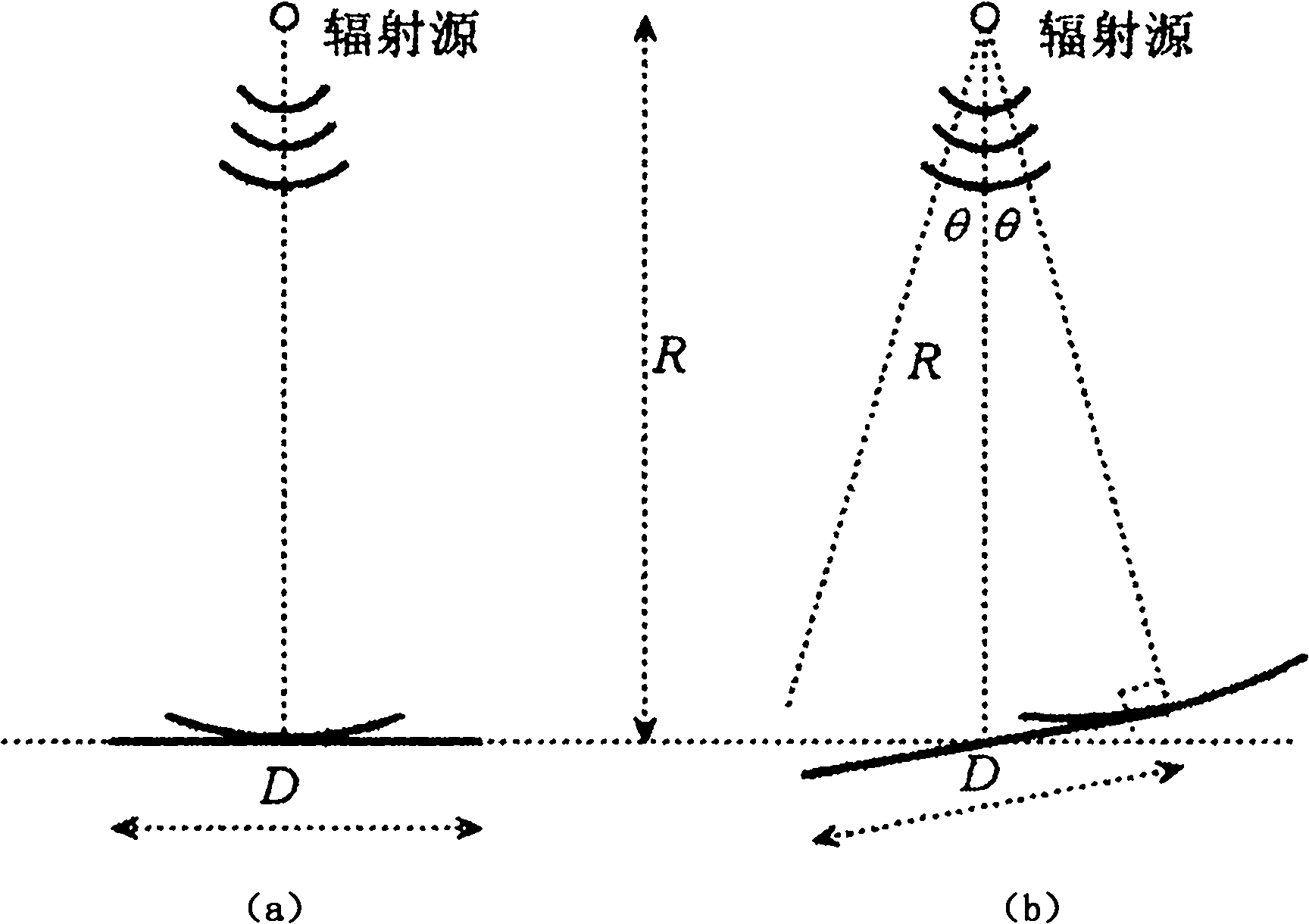
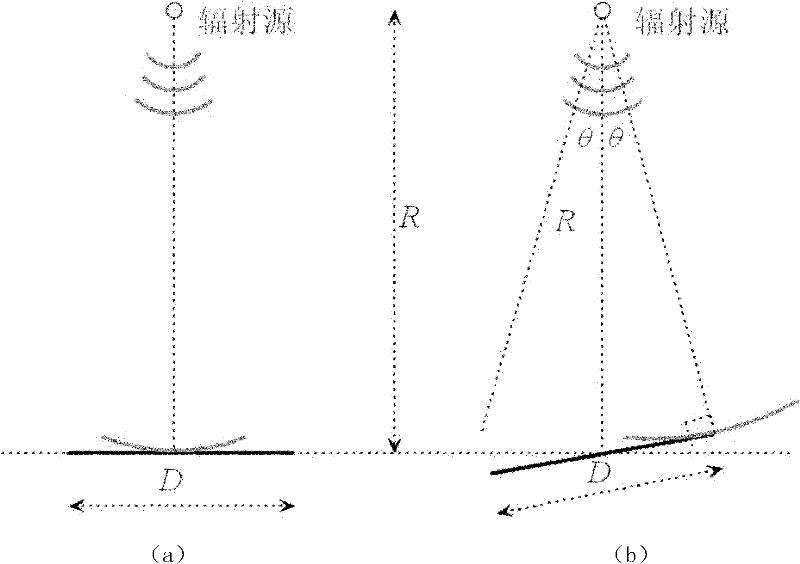
Flat top effect estimation method for near-field radar scattering cross section of rectangular flat plate
ActiveCN102062857AAvoid blind spotsThe conclusion is accurateWave based measurement systemsScattering cross-sectionEstimation methods
The invention provides a flat top effect estimation method for a near-field radar scattering cross section of a rectangular flat plate. A critical state is reached when the included angle between a connecting line from a radiation source to one end point of the rectangular flat plate and the rectangular flat plate is 90 degrees, and the included angle between the connecting line from the radiation source to the end point of the rectangular flat plate and an R is a critical incident angle Theta, wherein the critical incident angle Theta is equal to arcsin (D / 2R), D is the length of the flat plate and R is the vertical distance from the radiation source to the flat plate, and the width M of the flat top is quantificationally estimated to be twice the corresponding critical incident angle Theta according to a geometric relationship. The invention provides a simple method for estimating the width of the flat top of the near-field RCS (Radar Cross Section), the width of flat top of the near-field RCS is quantificatioinally estimated from the point of the geometric relationship, the blind spot of the field is solved, and the obtained conclusion is more accurate. Moreover, by virtue of the method, a favorable ground is provided for analyzing the near-field scattering flat top phenomenon of the flat plate and a building thereof, and the method is good for the prediction and the analysis on the near-field RCS of various targets with a similar flat plate structure.
Owner:CHINA SHIP DEV & DESIGN CENT
Target contour inversion method based on near field surrounding surface to scan polarization scattering data
InactiveCN109633583AImplement diagnosticsAchieve positioningWave based measurement systemsComplex mathematical operationsScattering functionRadar
The invention relates to a target contour inversion method based on a near field surrounding surface to scan polarization scattering data. The method comprises the following steps that S1, according to the length direction of a target, the near field scanning elliptical column-shaped surrounding surface of the target is built; S2, two orthogonal dipoles are adopted as a transmitting antenna and areceiving antenna for near field scanning, and distribution data of near field scattering functions on the elliptical column-shaped surrounding surface of the target is acquired; S3, Huynen parameters of the distribution data of the near field scattering functions of the target are calculated; and S4, the target contour contour features are inverted on the basis of the Huynen parameters. According to the method, diagnosis and positioning of a target strong scattering source or a scattering center under different polarization states can be realized, so that a theoretical data reference is provided for design of the low-detectable geometric contour of a radar target, and an important reference base can be provided for radar target detection and recognition by utilizing polarization parameter changes caused by the target geometric contour.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
Particle granularity measuring device and method based on near-field scattering
InactiveCN104697906AHigh precisionEasy to eliminate the influence of stray lightParticle size analysisMeasurement deviceGaussian beam
The invention discloses a particle granularity measuring device and a particle granularity measuring method based on near-field scattering, wherein the particle granularity measuring device based on near-field scattering comprises a laser device, a spatial filter, a collimating lens, a lens group, a CCD camera, and a computer. The laser device is used for emitting a coherent light beam; the spatial filter filters the coherent light beam emitted by the laser device and obtains a Gauss light beam; the collimating lens converts the Gauss light beam into a straight light beam; the lens unit is used for setting a focal length, and images scattered spots at a Z position from a measurement zone; the CCD camera is used for collecting a near-field scattered spot image that is imaged by the lens unit; and the computer processes the near-field scattered spot image collected by the CCD camera in order to obtain a particle granularity distribution. Comparing the prior art, the particle granularity measuring device and the particle granularity measuring method based on near-field scattering make the system equipment simple in the condition of not adding a complex device for removing the central light strength; the particle granularity measuring device and the particle granularity measuring method based on near-field scattering are able to achieve the measurements of the granularity and the distribution of the measured particles without any angle resolved detections, thereby expanding the range of the scattering angle and achieving the granularity measurement of nanometer particles.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Amplitude calibrating method used for multi-probe near-field scattering imaging
The invention provides an amplitude calibrating method used for multi-probe near-field scattering imaging. The method includes the steps of (1) background scattering data are measured through a multi-probe detection system; (2) scattering data of a target to be measured are measured; (3) scattering data of a metal plate are measured; (4) background cancellation is carried out on the target to be measured to obtain scattering data, and imaging processing is carried out on the scattering data to obtain an imaging result; (5) background cancellation is carried out on the calibration metal plate to obtain scattering data, and imaging processing is carried out on the scattering data in an RMA algorithm to obtain an imaging result; (6) the imaging result is calibrated according to a first formula, and the calibrated imaging result of the target to be measured is obtained. According to the technical scheme, microwave / millimeter wave imaging azimuth amplitude calibration can be carried out, the amplitude calibrating method is mainly used for the multi-probe imaging system poor in amplitude precision, the imaging result is directly calibrated through a simple calibration element, and imaging precision is improved.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIS TECH INSTR CO LTD
Poynting vector-based target near-field like-polarized scattering characteristic calibration method
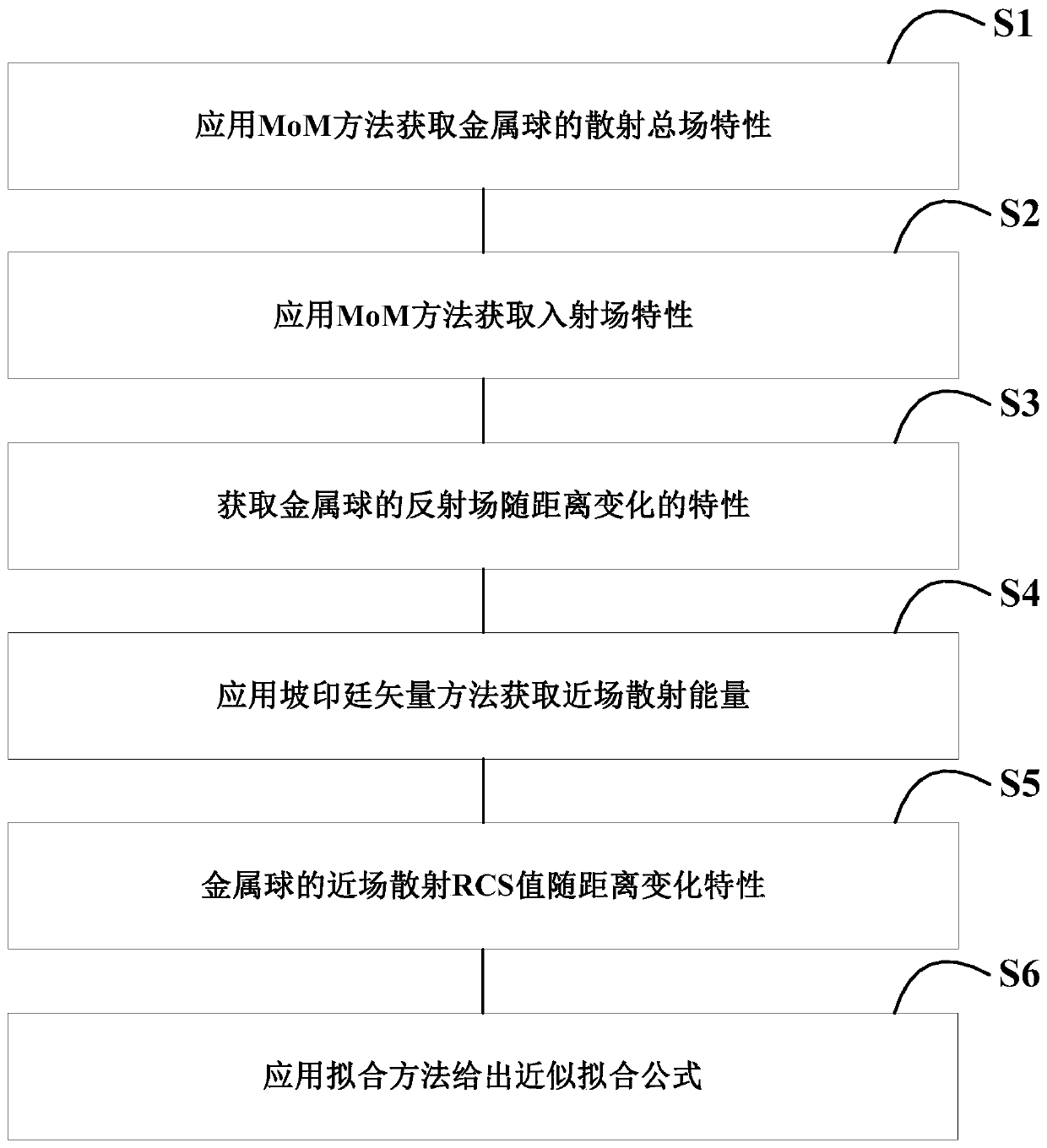
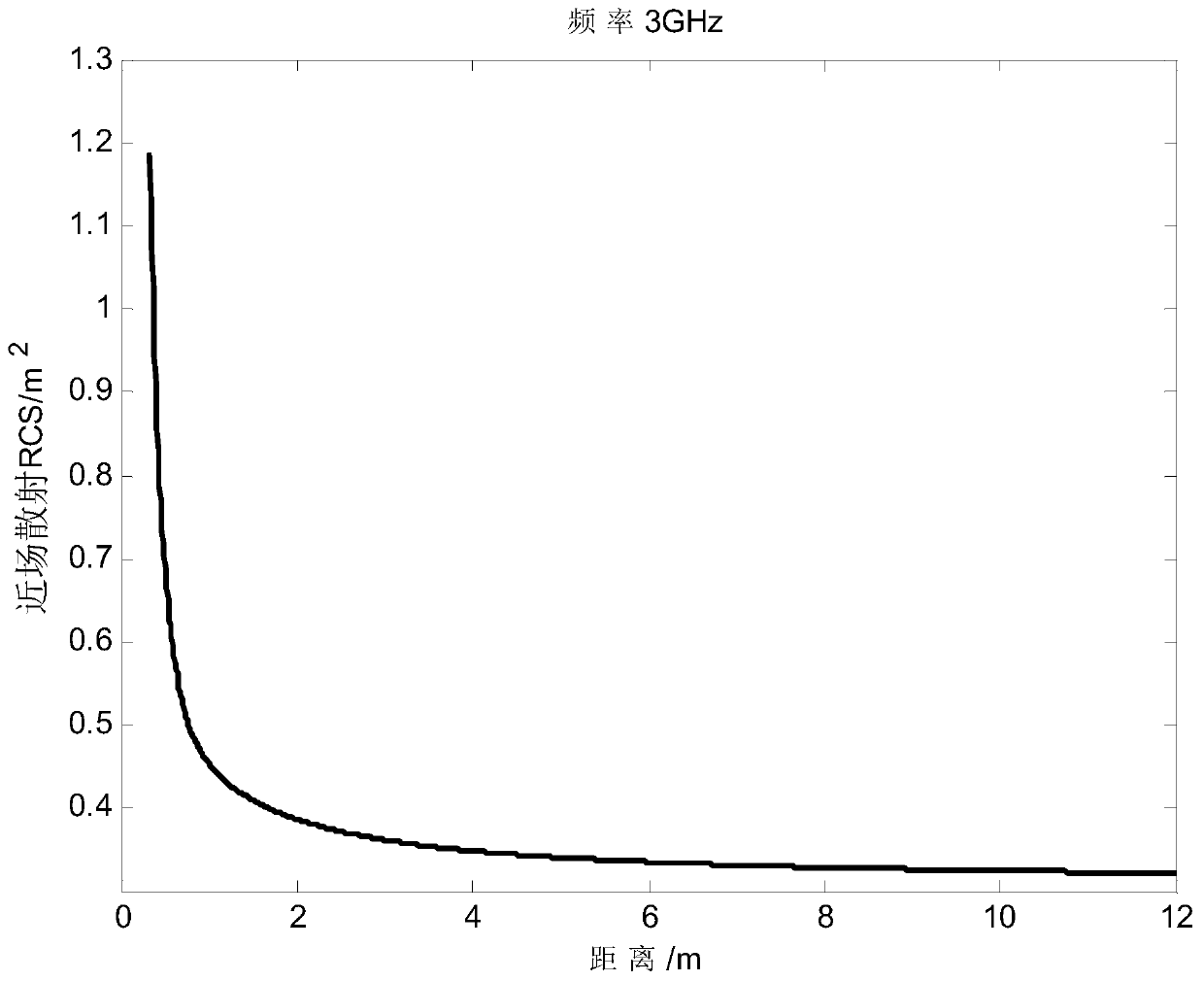
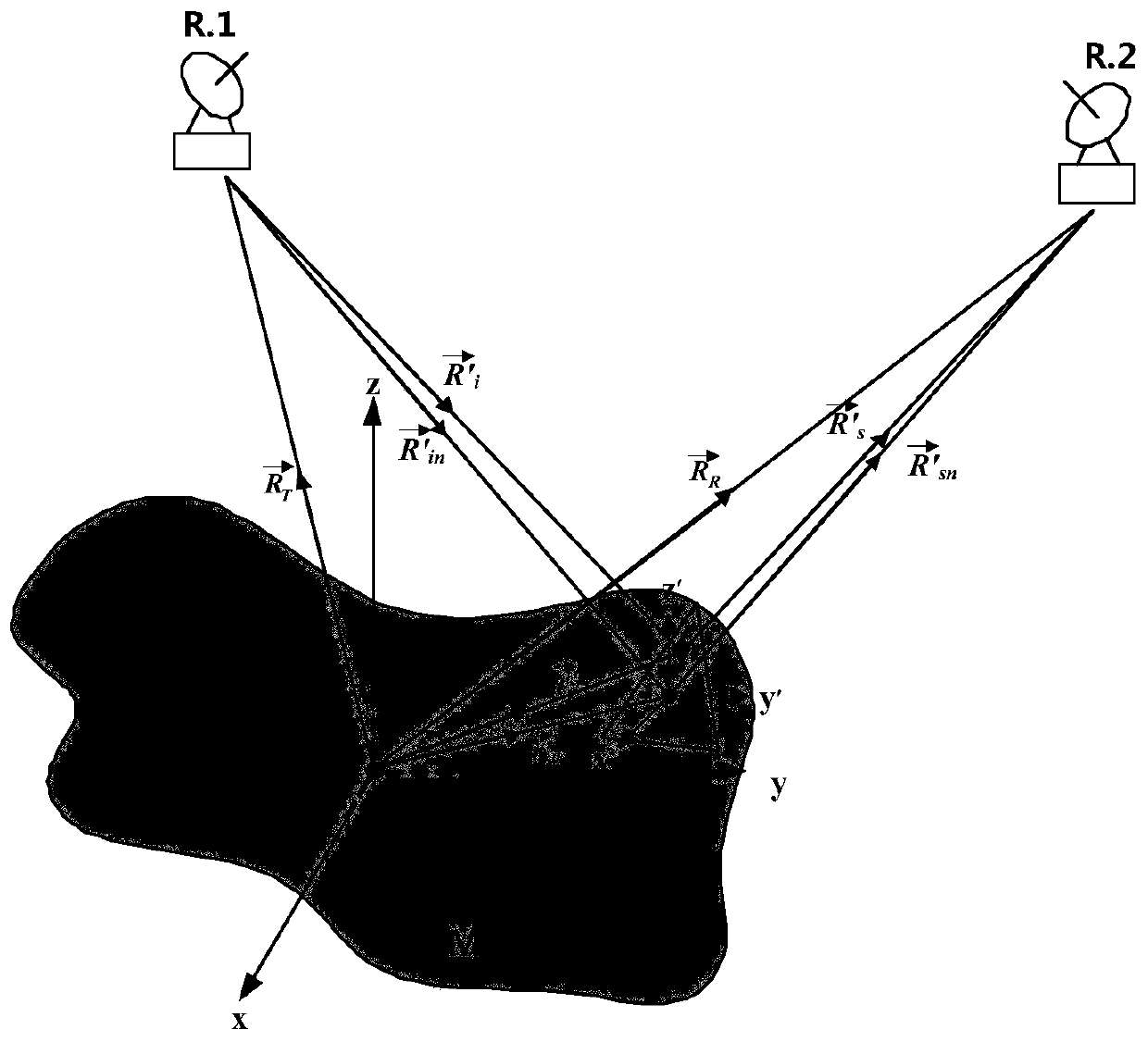
ActiveCN110441747AExact solution for RCS magnitudeWave based measurement systemsSpecial data processing applicationsPoynting vectorTotal field
The invention relates to a Poynting vector-based target near-field like-polarized scattering characteristic calibration method. The Poynting vector-based target near-field like-polarized scattering characteristic calibration method comprises the steps of S1, acquiring scattering total field characteristic of a metal ball under different distances by simulation calculation and by a MoM method; S2,acquiring incident field characteristic under different distances by simulation calculation and by the MoM method in the absence of metal ball; S3, acquiring characteristic of an emission field of themetal ball changing with the distances; S4, acquiring near-field scattering energy and incident field energy of the metal ball under different distances; S5, calibrating characteristic of near-fieldscattering RCS of the metal ball changing with the distances; and S6, introducing a large-number fitting method to obtain a near-field scattering RCS fitting formula of the metal ball under differentdistances. By accurate moment method and a Poynting vector theory, the near-field scattering characteristic of the metal ball target with different distance under planar wave excitation is acquired, and a foundation is provided for subsequent calibration of different detectors on target scattering RCS.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
Near-field electromagnetic scattering simulation method for super-electric large-size scale target
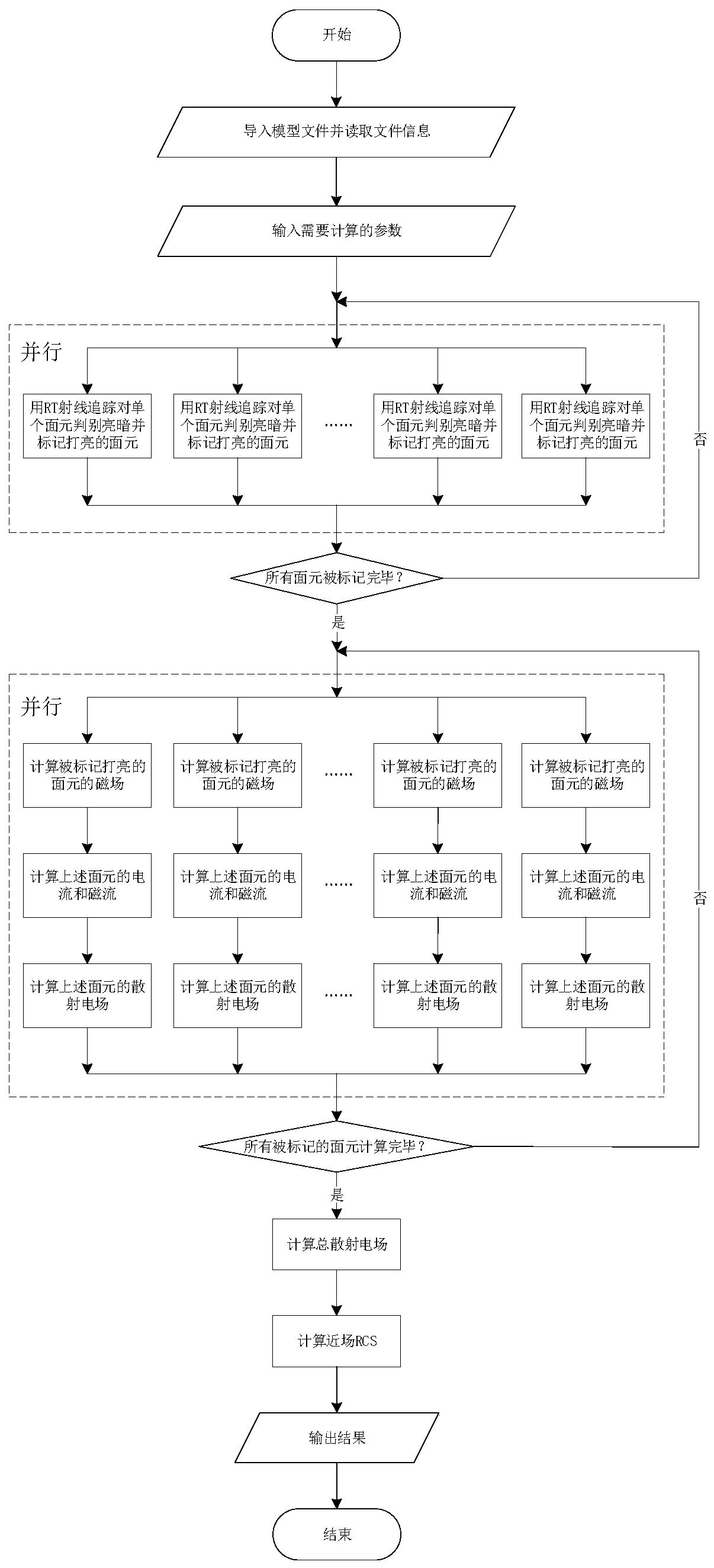
ActiveCN110705058AAdapt to actual engineering scenariosQuick solveDesign optimisation/simulation3D modellingMagnetic currentEngineering
The invention discloses a near-field electromagnetic scattering simulation method for a super-electric large-size target. The near-field electromagnetic scattering simulation method comprises the following steps: importing a model file in an STL format, and reading related information of each triangular surface element forming a radar target; inputting parameters needing to be calculated; judgingwhether the surface elements are illuminated by incident waves or not, and marking the illuminated surface elements; calculating the surface current and the magnetic current of each triangular surfaceelement marked to be illuminated: solving a scattering field caused by each triangular surface element marked to be illuminated, solving all scattering fields Esn of the triangular surface elements marked to be illuminated, and adding all the scattering fields Esn according to a vector superposition principle to obtain a total scattering field; according to the following formula, obtaining an RCSvalue sigma0 of the radar target under the near-field situation, and outputting the result. The near-field electromagnetic scattering simulation method fills up the blank in the field of target near-field RCS simulation algorithms, and particularly, electromagnetic simulation processing modes of different surface elements under the near-field scattering condition are more suitable for actual engineering scenes.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
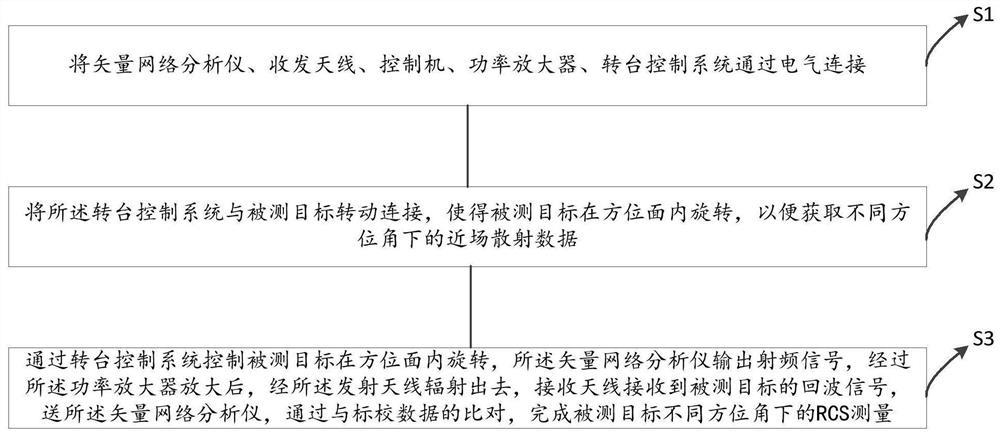
RCS measurement system and method
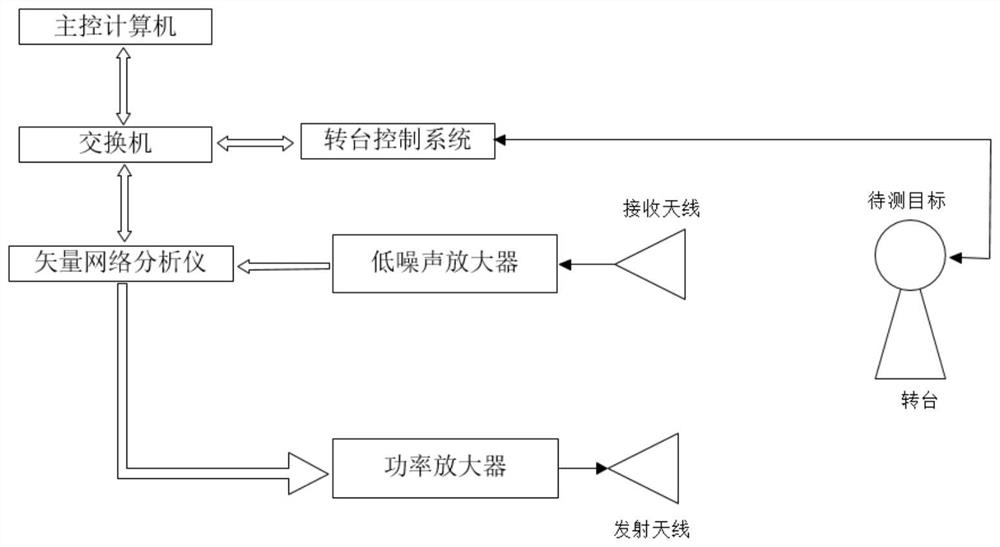
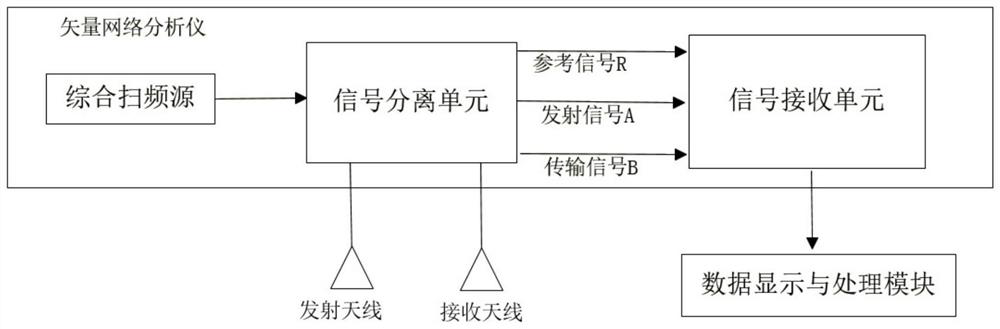
PendingCN113156388AWide measurement rangeLarge measurement field of viewWave based measurement systemsEcho signalNear field scattering
The invention discloses an RCS measurement system and method. The system comprises a vector network analyzer, a transceiving antenna, a control machine, a power amplifier and a rotary table control system which are electrically connected. The vector network analyzer is used for transmitting and receiving radio frequency signals; the control machine controls the vector network analyzer through an LAN (Local Area Network) bus; the turntable control system is used for controlling a to-be-measured target to rotate in an azimuth plane so as to acquire near-field scattering data under different azimuth angles; and a to-be-measured target is controlled by the turntable control system to rotate in an azimuth plane, the vector network analyzer outputs a radio frequency signal, the radio frequency signal is amplified by the power amplifier and then radiated by the transmitting antenna, the receiving antenna receives an echo signal of the to-be-measured target, the echo signal is sent to the vector network analyzer and compared with calibration data, and RCS measurement of the to-be-measured target under different azimuth angles is completed. The measurement range is wide, the measurement field of view is large, the RCS scattering matrix and target broadband multi-dimensional imaging characteristics can be measured, and electromagnetic scattering characteristic data can be visually obtained.
Owner:佛山蓝谱达科技有限公司
Flat top effect estimation method for near-field radar scattering cross section of rectangular flat plate
ActiveCN102062857BAvoid blind spotsThe conclusion is accurateWave based measurement systemsGeometric relationsScattering cross-section
The invention provides a flat top effect estimation method for a near-field radar scattering cross section of a rectangular flat plate. A critical state is reached when the included angle between a connecting line from a radiation source to one end point of the rectangular flat plate and the rectangular flat plate is 90 degrees, and the included angle between the connecting line from the radiation source to the end point of the rectangular flat plate and an R is a critical incident angle Theta, wherein the critical incident angle Theta is equal to arcsin (D / 2R), D is the length of the flat plate and R is the vertical distance from the radiation source to the flat plate, and the width M of the flat top is quantificationally estimated to be twice the corresponding critical incident angle Theta according to a geometric relationship. The invention provides a simple method for estimating the width of the flat top of the near-field RCS (Radar Cross Section), the width of flat top of the near-field RCS is quantificatioinally estimated from the point of the geometric relationship, the blind spot of the field is solved, and the obtained conclusion is more accurate. Moreover, by virtue of the method, a favorable ground is provided for analyzing the near-field scattering flat top phenomenon of the flat plate and a building thereof, and the method is good for the prediction and the analysis on the near-field RCS of various targets with a similar flat plate structure.
Owner:CHINA SHIP DEV & DESIGN CENT
Measurement method of particle size distribution of particle system
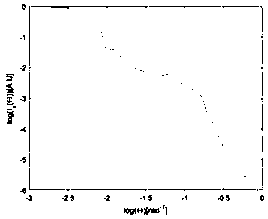
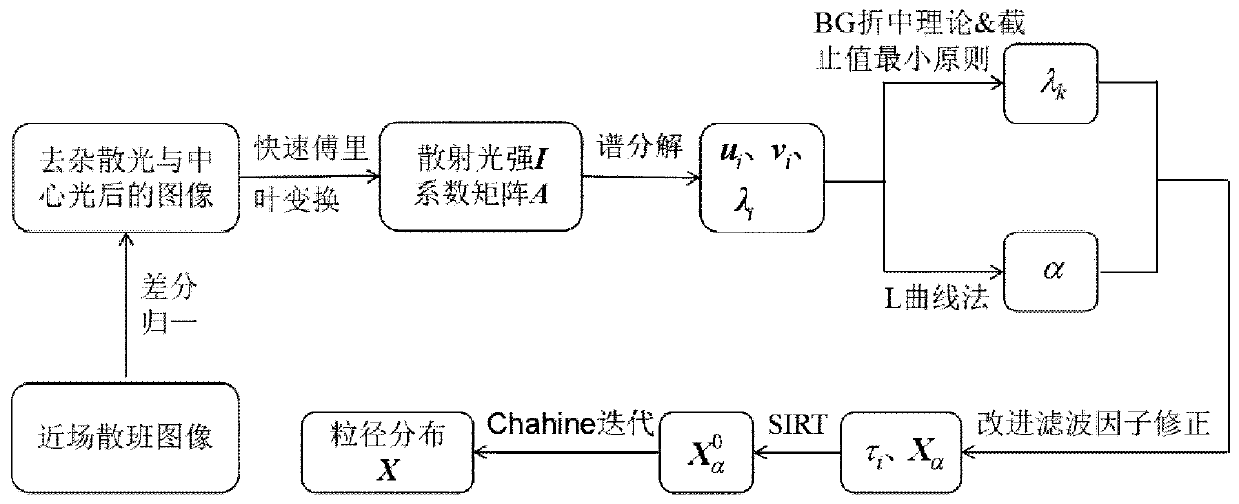
InactiveCN109856019AAvoid interferenceReduced requirements for cleanliness of the measurement environmentParticle size analysisComputational physicsDiscretization
The invention discloses a measurement method of particle size distribution of a particle system. The measurement method comprises following steps of establishing an integral equation relation betweenscattered light intensity distribution and particle size of a particle swarm by using a near-field scattering technique and performing discretization; constructing a function e, and determining a cutoff value of a best singular value by minimizing the function e; selecting a regularization parameter alpha by using an L curve method, and constructing a filter factor by combining the cutoff value ofthe best singular value, so as to obtain an approximate solution form of a particle size distribution column vector; and performing iteration calculation by using a Chahine iteration algorithm, so asto obtain a convergent solution to realize measurement of particle size distribution of the particle swarm. The introduced improved filter factor exerts model effective information greatly, and particle size distribution of particle systems with close particle size peak interval can be measured highly accurately and stably.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Near-field scattering characteristic modeling method, electronic equipment and storage medium
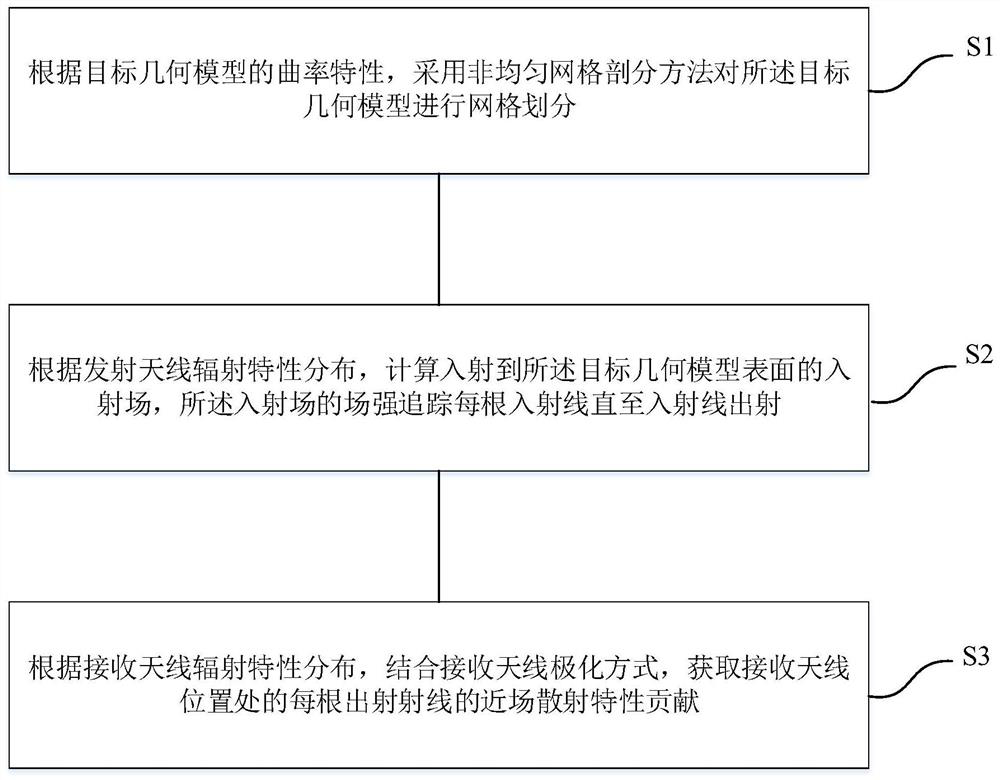
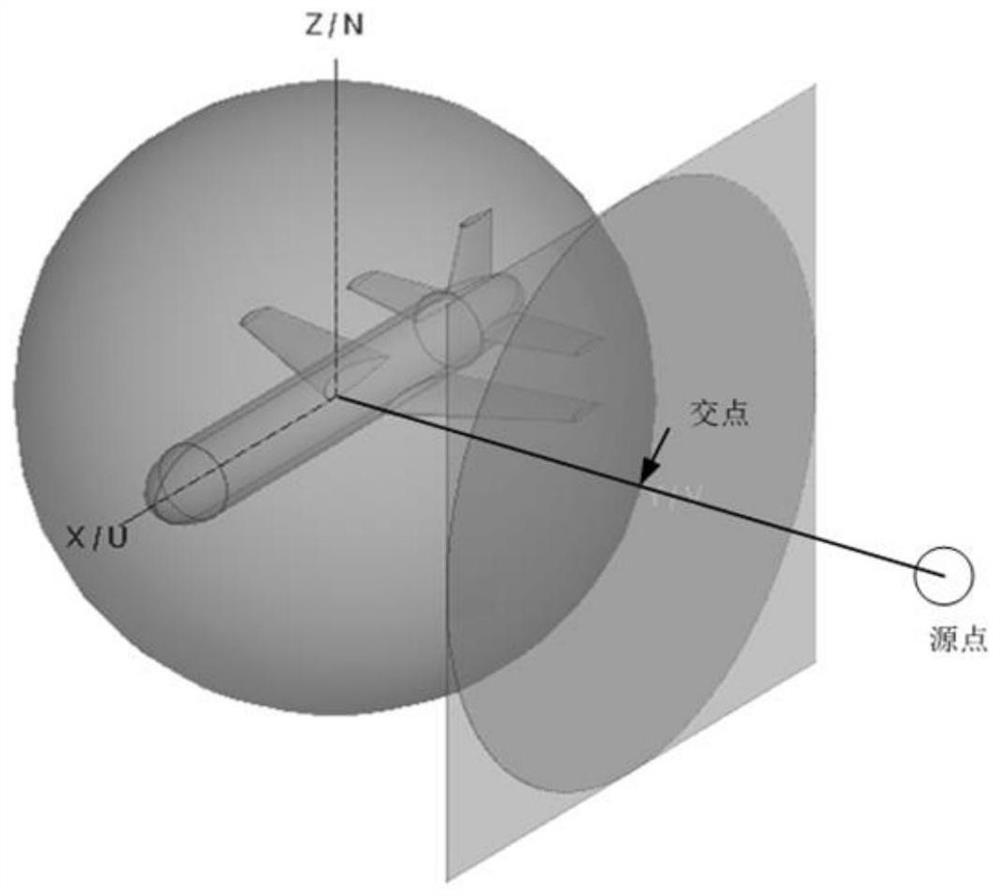
ActiveCN112069713APerfect modelingAccurate and efficient simulation technology meansDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAntenna polarizationGeometric modeling
The invention discloses a near-field scattering characteristic modeling method, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of carrying out the mesh generation of a target geometric model through employing a non-uniform mesh generation method according to the curvature characteristics of the target geometric model; and calculating an incident field incident to the surface of the target geometric model according to the radiation characteristic distribution of the transmitting antenna, and tracking each incident ray by the field intensity of the incident field untilthe incident rays are emitted; and acquiring the near-field scattering characteristic contribution of each emergent ray at the position of the receiving antenna according to the radiation characteristic distribution of the receiving antenna in combination with the polarization mode of the receiving antenna. According to the method, the incident wave polarization component and the receiving characteristics of the receiving antenna are considered, the obtained near-field characteristics include the radial component, near-field information is perfected, and the method is an accurate and efficient simulation technical means.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
Method of converting near field scattering function to missile target encounter echoes based on local scattering source inversion
ActiveCN108061883AImprove application rateQuick calculationWave based measurement systemsTarget surfaceScattering function
The invention relates to a method of converting a near field scattering function to missile target encounter echoes based on local scattering source inversion. For a target with a known geometric shape, target dynamic echoes under irradiation of a detection antenna are generated. The method comprises steps: S1, an enveloping surface in an elliptical cylindrical shape is built according to the length direction of the target, and the target is totally enveloped inside; S2, based on a cross dipole, distribution data of the near field scattering function on the enveloping surface are acquired; S3,during a missile target encounter process, weighted calculation of a detection antenna pattern is carried out on the near field scattering function; S4, based on the weighted near field scattering function, a local scattering source of the target surface is calculated by inversion; and S5, based on the inverted local scattering source, the dynamic echoes of the target are generated. Fast calculation on the missile target encounter echoes under different observation antennas can be realized, the target near-field scattering function and the observation antenna are subjected to decorrelation, and the application rate of characteristic data is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
Method for acquiring target scattering data in circular scanning mode
InactiveCN108732548AAccurately determineAvoid the deconvolution problemWave based measurement systemsComputer scienceDeconvolution
The invention relates to a method for acquiring target scattering data in a circular scanning mode. The method belongs to the technical field of scattering measurement. The specific implementation manner of the method comprises the steps of: acquiring near-field frequency domain scattering data of a target in the circular scanning mode; performing inverse Fourier transform on the near-field frequency domain scattering data to determine near-field distance domain scattering data of the target; determining far-field distance domain scattering data of the target according to the near-field distance domain scattering data; and determining far-field frequency domain scattering data of the target according to the far-field distance domain scattering data of the target. The method can avoid the deconvolution problem of transforming from far-field scattering to near-field scattering, calculates a near-field scattering response reversely by means of far-field scattering, and expands the application range of the scattering test.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL FEATURES
An Accurate Method of Near-field Echo Acquisition
ActiveCN103675781BSolve the distance problemAccurate near-field echo dataWave based measurement systemsEcho intensityPolarization scattering matrix
The invention belongs to technical field of signal characteristic control and specifically relates to a method for accurately acquiring near field echo. The method comprises following steps of: a step 1, establishing a target coordinate system O-XtYtZt, an antenna coordinate system O-XaYaZa, and a scattering unit coordinate system O-XmYmZm; a step 2, acquiring a field incident on a mth scattering unit from the surface of a scattering body; a step 3, acquiring scattered fields of the scattering units; a step 4, acquiring a scattered field of the mth scattering unit received by a receiving antenna; a step 5, superposing the scattered fields of each scattering unit received by the receiving antenna in order to acquire a total scattered field; and a step 6, calculating the total scattered field so as to acquire near field echo intensity and power characteristics. The method establishes a complex target near field scattering model with a PO+PTD+GP method and introduces a concept of near field polarization scattering matrix so as to express scattering properties with different mechanisms by using a unified expression, thereby simplifying a calculating process.
Owner:中国航天科工集团第二研究院二〇七所
A device and method for measuring flow two-dimensional velocity field based on near-field scattering
ActiveCN104698219BReduce alignment requirementsIncrease concentrationFluid speed measurementCcd cameraWavelength
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
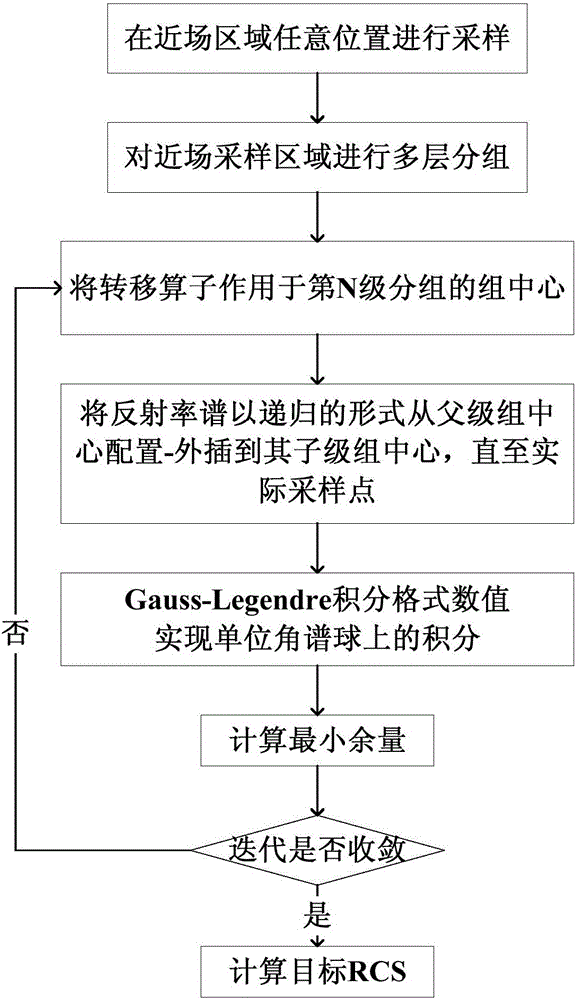
Near field and far field conversion method of multilayer grouping structure
ActiveCN106485071AReduce complexityReduce usageInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsDecompositionField tests
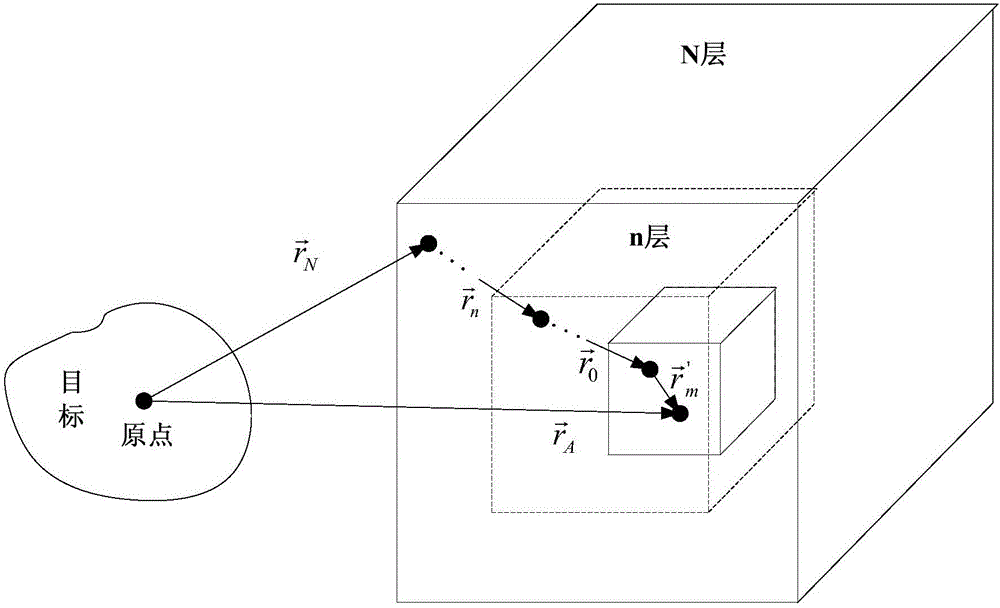
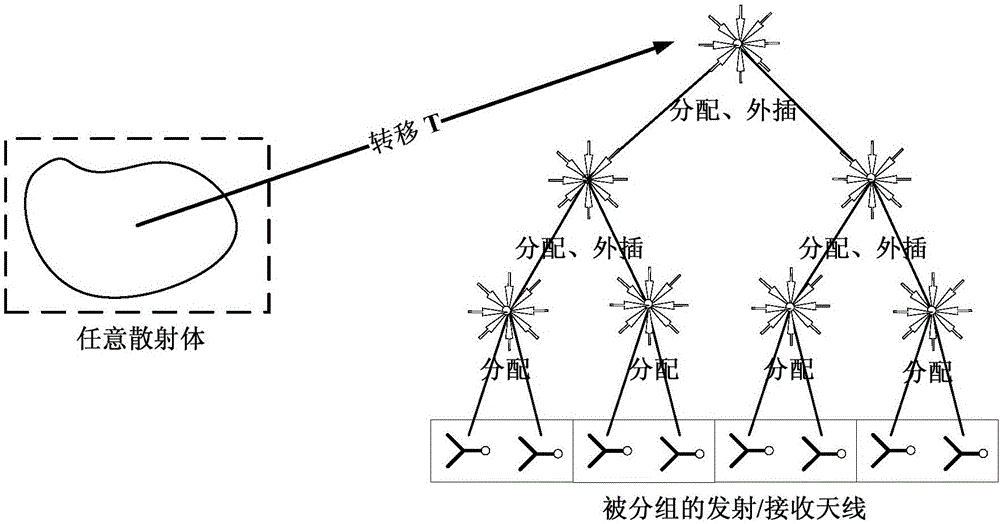
The invention relates to a near field and far field conversion method of a multilayer grouping structure. According to an addition theorem, near field scattering is decomposed by a multilayer plane wave, and a relational expression between a reflectivity spectrum and the near field scattering is obtained, wherein the relational expression can be discretized into a matrix equation. For an electrically large dimension target, the quantity of the unknown numbers of the above matrix equation is huge, a huge calculated amount and huge computer memory need to be consumed by direct solving or solving in an iterative way. Therefore, by use of the method disclosed by the invention, the addition theorem is utilized, a transfer operator is acted on the center of a high-hierarchy group, the plane wave is decomposed to the center of a next hierarchy group, and the process is carried out in a recursion way until last decomposition is acted on a sampling point. By use of the method, near field data which is on any position and is subjected to any polarization sampling can be processed, a near field test system is greatly simplified, and algorithm complexity and computer memory requirements can be effectively lowered and reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
RCS measurement method based on three-dimensional sparse imaging
InactiveCN112230221AWide applicabilityImprove image qualityRadio wave reradiation/reflection3D modellingRadiologySide lobe
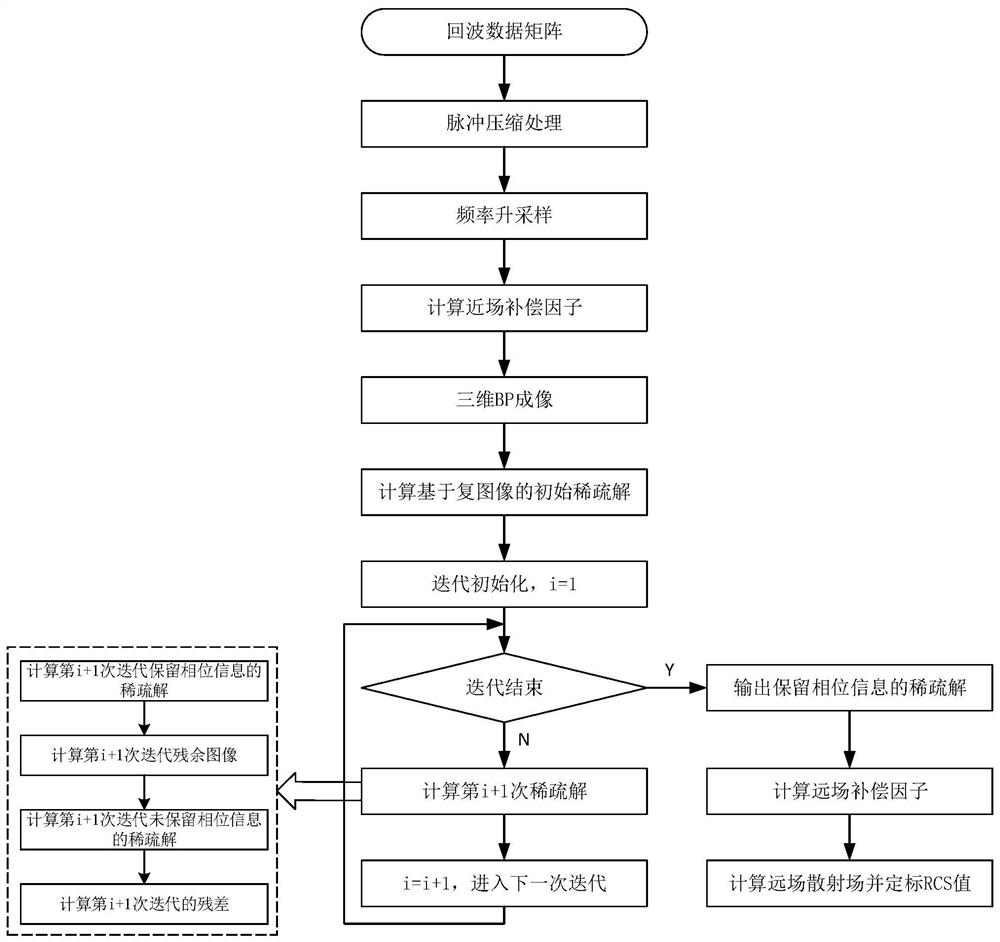
The invention discloses an RCS measurement method based on three-dimensional sparse imaging. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an echo data matrix of a measured target area by usingan array three-dimensional SAR; completing preliminary signal processing by using pulse compression and frequency up-sampling technologies; utilizing a three-dimensional BP algorithm to obtain a three-dimensional complex image of target near-field scattering distribution; adopting a novel sparse imaging method based on a complex image to suppress target sidelobes and clutters; and finally obtaining an RCS directional diagram of the measured target by using a compensation factor and a calibration technology. Compared with a classic RCS measurement method based on images, the method is not influenced by sidelobes and clutters, can extract three-dimensional scattering characteristic distribution of the target, and has the advantages of high measurement precision, wide applicability and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Rapid simulation method for target near-field radar echoes
ActiveCN111767640AImprove reuseAvoid ad-hoc calculationsWave based measurement systemsDesign optimisation/simulationRadarComputational physics
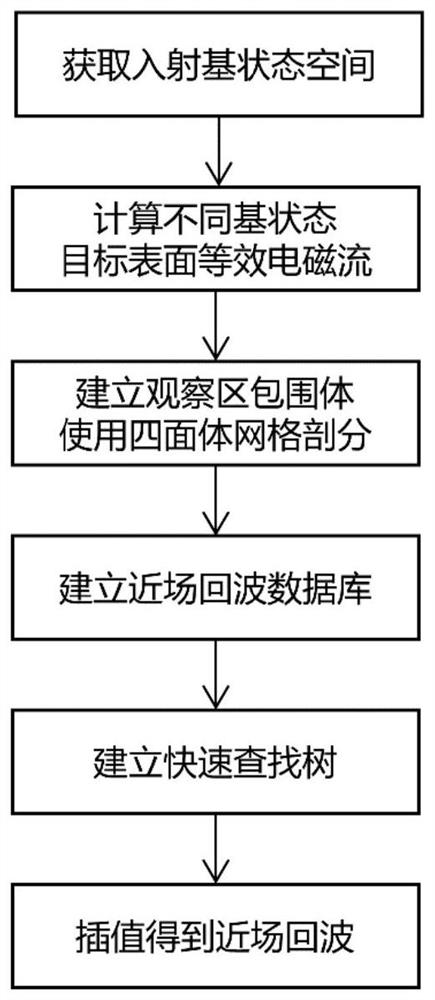
The invention discloses a rapid simulation method for target near-field radar echoes. Rapid calculation of the near-field echoes in different states is achieved. A near-field scattering database can be rapidly obtained by utilizing a multilayer matrix decomposition or multilayer rapid multipole technology; a quick search tree is established, a database can be quickly retrieved, and near-field echoes of any field point in an observation area can be accurately obtained.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com