Submarine cable protection based ship external destruction risk assessment method
A technology for submarine cable and risk assessment, applied in the direction of instruments, data processing applications, resources, etc., can solve the problems of inability to form standardized qualitative risk identification, grading standards, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
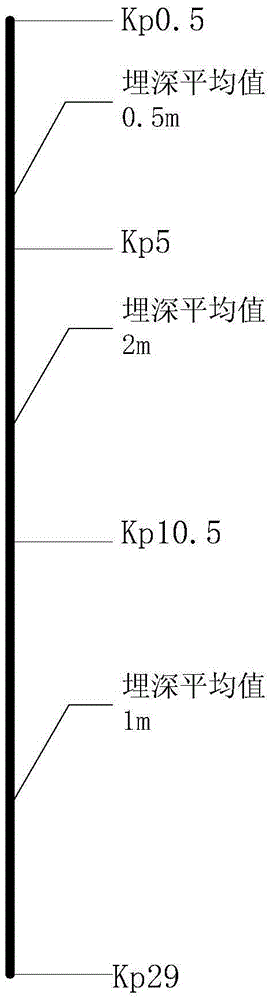
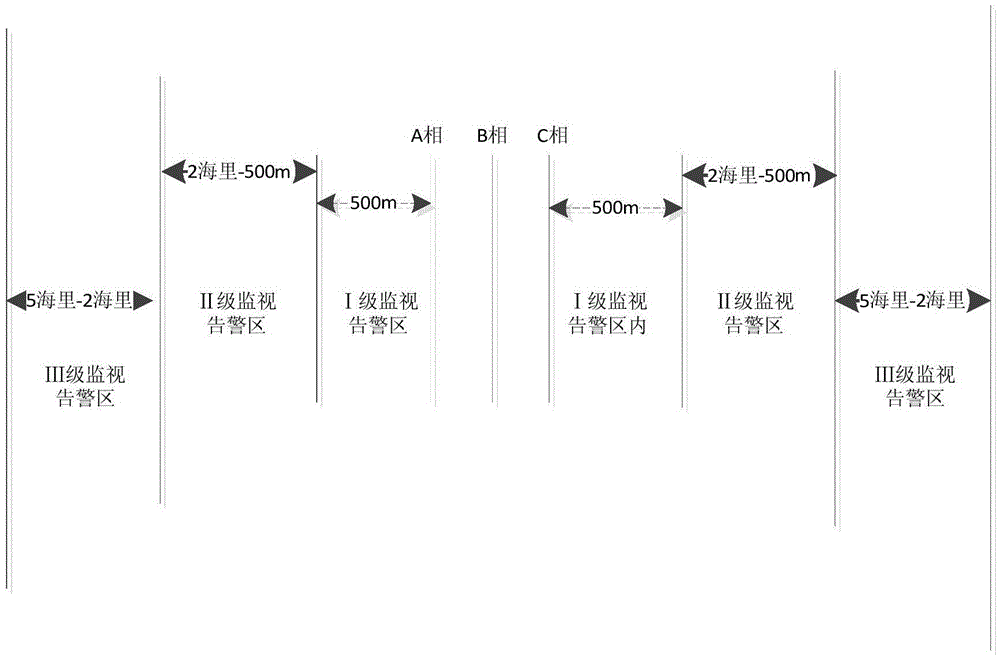
[0135] Example 1: At 22:17 on April 02, 2013, a 498-ton cargo ship "Xin Hisense 888" registered in Fangchenggang was directly above phase B of the 500kV submarine cable in the protection area of the 500kV Fugang Line submarine cable, and the speed of the ship dropped to 0.5 knots. Suspected of breaking down, it is 8,000 meters away from Nanling Terminal Station, and the ship is equipped with an anchor of 1.5 tons.
[0136] Use the risk assessment decision-making model to analyze Example 1:
[0137]
[0138]
[0139] Through analysis, it can be concluded that the accident ship "New Hisense 888" is located directly above phase B of the submarine cable. Suspected anchoring is at a high risk level relative to submarine cable safety, and emergency response work should be carried out immediately according to the disposal measures corresponding to the risk level.
example 2
[0140] Example 2: At 09:46 on April 10, 2012, a Vietnamese 961-ton cargo ship "HOANGPHUONG16" (Huang Fang 16) broke down in the protection area of the 500kV Fugang Line submarine cable. Ling terminal station is about 14.9 kilometers away, and the ship is equipped with an anchor of 1 ton.
[0141] Use the risk assessment decision-making model to analyze Example 2:
[0142]
[0143]
[0144] Through the analysis, it can be concluded that the accident ship "HOANGPHUONG16" (Huang Fang 16) is located in the Class I warning area, because the average buried depth of the submarine cable routing area is 2m, the mechanical protection is in good condition, and the ship's anchor is light, the safety index value Smaller, because the ship's speed is continuously lower than 0.5 knots, it can be determined that the ship is suspected of breaking down, and it is at a medium risk level relative to the safety of submarine cables.
example 3
[0145] Example 3: At 18:35 on July 16, 2011, the Guangzhou-registered 498-ton cargo ship "Shitai 138" broke down in the protection area of the 500kV Fugang Line Submarine Cable. About 3.5 kilometers, the ship is equipped with an anchor of 1 ton.
[0146] Use the risk assessment decision-making model to analyze Example 3:
[0147]
[0148] Through the analysis, it can be concluded that the accident ship "Shitai 138" is located in the second-level warning area. Since the average buried depth of the submarine cable routing area is 0.5m, the ship's anchoring poses a greater threat to the buried depth of the submarine cable in this area, and the safety index The value is relatively large, but because the accident ship is far away from the submarine cable, the probability index of anchor damage to the submarine cable is low, and the ship’s speed is continuously lower than 0.5 knots, it can be determined that the ship is suspected of breaking down. risk level.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com