Grid-connected microgrid asymmetrical fault region detection device and diagnosis method
A technology of fault area and detection device, which is applied in the field of power grid system, can solve problems such as failure diagnosis of micro grid main network or contact area, and achieve the effect of meeting protection selectivity requirements, ensuring continuous power supply, and small power failure range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] Such as figure 1 The illustrated embodiment is a detection device for an asymmetrical fault area of a networked microgrid. The microgrid 1 is connected to the main grid 332 through the contact area 2, and the contact area includes the first circuit breakers CB connected in series. A , contact transformer 21 and the second circuit breaker CB B The fault detection device includes a first impedance measurement element 3 connected to the main grid side bus data, a second impedance measurement element 4 connected to the micro grid side bus data, an access switch 5 installed at the micro grid common connection point, and The negative-sequence voltage starting element 7 connected to the microgrid side bus bar data; also includes a microprocessor 6, an alarm 9 and a display 10, and the microprocessor is connected with the alarm, the display, the first impedance measuring element, and the second impedance measuring element respectively It is electrically connected with the ne...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Embodiment 2 includes all structures and steps of Embodiment 1, such as figure 1 As shown, embodiment 2 also includes a memory 8 and a voltage transformer 11, the negative sequence voltage starting element is electrically connected to the microgrid side bus through the voltage transformer, and both the memory and the voltage transformer are electrically connected to the microprocessor.
[0082] Step 100 in said embodiment 1 is replaced by the following steps:
[0083] (8-1) The microprocessor reads a certain phase voltage signal u(t) detected by the voltage transformer, sets the initial value of j to 1, and sets the initial value of i to 1; the fault threshold E is set in the memory ;
[0084] (8-2) Calculate the local maximum value of u(t) and obtain the upper envelope u through cubic spline interpolation up (t);
[0085] (8-3) Calculate the local minimum of the signal u(t) and obtain the lower envelope u through cubic spline interpolation low (t);
[0086] (8-4) ...
Embodiment 3
[0096] Embodiment 3 includes all structures and steps in Embodiment 1, and Embodiment 3 adopts the following steps to replace step 200 of Embodiment 1:
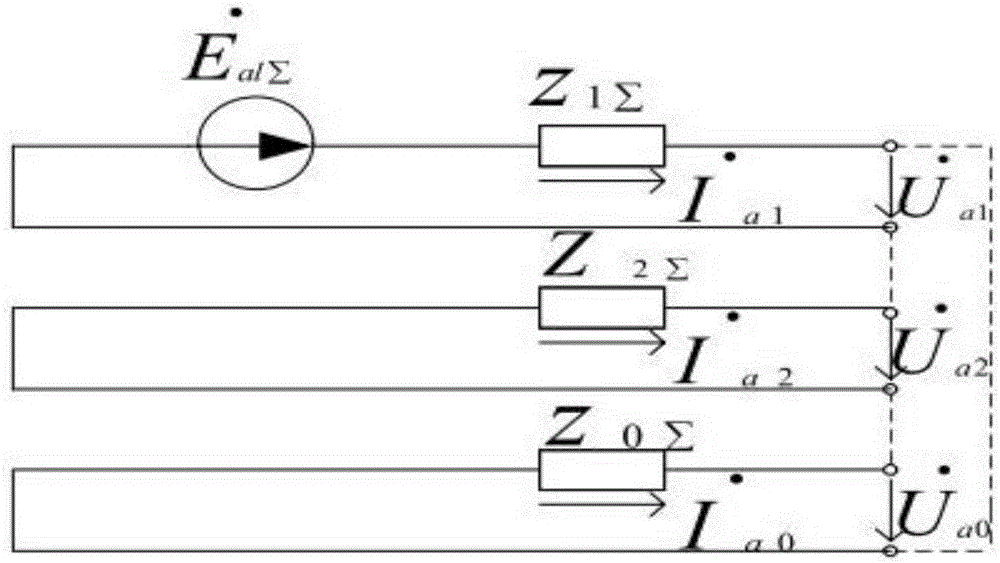
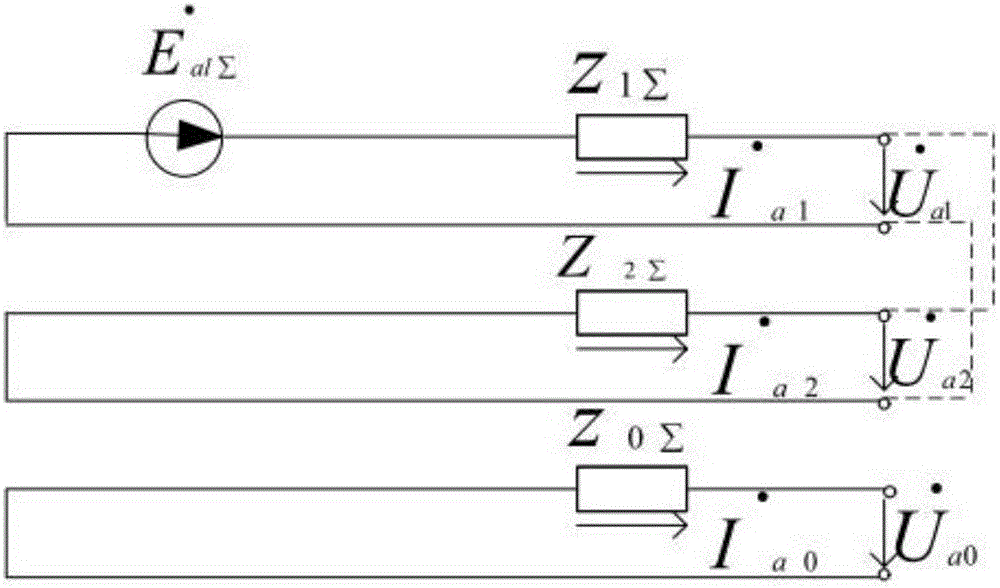
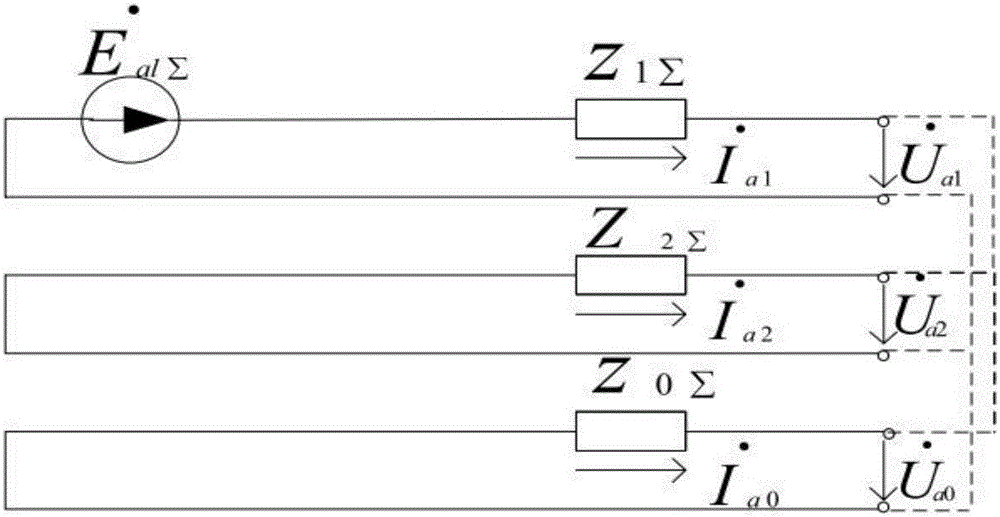
[0097] Step 210, calculate the real and imaginary parts of the impedance
[0098] The microprocessor reads the impedance value Z detected by the first impedance measuring element I and the impedance value Z detected by the second impedance element II ; set Z I The real part of Re(Z I ),Z II The imaginary part of is Im(Z I );
[0099] Step 220, using the rectangular coordinates of the impedance to judge the fault of the main network or the contact area
[0100] when and and and ,or and and and Then the microprocessor makes a judgment that there is a fault in the main network or the contact area, the display shows that there is a fault in the main network or the contact area, and the alarm sends out an alarm message; the microprocessor controls the access switch to disconnect, thereby connecting the micro ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com