Improved distributed auction Ik-SAAP algorithm for task distribution in WSAN
A task allocation and distributed technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, transmission systems, etc., can solve the problems of not considering the status of actuator nodes, the impact of network real-time performance, and the unbalanced load of actuator nodes.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0061] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
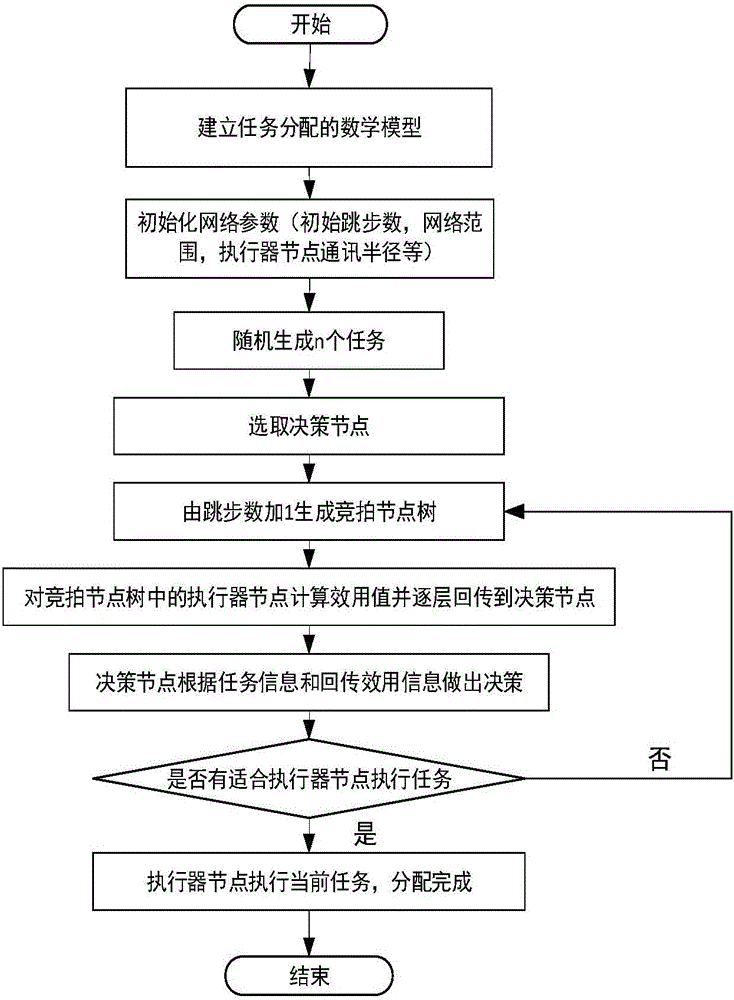
[0062] The system block diagram of the present invention is as figure 1 shown. The improved distributed bidding Ik-SAAP algorithm of task assignment in a kind of WSAN of the present invention comprises the following parts: set up the mathematical model of task assignment; Initialize network parameter; Select decision-making node; Generate bidding node tree; Calculate bidding node utility value and return ; Decision-making node decision-making; Task allocation ends, the selected executor node executes the current task.
[0063] Step 1 establishes a mathematical model of task assignment for executor collaboration;
[0064] The establishment of the task allocation mathematical model includes the following two steps:
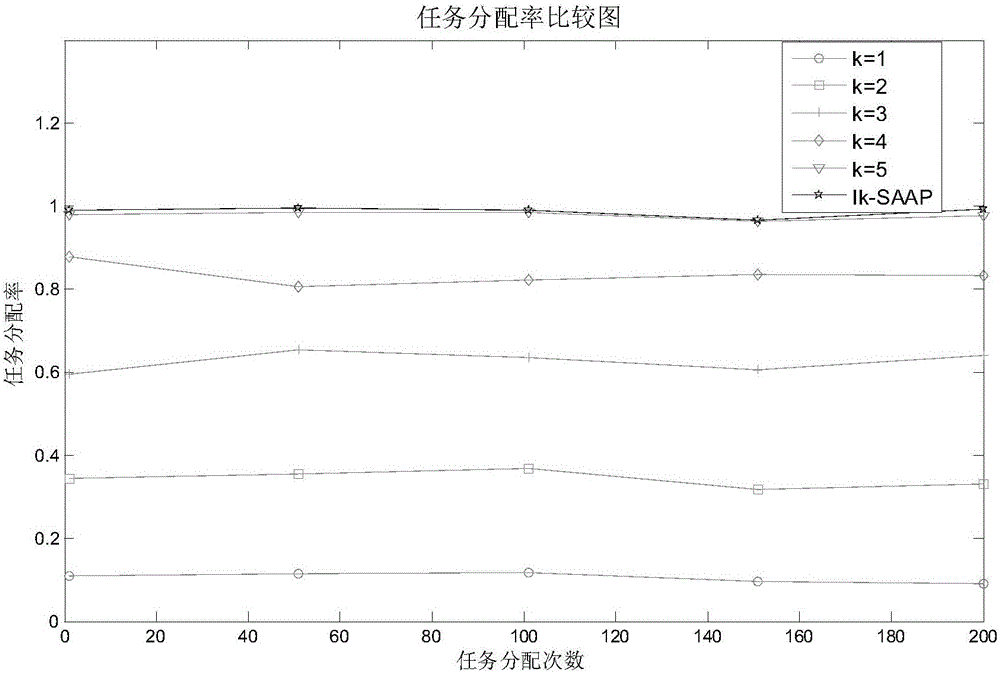
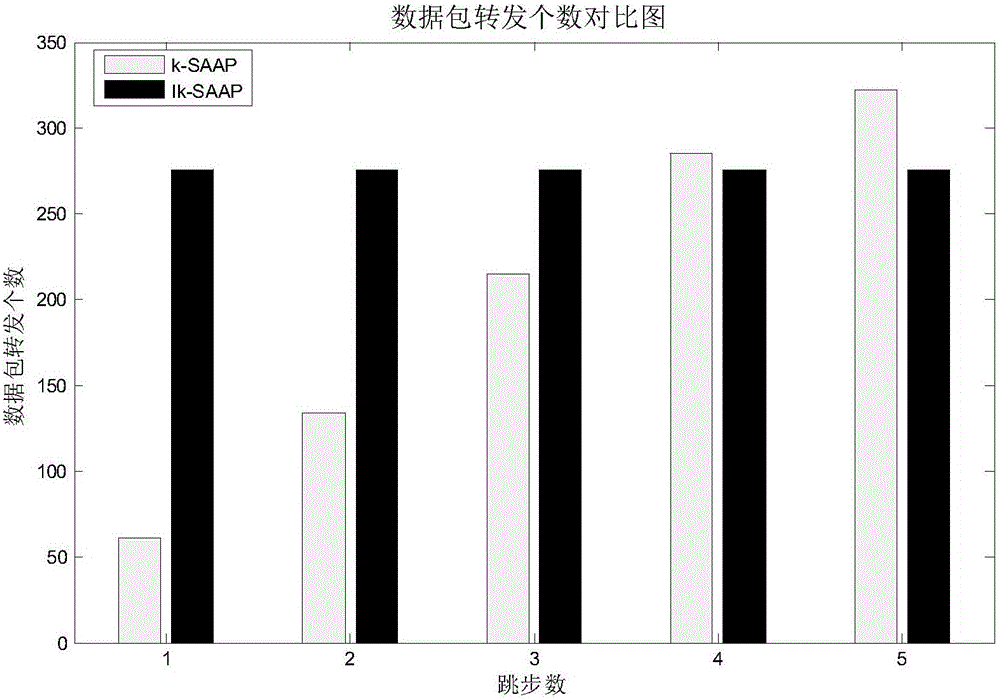
[0065] 11) Task assignment problem description: there are n in the assignment process t tasks, n a executor nodes; each task has its own duration and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com