Preparation method of medical PLLA (poly-l-lactic acid) melt-spun fibers
A poly-L-lactic acid and melt-spinning technology, which is applied in melt-spinning, medical science, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve unknown problems, melt-spun fibers do not have good biocompatibility, and no one prepares medical PLLA melt-spun fibers Scaffold cell performance and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] 1) PLLA purchased from Jinan Daigang Bioengineering Co., Ltd. has a molecular weight of 300,000 and a melting point of 176.90°C. The PLLA slices were dried at 60 °C for 24 h in a DHG-9240A electric blast drying oven to remove moisture.
[0031] 2) The PLLA melt-spun nascent fiber was prepared by extruding with a single-orifice screw extruder. The screw speed was controlled at 84.2 rad / min, the temperature of the left hot plate was 240 °C, the temperature of the right hot plate was 240 °C, and the pressure was 12.5 MPa.
[0032] 3) GKR103 winding machine was used to draw and wind the prepared melt-spun nascent fiber at a winding speed of 150 m / min.
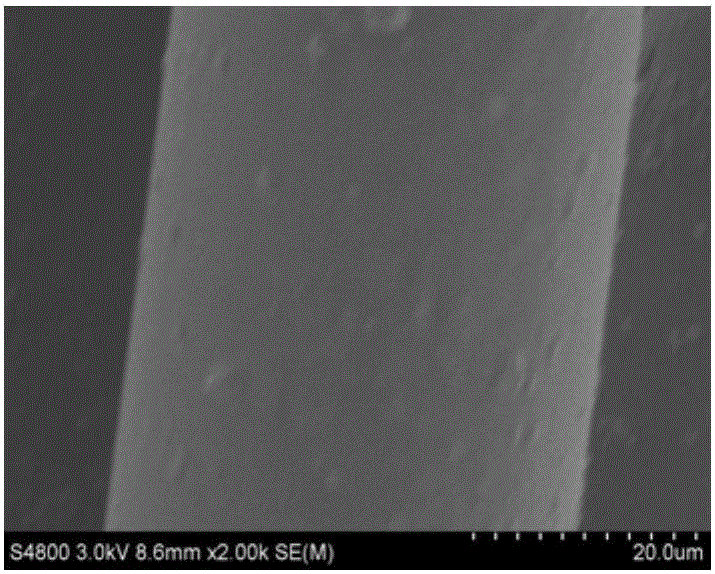
[0033] The medical PLLA melt-spun fibers with a diameter of 27.95±5.81 μm, a smooth surface, a circular cross section and a melting point of 170.69°C were obtained.
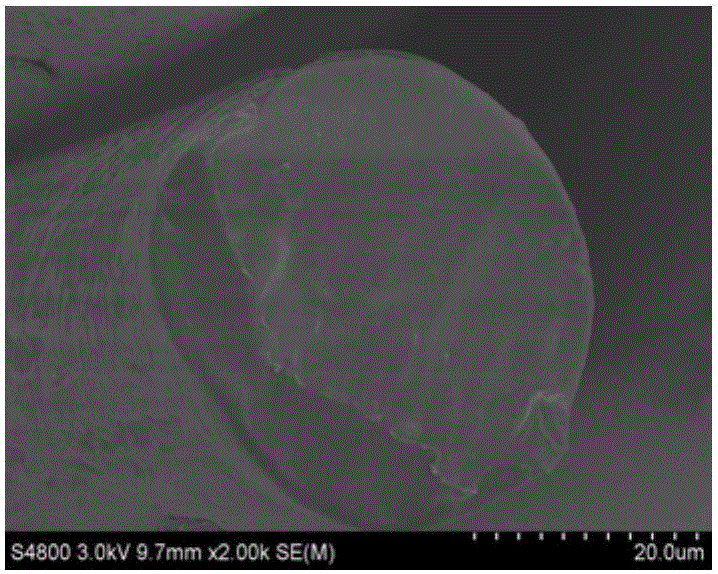
[0034] The surface and cross-sectional morphology of the medical PLLA melt-spun fiber made in this example are as follows: figure 1 , 2 As shown, the fiber ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] 1) with embodiment step 1);
[0037] 2) PLLA melt-spun nascent fibers were prepared by extruding with a 36-orifice screw extruder. The hole diameter D of the 36-orifice plate was 0.3 mm, the hole length L / hole diameter D=3, the screw speed was controlled to be 88 rad / min, and the screw temperature is 230°C.
[0038] 3) The prepared melt-spun as-spun fibers were wound by a winding machine at a winding speed of 70 m / min. The medical PLLA melt-spun fibers with a diameter of 160±30 μm, a smooth surface, a circular cross section and a melting point of 170.69°C were obtained.
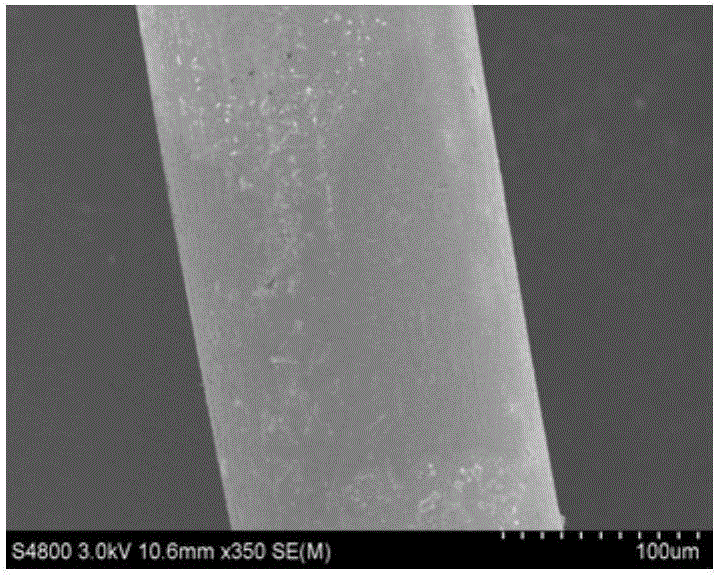
[0039] The surface and cross-sectional morphology of the medical PLLA melt-spun fiber made in this example are as follows: image 3 , 4 As shown, the fiber diameter is as Figure 7 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0041] 1) with embodiment step 1);
[0042] 2) PLLA melt-spun nascent fibers were prepared by extruding with a 24-orifice screw extruder. The hole diameter D of the 24-orifice plate was 0.3 mm, the hole length L / hole diameter D=3, the control screw speed was 88 rad / min, and the screw temperature is 230°C.
[0043] 3) The prepared melt-spun as-spun fibers were wound by a winding machine at a winding speed of 70 m / min. The medical PLLA melt-spun fibers with a diameter of 70.30±11.41 μm, a smooth surface, a circular cross section and a melting point of 170.69°C were obtained.
[0044] The surface and cross-sectional morphology of the medical PLLA melt-spun fiber made in this example are as follows: Figure 5 , 6 As shown, the fiber diameter is as Figure 7 As shown, the DSC curve is as Figure 8 shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Hole diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap