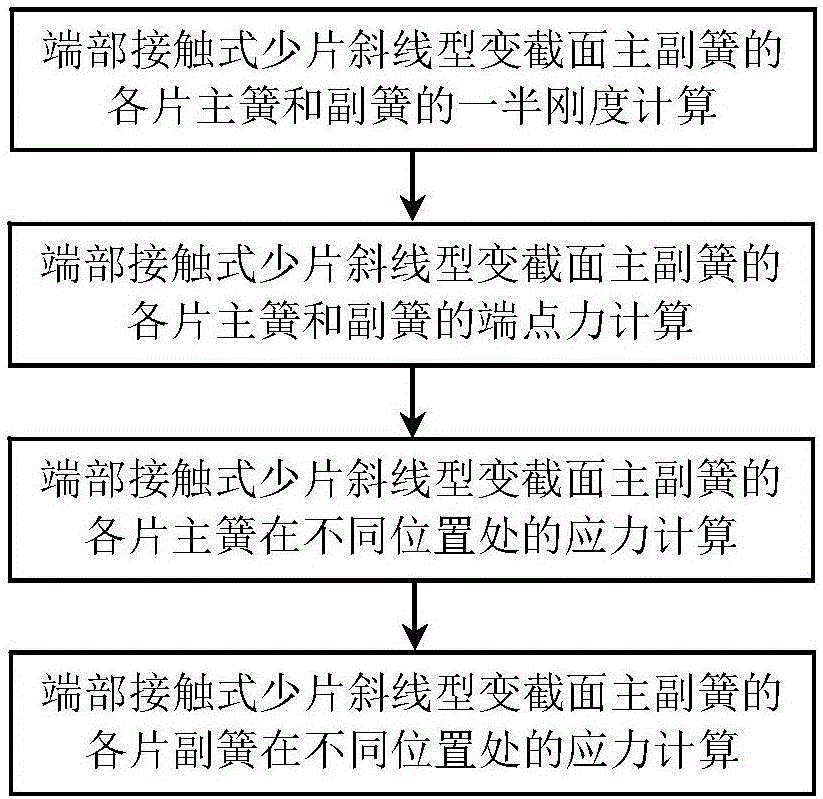
Method for calculating stress of each leaf of end part contact type few-leaf diagonal main and assistant springs
A calculation method and technology of primary and secondary springs, applied to leaf springs, calculations, springs, etc., can solve problems that are not given, stress analysis and calculation are complicated, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
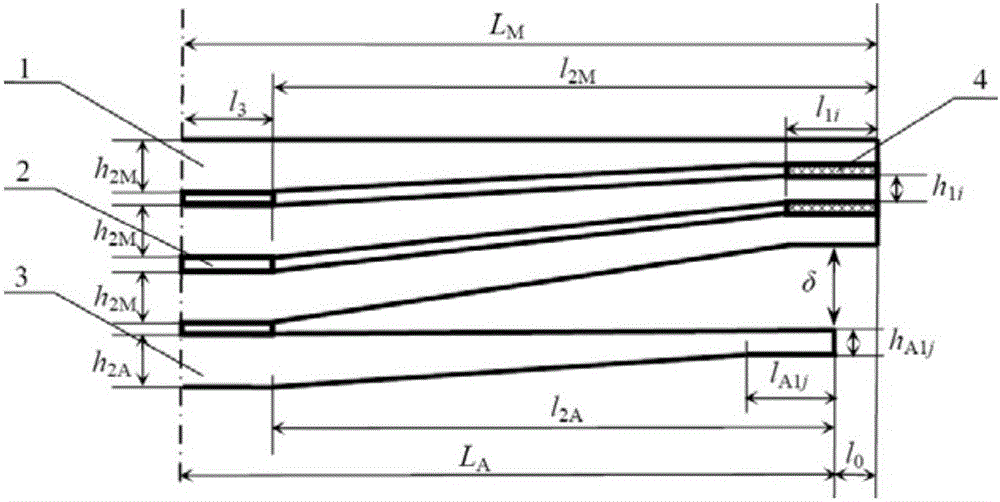
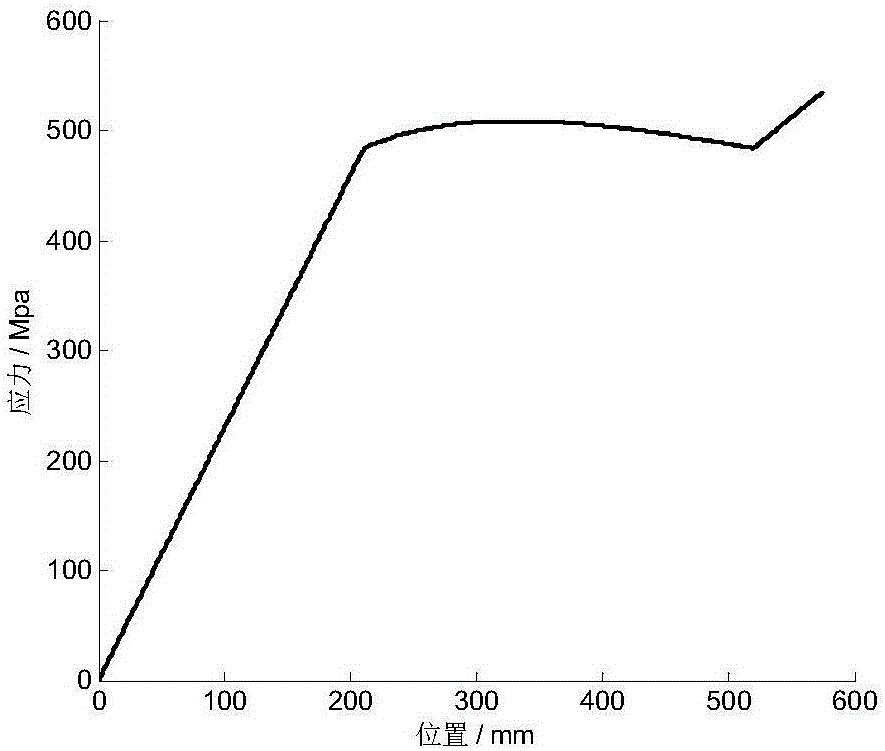
[0057] Embodiment: The number of main reeds m=2 of a certain end-contact type few-piece slanted-line variable-section leaf spring, wherein, half the length L of each main spring M =575mm, width b=60mm, elastic modulus E=200GPa, half of the installation distance l 3 =55mm, the distance l from the root of the oblique line to the end of the main spring 2M =L M -l 3 =520mm; the thickness h of the straight section at the root of each piece of main spring 2M = 11mm, the thickness h of the end straight section of the first main spring 11 =7mm, that is, the thickness ratio β of the oblique line section of the first main spring 1 =0.64; the thickness h of the straight section at the end of the second main spring 12 =6mm, that is, the thickness ratio β of the oblique line section of the second main spring 2 =0.55; the number of sheets of the secondary spring n=1, half the length L of the secondary spring A =525mm, the distance l from the root of the oblique line to the end of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com