Adaptive infrared non-uniformity calibration method based on motion state estimation
A non-uniformity correction, motion state technology, applied in radiation pyrometry, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of high algorithm complexity, inconvenient operation, poor real-time performance, etc., achieve low algorithm complexity, power-on The effect of short preparation time and large dynamic range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
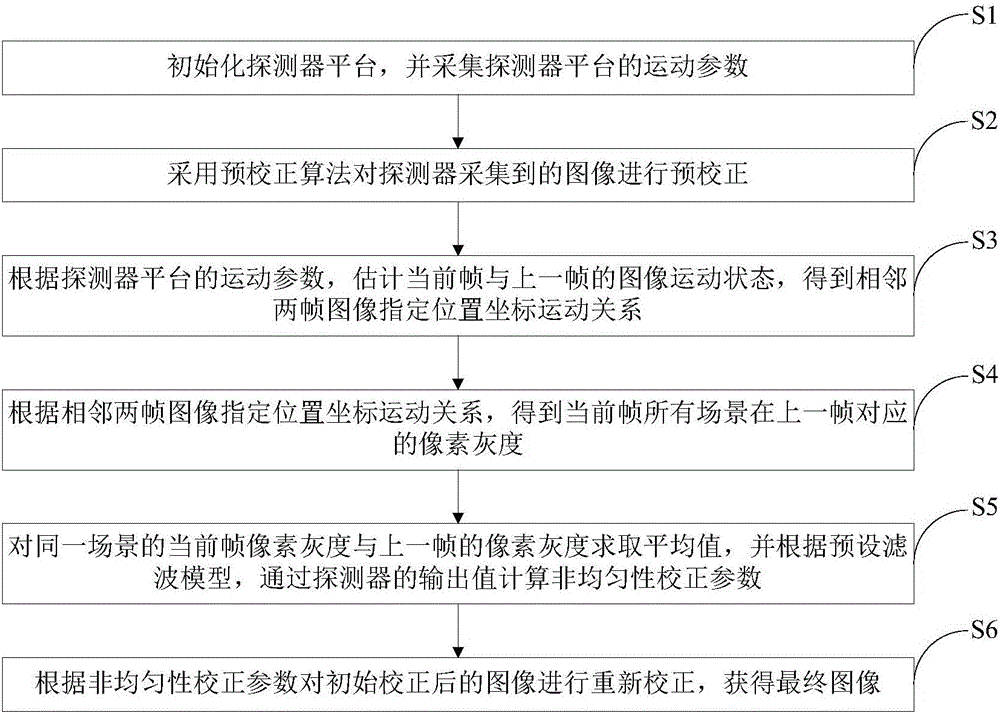
[0030] The present invention will be further elaborated below by describing a preferred specific embodiment in detail in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
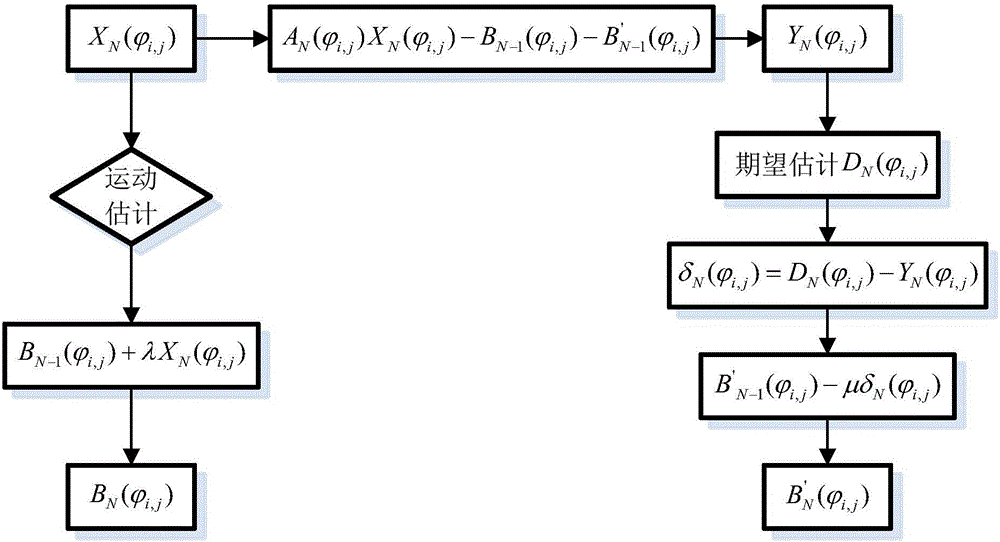
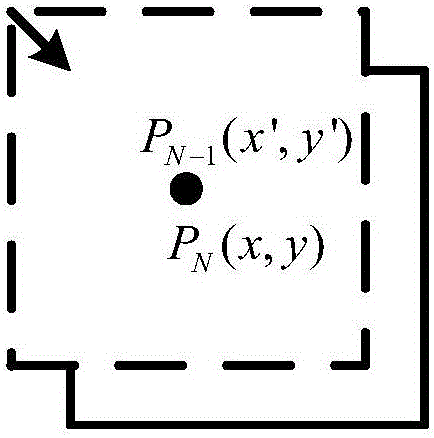
[0031] The non-uniformity of infrared detectors can be divided into intrinsic non-uniformity and additive inhomogeneity Indicates the inhomogeneity caused by the inherent characteristics of the detector element, the inherent characteristics of the optical system, etc.; Indicates the non-uniformity caused by changes in detector sensitivity, optical system aging, and changes in circuit characteristics. From the perspective of non-uniformity correction (NUC), the and Further classification, the establishment of the following mathematical model:
[0032] The first category is the spatial non-uniformity R ij , showing that under the same irradiance conditions, the gray values corresponding to different pixels of the image at the same time are not equal; the second type is the time non-uniformity R t , w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com