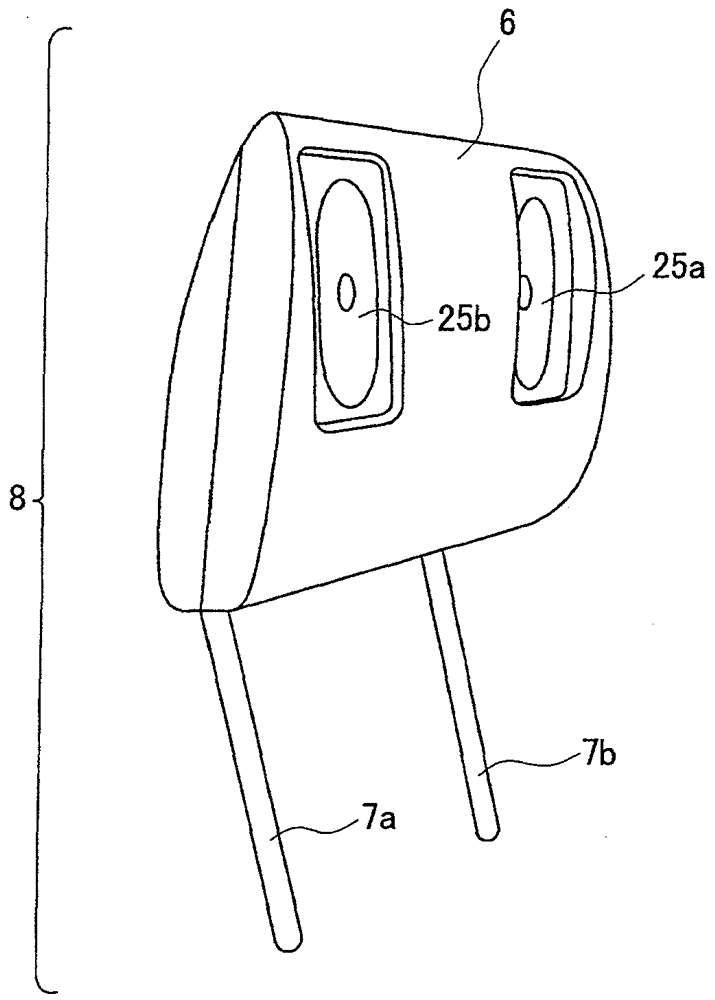
Headrest and vehicle seat
A technology for headrests and seat cushions, which is applied to vehicle seats, headrests, and vehicle parts, and can solve problems such as functional degradation, polyurethane pads that are difficult to transmit sound, and passengers who are difficult to hear speaker sounds, so as to prevent Effects of sound pressure and sound quality degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Deformed example 1
[0078] In the above embodiment, if Figure 4 As in the illustrated headrest 4A, the shape of the sound-insulating pad 16 is such that it expands in the left-right direction in the horizontal plane as it moves away from the speakers 25a and 25b. However, it is also possible to substitute Figure 7 Like the illustrated headrest 4B, the sound-insulating pad 16 is formed into a shape having a constant width W0 in the left-right direction, that is, a substantially rectangular parallelepiped shape. Also in this case, the sound emitted from the speakers 25a, 25b can be made directional by the duct structure 18 composed of the fiber backing board 15 and the sound insulation backing boards 16, 16a, 16b. In addition, the sound insulation spacer 16 can prevent the sound from the speaker 25a and the sound from the speaker 25b from interfering with each other, and as a result, the ability to separate the left and right sounds can be kept high.
Deformed example 2)
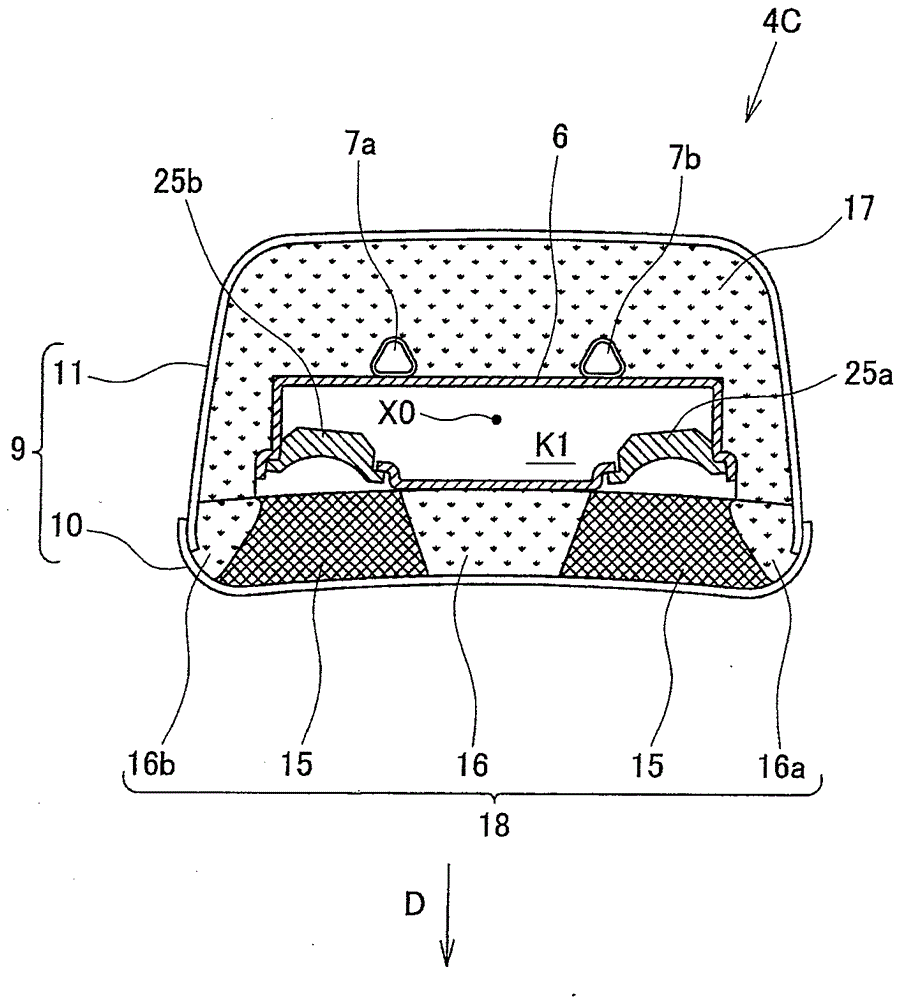
[0080] In the above embodiment, if Figure 4 As in the illustrated headrest 4A, the shape of the sound-insulating pad 16 is made into a shape that expands in the left and right directions in the horizontal plane as it moves away from the speakers 25a, 25b, or a shape such as Figure 7 As in the illustrated headrest 4B, the shape of the sound-insulating pad 16 is such that the width W0 in the left-right direction is constant. However, it is also possible to substitute Figure 8 As in the illustrated headrest 4C, the sound-insulating pad 16 has a shape that narrows toward the center portion in the horizontal plane as it goes forward indicated by the arrow D. As shown in FIG. Also in this case, the sound emitted from the speakers 25a, 25b can be made directional by the duct structure 18 composed of the fiber backing board 15 and the sound insulation backing boards 16, 16a, 16b. In addition, the sound insulation spacer 16 can prevent the sound from the speaker 25a and the sound ...
Deformed example 3)
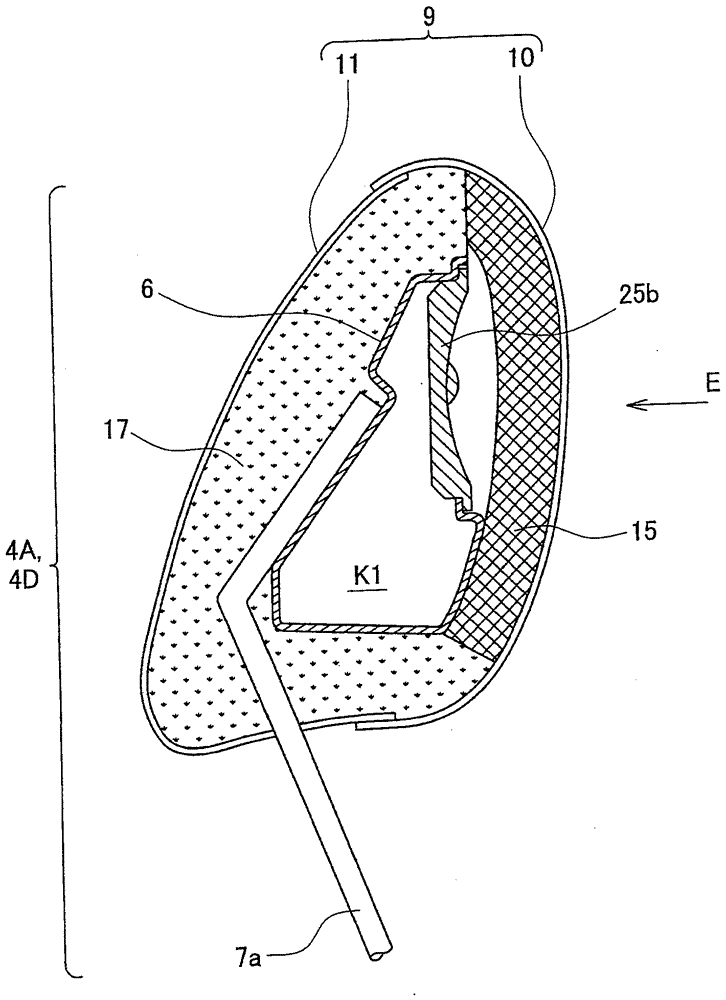
[0082] In the above embodiment, if Figure 4 , Figure 5 and Image 6 As shown, the duct structure 18 is constituted by a substantially rectangular fiber mat 15 and sound-insulating mats 16, 16a, 16b. It is also possible to use instead Figure 4 , Figure 5 and Figure 9 The pipeline structure of this modification of the structure shown. Figure 9 is according to Figure 4 The longitudinal section structure of the CC line.
[0083] The duct structure used in the headrest 4D of this modified example has a fiber backing board 15 and sound-insulating backing boards 16, 16a, 16b, which is the same as Figure 4 , Figure 5 and Image 6 The piping shown is of the same construction. This modification and Figure 4 , Figure 5 and Image 6 The difference between the shown pipe structures is that the sound insulation pad 16 sandwiched by the left and right fiber pads 15, 15 is as follows: Figure 9 It is integral with the elastomer 17 of the rear surface as shown. With t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com