Austenitic heat-resistant alloy
A technology of austenitic and heat-resistant steel, applied in the field of austenitic heat-resistant steel, can solve the problems of coarsening of grains and reduced water vapor oxidation resistance, and achieve the effect of excellent creep strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
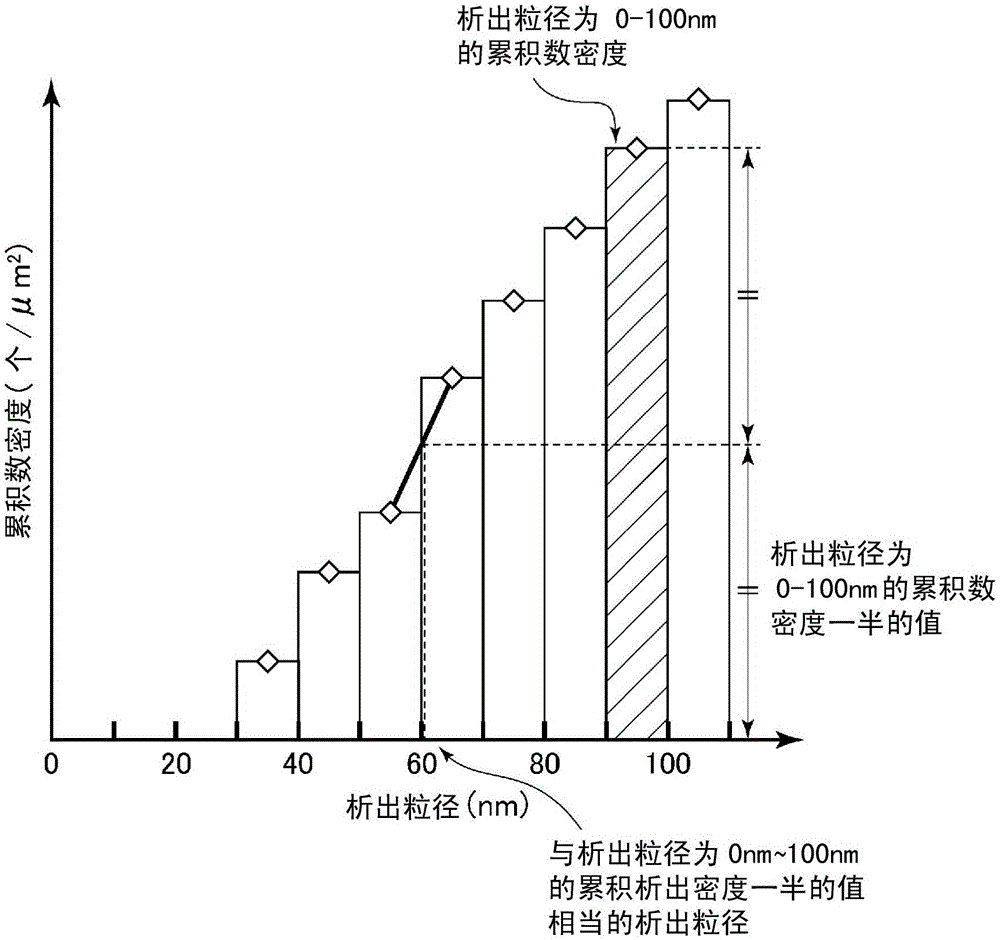
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0130] Next, the contents of the present invention will be specifically described with reference to Examples in which the effects of the present invention are exhibited and comparative examples in which the effects are not exhibited.
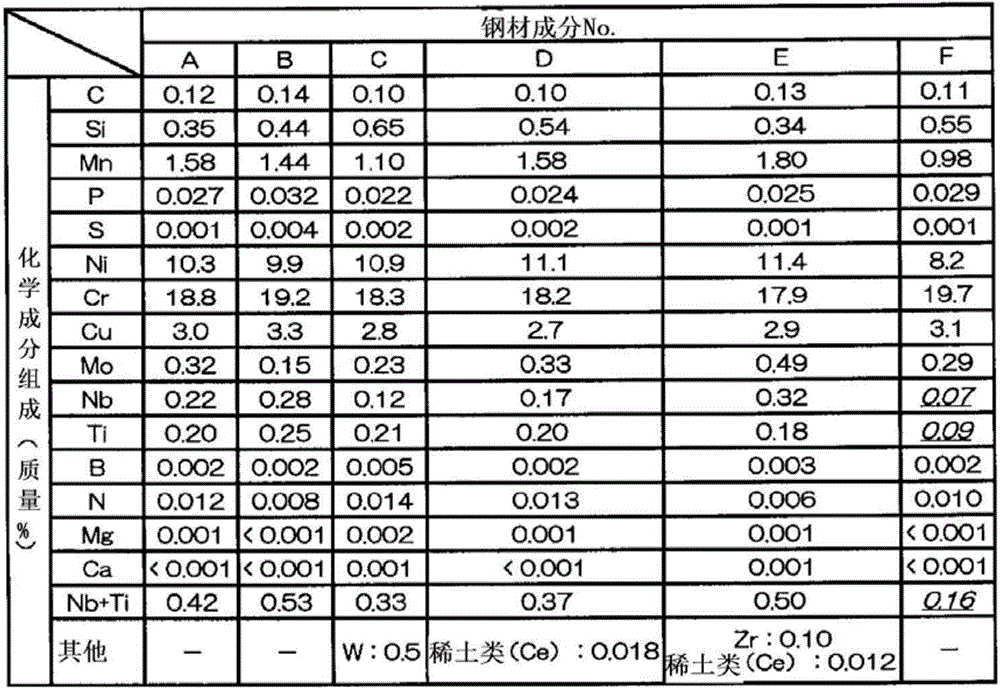
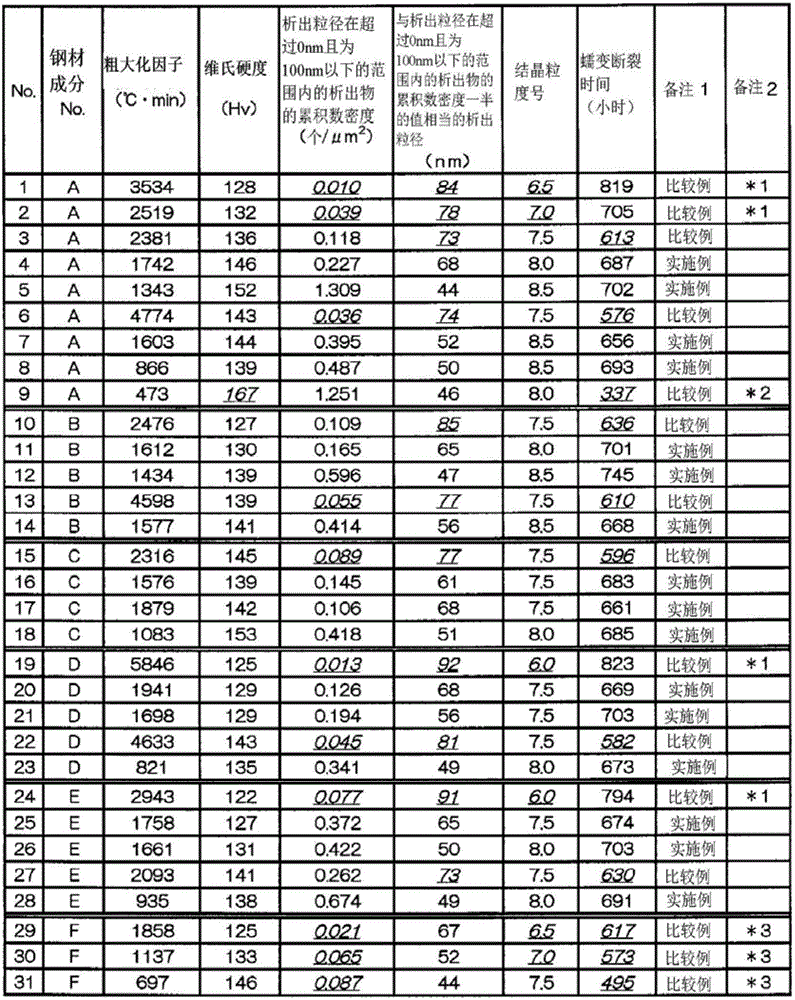
[0131] Various steel materials shown in steel material composition No.A to F shown in Table 1 were melted, and a 20 kg ingot melted in a vacuum melting furnace (VIF) was hot forged into a size of 130 mm in width and 20 mm in thickness.
[0132] Then, softening heat treatment was performed at 1250° C., and it was processed to a thickness of 13 mm by cold rolling to obtain a base material. In addition, No.A-E among No.A-F steel materials shown in Table 1 belong to the type of so-called fire SUS321J2HTB steel, and are the steel materials of the composition which satisfy|fills the chemical composition prescribed|regulated by this invention. On the other hand, No. F is a steel material deviated from the chemical composition specified in the present i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com