Fault location in DC networks
A technology of fault location and network, which is applied in the direction of fault location, fault detection according to conductor type, emergency protection device for automatic disconnection, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
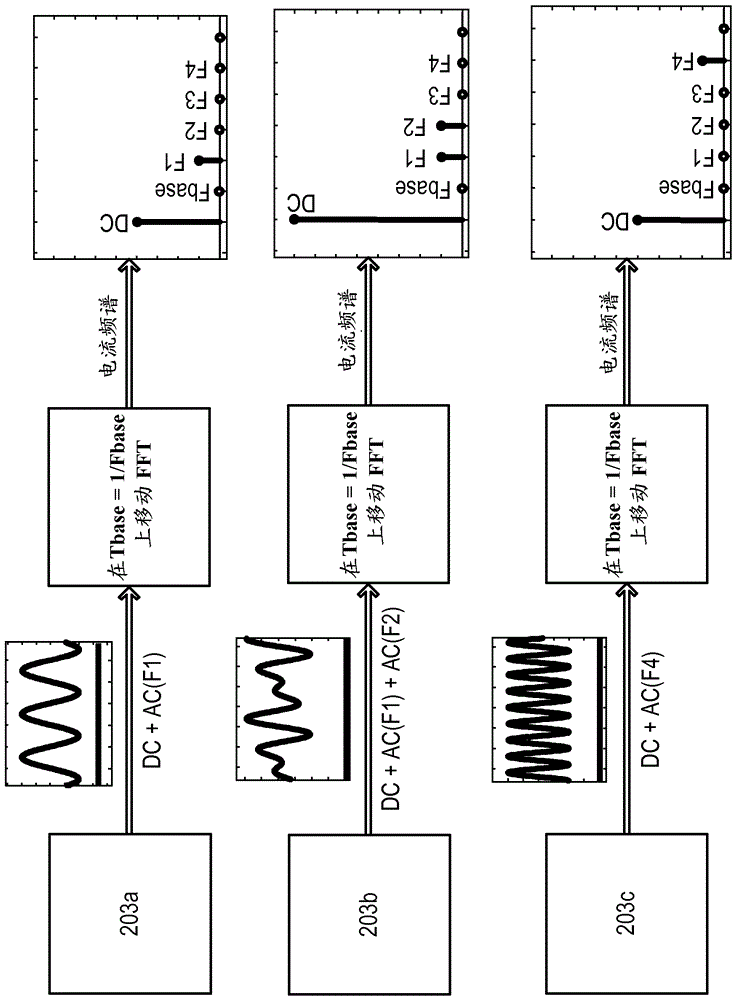
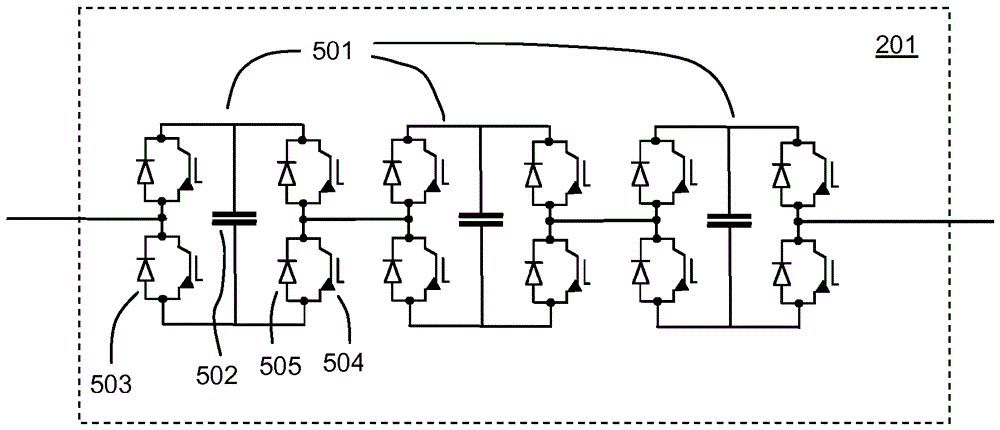
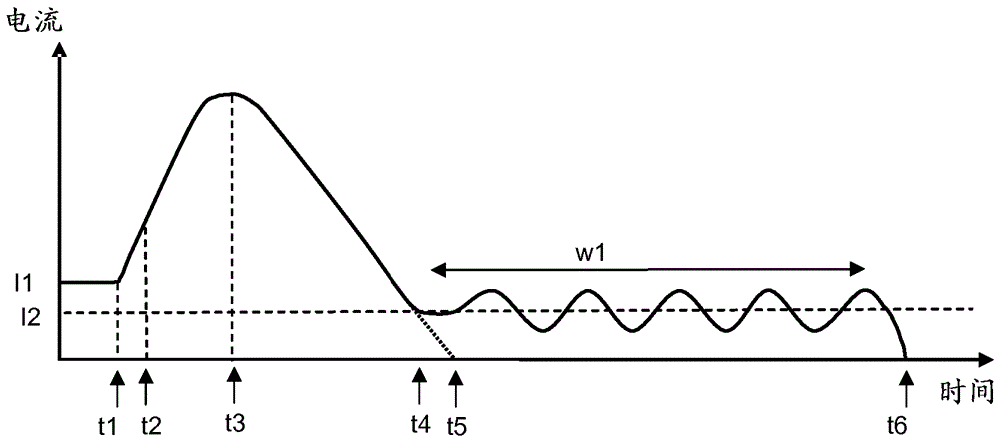
[0051] figure 1 One example of a DC network 100 is illustrated. A plurality of voltage source converters (VSCs) 101 are connected to each other via a plurality of DC transmission paths, which may include transmission lines such as overhead power lines, submarine or buried cables, and the like. In the examples below, various transmission paths are collectively referred to as DC lines, this term shall cover any type of DC transmission paths such as overhead lines and submarine or buried cables. At least a part of the DC line may also comprise a power supply station or substation or a transmission path within other parts of the network. figure 1 An example of a radial network is shown where different DC lines linking VSC, DC lines 1-4 are connected together. It is of course recognized that this is merely an illustrative example and that the number of converters and connection paths may vary depending on the application and that many other network configurations exist.
[0052]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com