Method for producing metal laminate material
A manufacturing method and metal technology, applied in the direction of metal layered products, manufacturing tools, metal processing equipment, etc., can solve the problems of reduced production efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
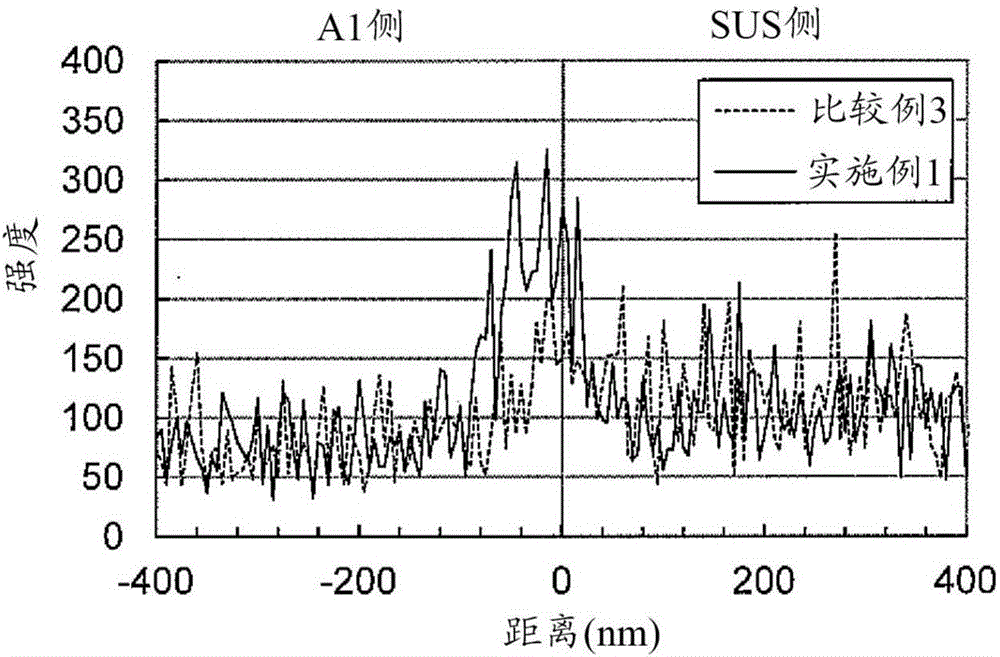
[0051] SUS304-BA (thickness 0.05mm) was used for stainless steel, and A1050-H18 (thickness 0.18mm) was used for aluminum. The surface of SUS304-BA and A1050-H18 was measured using a scanning Auger electron spectroscopy (AES). 150nm.
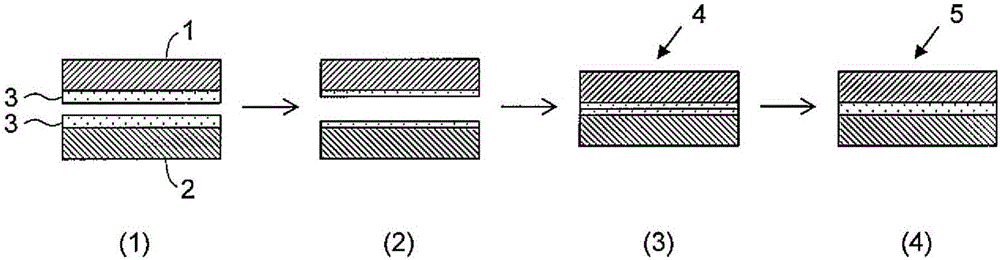
[0052] Next, sputtering treatment was performed on SUS304-BA and A1050-H18. The sputtering treatment of SUS304-BA is carried out in a vacuum of 0.1Pa with a plasma power of 800W and a linear velocity of 3.5m / min; the sputtering treatment of A1050-H18 is carried out in a vacuum of 0.1Pa with a plasma power of 2600W and a linear velocity of 3.5m / min, the surface adsorption layer of SUS304-BA and A1050-H18 is completely removed. Ar was used as an inert gas. The etching amount of SUS304-BA is about 2nm, and the etching amount of A1050-H18 is about 6nm. At room temperature, the sputtered SUS304-BA and A1050-H18 were temporarily bonded by seam welding with a rolling line load of 2tf / cm (rolling load 0.4MN) to form a laminated material.
[0053] AE...
Embodiment 2~5 and comparative example 5~7
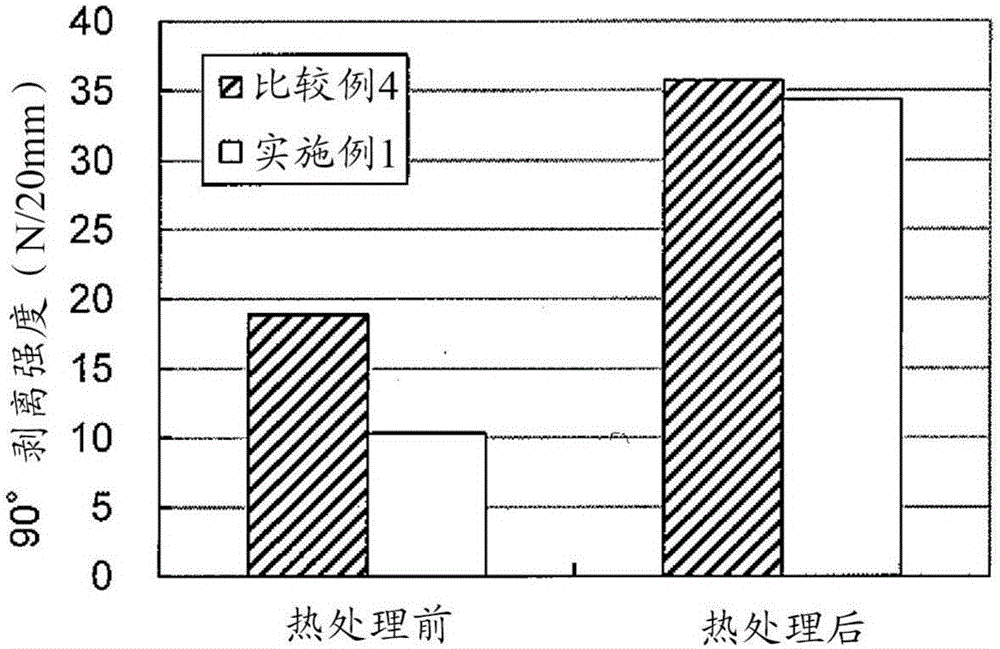
[0068] In Examples 2 to 5 and Comparative Examples 5 to 7, the influence of the temperature of the heat treatment of the temporarily bonded laminated material on the peel strength and hardness of the obtained metal laminated material was investigated.
[0069] In Examples 2 to 5 and Comparative Examples 5 to 7, SUS304-1 / 2H with a thickness of 0.1 mm was used instead of SUS304-BA with a thickness of 0.05 mm, and AL1050 (H24) with a thickness of 0.4 mm was used instead of A1050-H18 with a thickness of 0.18 mm , change the line speed from 3.5m / min to 3.0m / min for sputtering treatment, change the rolling line load from 2tf / cm to 2.8tf / cm in seam welding, and implement temporary seam welding Bonding, except that, was the same as in Example 1, and a temporarily bonded laminated material was obtained. The etching amount of SUS304-1 / 2H is 3nm, and the etching amount of AL1050(H24) is 5nm. The obtained temporarily bonded laminate was heat-treated at a prescribed temperature for 240 mi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com