Patents
Literature
112 results about "Roll bonding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
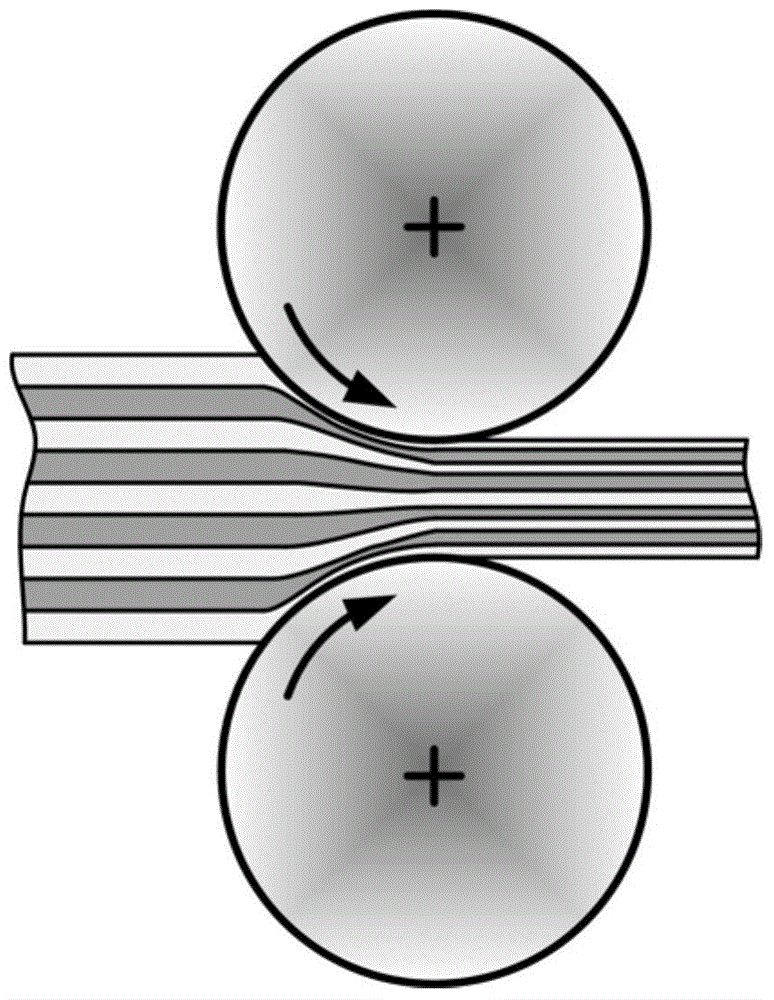
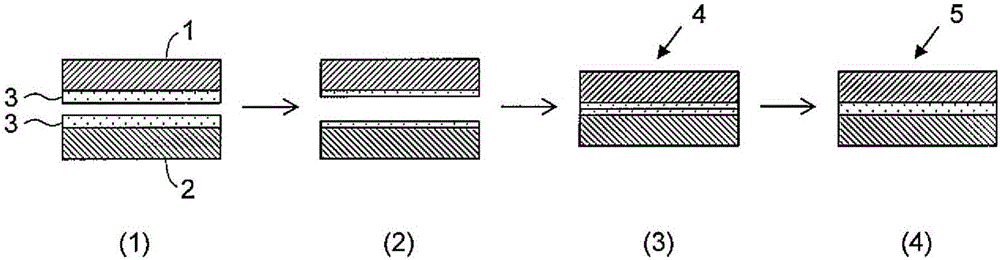
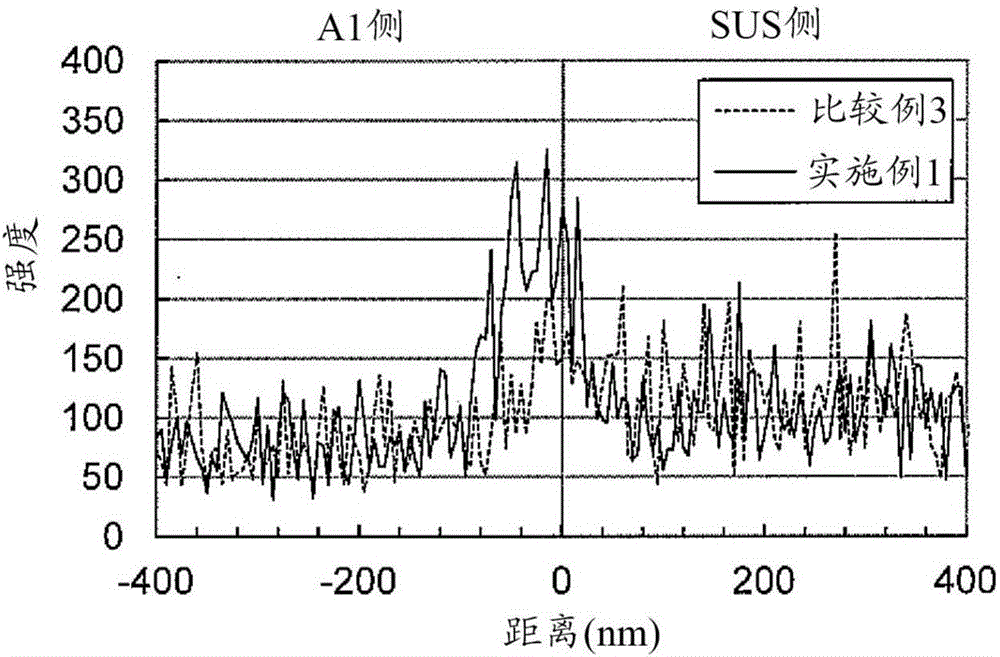
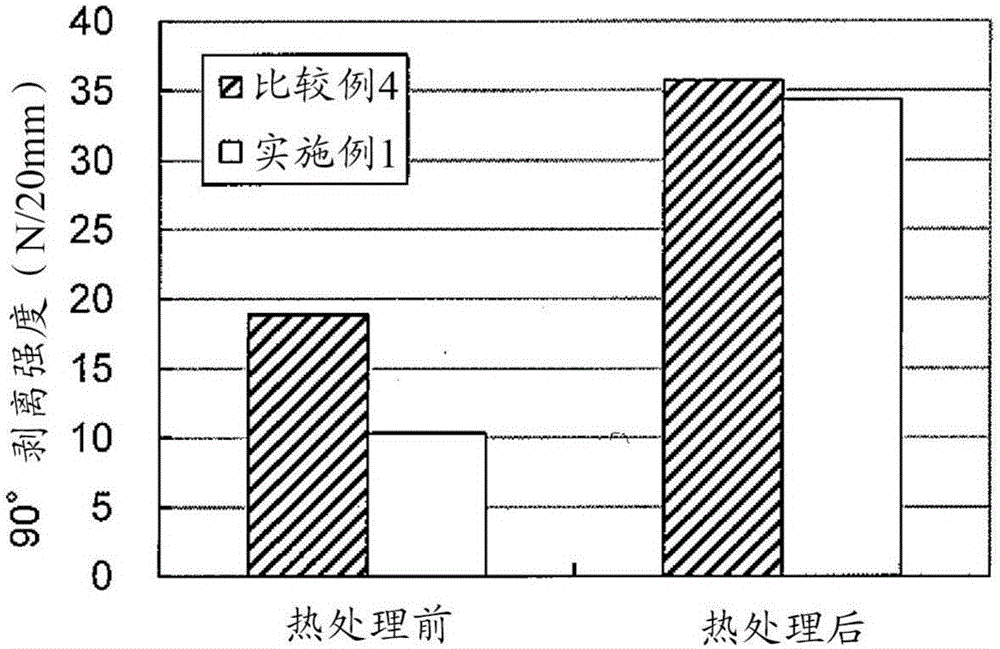
Roll bonding is a solid state, cold welding process, obtained through flat rolling of sheet metals. In roll bonding, two or more layers of different metals are passed through a pair of flat rollers under sufficient pressure to bond the layers. The pressure is high enough to deform the metals and reduce the combined thickness of the clad material. The mating surfaces must be previously prepared (scratched, cleaned, degreased) in order to increase their friction coefficient and remove any oxide layers. The process can be performed at room temperature or at warm conditions. In warm roll bonding, heat is applied to pre-heat the sheets just before rolling, in order to increase their ductility and improve the strength of the weld. The strength of the rolled bonds depends on the main process parameters, including the rolling conditions (entry temperature of the sheets, amount of thickness reduction, rolling speed, etc.), the pre-rolling treatment conditions (annealing temperature and time, surface preparation techniques, etc.) and the post-rolling heat treatments.
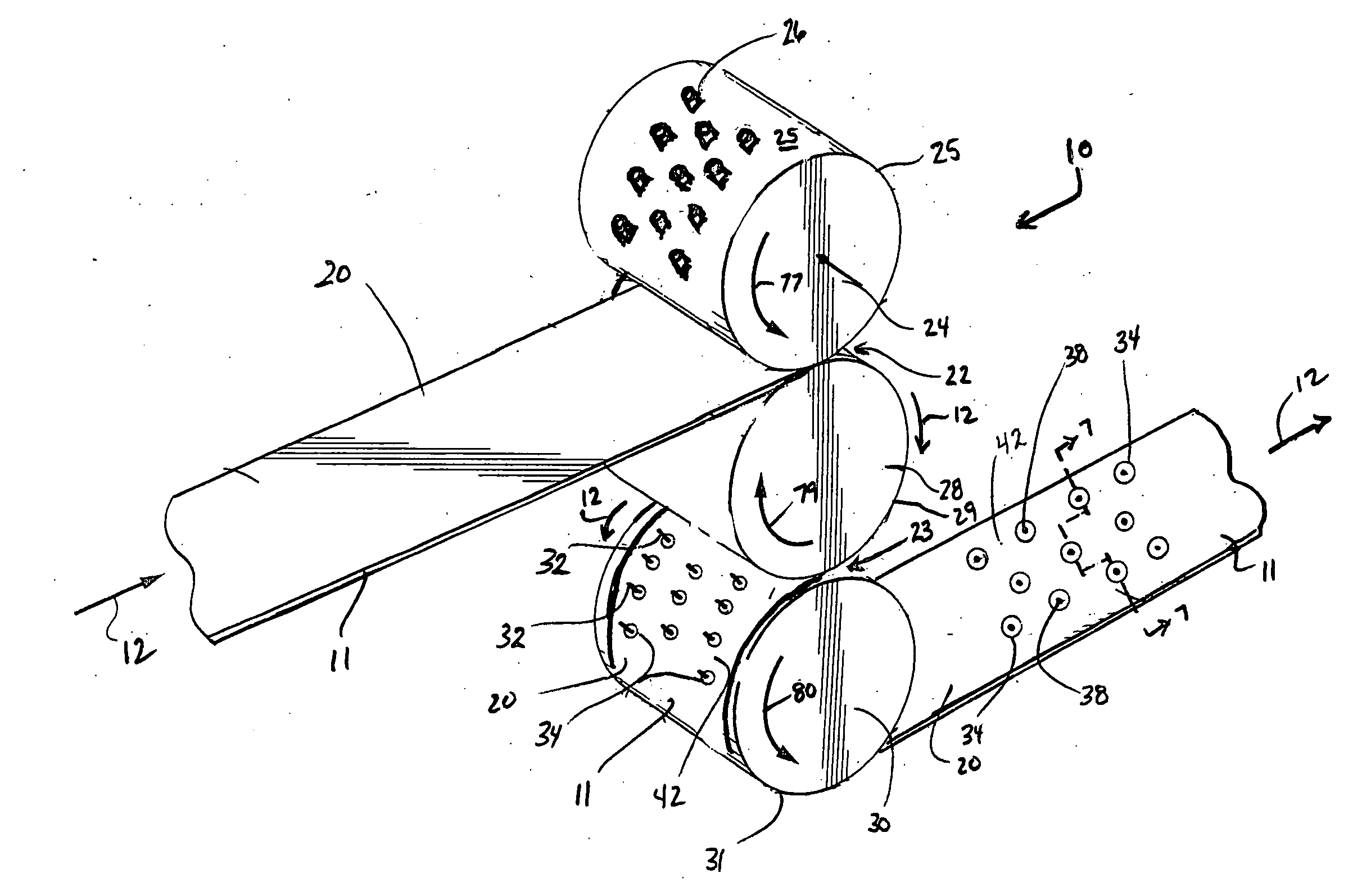
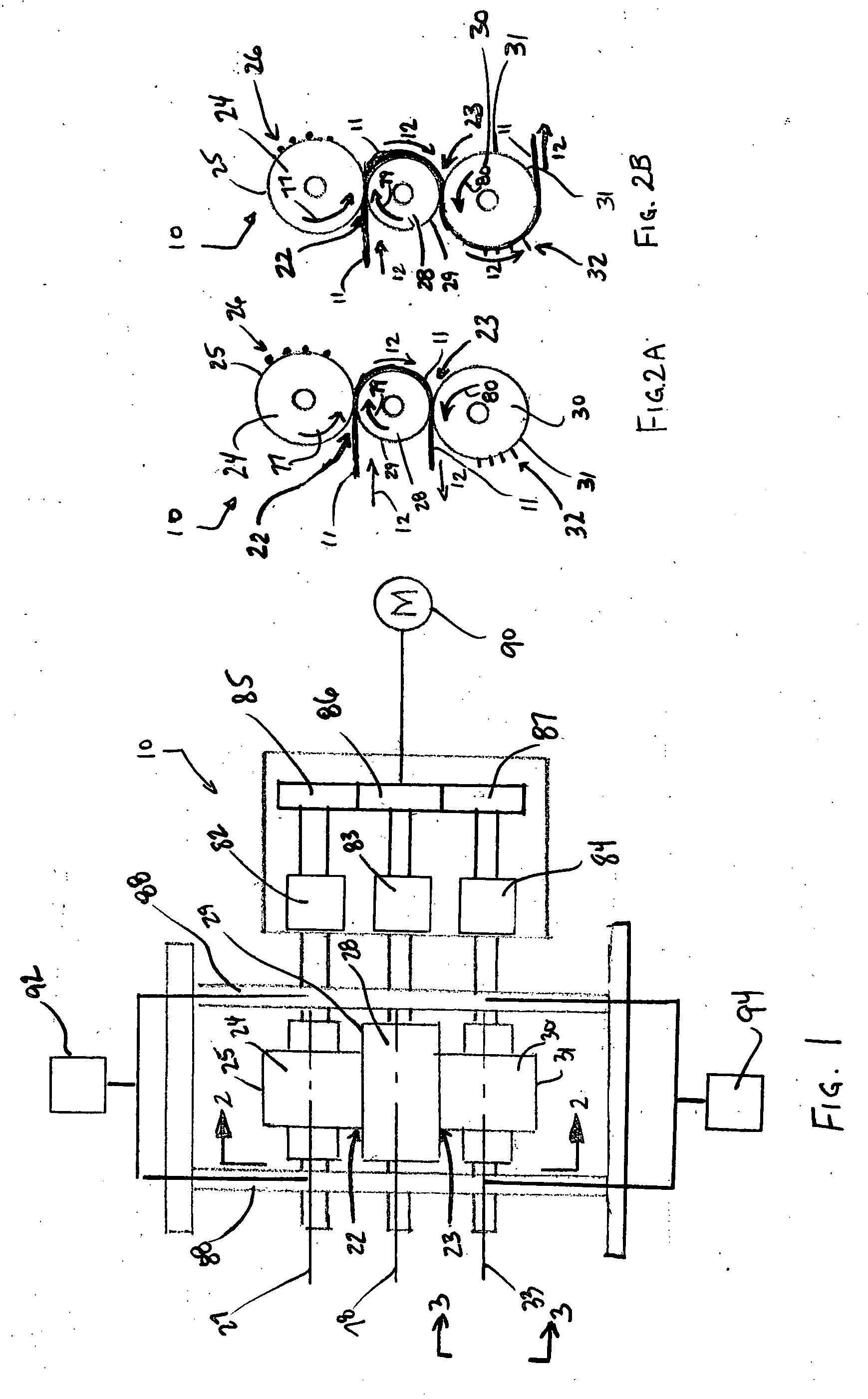
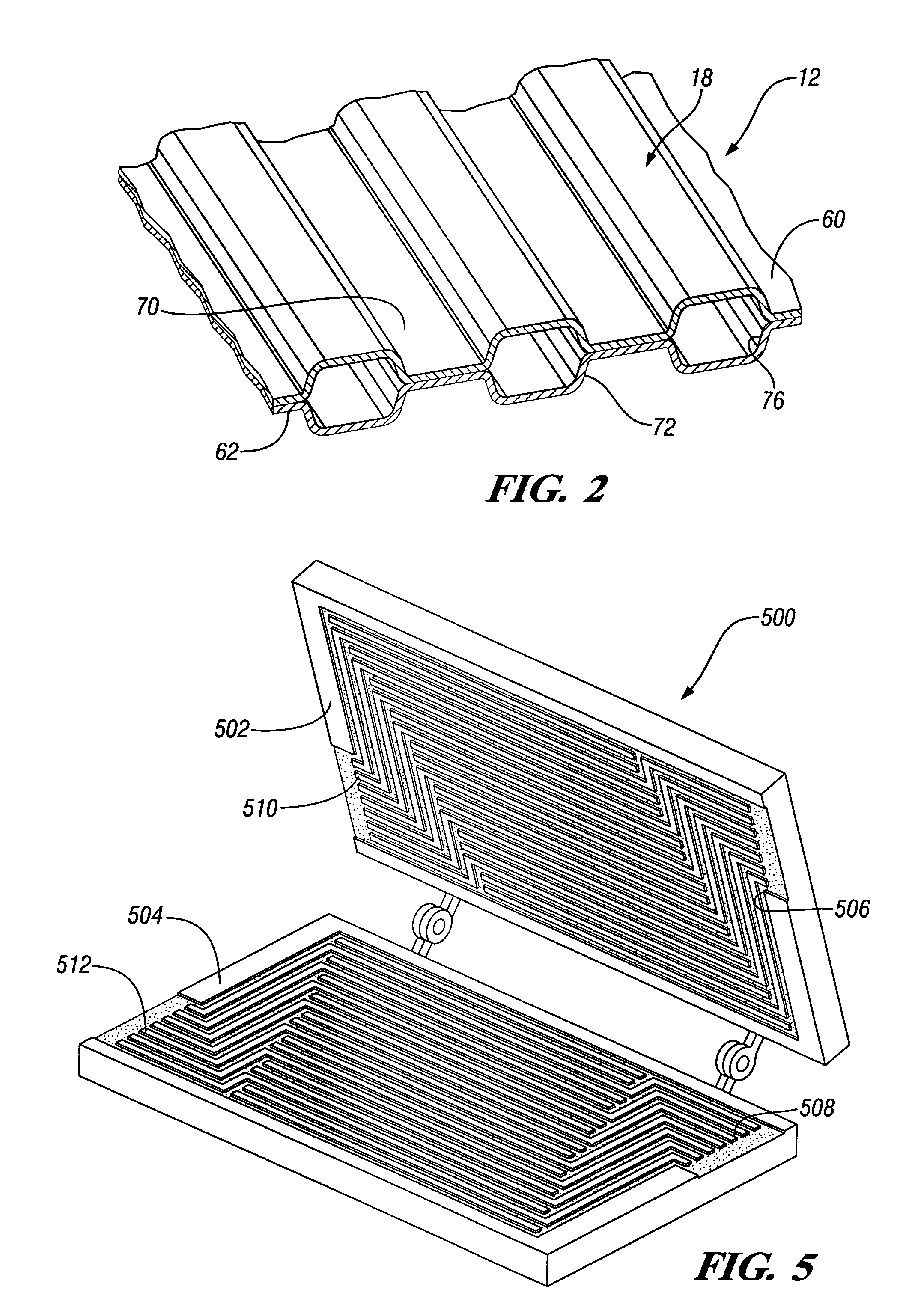
Multi-roll bonding and aperturing
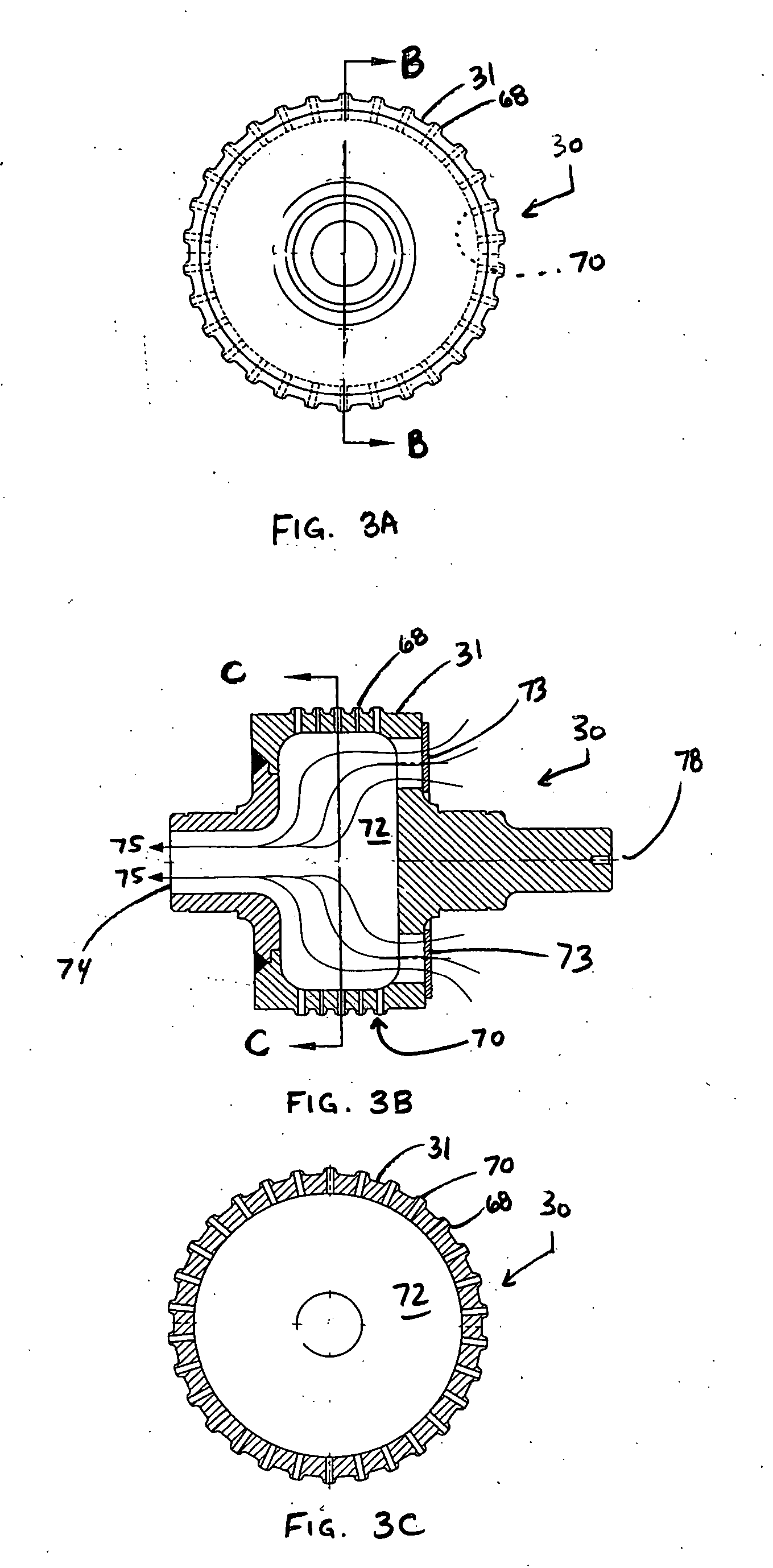
InactiveUS7323072B2Mechanical working/deformationWood working apparatusMechanical engineeringRoll bonding
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
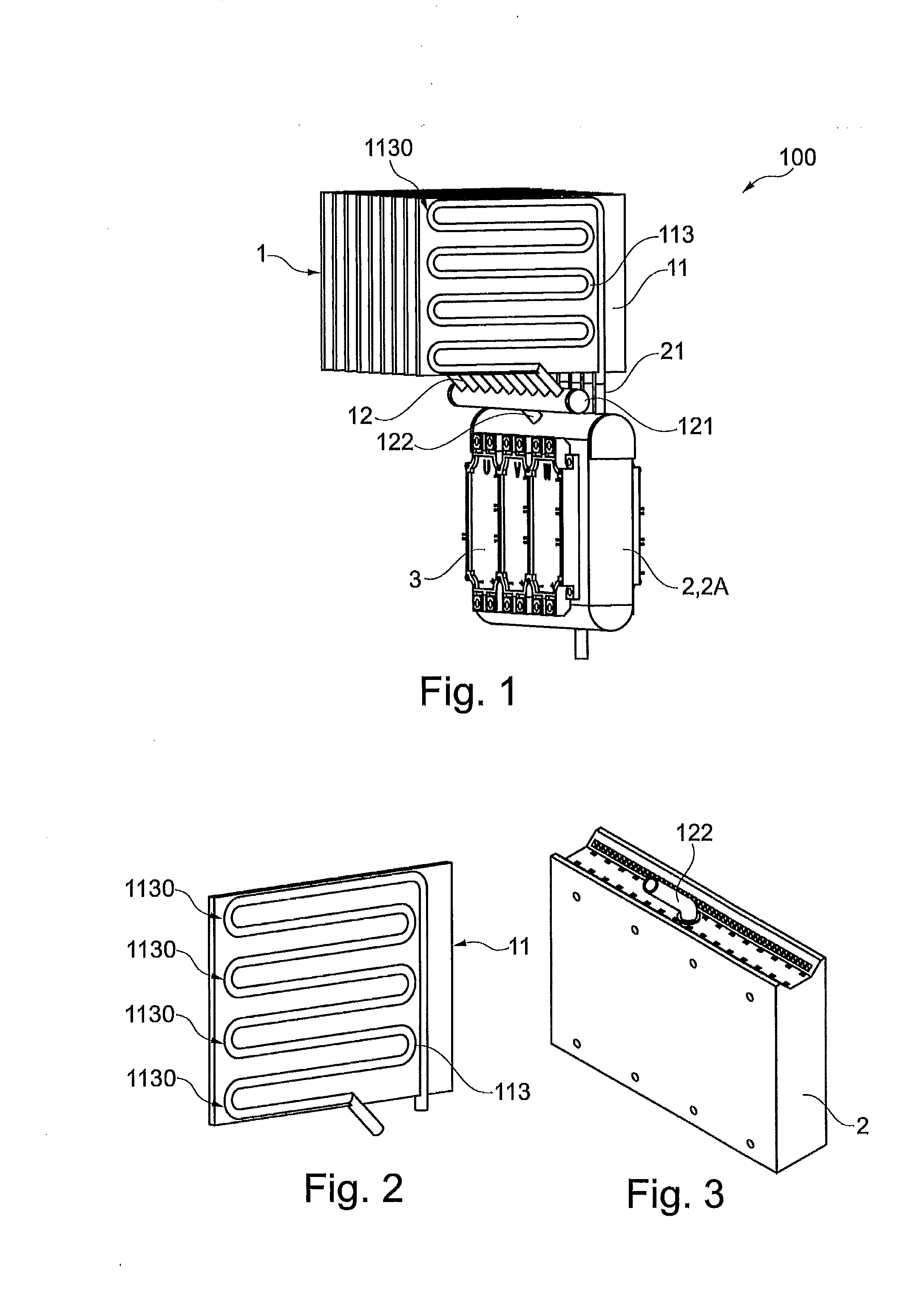
Cooling module for cooling electronic components
InactiveUS20130077245A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEvaporationComputer module
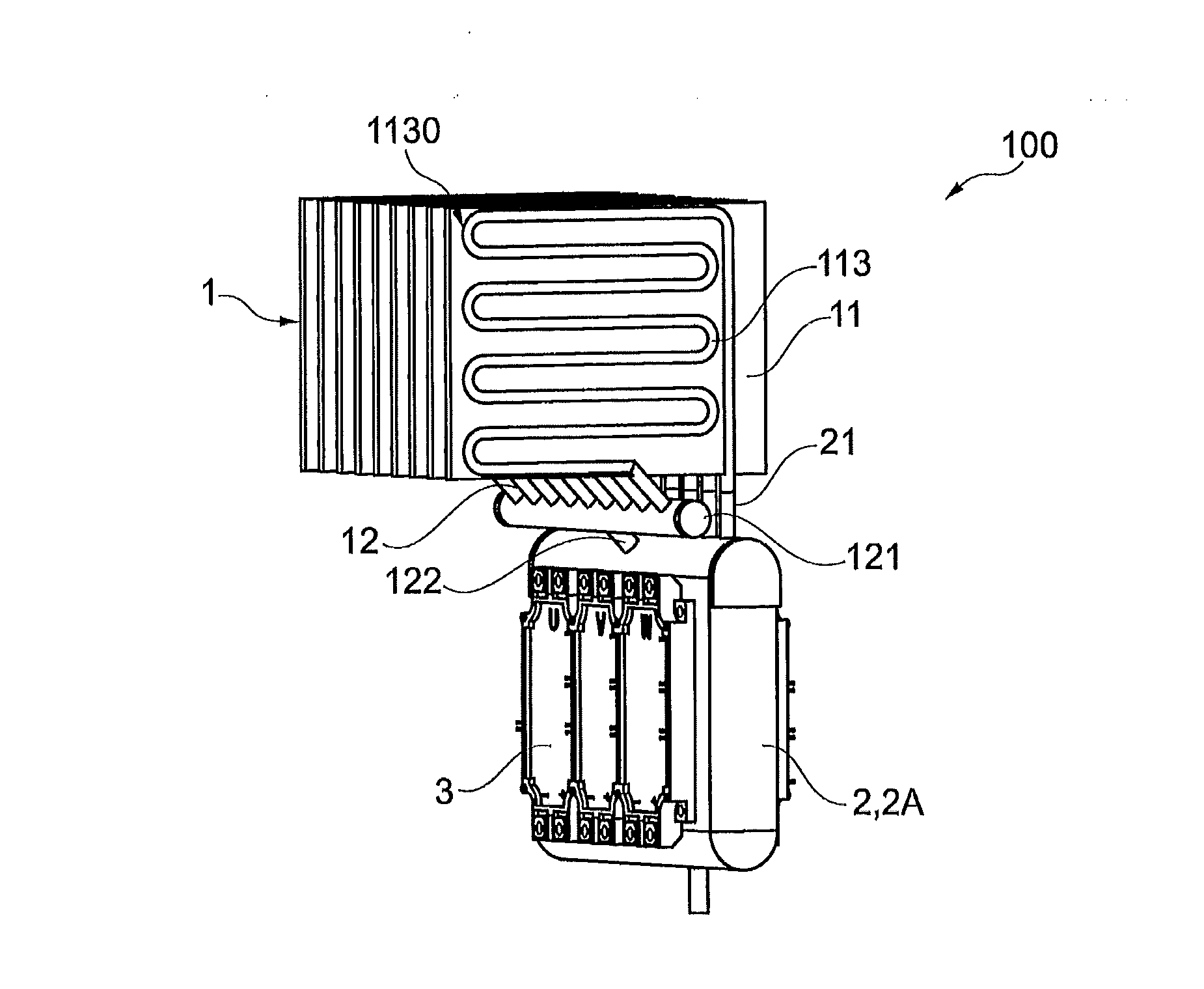
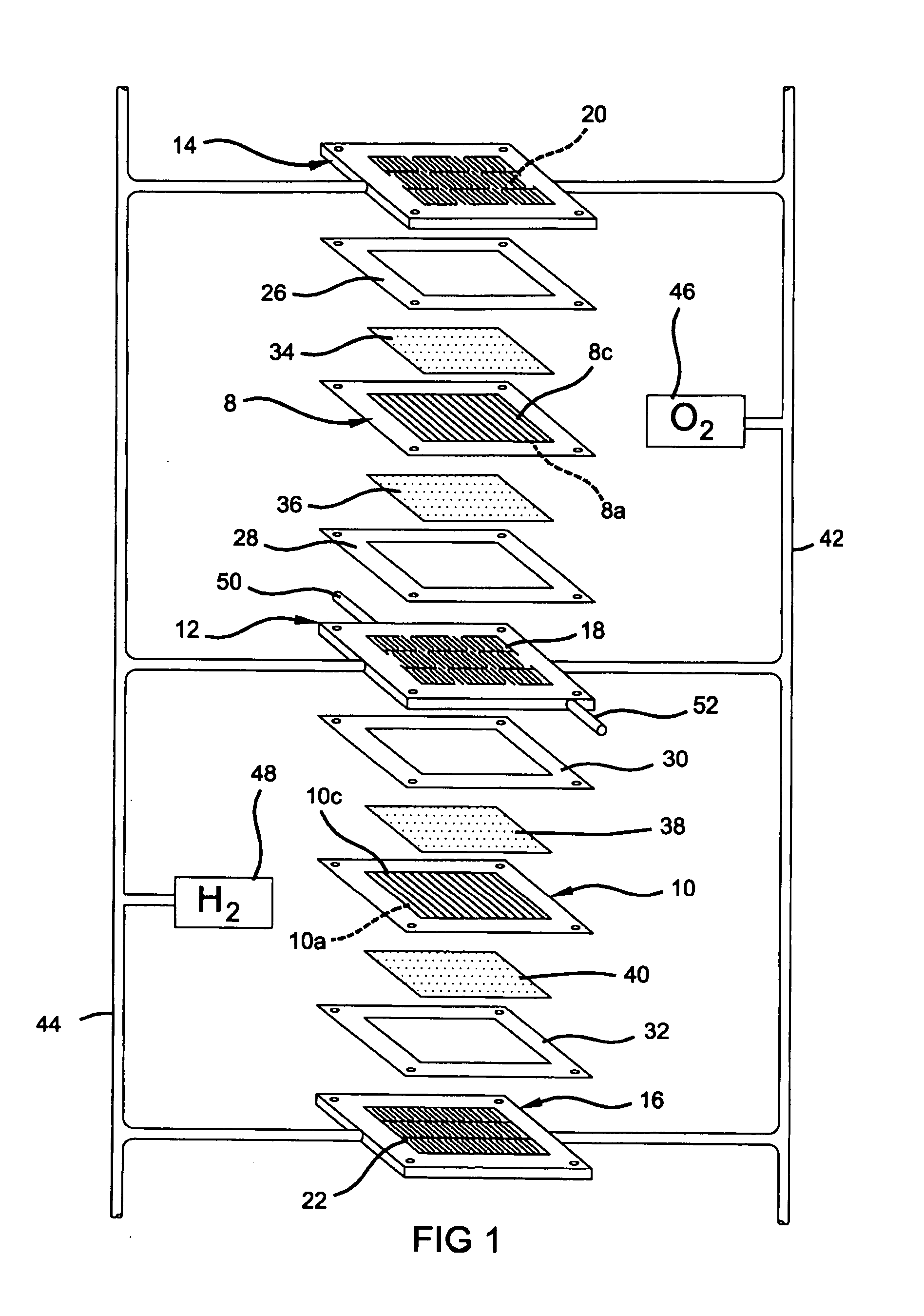
A cooling module including a condenser, a power module including the cooling module and a method for cooling electric and / or electronic components are provided. The condenser of the cooling module includes at least one panel for cooling electric and / or electronic components. Two sheets of the panel are attached to one another by a process involving roll-bonding such that a conduit is formed between the two sheets. The conduit extends in a direction of a plane formed by the sheets. Cooling may be provided by evaporating coolant in the conduit at an evaporation section of the panel and by condensing the coolant at a condensing section of the panel. A heat load may be transferred from a heat source to a heat receiving unit. The heat receiving unit is adapted to transfer the heat load to the panel which transfers the heat load to an ambient environment by a thermal carrier.
Owner:ABB RES LTD
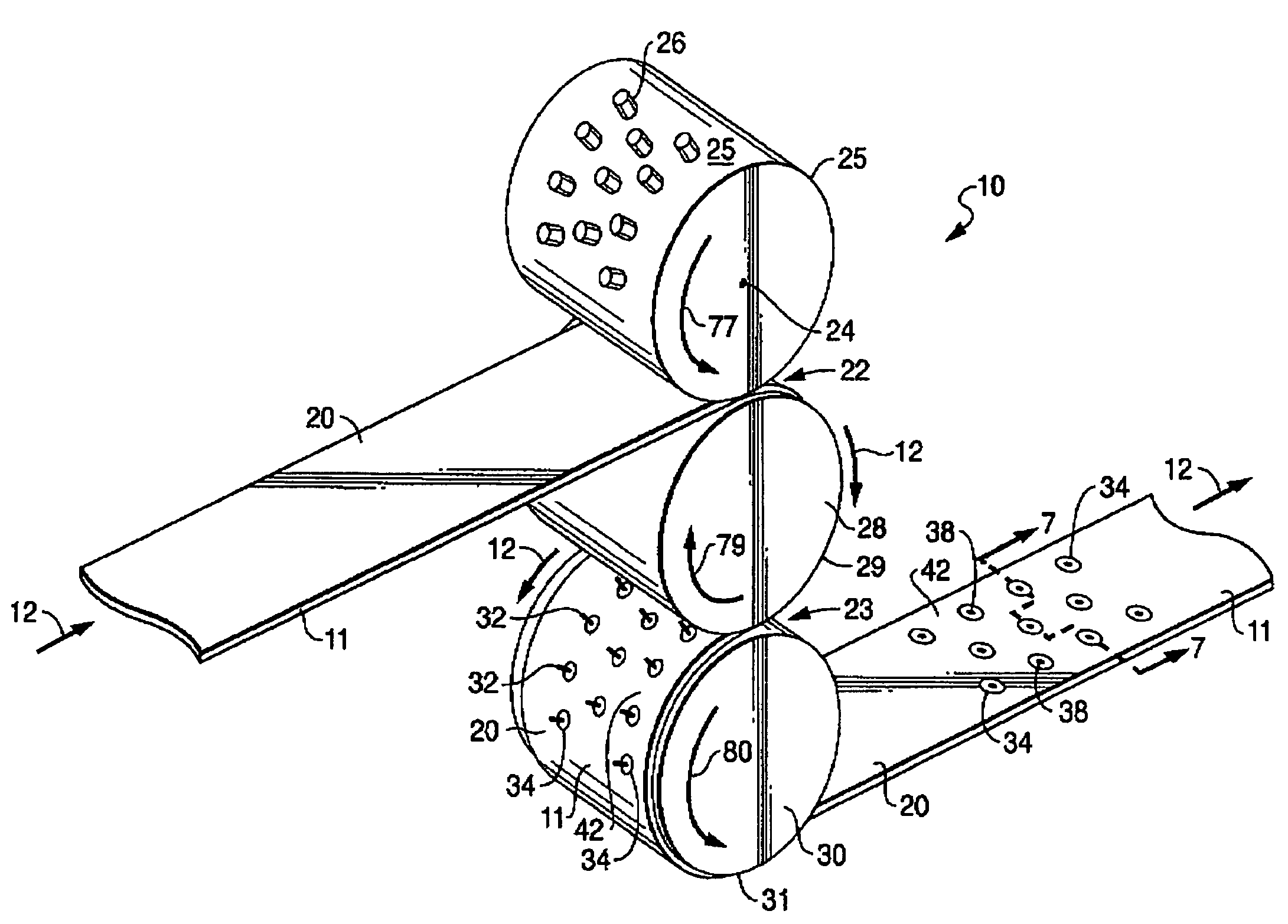
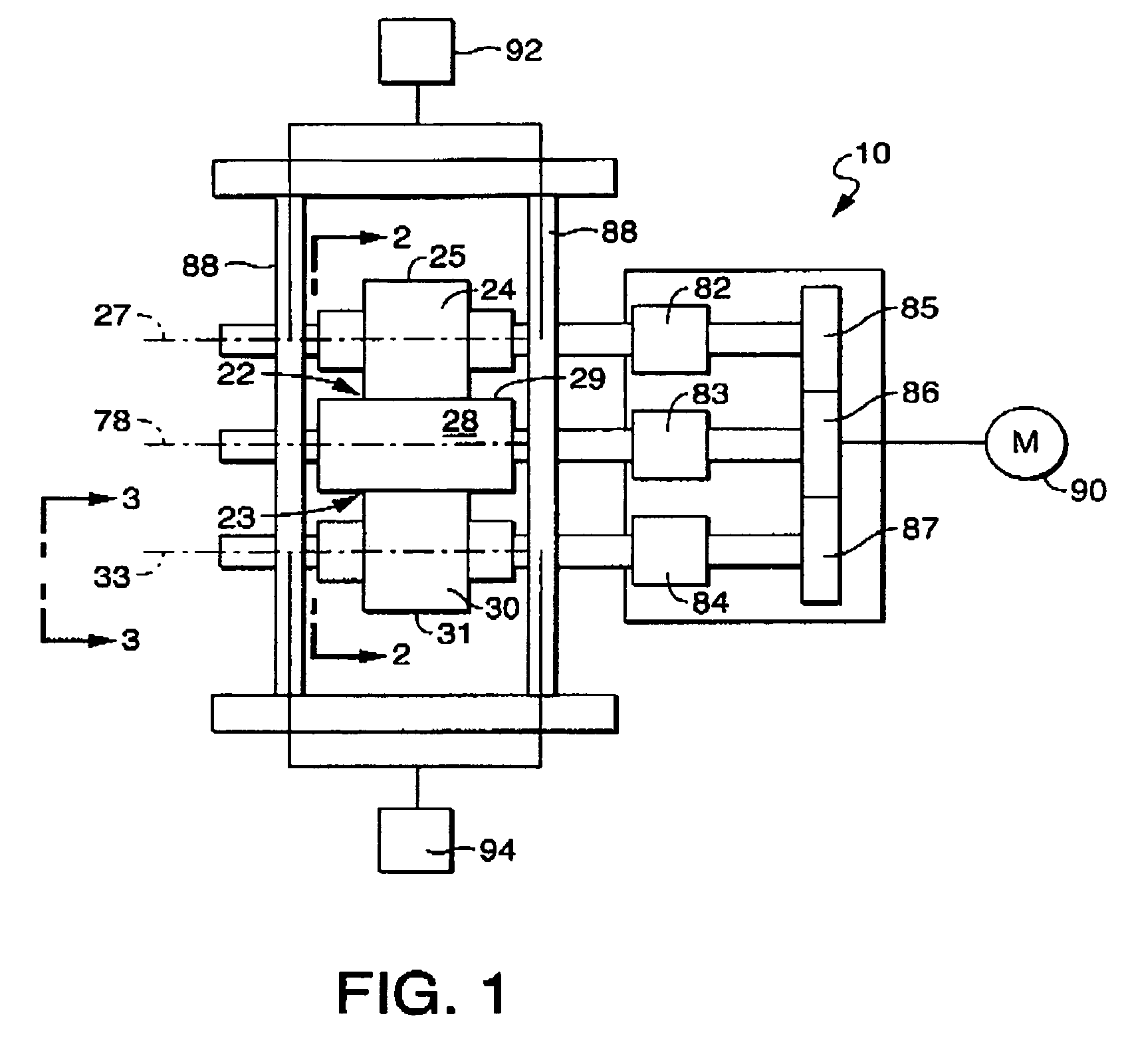
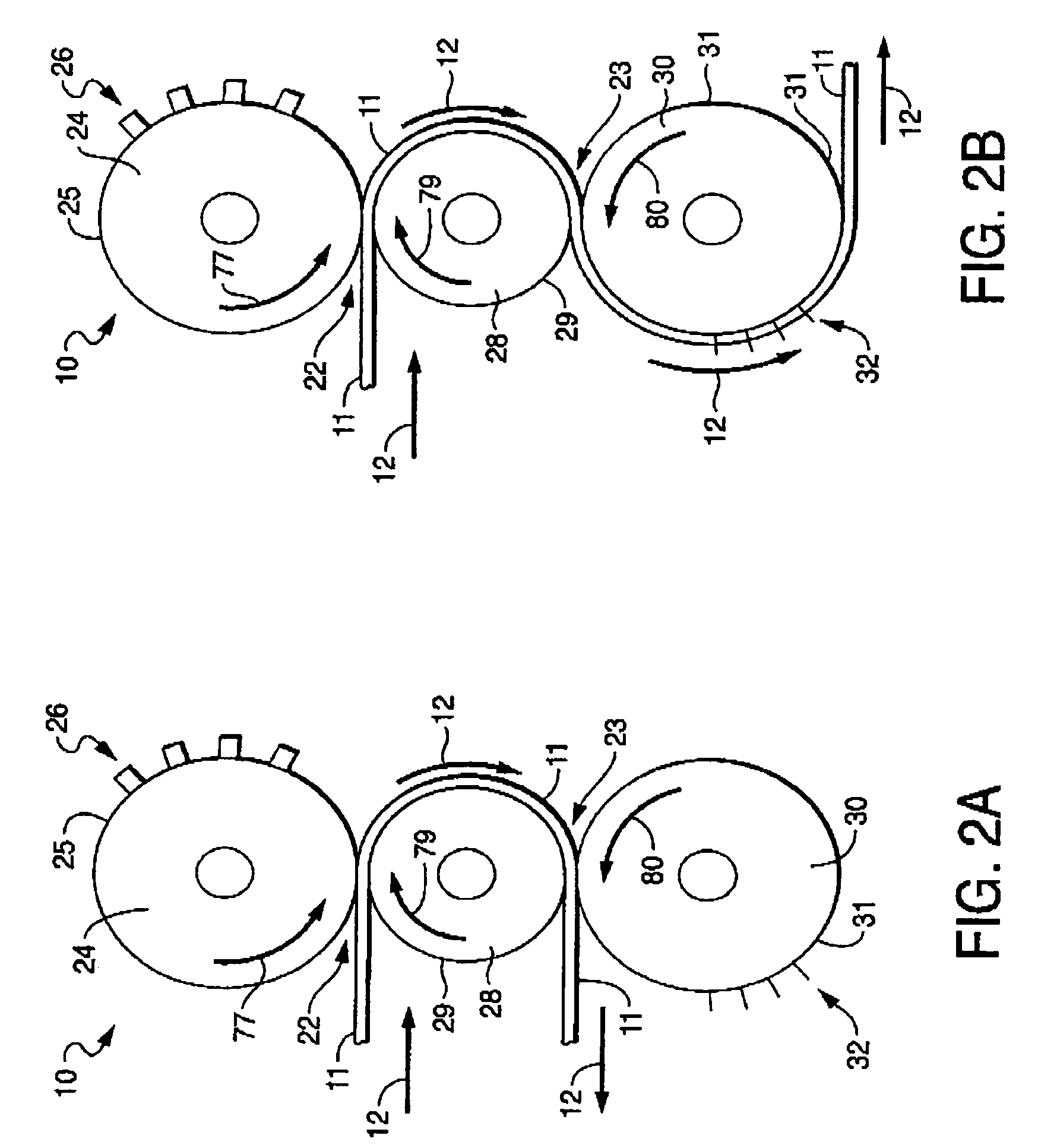
Multi-roll bonding and aperturing
A method and apparatus for bonding and aperturing one or more fibrous webs including bonding at least one fibrous web in a bonding nip created by a rotatable bonding roll and a rotatable anvil roll and aperturing the at least one fibrous web in an aperturing nip created by a rotatable aperture roll and an anvil roll. The bonding roll has a plurality of protuberances extending from the peripheral bonding surface that define a bonding pattern and result in highly bonded regions within the fibrous web. The aperture roll has a plurality of projections extending from the peripheral aperture surface that define an aperturing pattern. The aperturing pattern substantially aligns with the bonding pattern thereby creating apertures within the highly bonded regions.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
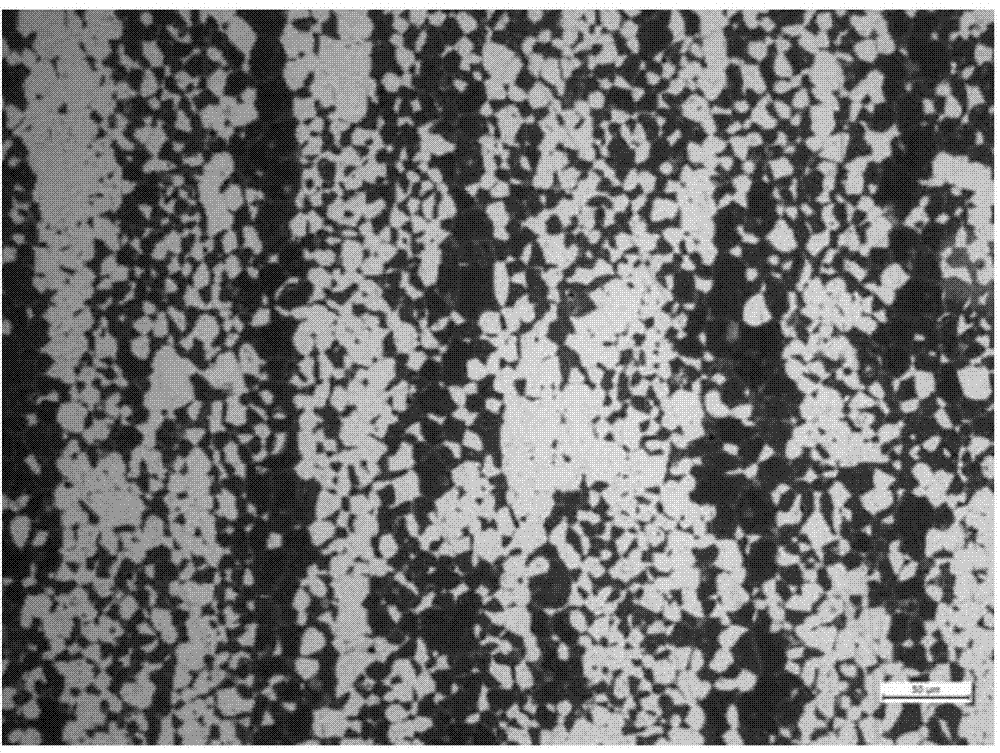
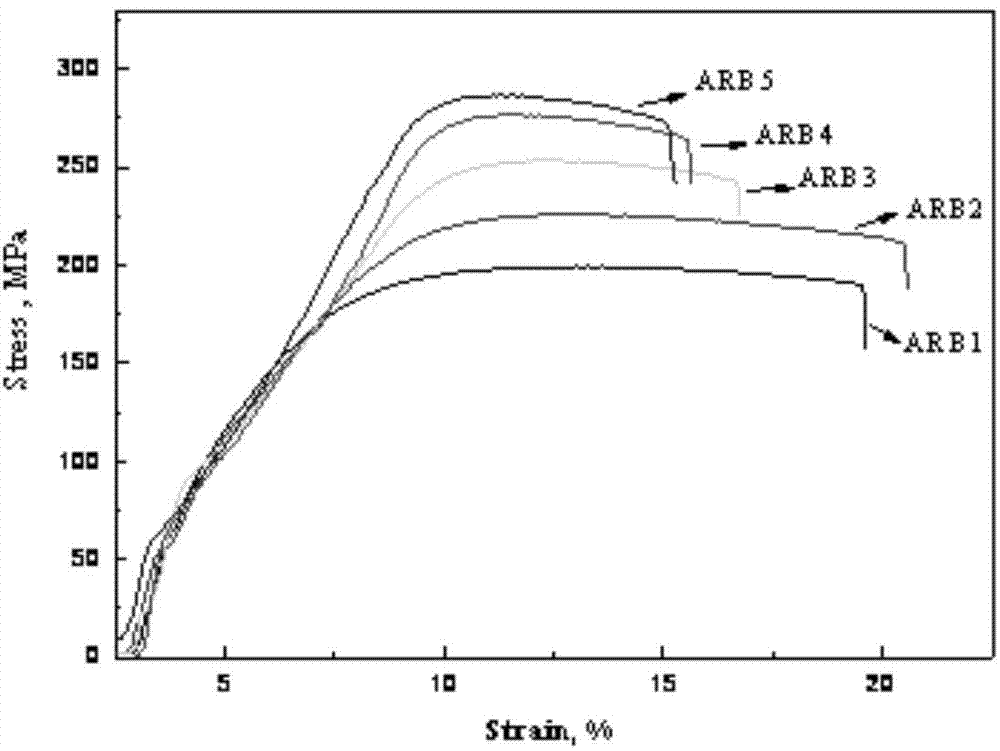
High-strength/toughness magnesium lithium alloy and preparation method thereof by accumulative roll bonding process
InactiveCN104498793AHigh fatigue limitImprove plasticityMetal rolling arrangementsLithiumThermal deformation
The invention provides a high-strength / toughness magnesium lithium alloy and a preparation method thereof by an accumulative roll bonding process. The method comprises the following steps: a) carrying out homogenizing treatment on a smelted magnesium lithium alloy cast ingot; b) carrying out thermal deformation processing to obtain a magnesium lithium alloy plate; c) carrying out stress-relief annealing; d) cutting the plate for accumulative roll bonding into two pieces with equal size, and carrying out surface treatment; e) fixing the two Mg-Li alloy plates; f) rolling; g) repeating the roll bonding according to the steps d)-f) 4-6 times; and h) carrying out annealing treatment. The obtained alloy comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 7.5-9.5% of Li, 2.5-3.5% of Al, 0.5-1.5% of Zn, less than 0.03% of inevitable impurities (Fe, Cu, Ni, Mn and Si), and the balance of Mg. The magnesium lithium alloy is reinforced according to the specific alloying elements and proportioning thereof, and subjected to multipass accumulative roll bonding at proper temperature to refine the magnesium lithium alloy crystal grains, so that the alloy has higher strength on the premise of keeping favorable plasticity.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
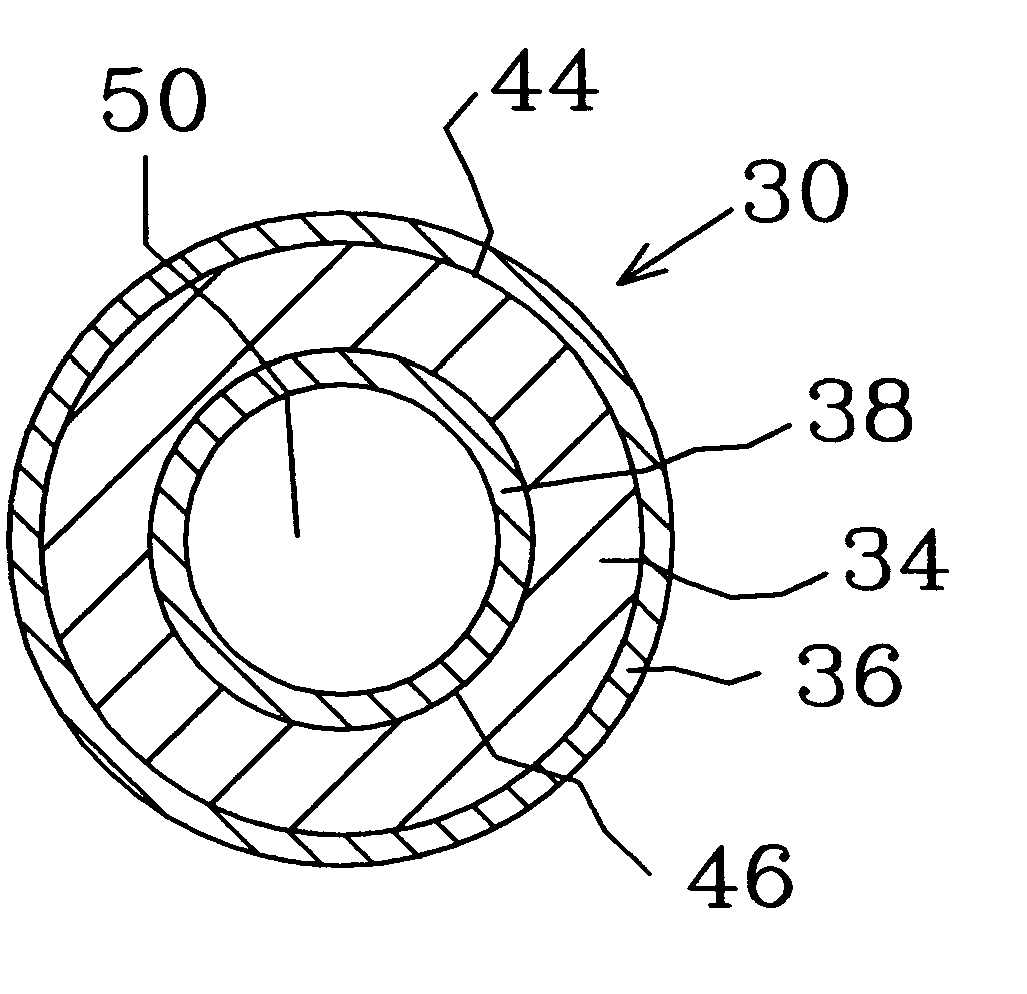
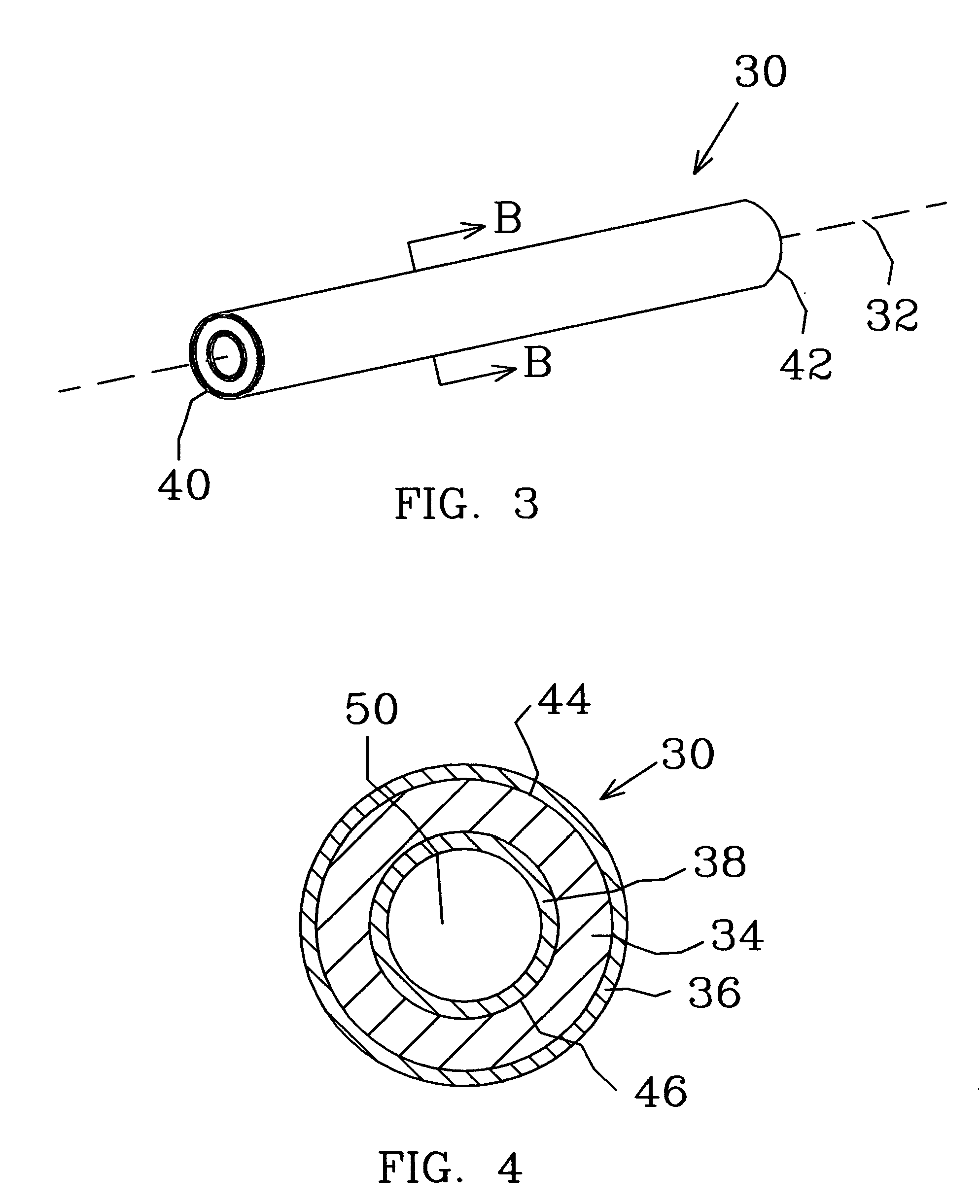
Bipolar plate fabrication by roll bonding
ActiveUS20050133575A1Heat exchange apparatusNon-electric welding apparatusConductive materialsFluid injection
An anti-bonding material is placed in a desired pattern onto a first sheet of conductive material. A second sheet of conductive material is roll bonded with the first sheet of material. Fluid is injected between the bonded first and second sheets of material to expand the sheets of material at the desired pattern. A flow channel is formed at the desired pattern between the first and second sheet during fluid injection.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method for preparing metal layered micro-gradient composite material
InactiveCN104438322AThe method is simpleRoll force/gap control deviceMetal rolling arrangementsChemical compositionUltimate tensile strength
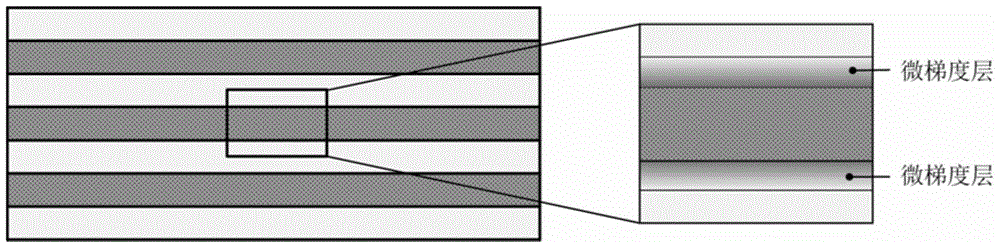
The invention discloses a method for preparing a metal layered micro-gradient composite material. The method is mainly characterized in that the micro-gradient composite material is obtained through interface diffusion of alloy elements with the homologous-series heterogeneous multi-layer metal rolling bonding and heat processing technology. Metal with two kinds of alloy content is adopted for rolling bonding, and the to-be-bonded surfaces are grinded and washed; after the ends are fixed, rolling bonding is carried out, and a multi-layer heterogeneous metal composite board is prepared; then heat processing is carried out on the composite board, the temperature is kept for a certain period of time according to requirements, the alloy elements are diffused on interfaces, and therefore the layered micro-gradient composite material is obtained. According to the metal layered micro-gradient composite material prepared with the method, obvious micro-gradients in chemical components and performance exist nearby the interfaces, and the good interface bonding strength can be achieved; the number of the micro-gradient interfaces and the thickness of micro-gradient layers can be adjusted and controlled by changing the rolling bonding technology, the laminating order and the heat processing technology.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
A method for preparing titanium alloy thin plates by cladding and rolling of steel plates
InactiveCN102274851AUniform vertical and horizontal performanceUniform transverse propertiesMetal rolling arrangementsThin slabMetal sheet
The invention discloses a method for preparing a titanium alloy thin plate by cladding and rolling of a steel plate, and relates to a processing method of a metal plate. It is characterized in that the rolling process is that the titanium alloy plate is hermetically covered by a steel plate to form a stacked rolling bag, and then rolling is carried out. The method of the invention has low rolling cost, and the titanium alloy thin plate is produced by cladding, welding, stacking and hot rolling, the process is simple, and the comprehensive performance of the obtained material is excellent.
Owner:BAOJI TITANIUM IND
Environmentally protected reinforcement dowel pins and method of making
InactiveUS20050265802A1Maintain integrityMaintain strengthPaving detailsFastener toolsZinc alloysSacrificial metal
Galvanically protected reinforcement dowel pins and methods of producing the same. In one embodiment, the reinforcement dowel pins comprise a bar or tube, the longitudinal exposed surfaces of which are covered by a heavy gauge of a sacrificial metal, such as zinc, zinc alloy, magnesium, magnesium alloy, aluminum, or aluminum alloy. The bar or tube comprises steel, carbon steel, or other ferrous metal. The heavy gauge of sacrificial metal is applied to the ferrous metal by various processes, such as roll bonding, lock seaming, welding, die casting, flame spraying, plasma spraying, dipping, sinking, and drawing. The resulting reinforcement dowel pins resist corrosion without sacrificing structural integrity, and are reasonable in materials and manufacturing costs. These dowel pins may be installed in adjacent concrete panels using conventional methods, and therefore do not introduce additional costs in installation.
Owner:JARDEN ZINC PRODS LLC
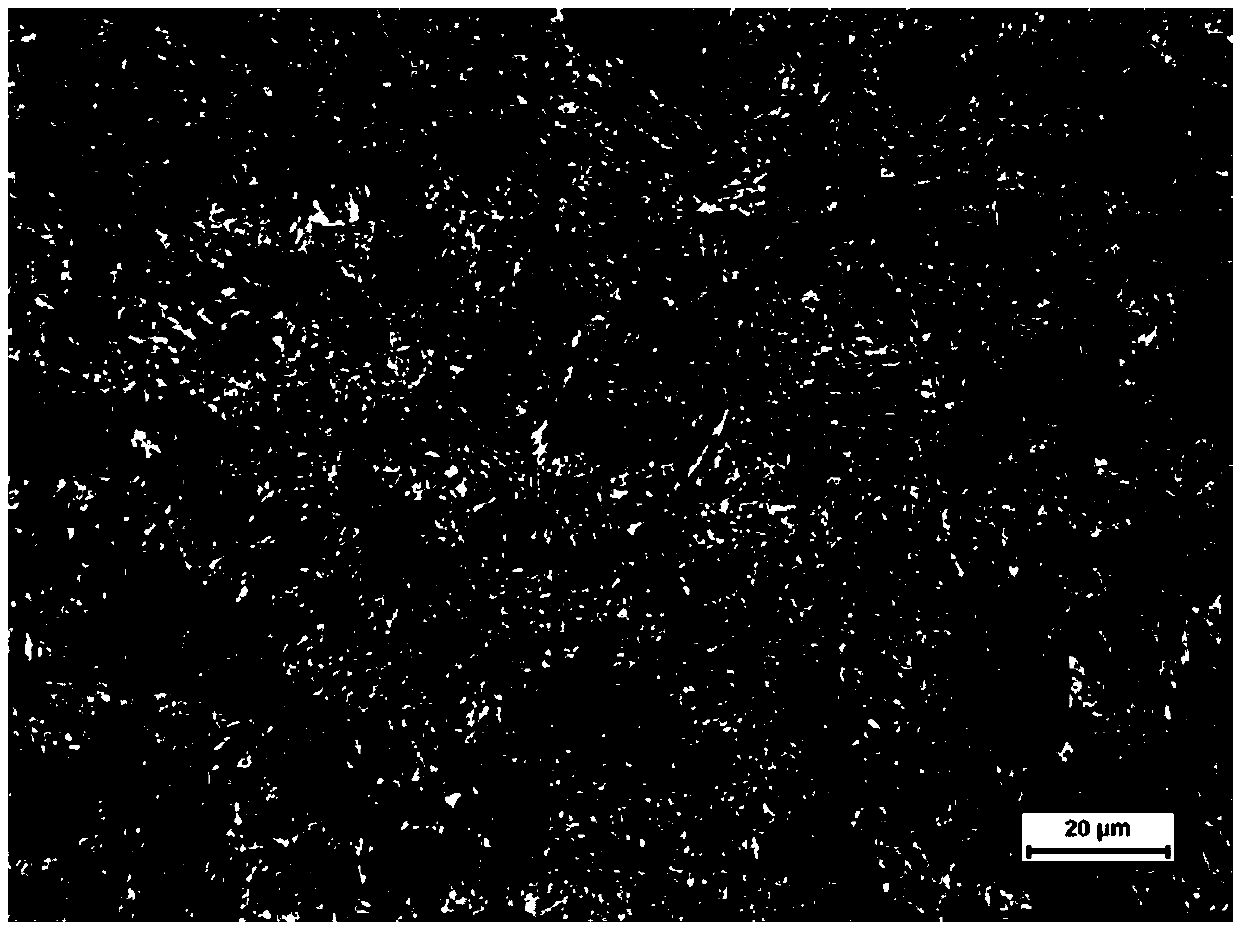
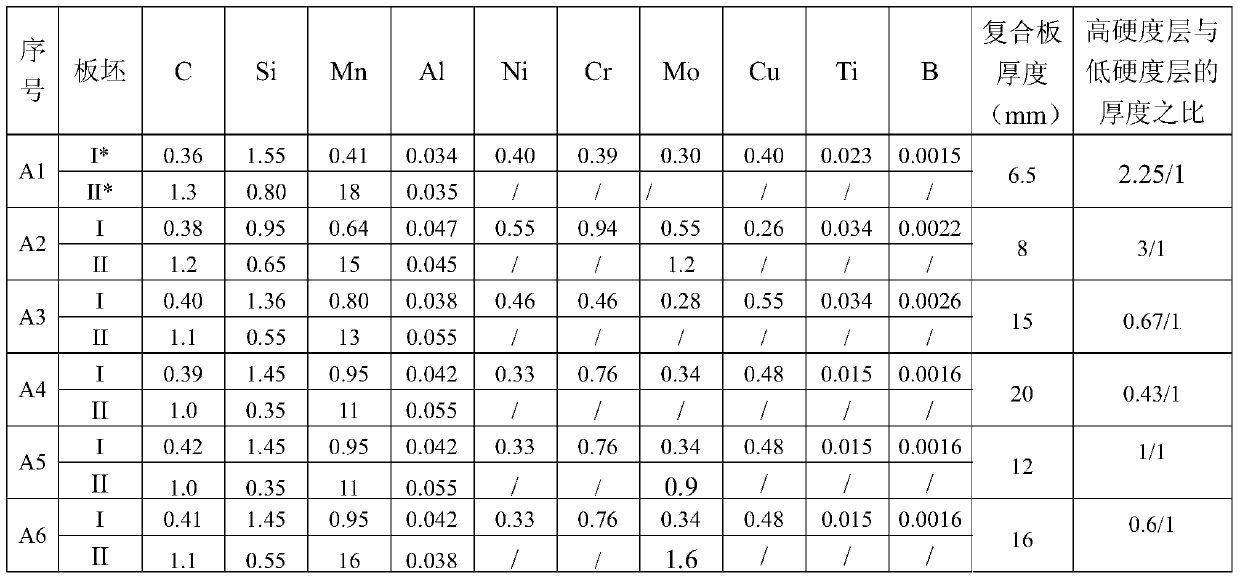
Dual-hardness clad steel plate and production method thereof
InactiveCN105499269AEasy to controlDifferent hardness characteristicsArmourTemperature control deviceHeating timeSheet steel
The invention discloses a dual-hardness clad steel plate. One surface of the steel plate is a high-hardness layer, the other surface of the steel plate is a low-hardness layer, and atom combination is achieved between the high-hardness layer and the low-hardness layer by rolling bonding, wherein Mn13 steel is adopted for the low-hardness layer, and the Brinell hardness of the high-hardness layer is greater than 600. The invention further discloses a production method of the dual-hardness clad steel plate, comprising the following steps: 1. respectively preparing a high-hardness layer slab and a low-hardness layer slab; 2. assembly: preprocessing the combined surface of the slabs, carrying out spherical welded sealing on the binding faces of the slabs, and carrying out vacuumizing treatment on a composite slab after welded sealing; 3. heating; 4. carrying out composite rolling; 5. cooling; and 6. carrying out thermal treatment, wherein the heating temperature is 1050-1100 DEG C, the heating time is 2-3min / mmx thickness, water cooling is performed on the heating slab, and the water temperature is lower than 40 DEG C. The steel plate has different hardness characteristics and good low-temperature toughness.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
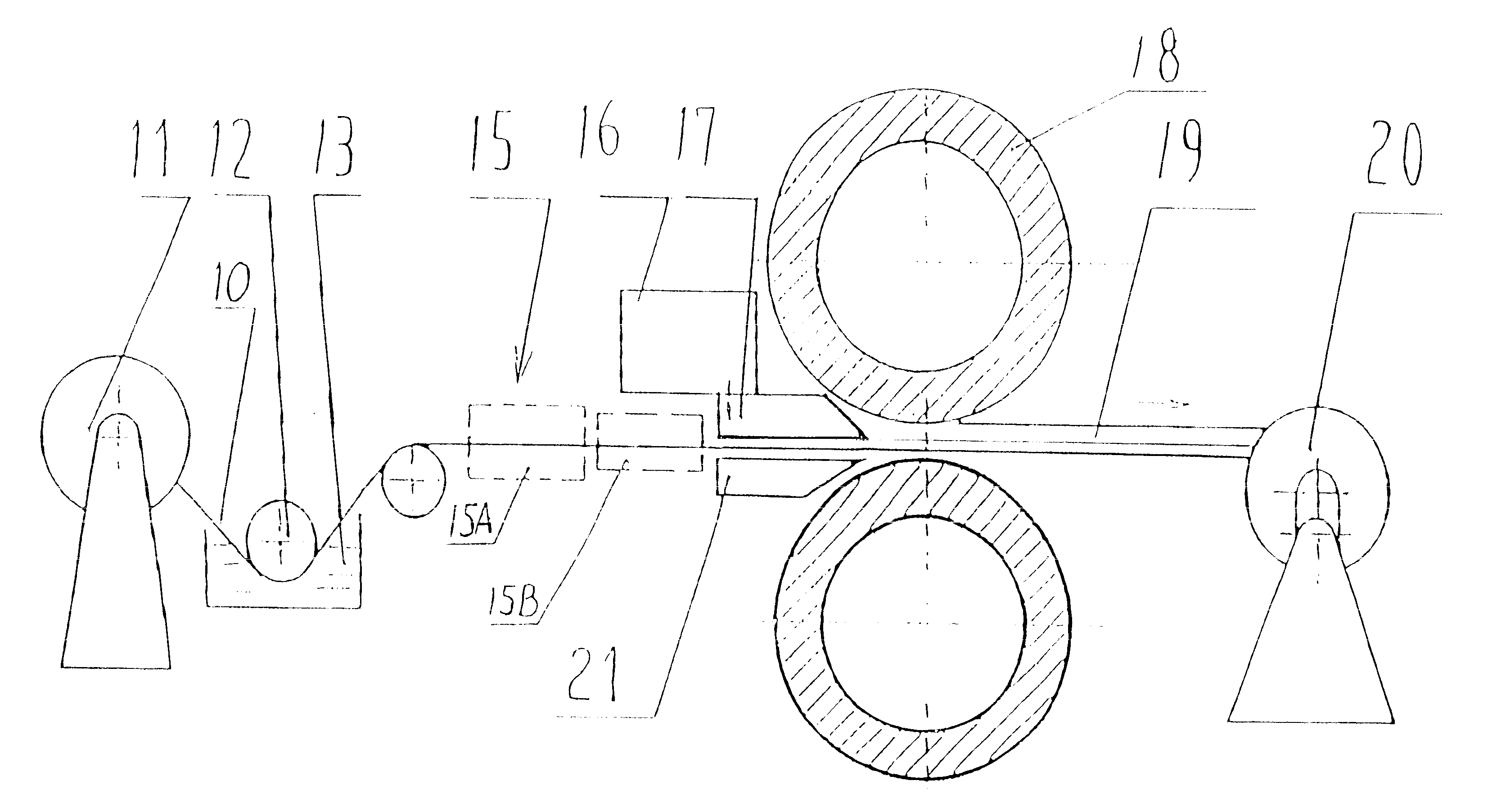
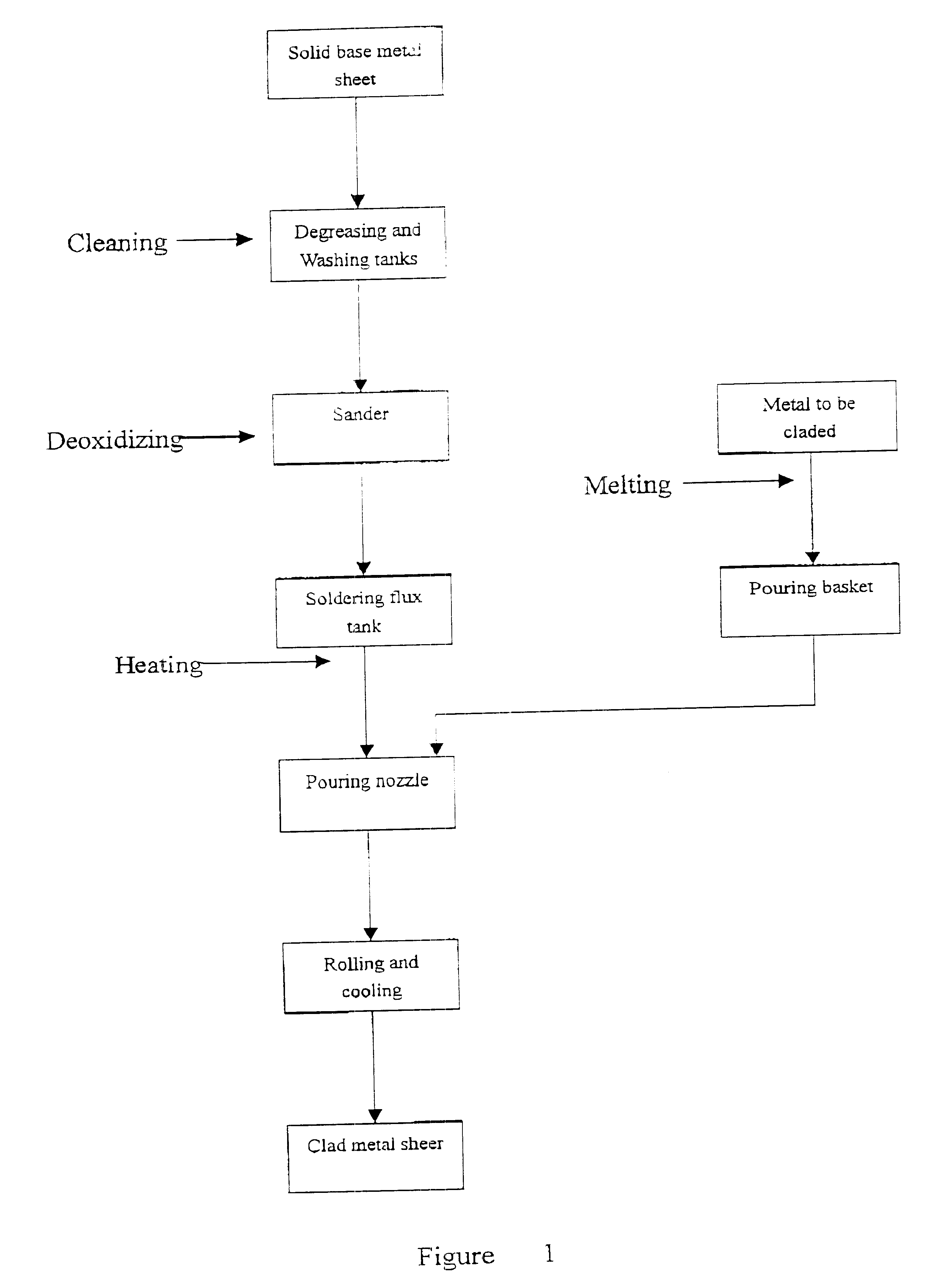
Liquid-solid rolling bonding method for different kinds of metals and the apparatus therefor
InactiveUS6681838B2High bonding strengthSimple procedureHot-dipping/immersion processesMolten casting coatingLiquid metalSurface binding
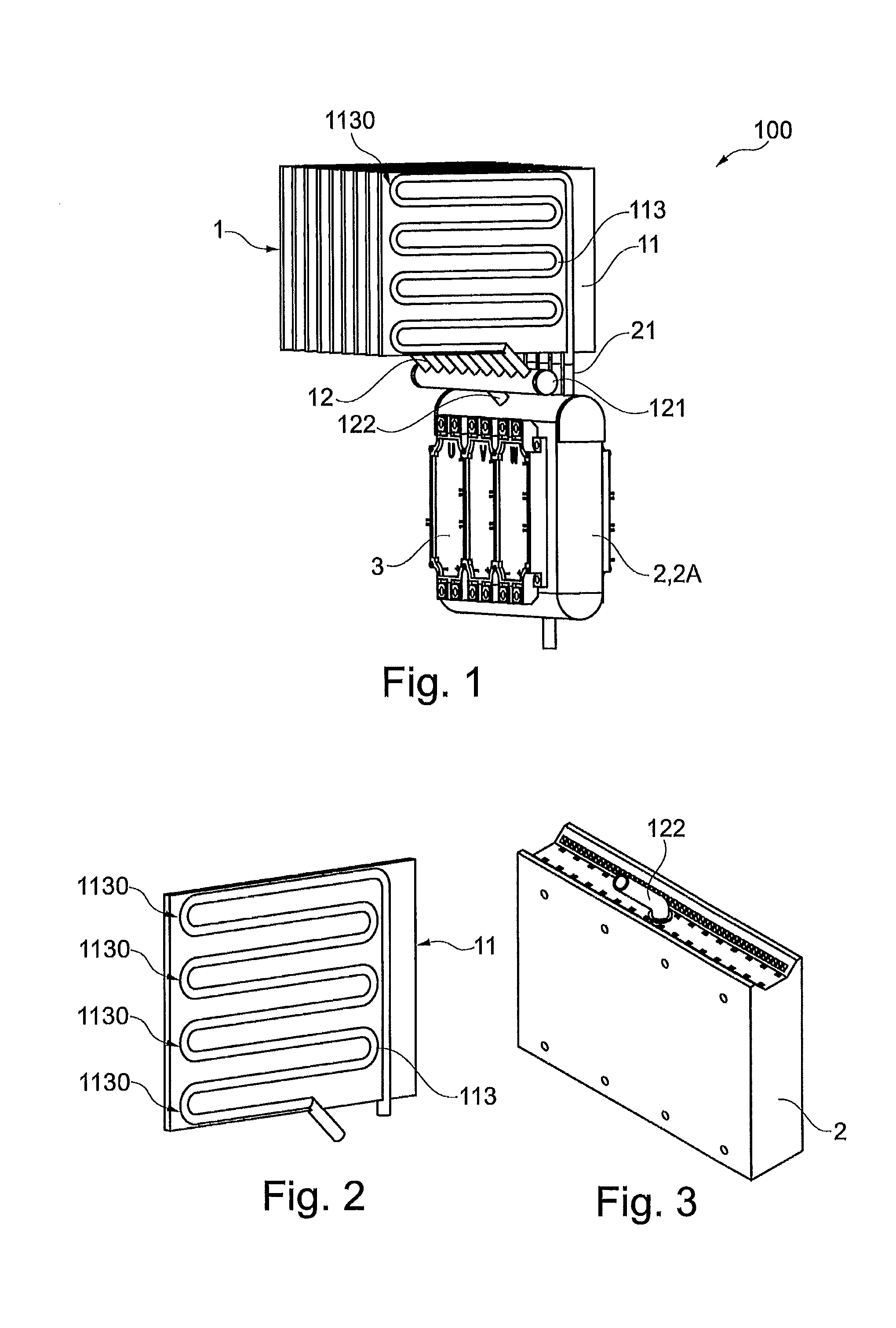
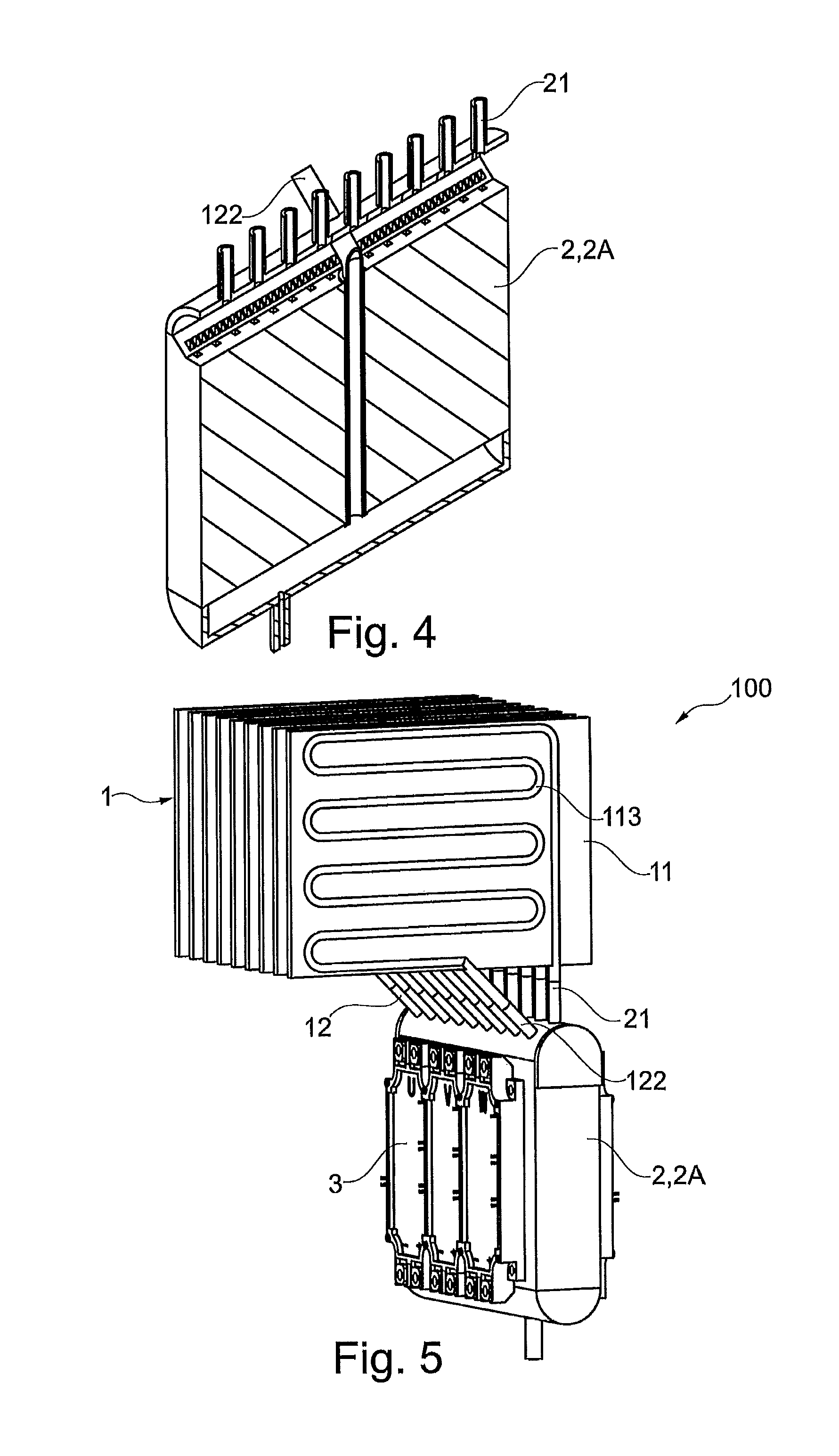
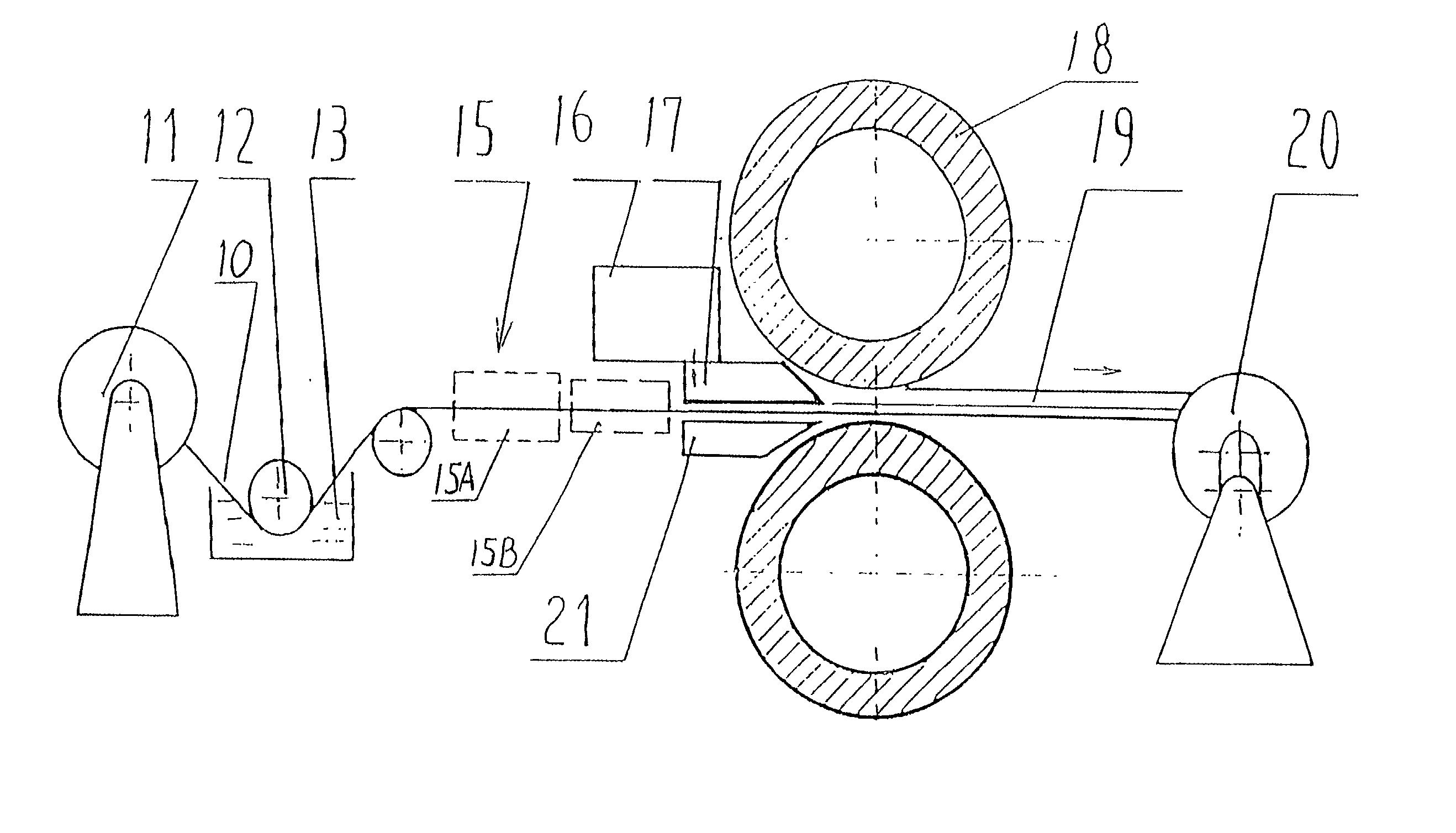
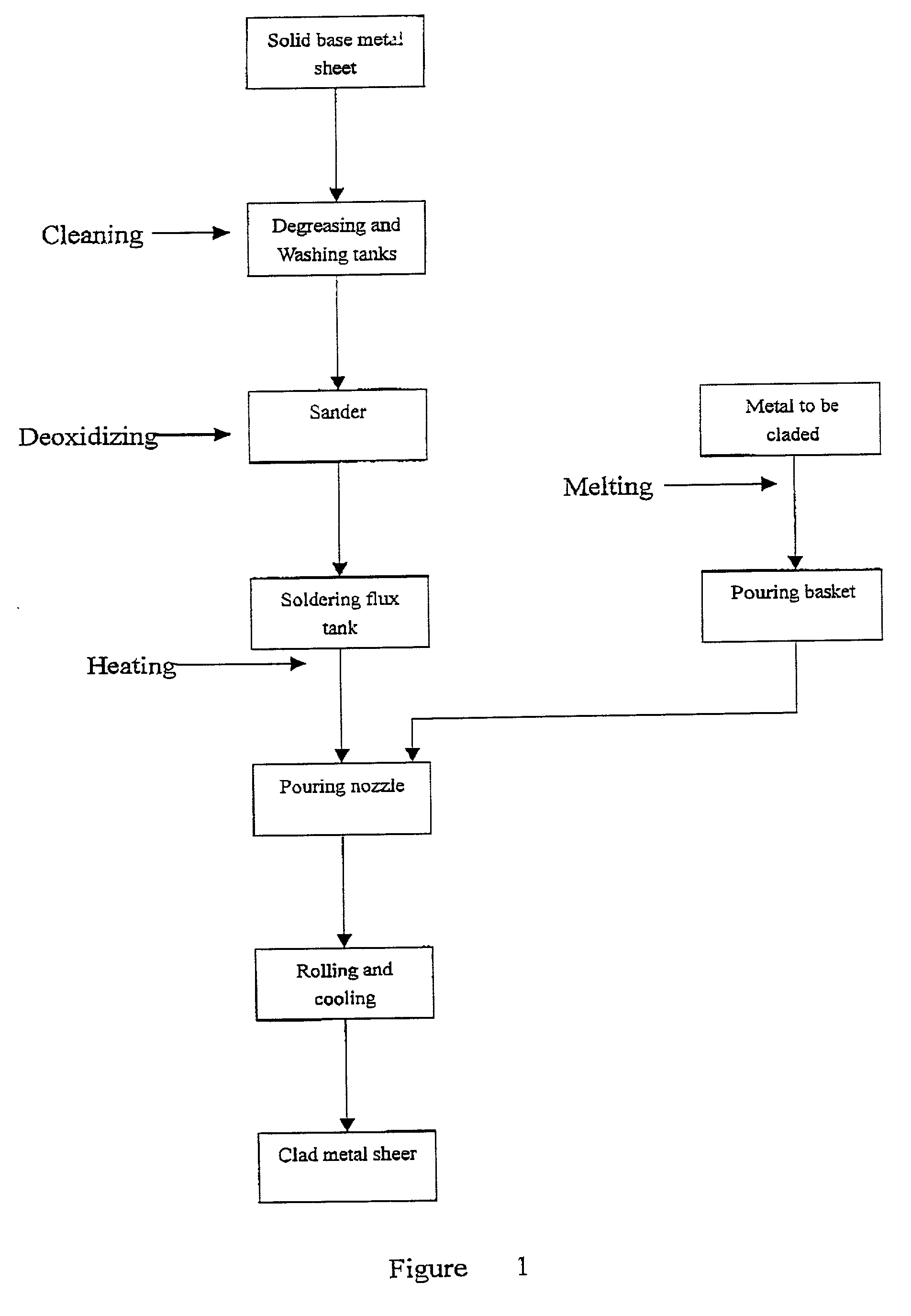
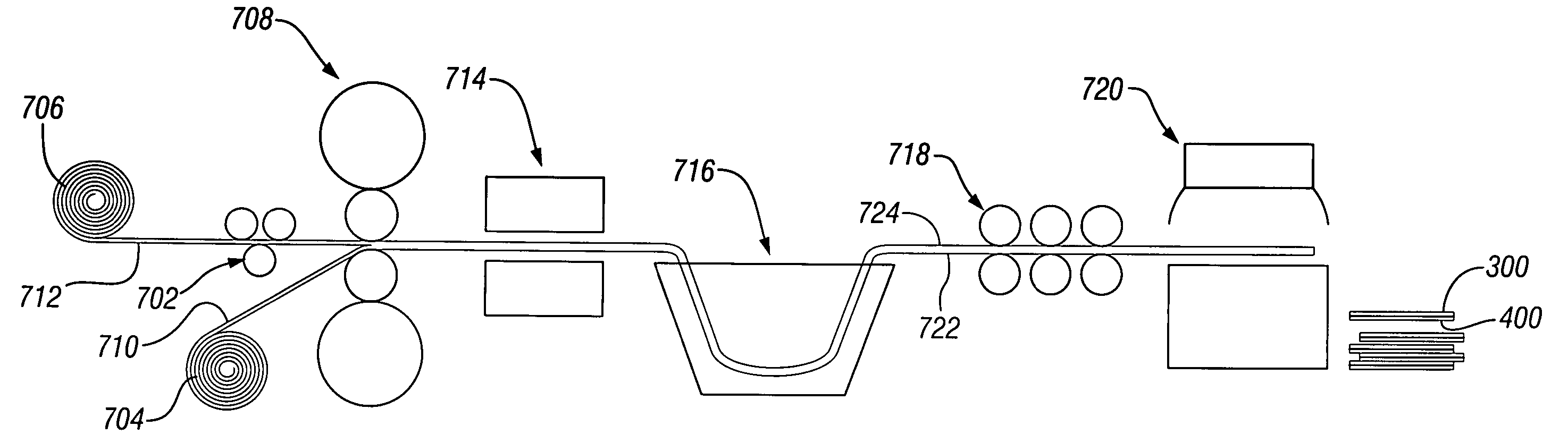
The present invention relates to a liquid-solid rolling bonding method for heterogeneous metals and an apparatus therefor. The method comprises: pouring a liquid metal onto the surface of a heterogeneous solid base metal coated with a soldering flux; rolling the liquid metal and the solid metal under pressure; solidifying the liquid metal and making it bond to the surface of the solid base metal under rapid cooling to realize metallurgical bonding of the two or more metals. The apparatus comprises an unrolling machine, a soldering flux tank, a drying-heating apparatus, a pouring nozzle, an interior water-cooling rollers and a roll-collecting machine arranged in order, a pouring basket is disposed above the pouring nozzle and a base frame is disposed below the pouring nozzle. The present invention has the advantages of high bonding strength, lower production cost, high production efficiency, good product quality, fewer investment for the apparatus and lower consumption of energy. The method of the present invention can replace the convention rolling bonding method in solid-solid phase and is suitable for the production of various clad metal sheets and strip.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV +1
Preparation method of electromagnetic shielding multi-layer composite material in electric vacuum device
InactiveCN102126112AHigh material strengthHigh magnetic screen effectMetal layered productsThermal expansionHigh dimensional
The invention relates to a preparation method of an electromagnetic shielding multi-layer composite material in an electric vacuum device, which belongs to the field of preparation of layered composite materials. The preparation process comprises the following steps: firstly performing large-deformation rolling bonding on oxygen-free copper after surface treatment and an electrical pure iron thin plate, and getting a Cu / Fe / Cu composite foil with higher parallelism and mechanical properties; and then combining and stacking the Cu / Fe / Cu foil with a molybdenum sheet and other low thermal expansion refractory metals, placing in a diffusion welding furnace to perform diffusion welding at a certain temperature and pressure, and further preparing the multi-layer composite material with good magnetic shielding effect, high dimensional precision, strong mechanical properties and good thermal matching. By adopting the new preparation process, not only the problem that the low thermal expansion metals are difficult to compound is solved, but also the advantages of rolling bonding and the diffusion welding process can be fully played, thereby realizing good parallelism among laminated layers, high dimensional precision and excellent mechanical properties of the material, simultaneously having relatively low cost and high production efficiency, and being easy to realize large-scale and industrialized production.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A method for compound centrifugal casting high-speed steel roll
The invention relates to a method for composite centrifugal casting of high-chromium steel rolls, which is characterized in that a semi-steel intermediate transition layer is set between the high-chromium working layer and the ductile iron core, and the chemical composition weight of the semi-steel intermediate transition layer The percentages are: C 1.0~2.4%, Si 0.4~1.5%, Mn 0.4~1.5%, P 0~0.1%, S 0~0.03%, Cr 0~0.2%, Ni 1.0~2.0%, Mo 0~0.2% , and the rest is Fe. The beneficial effects of the invention are: the bonding strength between the high chromium working layer and the core nodular cast iron is improved, and the peeling of the bonding layer of the high chromium composite cast steel roll and the occurrence of roll breaking accidents are prevented.
Owner:ANSTEEL HEAVY MACHINERY CO LTD
Aluminum Clad Steel Composite for Heat Exchanger Tubes and Manifolds
InactiveUS20080099183A1Well formedEasy to joinReinforcing meansMetal-working apparatusCarbon steelSteel belt
A brazable composite metal material for a heat exchanger tube or manifold, a method of making the tube or manifold, and a heat exchanger made therefrom. The composite metal suitable for making the heat exchanger tube or manifold has one of an aluminized carbon steel, galvanized carbon steel, or steel wire mesh core roll bonded to at least one outer layer of a brazable aluminum alloy, such as type 3003 aluminum alloy. The method of making the heat exchanger tube includes the steps of (a) providing a core of one of an aluminized carbon steel, galvanized carbon steel, or steel wire mesh sheet or strip material; (b) placing at least one sheet or strip of brazable aluminum alloy material on the steel core; (c) roll bonding the aluminum alloy material to the aluminized surface of the steel core to form a roll bonded composite sheet or strip material; (d) forming the composite material to a desired configuration; and (e) joining abutting aluminum edges of the formed composite to form a fluid tight joined edge defining a shape having an open interior.
Owner:CLAD METALS
Chassis and method for producing chassis
ActiveCN103858529AImprove corrosion resistanceImprove thermal conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAustenitic stainless steelChassis
This chassis (2) comprises a clad material obtained by roll bonding a first layer (21), which is formed from an austenitic stainless steel, a second layer (22), which is formed from Cu or a Cu alloy and which is laminated on the first layer, and a third layer (23), which is formed from an austenitic stainless steel and which is laminated on that side of the second layer which is opposite the first layer, wherein the thickness of the second layer is 15% or more of the thickness of the clad material.
Owner:PROTERIAL LTD
Composite technique for rolling semi-solid state copper-lead bearing alloy/steel bi-metal
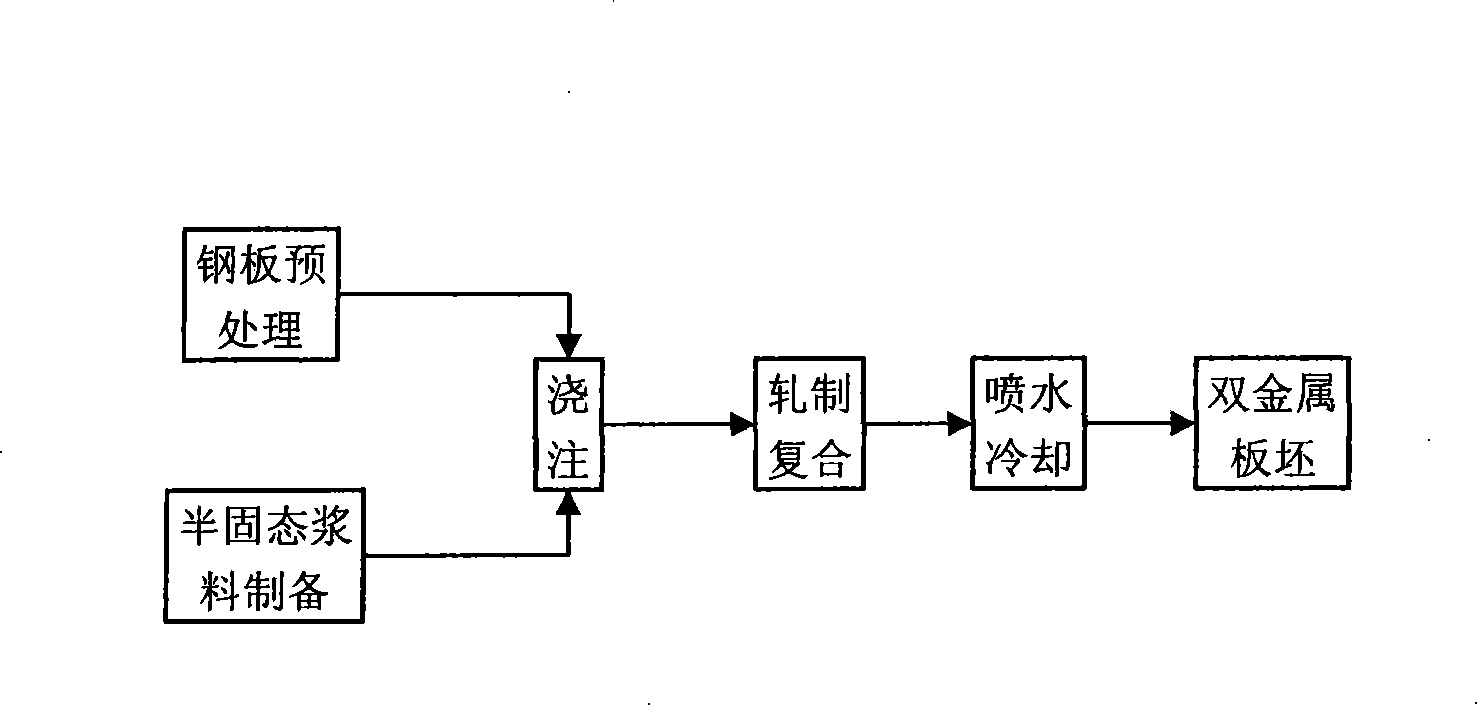
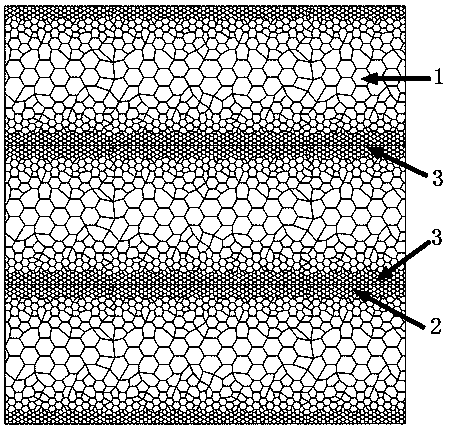
InactiveCN101244430ASolve the problem of lead segregationPromote interdiffusionTemperature control deviceWork treatment devicesRare earthComposite plate
The invention relates to a roll-bonding process for semisolid copper-lead bearing alloys / steel bimetals. The weight content percentage of the lead in the copper-lead bearing alloy is 10.0 to 30.0%. In order to refine the crystalline grain of the lead and improve the mechanical property of the alloy, sulfur, tin, nickel, manganese, rare earth and other the third alloy elements can be added in the copper-lead alloy. The process comprises four steps: pretreatment of steel plates, preparation of semisolid sizing agent, roll bounding and water cooling. The detailed process comprises the following steps: performing mechanical agitation to the melted copper-lead bearing alloys at 930 to 1050 DEG C to obtain the semisolid sizing agent; pouring the semisolid sizing agent on the pretreated steel plates; synchronously feeding the semisolid copper-lead bearing alloys and solid steel plates in to a mill for rolling; spraying water for cooling to obtain the bimetallic composite plate. The invention effectively overcomes the defect of lead segregation in the production of the copper-lead bearing alloys in the prior art, therefore, metallographic structure with fine lead particle and even distribution is obtained. According to mechanical test results, the interfacial shear strength of the copper-lead bearing alloys / steel bimetallic slabs prepared using the process is more than 60Mpa, increased by about 10Mpa.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Process for preparing magnesium alloy with layered gradient structure
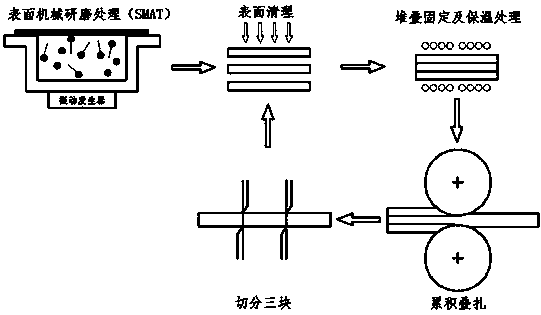
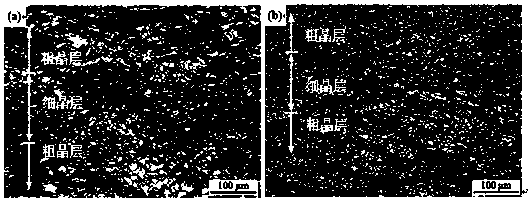
InactiveCN107649514AHigh surface hardnessHigh yield strengthAuxillary arrangementsMetal rolling arrangementsRoom temperatureMaterials processing
The invention relates to the field of metal material processing, in particular to a process for preparing magnesium alloy with a layered gradient structure. The process includes the following steps that a, two or more magnesium alloy plates in the same specification are selected, and the magnesium alloy plates are subjected to surface mechanical attrition treatment; b, the bonding surfaces of eachplate are cleaned to remove oxide layers and dirt; c, the processed plates are laminated together and tightly jointed so as to reach the standard that there is no relative movement between the plates; d, the laminated plates are put into an incubator, and heat preservation is carried out for 5-30 min after the temperature is raised to the set temperature of 150-450 DEG C; e, the plates are takenout and immediately put in a rolling mill to be subjected to rolling with the rolling reduction of 30%-70%, and one-time pack rolling is completed; and f, the plates are subjected to air cooling to reach the room temperature. The process is simple and convenient, safe and reliable, low in production cost and suitable for improving the comprehensive mechanical property of the magnesium alloy platesin industrialized production.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Rolling level thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a rolling level thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer and a preparation method thereof. The thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer is mainly prepared of the following components in parts by weight: polymeric glycol, isocyanate mixture, diethylene glycol, nano SiO2 modified polypropylene and hydroxyethyl acrylate, wherein the polymeric glycol is a polytetramethylene glycol and adipic acid 1,4-butyl glycol ether glycol mixture; the isocyanate mixture is a toluene diisocynate and hexamethylene diisocyanate mixture. Under the synergistic effect of polytetramethylene glycol and adipic acid 1,4-butyl glycol ether glycol and the synergistic effect of toluene diisocynate and hexamethylene diisocyanate, the prepared rolling level thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer is high in processing performance and resilience performance due to nano SiO2 modified polypropylene and hydroxyethyl acrylate serving as a crosslinking agent; meanwhile, the phenomenon of roll bonding can be avoided in a working process.
Owner:DONGGUAN JIXIN POLYMER SCI & TECH
Method for producing metal laminate material
InactiveCN106102978ASufficient binding strengthImprove productivityElectric discharge tubesLaminationSurface layerBonding strength
Owner:TOYO KOHAN CO LTD
Cooling module for cooling electronic components
InactiveUS8913386B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEvaporationEngineering
Owner:ABB RES LTD
Liquid - solid rolling bonding method for different kinds of metals and the apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20020069998A1High bonding strengthSimple procedureHot-dipping/immersion processesMolten casting coatingLiquid metalSurface binding
The present invention relates to a liquid-solid rolling bonding method for heterogeneous metals and an apparatus therefor. The method comprises: pouring a liquid metal onto the surface of a heterogeneous solid base metal coated with a soldering flux; rolling the liquid metal and the solid metal under pressure; solidifying the liquid metal and making it bond to the surface of the solid base metal under rapid cooling to realize metallurgical bonding of the two or more metals. The apparatus comprises an unrolling machine, a soldering flux tank, a drying-heating apparatus, a pouring nozzle, an interior water-cooling rollers and a roll-collecting machine arranged in order, a pouring basket is disposed above the pouring nozzle and a base frame is disposed below the pouring nozzle. The present invention has the advantages of high bonding strength, lower production cost, high production efficiency, good product quality, fewer investment for the apparatus and lower consumption of energy. The method of the present invention can replace the convention rolling bonding method in solid-solid phase and is suitable for the production of various clad metal sheets and strip.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV +1
Lithium supplement device for pole piece and lithium supplement method
PendingCN109360943ASolve the sticky rollerSolve problems such as adhesionCell electrodesLithiumBiochemical engineering
The invention provides a lithium supplement device for a pole piece and a lithium supplement method of the device. The device is provided with a sealing shell, a pole piece unrolling assembly, a lithium liquid coating assembly, a cooling assembly, a normal-temperature roll-in assembly and a pole piece rolling assembly, and the pole piece unrolling assembly, the lithium liquid coating assembly, thecooling assembly, the normal-temperature roll-in assembly and the pole piece rolling assembly are arranged in the sealing shell and connected in sequence; the lithium liquid coating assembly comprises a pair of rollers composed of an intaglio roller and a hot back roller, and a lithium liquid storage groove is formed below the intaglio roller and connected with a lithium liquid production devicethrough a pipe. The lithium supplement device is simple in structure, the equipment cost is greatly lowered, the problems such as rolling bonding and adhesion during pressing fit of a lithium band arecompletely solved, the consistency of lithium supplement is greatly improved, the production high-quality rate is greatly increased, and the production efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:CONTEMPORARY AMPEREX TECH CO
Dissimilar metal rolling bonding method with embedded type rib and groove interlocking
ActiveCN111318565AHigh bonding strengthIncrease binding areaMetal rolling stand detailsRollsComposite plateUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a dissimilar metal rolling bonding method with embedded type rib groove interlocking, and belongs to the field of bi-metal composite plate preparing. The method comprises the following steps of S1, single-side convex rib rolling, wherein a flat roller and a figure roller with a groove are matched, a first plate blank is rolled, and a convex rib is formed on the single sidesurface of the first plate blank; S2, preassembling rolling, wherein a second plate blank and the first plate blank are embedded, the first plate blank is embedded into the second plate blank to formchain type connection, and an embedded composite workpiece is formed; and S3, asymmetrical rolling, wherein the embedded composite workpiece is subjected to asymmetrical forming rolling, and a dissimilar metal composite plate is formed. The problem that in the prior art, the bonding strength of a dual-metal composite plate is low totally can be solved, the rolling bonding method that embedded typeribs and grooves are manufactured in dissimilar metal contact, and through asymmetrical rolling, rib and groove interlocking is achieved is adopted, measures of combining mechanical type connection,generation of an interlocking structure and increasing the diffusion rate are used, and the interface contact strength can be sufficiently improved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Metal Laminate
InactiveUS20080251389A1Improve corrosion resistanceLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingSuperimposed coating processUltimate tensile strengthElectroplating
A method for making a metal laminate comprising at least one plating step and at least one cold roll bonding step. A metal laminate comprising a plurality of alternating structural layers and non-structural layers, where the structural layers contribute significantly to the overall strength of the metal laminate, while the non-structural layers do not contribute significantly to the overall strength of the metal laminate, but serve to bind the structural layers together.
Owner:KINGSTON WILLIAM RUSSELL
Use of a metal composite material in a vehicle structure
InactiveCN102015423AFlexible settingsReduce weightThin material handlingMetal layered productsUltimate tensile strengthMaterials science
The invention relates to a use of a multi-layer metal composite material, which is produced by way of roll-bonding and can be wound, in a vehicle structure, particularly a body structure. It is the object of the invention to provide a use of a metal composite material as an alternative to monolithic materials. The object is achieved in that the composite material is a lightweight composite material and comprises three layers of a steel alloy, wherein at least one of the layers is made of a steel alloy having higher strength or maximum strength.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP STEEL EURO AG
Environmentally protected reinforcement dowel pins and method of making
ActiveUS7553554B2Provide protectionMaintain integrityPaving detailsBuilding reinforcementsZinc alloysSacrificial metal
Owner:ARTAZN LLC
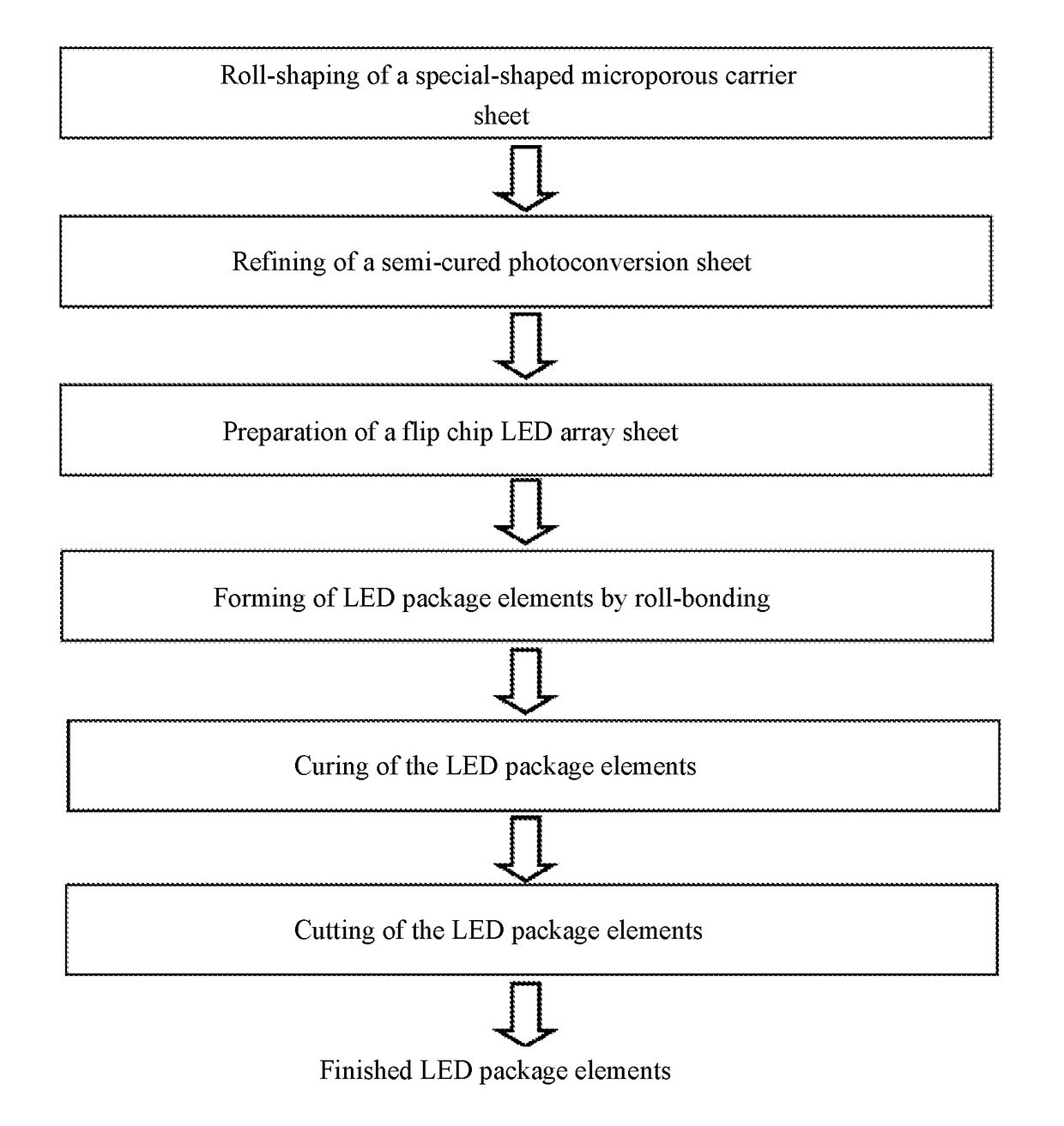
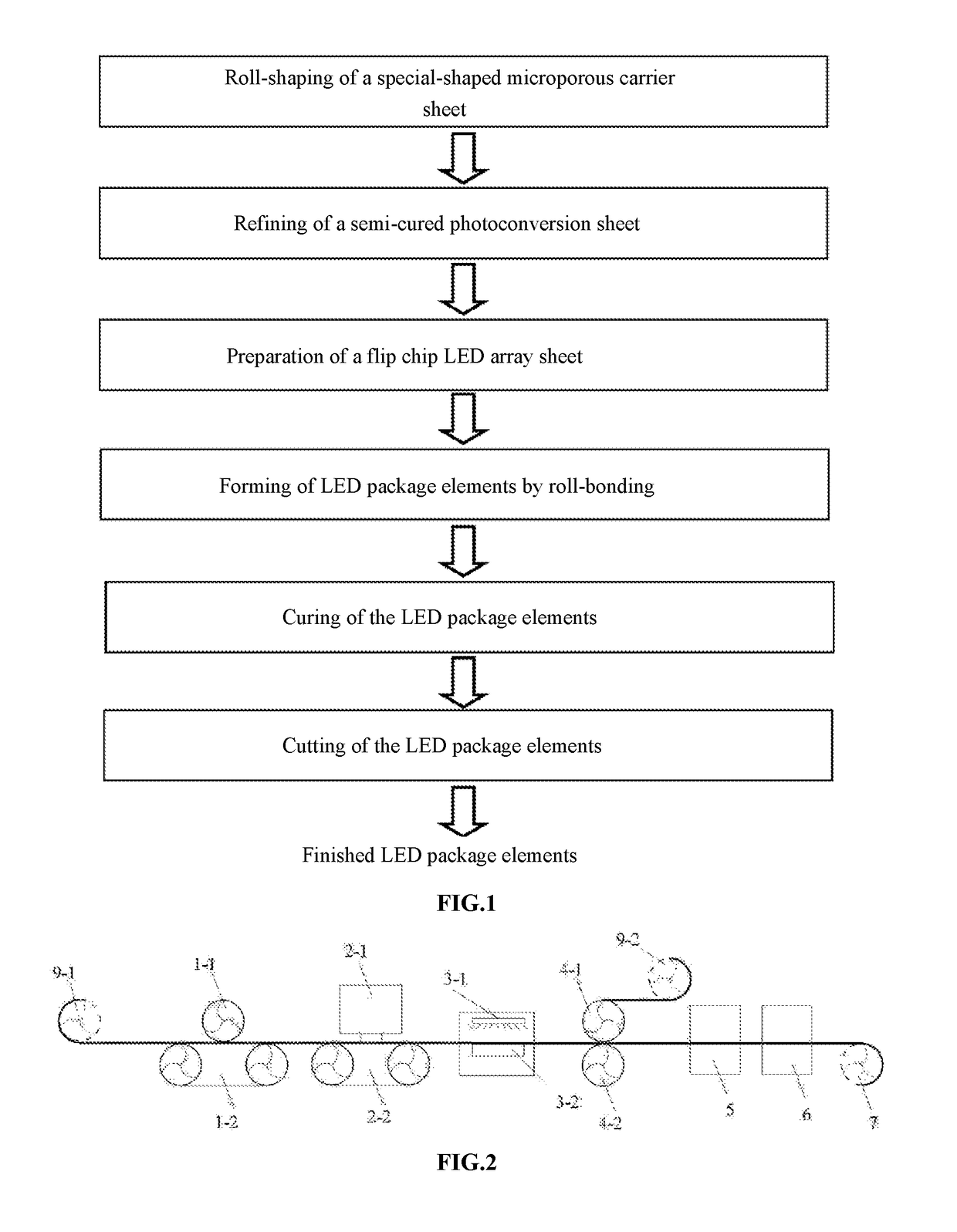
Process Method for Refining Photoconverter to Bond-Package LED and Refinement Equipment System
ActiveUS20180198032A1Improve production efficiencyHigh yieldSemiconductor devicesLed arrayEngineering
Provided are a process method for bond-packaging an LED using a refined photoconverter, and a refining equipment system. The process method includes the following continuous process flow: roll-shaping of a special-shaped microporous carrier sheet, refining of a semi-cured photoconversion sheet, preparation of a flip chip LED array sheet, forming of LED package elements by roll-bonding, curing of the LED package elements, and cutting of the LED package elements. The present invention has a significant advantage of a refined photoconverter, and especially can meet a requirement of a continuous process flow of bond-packaging an LED using an organic silicone resin photoconverter, so as to enhance the production efficiency and yield of LED packages in industrialized batch production.
Owner:JIANGSU CHERRITY OPTRONICS CO LTD
Method for bonding gas barrier film and electronic device, and electronic device and method for producing same
InactiveUS20110068682A1Improve production efficiencySimple methodDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamination ancillary operationsDevice formElectron
A method for bonding a gas barrier film and an electronic device, comprising continuously feeding a film composite that contains a gas barrier film having a support and a gas barrier layer, and an adhesive layer; blanking or slitting a part of the film composite to form a wire lead-out part therein; and continuously roll-bonding the film composite to a substrate with an electronic device formed thereon; wherein the feeding of the film composite, the forming of the wire lead-out part and the roll-bonding are carried out through in-line operation.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Package based on technology that frame is connected through bonding wires and manufacturing process of package
InactiveCN103346135ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSilver platePlastic packaging
The invention discloses a package based on the technology that a frame is connected through bonding wires and a manufacturing process of the package. The package comprises a chip, a plastic packaging body, a silver-plated layer and the bonding wires. The silver-plated layer is composed of silver-plated layer sections which are independent from each other, the chip is located on a part of the silver-plated layer, the chip is connected with the portions, without the chip, of the silver-plated layer through the bonding wires, the plastic packaging body wraps the chip, the silver-plated layer and the bonding wires, and the chip, the silver-plated layer and the bonding wires constitute a power source and signal channel of a circuit. The package further comprises metal bumps. The manufacturing process comprises silver plating of the frame, wafer thinning, scribing, assembly of the chip, manufacturing of the metal bumps, pressure welding, plastic packaging, corrosion of the frame, cutting and packing, wherein the step of manufacturing of the metal bumps can be eliminated. According to the package and the manufacturing process thereof, due to the fact that pressure welding is directly conducted on the metal bumps after electrosilvering or the method of direct wiring after electrosilvering is used, design of a frame graph is finished when the frame is manufactured, the manufacturing period is shortened, interconnection of the chip and carriers is achieved better, the higher I / O density is achieved, and cost is lower.
Owner:CHINA CHIPPACKING TECH
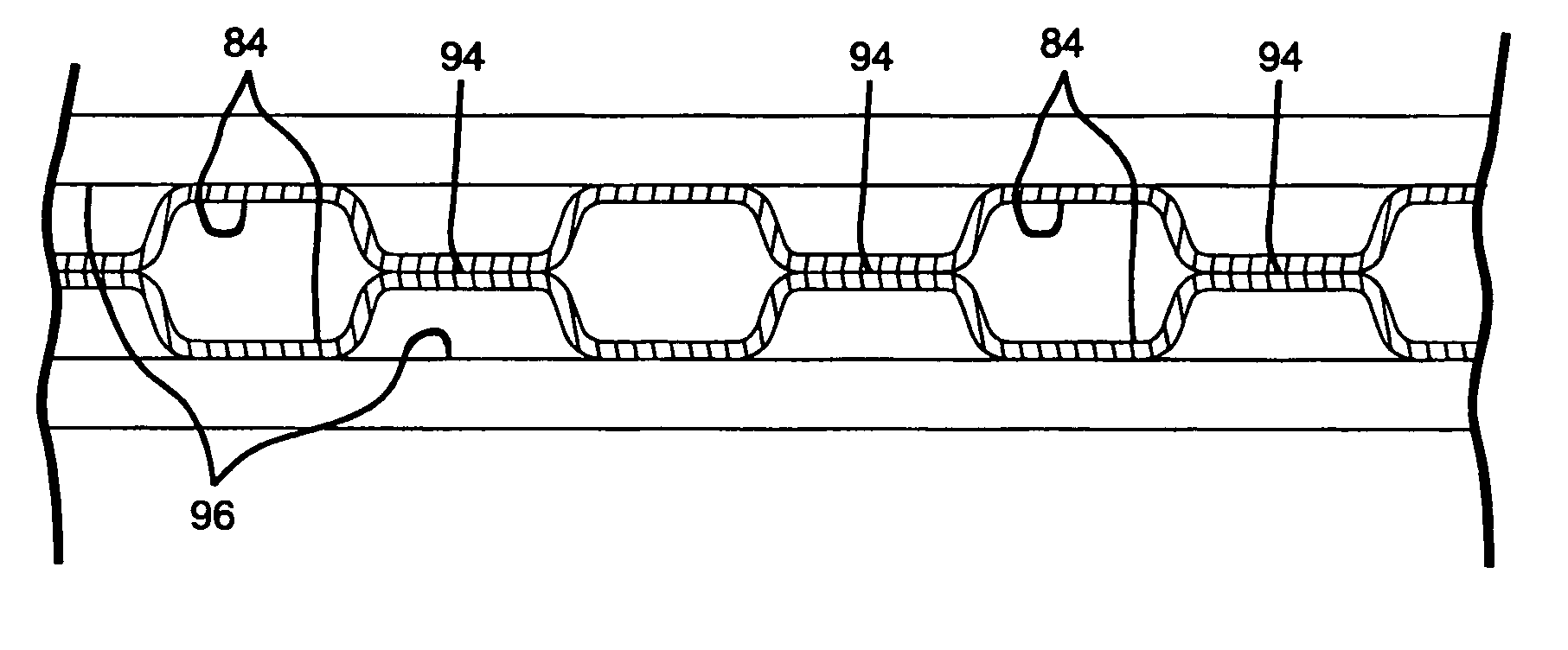
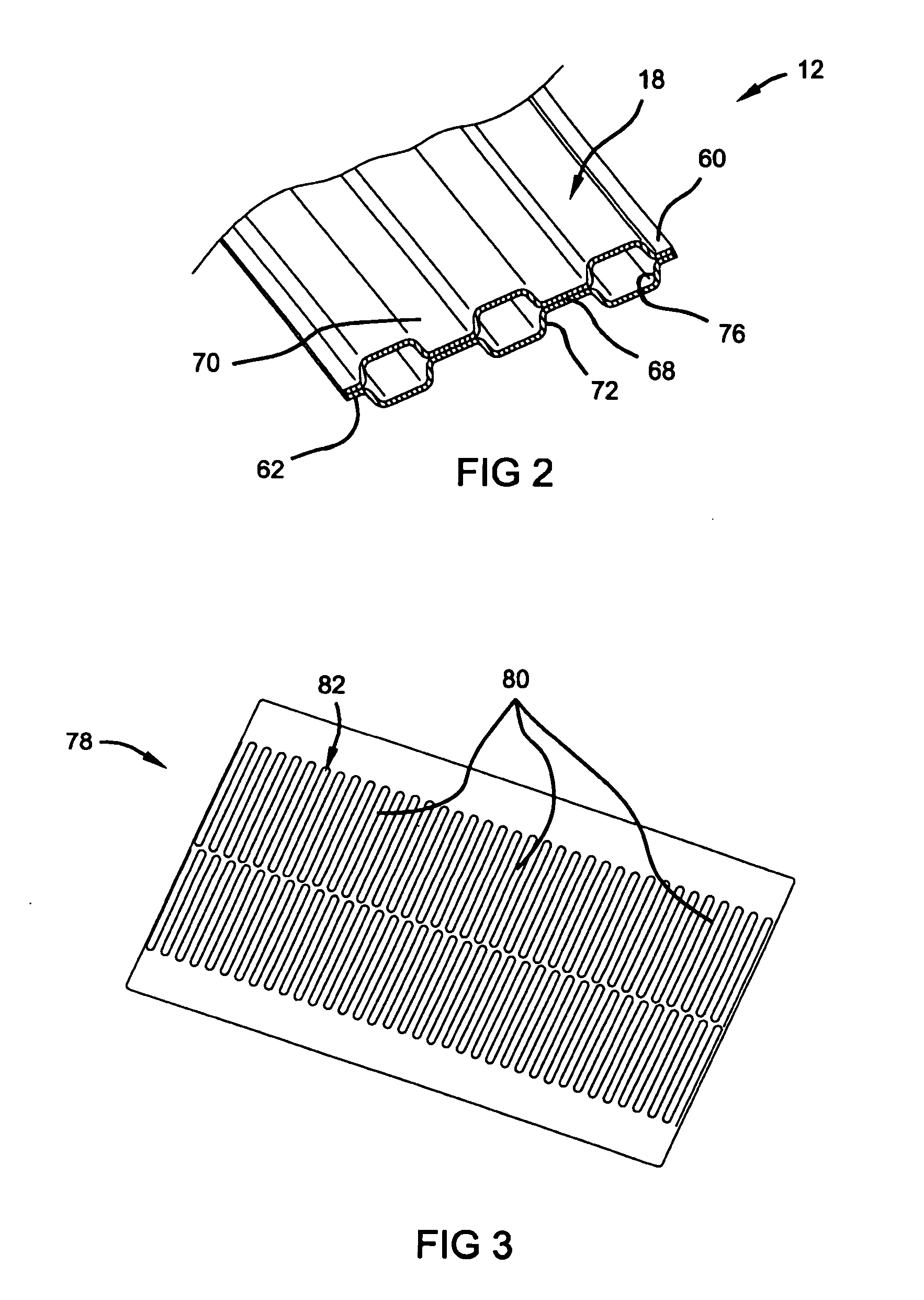
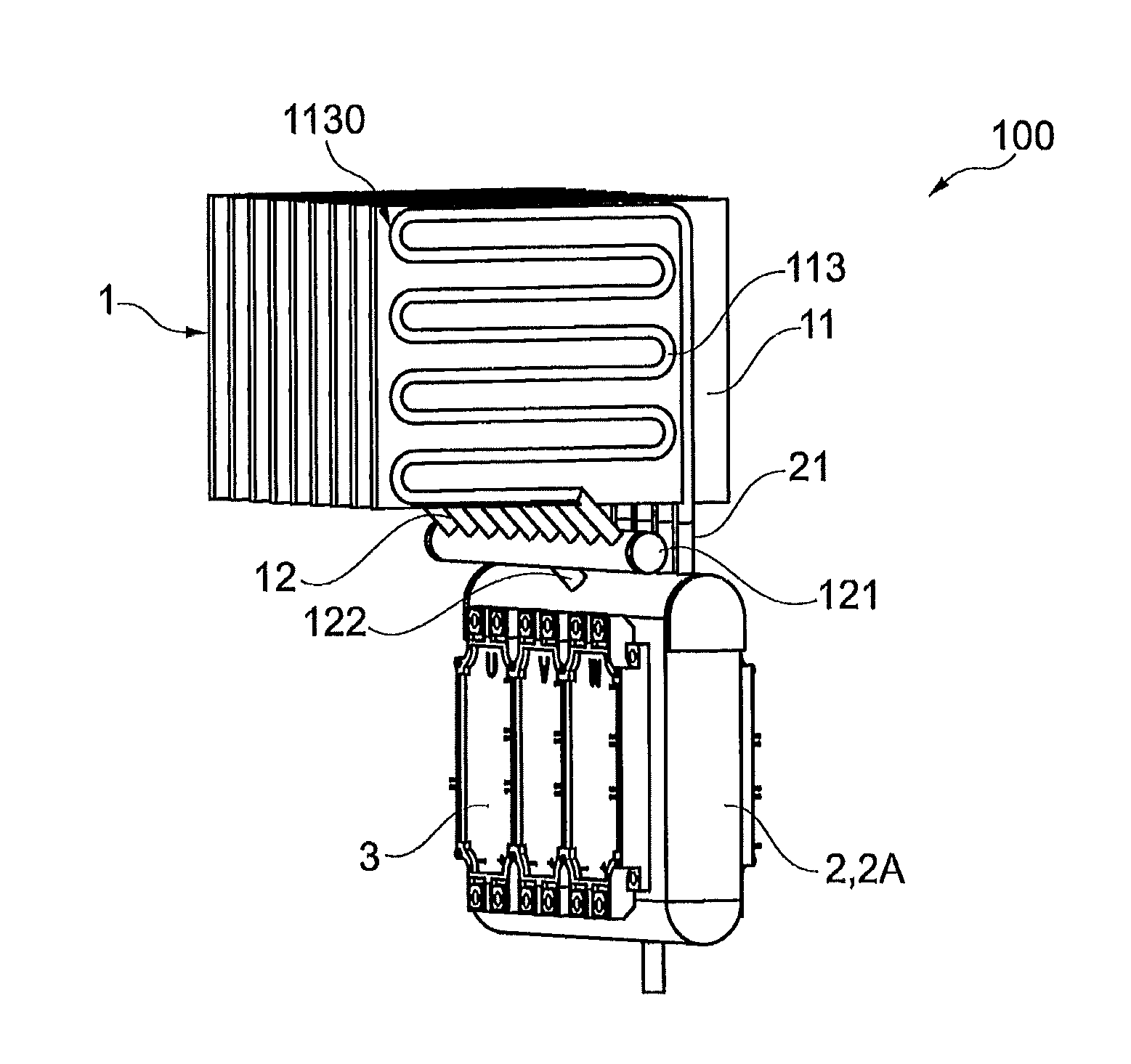
Roll bonding of bipolar plates
ActiveUS7451907B2High bonding strengthWelding/cutting media/materialsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesHydrogenFuel cells
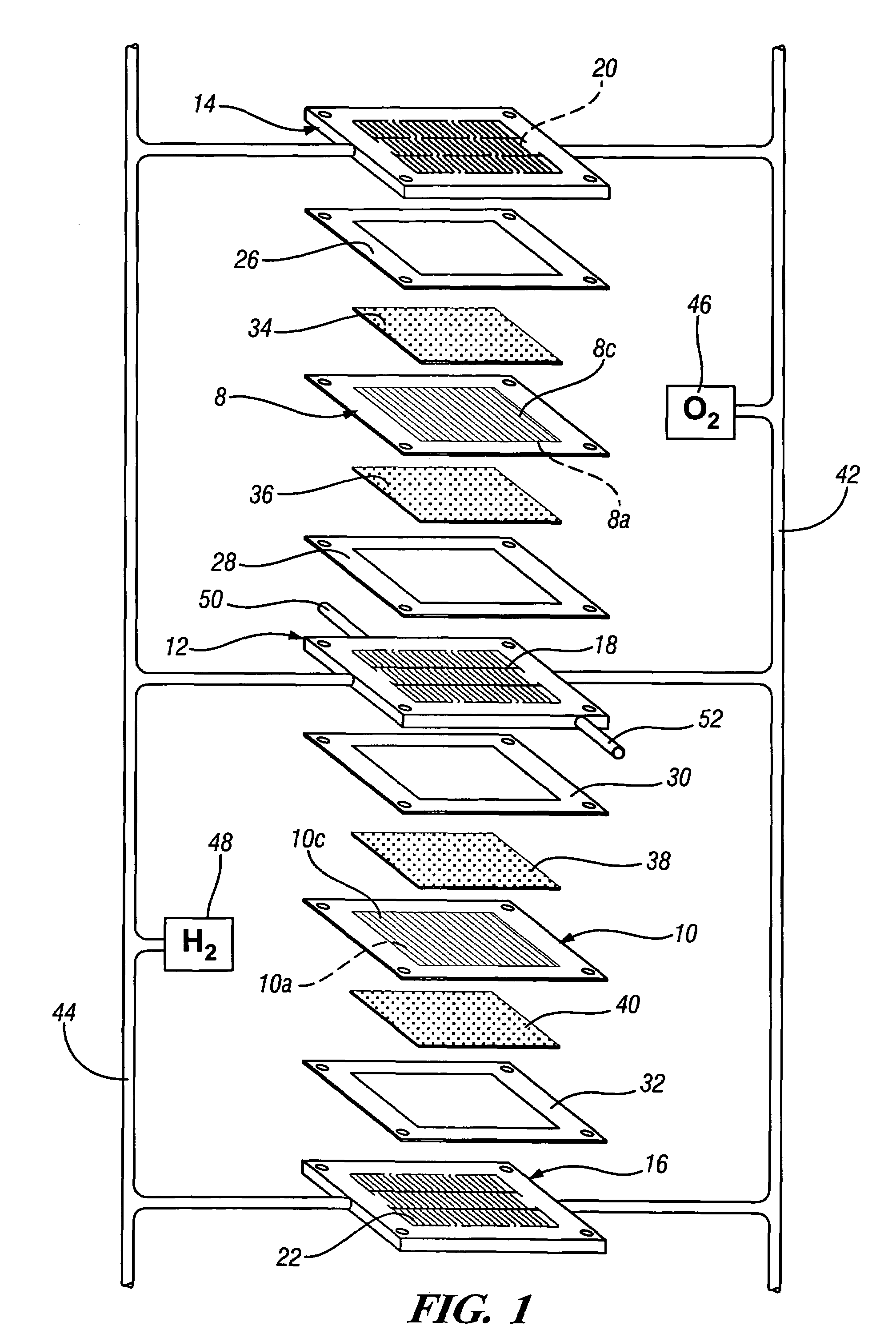
A current collector plate, also called a bipolar plate, for a fuel cell includes two facing metal sheets with fluid channels for the fuel (often hydrogen) on the non-facing side of one sheet and fluid channels for air on the non-facing side of the other sheet. Such a plate is made by applying a patterned coating of particles of a soft and reactive metal to at least one of the sheets and rolling them together so that the soft metal particles deform and interact with the facing sheets to selectively join them at the patterned areas. Pressurized fluid is introduced between the sheets to expand non-bonded portions and define the fluid channels.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Heat spreader and method for manufacturing the same
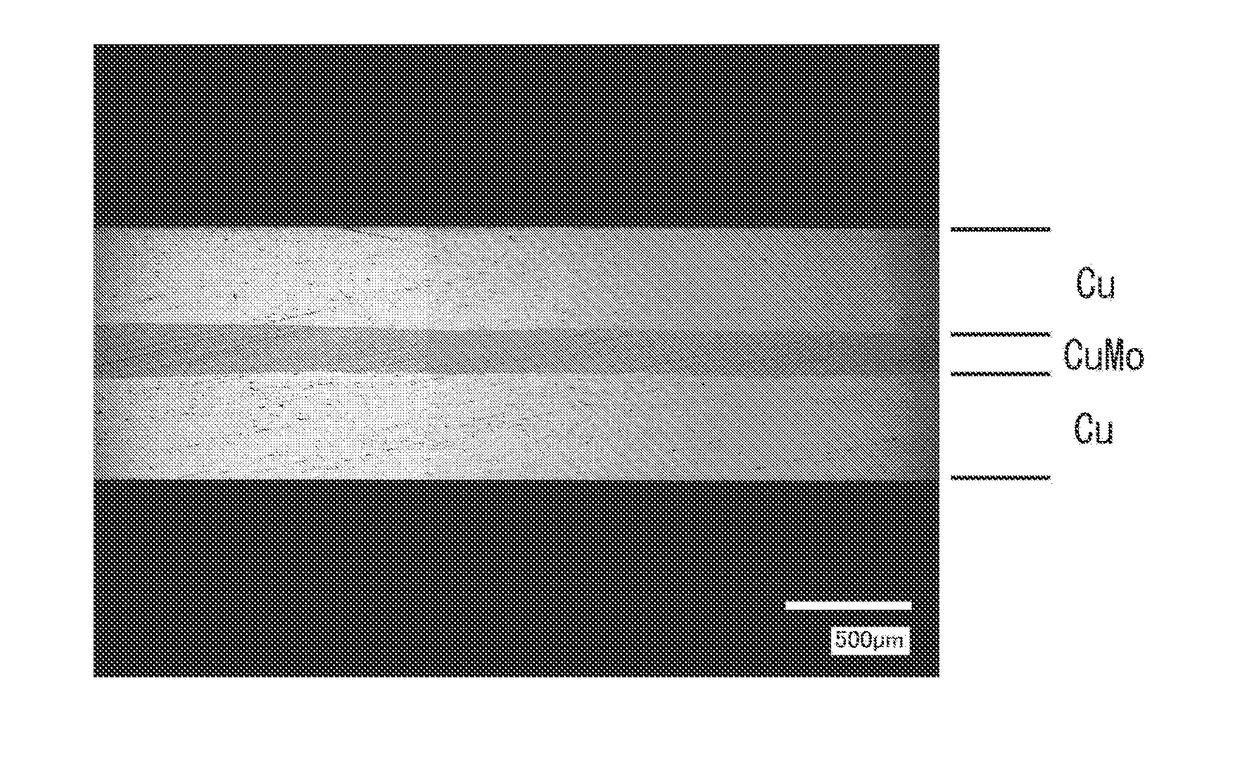
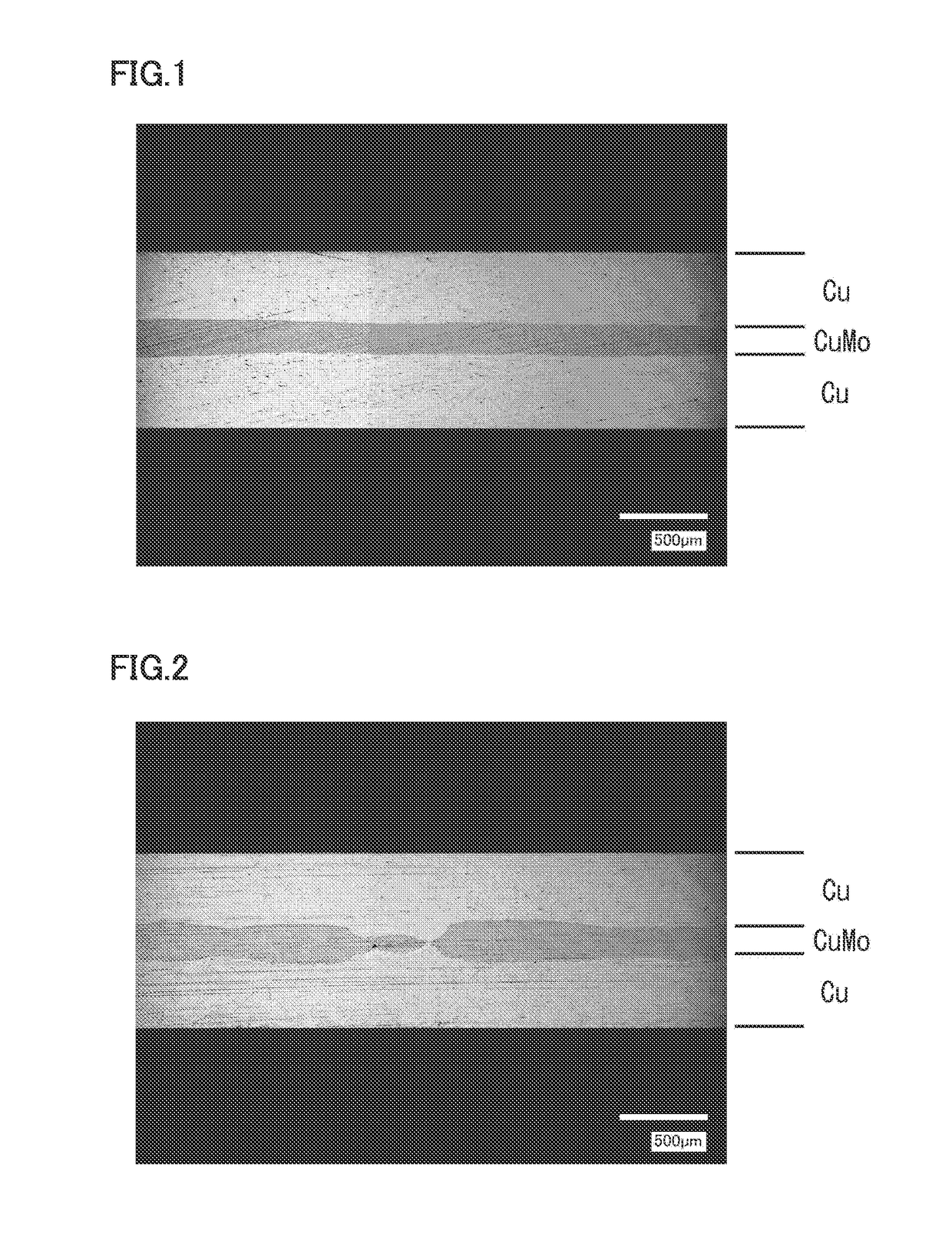
ActiveUS20170198991A1Suppressing variation in Cu-MoMinimize changesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMetallurgyHeat spreader
[Problem] To provide a heat spreader capable of removing heat from an element more efficiently and immediately than an existing one, and also capable of satisfactorily responding to further enhancement in performance and output of various apparatuses, and a method for efficiently manufacturing the same. [Solution] A heat spreader includes a Cu—Mo layer made of a Cu—Mo composite material and having an average thickness of less than or equal to 0.6 mm and a variation in thickness of less than or equal to 0.1 mm, and a Cu layer directly stacked on each of both surfaces thereof. A method for manufacturing the heat spreader includes planarizing a plate material of the Cu—Mo composite material constituting the Cu—Mo layer, and roll-bonding a Cu plate constituting the Cu layer to each of both surfaces thereof.
Owner:ALLIED MATERIAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com