Method for identifying multi-element characteristic spectrum peaks in energy dispersion X-ray fluorescence spectrum
A technology of energy dispersion and fluorescence spectroscopy, which is applied in the field of X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy detection, can solve the problems of inability to judge and identify spectral peaks, and cannot accurately explain the simultaneous existence of spectral peaks, so as to achieve the effect of accurate identification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
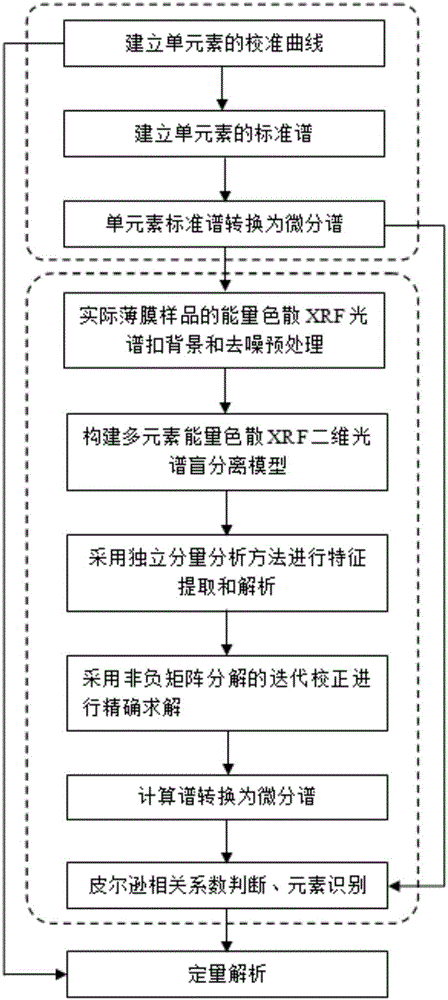
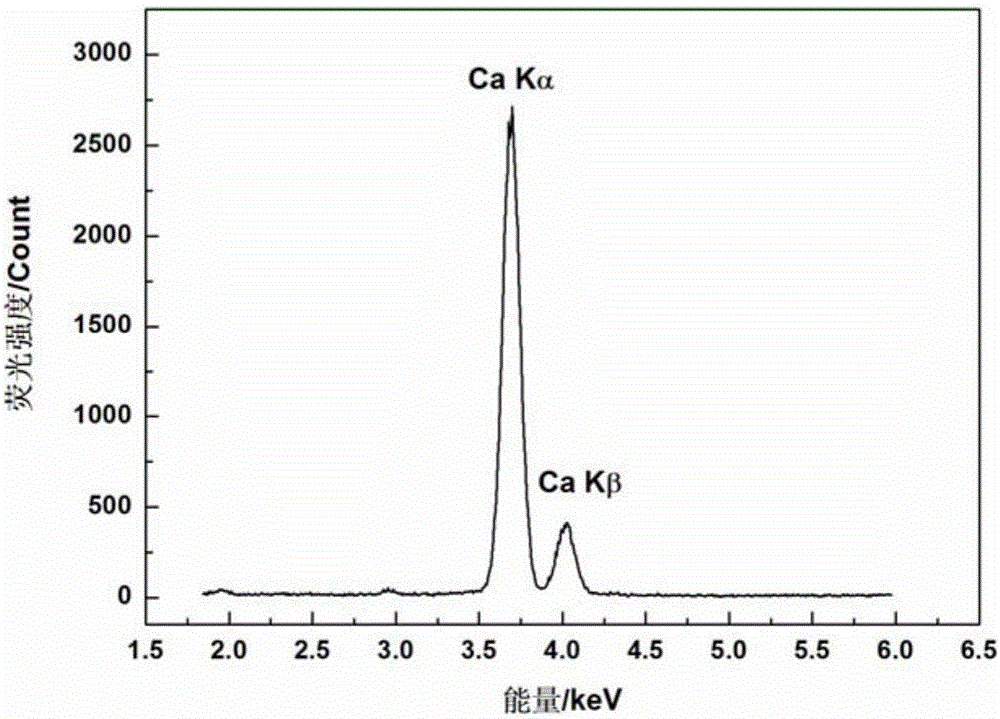
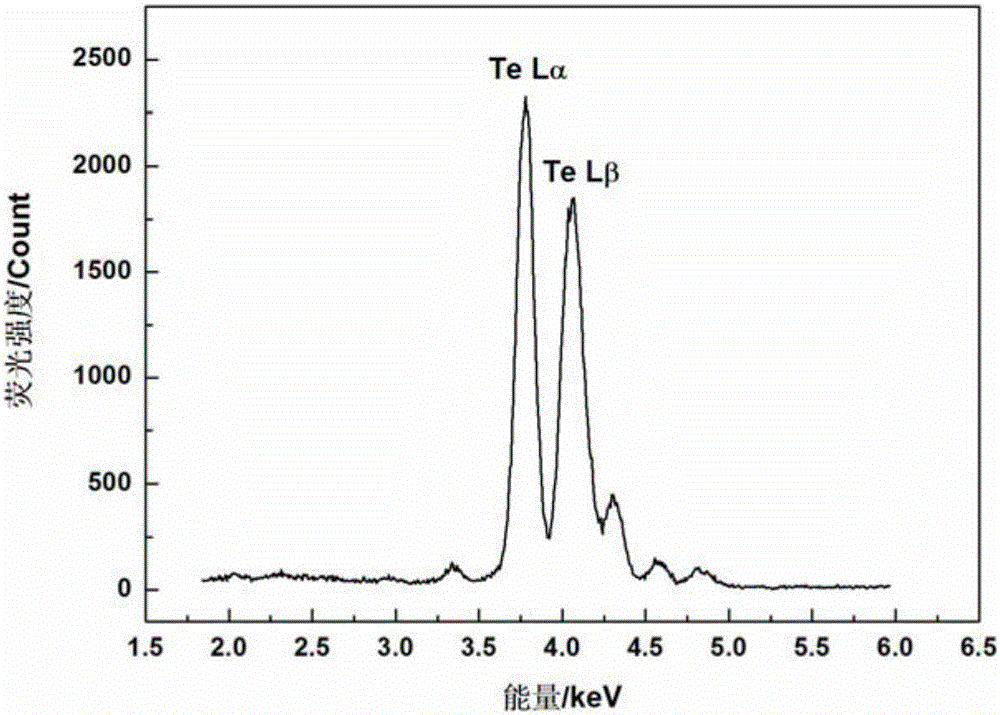
[0061] This embodiment takes the energy dispersive XRF spectrum of calcium (Ca) element and tellurium (Te) element and the energy dispersive XRF spectrum of a film sample mixed with the two elements as examples. In the energy dispersive XRF spectrum, the energy dispersive XRF spectrum of Ca element and Te element The peak-to-peak energies of the characteristic spectra are shown in Table 2:
[0062] Table 2: Peak energy of characteristic spectrum peaks of Ca element and Te element
[0063]
[0064] Among them, the peak-to-peak energies of Kα and Kβ characteristic spectra of Ca element are very close to the peak-to-peak energies of Lα and Lβ characteristic spectra of Te element, and the energy differences are 0.08keV and 0.02keV, respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com