A Method for Evaluating Drying Stress of Sawn Timber for Timber Quality Control
A technology for wood drying and evaluation methods, which is applied in the direction of wood testing, measuring devices, and material inspection products, and can solve problems such as low technical precision, inability to control drying quality, and shorten drying cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0024] Specific embodiment one: a kind of sawn timber drying stress evaluation method for timber quality control comprises the following steps:
[0025] Step 1: Obtain the free drying shrinkage strain ε based on the principle of wood drying rheology fs The calculation formula is:
[0026] ε fs =ε N +ε e +ε ve +ε ms (1)
[0027] where the ε N is the shrinkage strain, ε e is the instantaneous elastic strain, ε ve is the time-varying viscoelastic strain, ε ms is the mechanically adsorbed creep strain associated with wood moisture changes;
[0028] Step 2: Obtain the mechanical adsorption creep strain difference between the wood surface layer and the core layer area according to Step 1;
[0029] Step 3: Obtain the relationship between the drying stress and the mechanical adsorption creep strain parameters of the wood surface and core regions according to Step 2;
[0030] Step 4: According to Step 3, the gradient variable corresponding to the difference of drying stres...
specific Embodiment approach 2
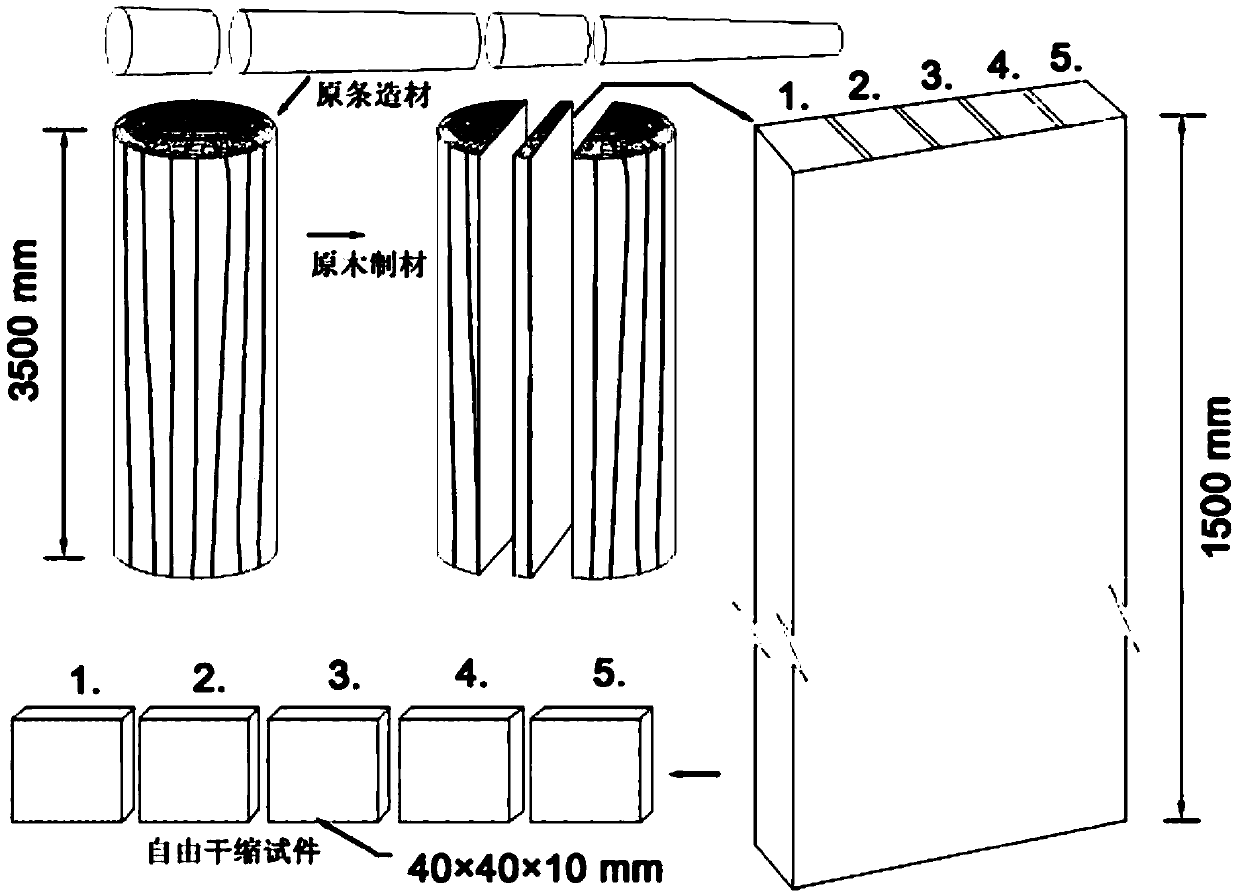
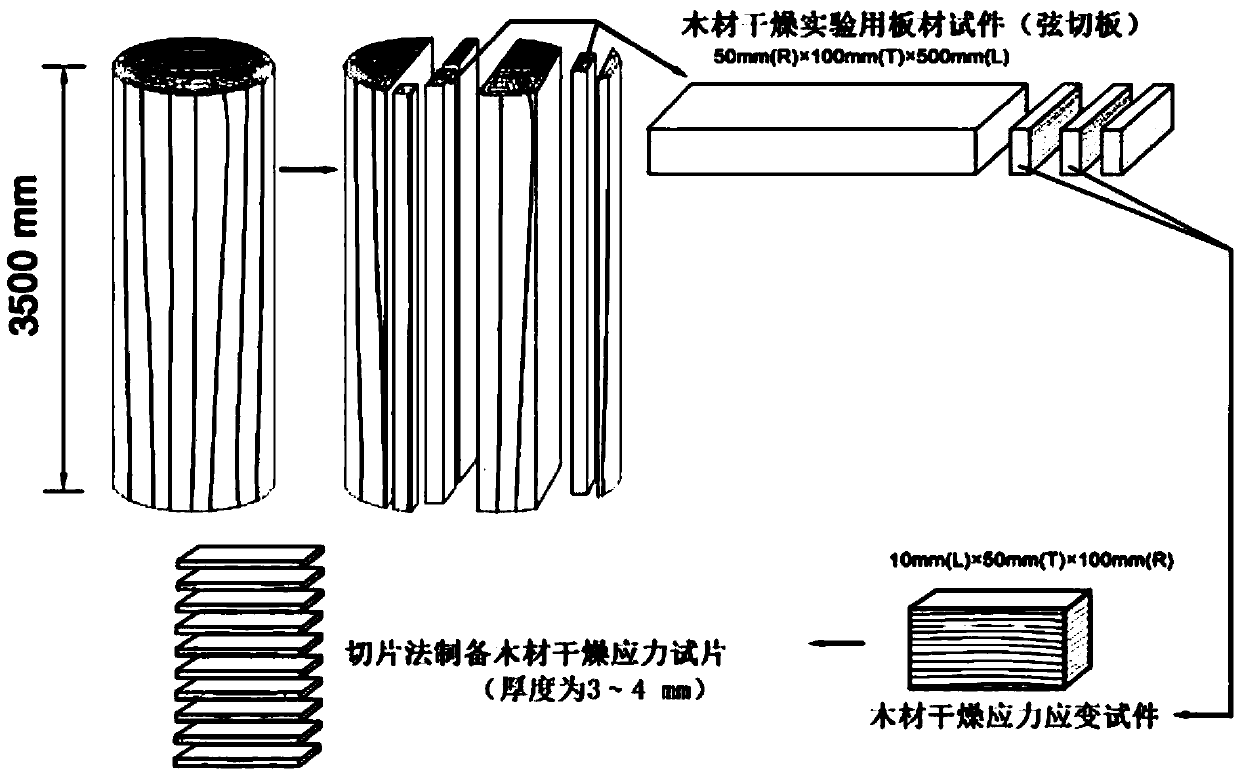
[0031] Specific implementation mode two: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is: image 3 It is a schematic diagram of cutting and deformation components of wood drying strain specimens determined based on previous research work. The detailed manufacturing process and details of wood free shrinkage specimens and wood drying strain specimens can be found in figure 1 and figure 2 shown. The mathematical calculation methods of the above wood drying deformation components are shown in the following formulas:
[0032] In the step one, ε N , ε e , ε ve , ε fs and ε ms The mathematical calculation method of is:
[0033]
[0034]
[0035]
[0036]
[0037]
[0038] in image 3 And the symbols in the formulas (1)~(6) represent the following variables, the said l 0 is the initial width of planed board in green state, l 1 is the length of the dry deformed specimen before cutting, l 2 is the length of the dry defo...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0040] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the specific process of obtaining the mechanical adsorption creep strain difference of the wood surface layer and the core layer area in the described step two is:
[0041]So far, the importance of the mechanical adsorption creep mechanism in the wood drying process is that it is the main supporting factor leading to the release of drying stress. However, the theoretical and thorough expression method for the relationship between wood drying stress and mechanical adsorption mechanism variables is far from perfect, so the drying (or residual) stress state parameters inside the chamber-drying board have not yet been effectively quantitatively expressed and dried. Quality rating. In view of the research status of wood drying stress-strain and its application in commercial wood production, this paper proposes a new concept, namely, the mechanical adsorption creep gradien...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com