Non-restraint face identification method based on HOG characteristic sparse representation
A sparse representation and face recognition technology, applied in the field of unconstrained face recognition, can solve problems such as poor sparsity, high redundancy, and high dictionary dimension, and achieve the effects of improving operating efficiency, high accuracy, and accurate description
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
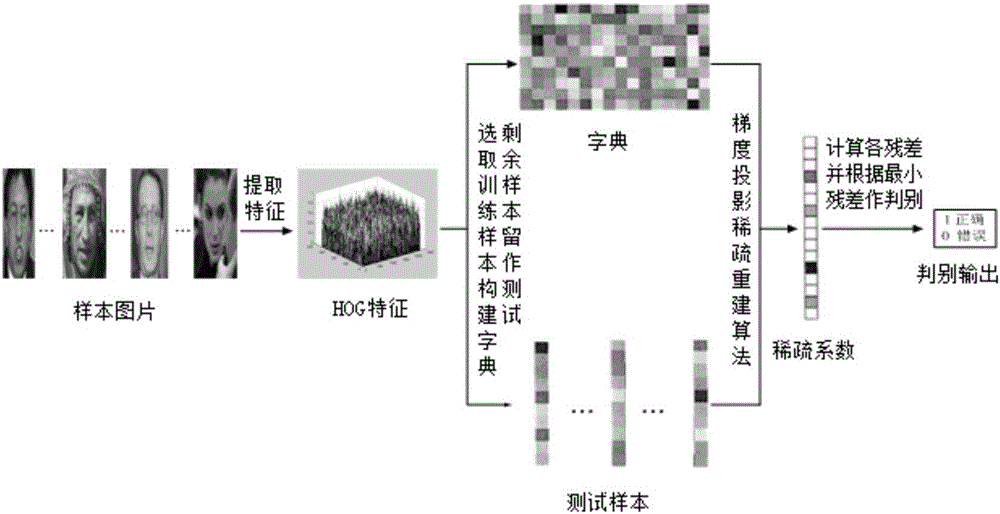
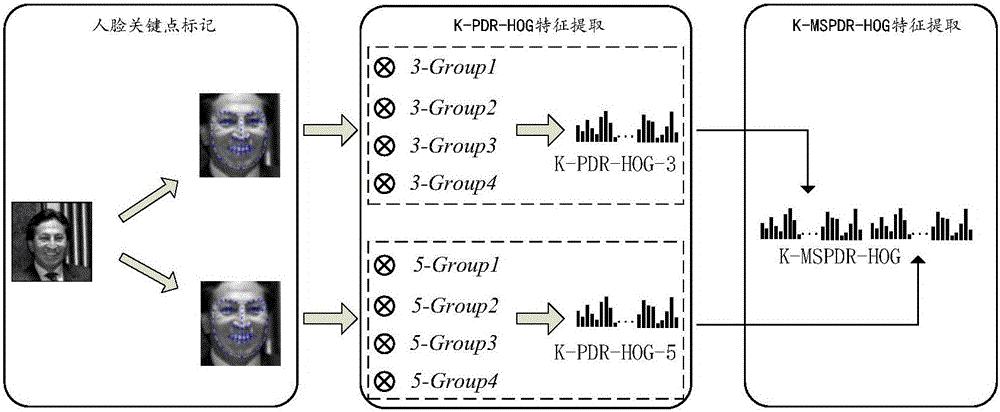
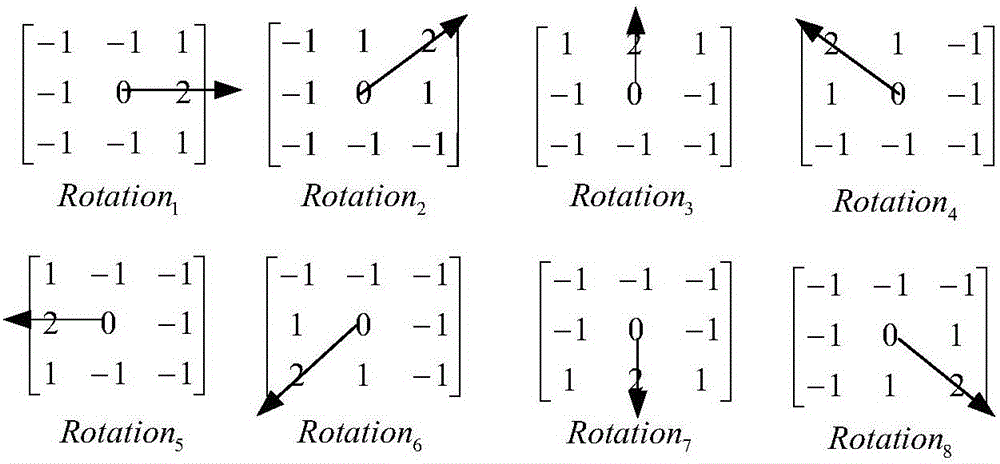
[0041] An unconstrained face recognition method based on sparse representation of HOG features, such as figure 1 shown. First input the face database picture, extract the HOG features of the input picture; randomly select 10 pictures from each type of people for training, and keep the rest for testing, and divide them into test samples and training samples; The feature column vector constructs a feature dictionary, and the number of dictionary columns is the same as the number of training samples; the gradient projection sparse reconstruction algorithm is used to obtain the HOG feature sparse representation coefficients of the test samples; the sparse coefficients are reserved in order by class, and the remaining coefficients are set to zero to obtain approximate sparse coefficients. The estimated value of the test sample is obtained by multiplying the dictionaries; the mean square error between the test sample and the estimated value is calculated, and the test sample categor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com