A lightweight approach to autonomous block management for data-intensive file systems
A data-intensive, file system technology, applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, data processing input/output process, instruments, etc., can solve the problem that the management method is not suitable for data-intensive file system management, increase address and other metadata maintenance cost, reduce the scalability of the master node, etc., to achieve the effect of improving recoverability and scalability, reducing storage space overhead, and improving scalability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
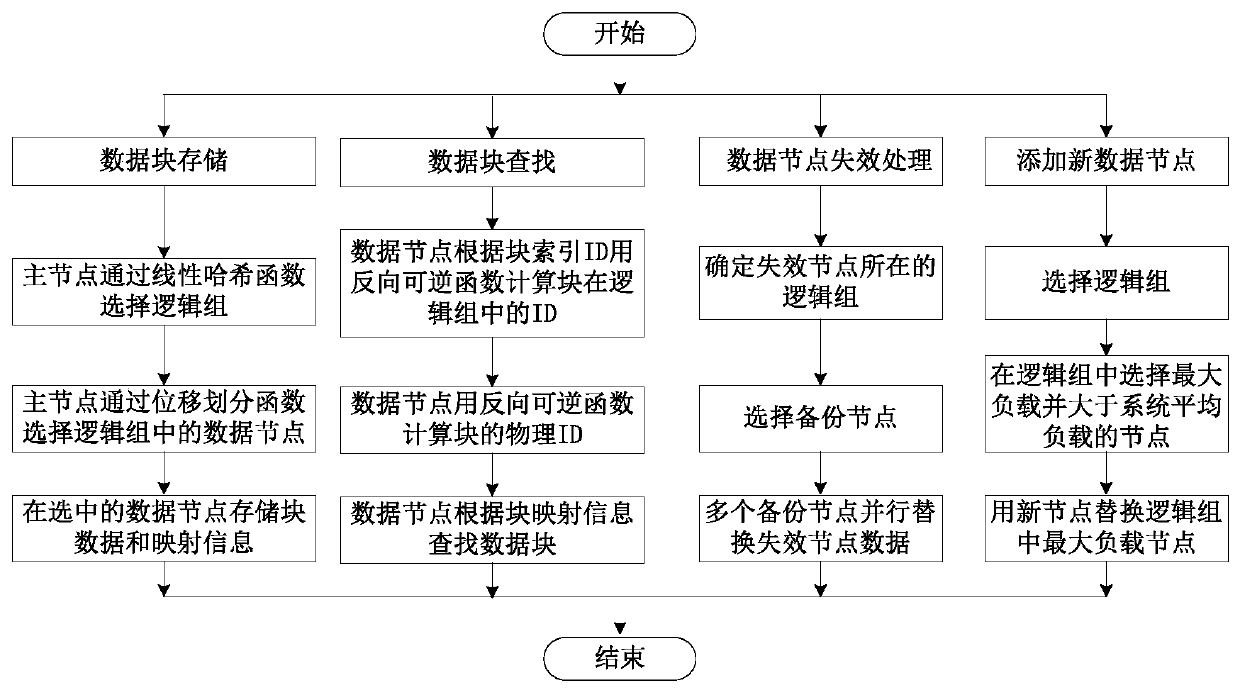
[0039] In order to make the technical means, creative features, goals and effects achieved by the present invention easy to understand, the following will further explain the autonomous block management of a light-weight data-intensive file system proposed by the present invention in combination with diagrams and specific embodiments method.
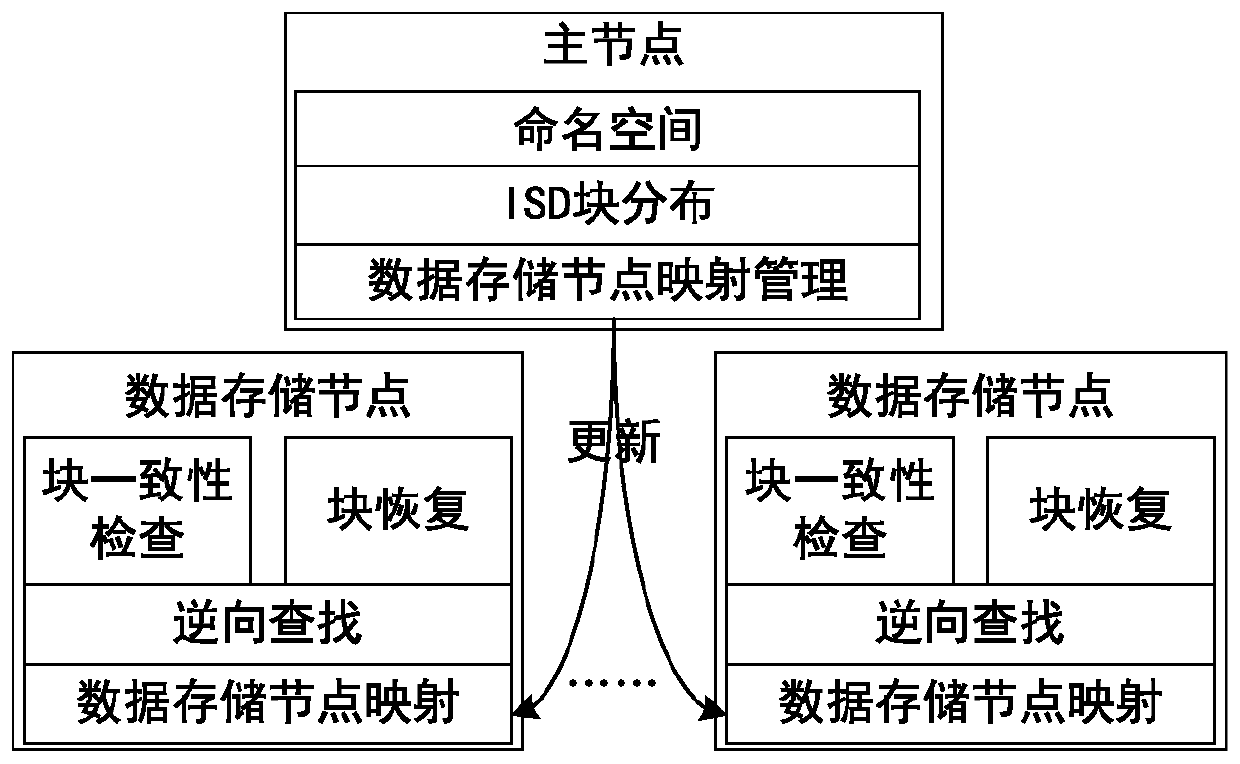
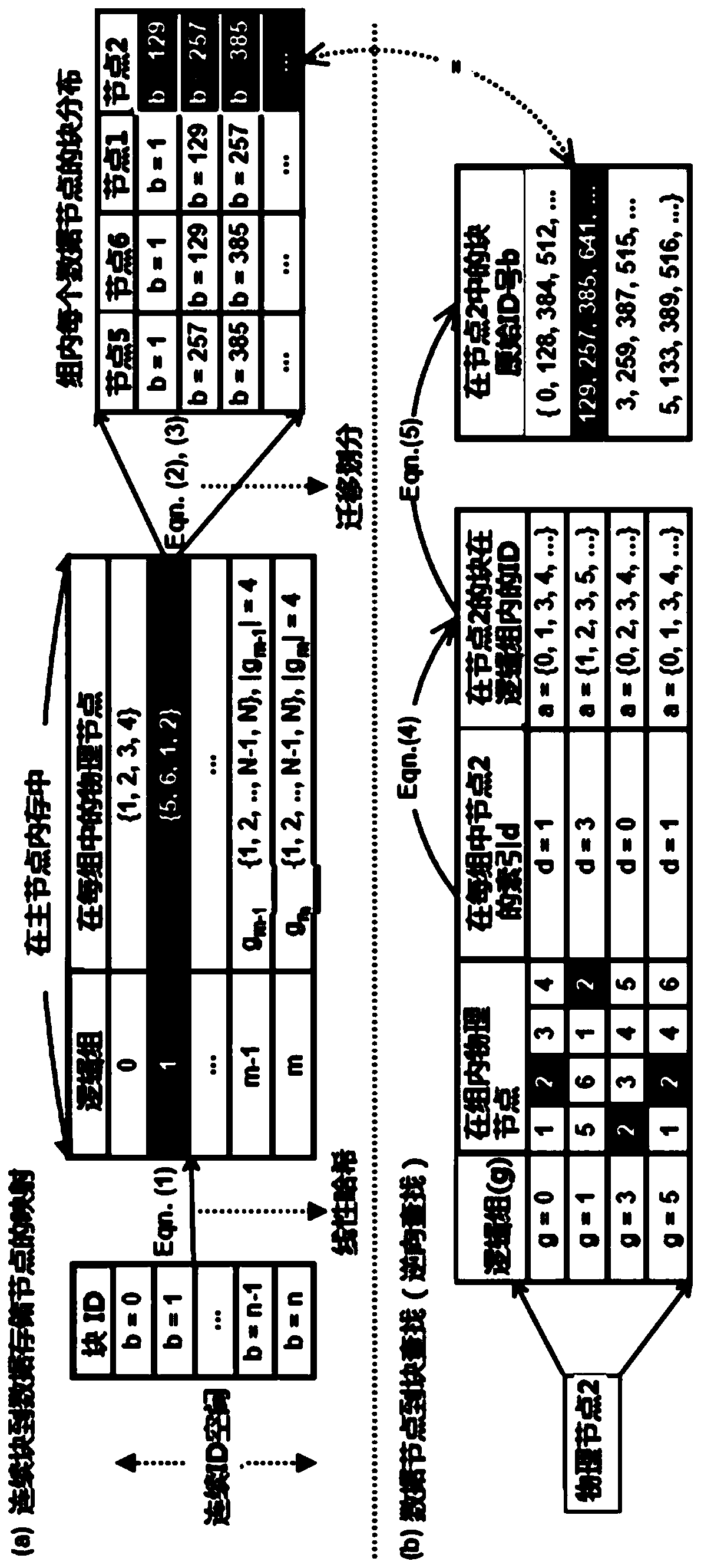
[0040] A lightweight autonomous block management method for data-intensive file systems, which implements the mapping from data blocks to data nodes and from data nodes to data blocks through a set of reversible mathematical functions. Such as figure 2 As shown, the division of the specific functions of each node in the present invention: the master node is only responsible for the maintenance of the system namespace, the distribution of data blocks to data storage nodes, and the management of each data storage node; each data storage node is responsible for the consistency check of data blocks, Data block recovery and mapping informat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com