Spiral spring damper with adjustable early-period rigidity
A helical spring and damper technology, which is applied in the field of shock absorbers, can solve the problems of waste of resources, reduce the cost of shock absorption, and the inability to change the early stiffness of the damper, and achieve the effect of shortening the length and reducing the cost of shock isolation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
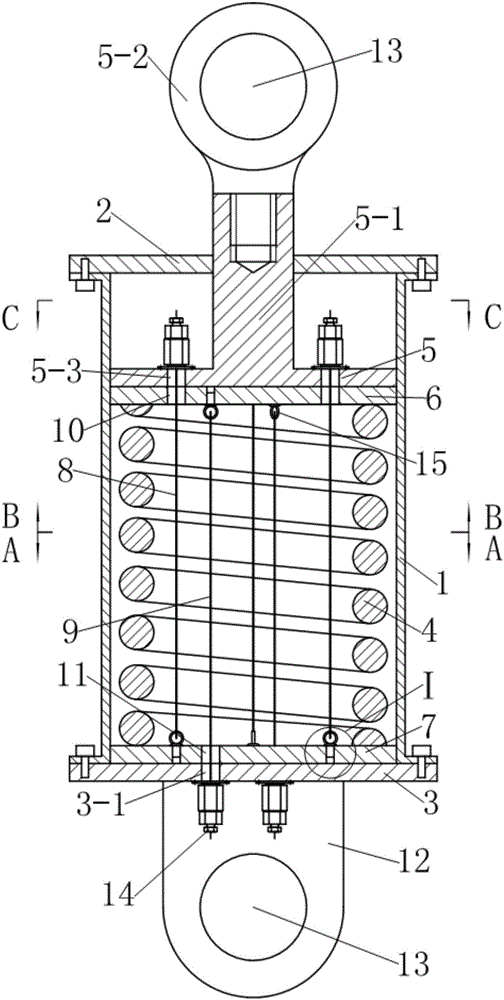
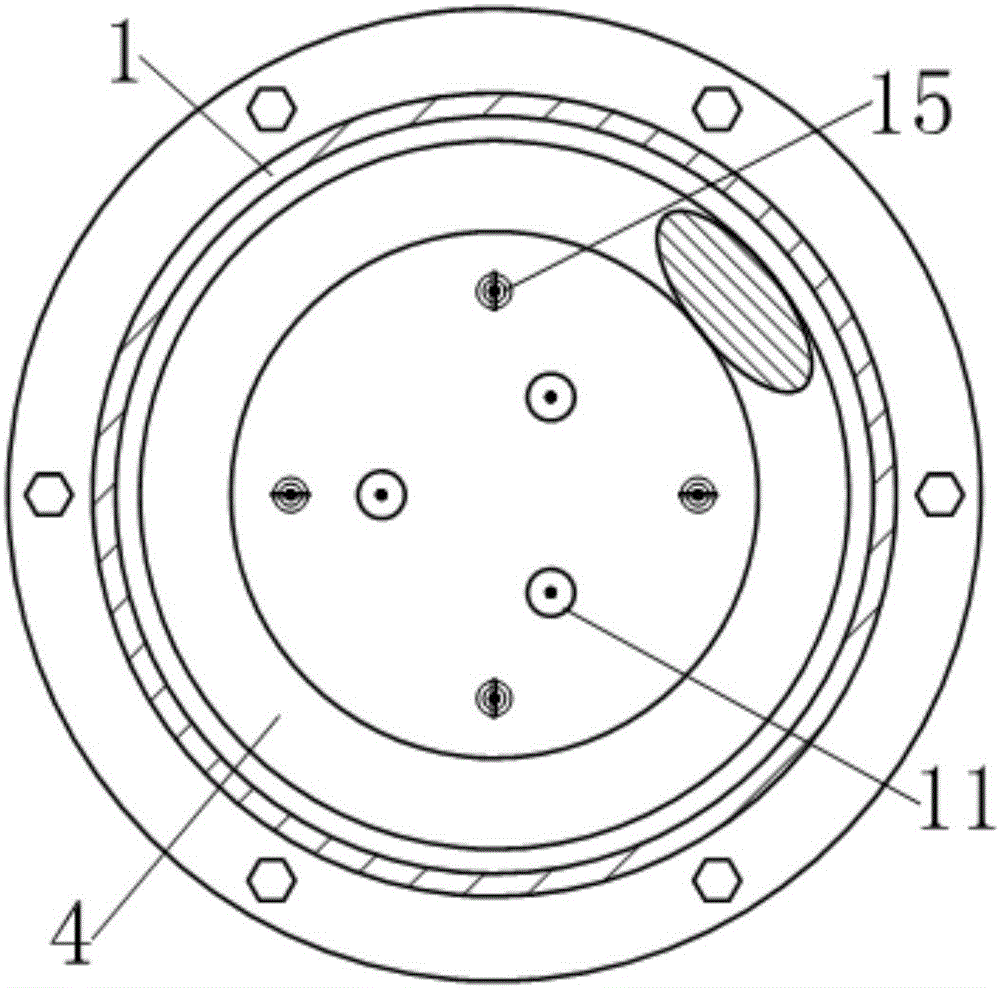
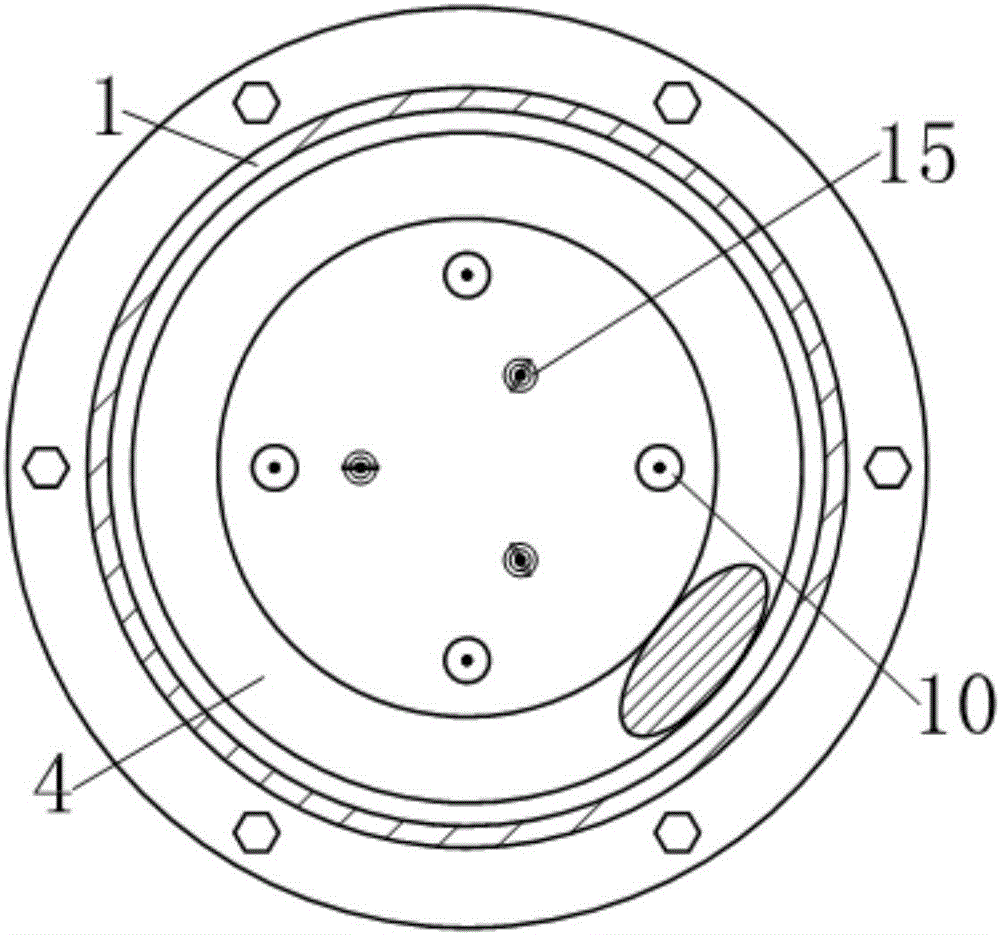
[0034] see figure 1 , the early coil spring damper with adjustable stiffness in this example is an energy-dissipating device that can be used for seismic reinforcement of building structures. It includes a guide sleeve 1, a first end cover 2 and a second The end cap 3, wherein, the first end cap 2 and the second end cap 3 are respectively fixedly connected to the two ends of the guide sleeve by screws. A cylindrical helical compression spring 4 is arranged axially in the guide sleeve 1, and a driving member extends from the center of the first end cover 2 into the guide sleeve 1 and presses on the cylindrical helical compression spring 4, Wherein, the driving member is composed of a dynamic pressure plate 5 located at the upper end of the cylindrical helical compression spring 4 and movably matched with the guide sleeve 1, and a driving rod 5-1 extending upward from the upper surface of the dynamic pressure plate 5 out of the guide sleeve 1. The end of the driving rod 5-1 lo...
example 2
[0049] see Figures 12 to 16 , the early coil spring damper with adjustable stiffness in this example is a kind of vibration isolation device (also called isolation support) that can be used for vertical isolation of buildings. Compared with Example 1, this example mainly has the following differences:
[0050] 1. As a vibration-isolation support, in order to facilitate installation, in this example, the connecting lug plate provided on the second end cover 3 in Example 1 is omitted, and the second end cover 3 is extended axially downward from the edge and then to the It extends radially outward, and is evenly provided with connecting bolt holes 16 at the edge. The second end cover 3 is used as the base of the shock-isolation support, and the length of the downward axial extension must be greater than the self-locking tension anchor of the steel cable With a height of 14. The driving rod 5-1 of the driving member is a metal tube that extends from the upper surface of the auto...
example 3
[0054] see Figures 17-21 , compared with Example 2, this example has the following main differences:
[0055] The first group of preloaded steel cables 8 and the second group of preloaded steel cables 9 are respectively composed of five preloaded steel cables, and the number of the steel cable self-locking tensioning anchors 14 is ten.
[0056] Other implementations of this example other than the above are the same as Example 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com