Power distribution network bidirectional allow type protection method based on FTU role identification
A permissive protection and distribution network technology, applied in the direction of emergency protection circuit devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of not being able to adapt to the exit circuit breaker not participating in signal transmission or reception, so as to avoid malfunction, reduce workload, The effect of accurate and fast positioning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] 1. Line equipment configuration
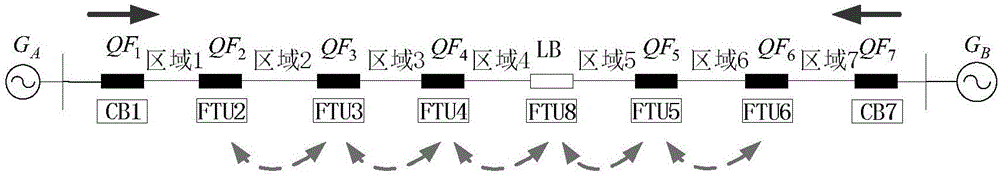
[0038] Generally, the distribution network in the hand-in-hand link is a closed-loop design and an open-loop operation. The system structure is as follows figure 1 shown. It is powered by two power sources A and B, and the circuit breakers for each segment protection on the line are installed corresponding to the FTU. , is the outgoing line circuit breaker in the substation, the outgoing line protection equipment does not participate in the receiving or sending of the permission signal, and the corresponding outgoing line protection is CB1, CB7; , is the section protection circuit breaker adjacent to the outgoing line circuit breaker, and defines the corresponding FTU2, FTU6 are outlet FTUs; , , are section protection circuit breakers, LB is a tie switch, and the corresponding FTU3, FTU4, FTU8, and FTU5 are defined as line FTUs; in normal operation, LB is in a disconnected state, and both sides supply power respectively , Areas 1, 2, ...
Embodiment 2
[0070] The difference from Example 1 is that, as attached Figure 4 As shown, after the line fault, part of the load is transferred to power supply, area 2 is fault isolated, areas 3 and 4 are transferred from B power supply, and area 1 is still powered by A power supply.
[0071] At this time, the contact switch LB is closed, and QF2 and QF3 are disconnected. The following only takes the B power supply area as an example for analysis.
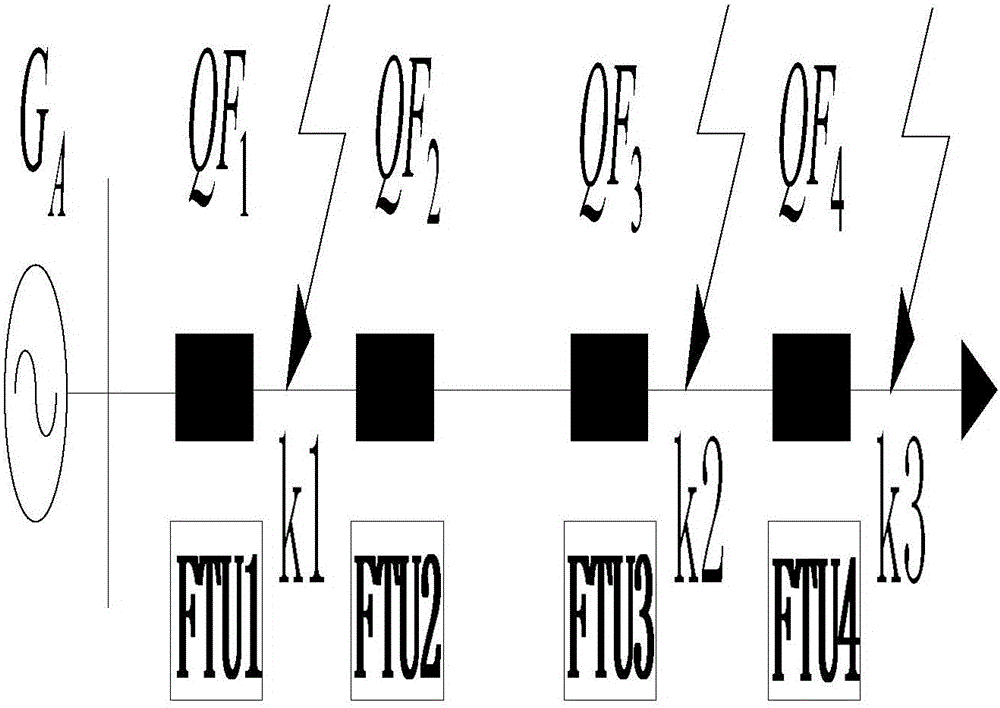
[0072] 1) If a short circuit fault occurs at k4,
[0073] Only CB7 feels the overcurrent. Other FTUs do not feel the overcurrent, and the corresponding section protection circuit breakers do not operate. After the delay time, CB7 can still feel the overcurrent, control the tripping of the outgoing circuit breaker in substation B, and successfully remove the fault at line k4.
[0074] 2) If a short circuit fault occurs at k2,
[0075] CB7, outlet FTU6, line FTU5, line FTU8, and line FTU4 all feel overcurrent.
[0076] ① The outlet FTU6 sen...
Embodiment 3
[0087] The difference from Example 1 is that, as attached Figure 5 As shown, if bus A fails or is overhauled, all the loads it carries will be transferred, and areas 1, 2, 3, and 4 will be transferred from B power supply.
[0088] At this time, the outlet circuit breaker QF1 is disconnected and the contact switch LB is closed.
[0089] 1) If a short-circuit fault occurs at k2, k4, etc., the fault handling process is similar to that described in (2), and will not be repeated here.
[0090] 2) If a short circuit fault occurs at k1,
[0091] ①FTU2, FTU3, FTU4, FTU8, FTU5, and FTU6 all feel overcurrent, and send trip request inquiry signals to adjacent FTUs;
[0092] The outlet FTU2 identifies the power direction, and the short-circuit current power direction is opposite to the positive direction defined by the outlet FTU2.
[0093] ② FTU2 directly sends a trip command to the corresponding section circuit breaker to remove the fault. The overcurrent disappears, and other prot...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com