Method for characterizing mode group properties of multimodal light traveling through optical components
A technology of optical components and modes, applied in the field of optical fiber transmission, can solve the problem of not allowing to evaluate the individual behavior of mode groups
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
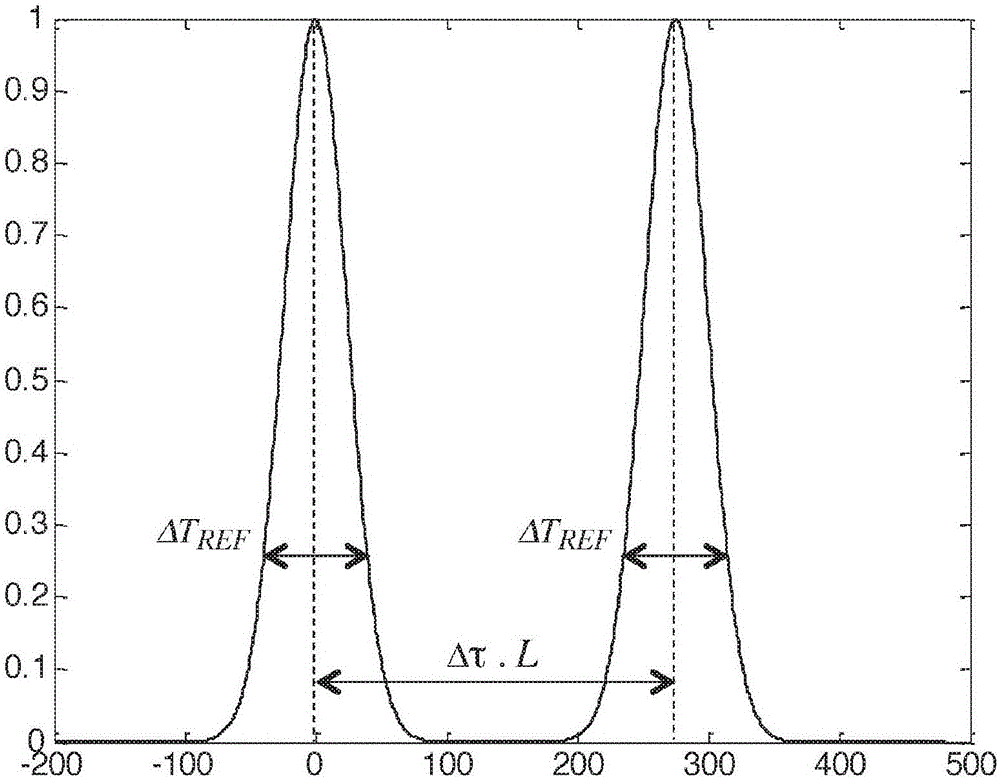
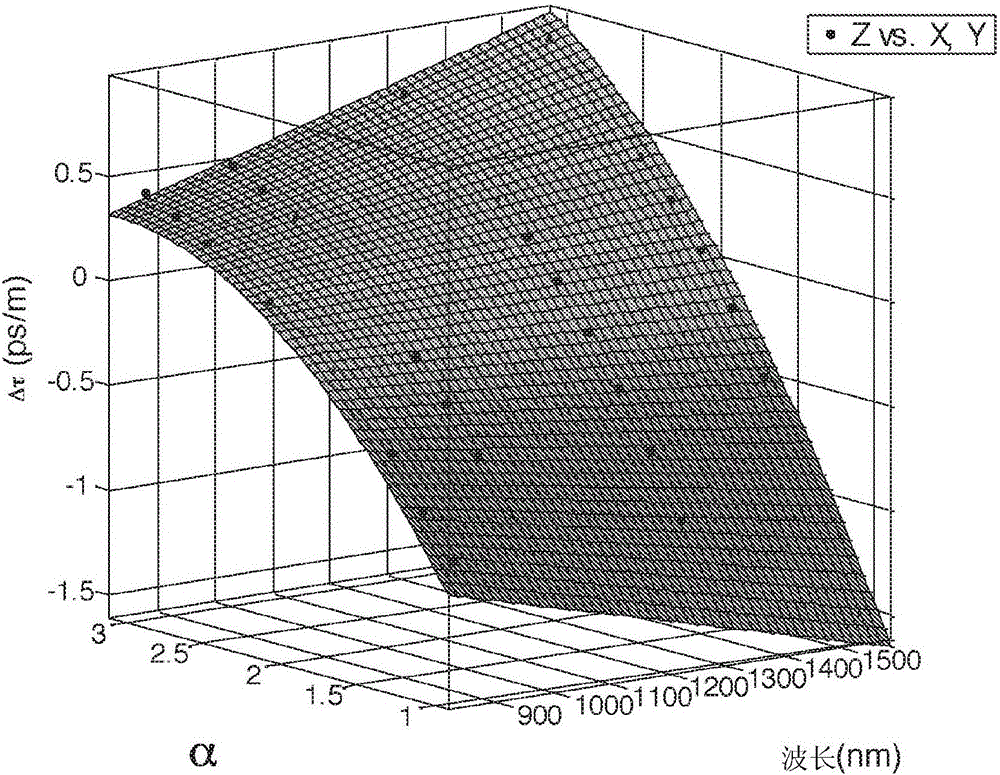
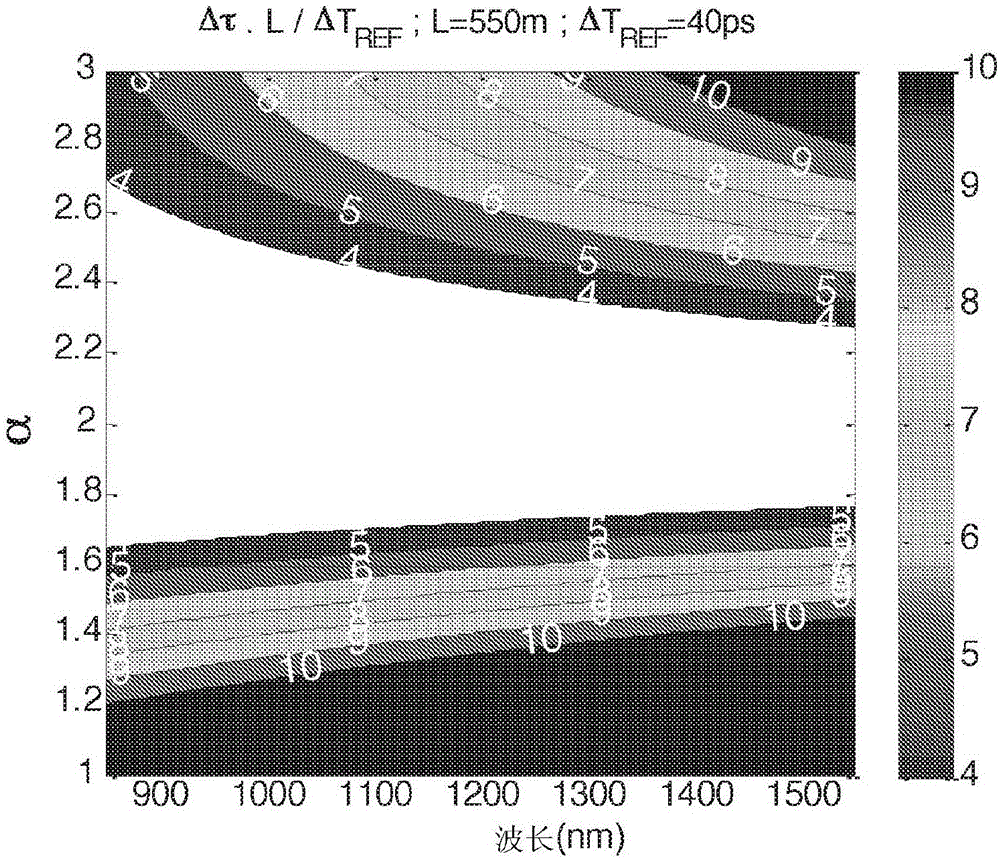
[0139] The general principle of the invention relies on the use of a specially designed mode group separation fiber inserted in the optical path between the light source and the optical component under test and having The ability to separate these mode groups in the temporal domain before or after the component. As a result, the behavior of these mode groups as they pass through optical components can be studied independently of each other.
[0140] Thus, embodiments of the present invention provide a simple and valuable method for characterizing the mode group properties of multimode light passing through an optical component. The experimental results so realized can be used to improve the design of multi-mode fiber and few-mode fiber as well as the design of optical components.
[0141] Figure 1~6 The characteristics of the mode group separation fiber according to the embodiment of the present invention will be described.
[0142] As stated earlier in this document, in an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com