Glass composition, glass substrate and chemical strengthening method thereof
A technology for glass substrates and compositions, applied in the field of glass compositions, glass substrates and their chemical strengthening, can solve the problems of low density, unsatisfactory surface stress and surface hardness, and inability to completely resist falling.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0047] The method for preparing the chemically toughened glass substrate of the present invention is by making the common glass substrate prepared by the above composition carry out chemical toughening treatment in molten salt containing potassium ions, and a layer of compressive stress layer will be formed on the glass surface, so that the glass surface has The higher surface stress and hardness improve the surface scratch resistance of the chemically toughened glass substrate, making it resistant to external forces such as dropping and abrasion.
[0048] Wherein, the specific operating conditions for preparing the glass substrate described in step (1) are well known to those skilled in the art. For example, the above composition can be weighed according to parts by weight and fully mixed uniformly, and then the molten glass is poured into the platinum In a rhodium crucible, keep warm at 1550-1650°C for 5-10h, preferably at 1580-1620°C for 6-8h; cool the molten glass to the te...
Embodiment 1-11
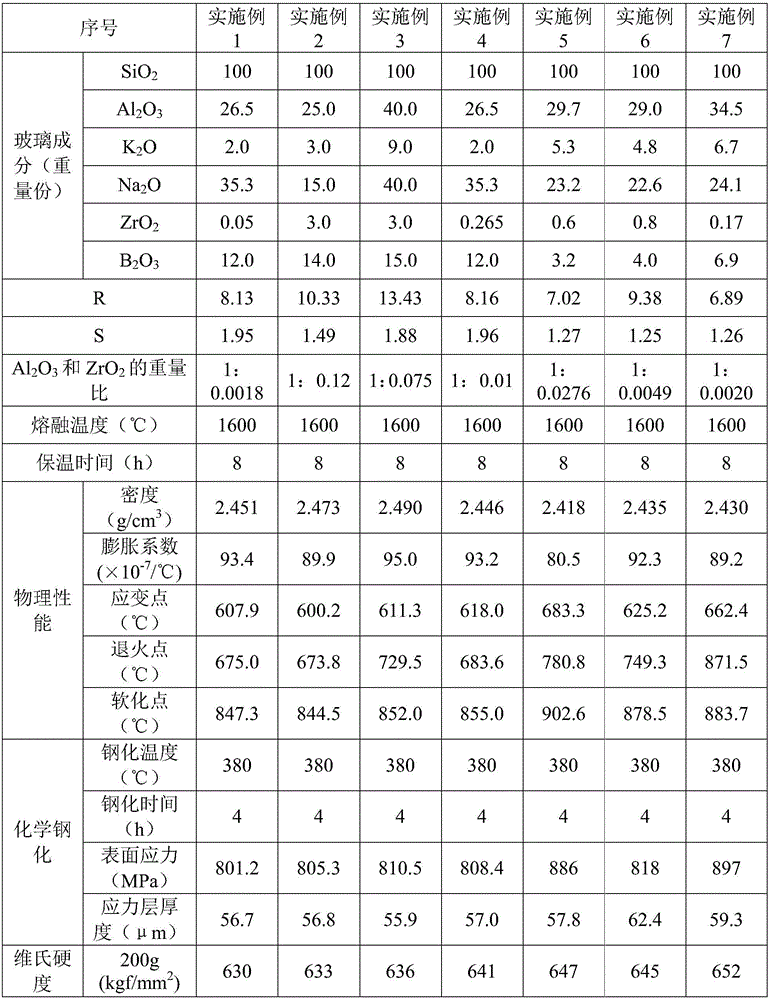
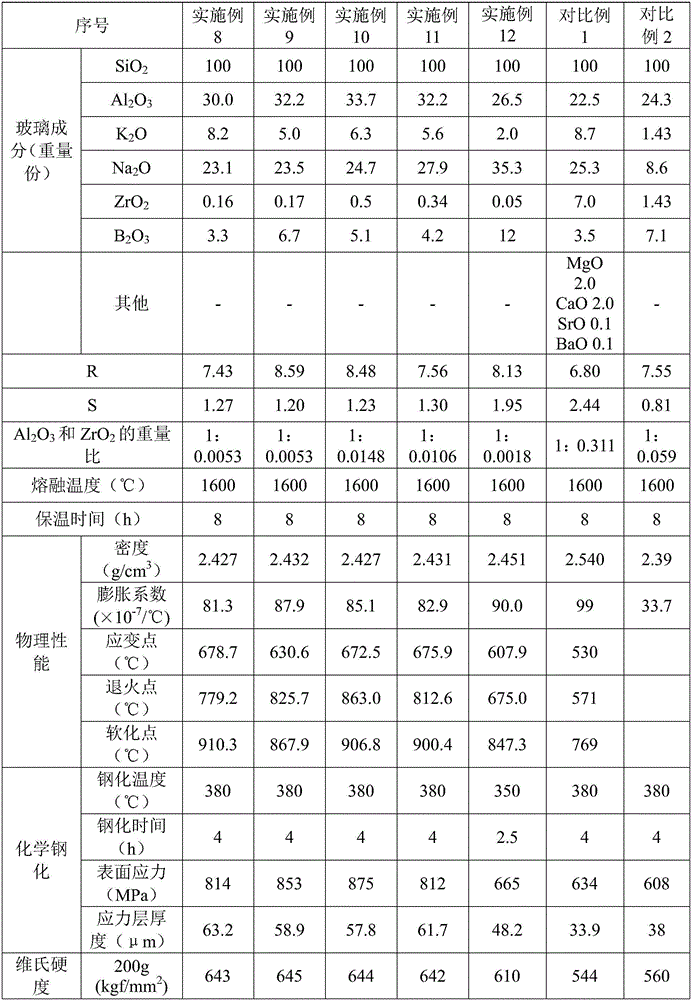
[0059] The components and contents of the compositions used to prepare glass in Examples 1-11 are shown in Table 1.
[0060] The glass substrates in each embodiment are prepared according to the following steps: weigh each component according to the weight part and fully mix them uniformly, pour the mixed components into a platinum-rhodium crucible, and keep the temperature at 1600°C for 8 hours; The temperature of the liquid is cooled to the temperature range required for forming, forming on a stainless steel plate, and annealing at 630°C for 0.5h to obtain a glass substrate. The density, expansion coefficient, strain point, annealing point and softening point of the glass substrate are tested, and the test results Listed in Table 1.
[0061] According to the measured annealing point, after the glass substrate is precision annealed, it is cut, ground, and polished to form a 60mm×45mm×0.7mm sheet, and placed in 380°C molten KNO 3 Chemical toughening treatment was carried out ...
Embodiment 12
[0064] The composition and content of the composition used to prepare the glass in this example are the same as in Example 1, and the preparation method of Example 1 is adopted, except that the temperature of the molten salt containing potassium ions is 350°C, and the time of immersion is 2.5h .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| strain point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface stress | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| depth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com