Data transmission method, device and system based on dual-carrier modulation (DCM)
A data transmission method and dual-carrier modulation technology, which is applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of high bit error rate in data transmission and the inability to obtain bit data at the receiving end, so as to reduce the bit error rate and improve reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
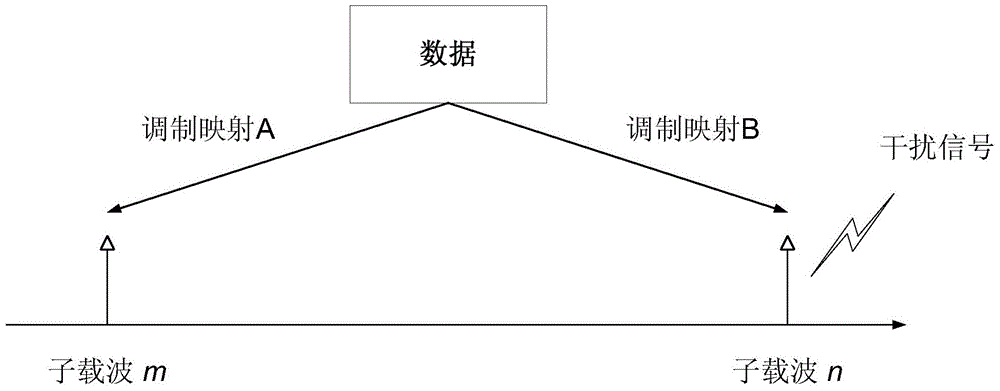
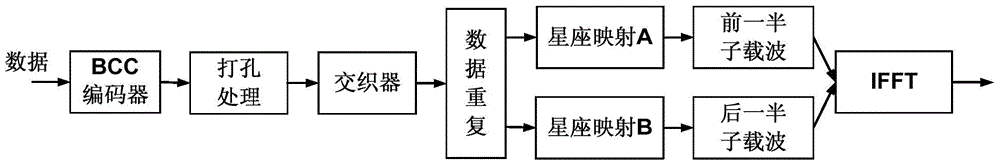
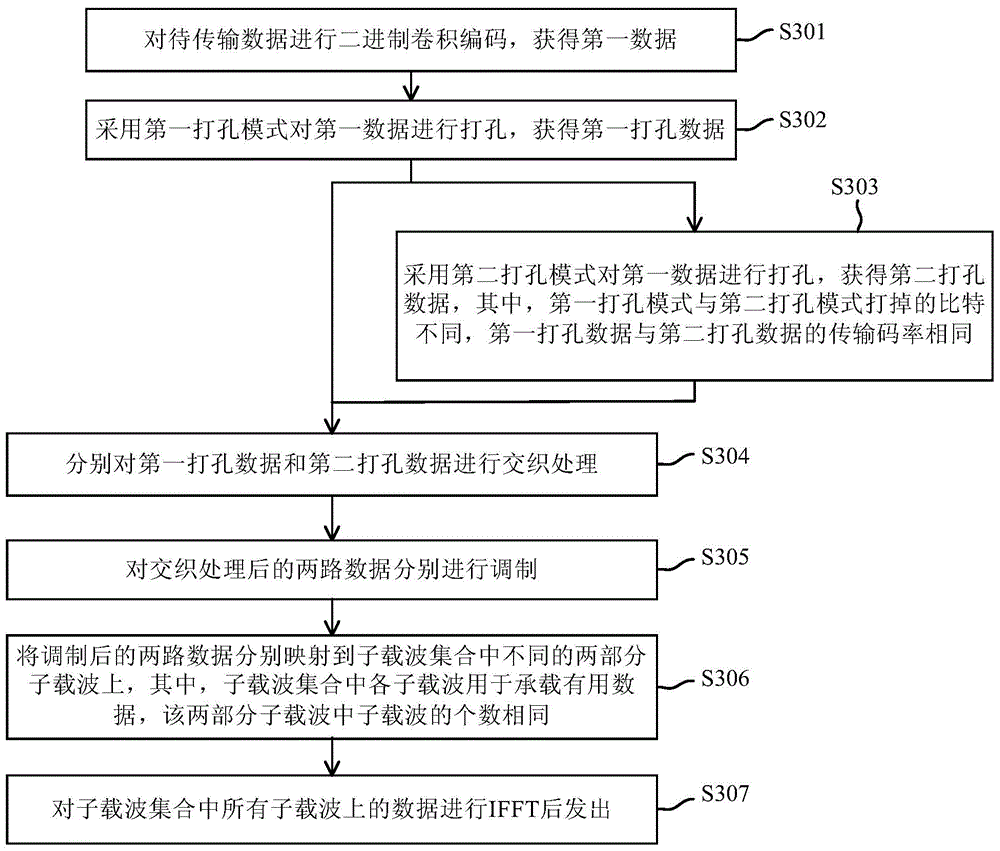
[0179] Scenario: Wi-Fi wireless network outdoor channel, downlink, OFDM, single-user single-input single-output (Single-user Single-input Single-output, hereinafter referred to as: SU-SISO), that is, the AP serves one STA, and adopts the present invention The transmission mode provided by the embodiment sends a signal field B (signalfield B, SIGB for short) signal to the STA. The transmission bandwidth is 20MHZ, and the number of subcarriers is 64. The 64 sub-carriers are numbered as {-32,-31,...,-1,0,1,...,31}. Wherein, the available 52 sub-carrier numbers are {-26,-25,...,-1,1,...,25,26}. Among the 52 available subcarriers, subcarriers numbered {-21,-7,7,21} are used to carry pilot signals, and the remaining 48 subcarriers are used to carry useful data. At the same time, suppose the size of the data to be transmitted is 72 bits, denoted as {x 0 ,...,x 71}, and set the modulation and coding method of the sent data to QPSK 3 / 4. Figure 24 The sender flow of the proposed t...
Embodiment 2
[0186] The scenario and sending and receiving process are the same as those in Embodiment 1, the difference is:
[0187] Suppose the size of the data to be transmitted is 64 bits, denoted as {x 0 ,...,x 63}, and set the modulation and coding method of the sent data to QPSK 2 / 3.
[0188] On the AP side (transmitter), the AP first sends the data to be transmitted {x 0 ,...,x 63} Input a BCC encoder with a coding rate of 1 / 2 to perform BCC, and obtain encoded bits {X 0 ,...,X 127}, namely the first data; copy the first data to get the second data {Y 0 ,...,Y 127}, here, the first data {X 0 ,...,X 127} and second data and {y 0 ,...,Y 127} are the same, except that different letters are used for symbol representation; then, in order to obtain a sequence with a transmission code rate of 2 / 3, the AP uses different puncturing modes to process the first data {X 0 ,...,X 127} and the second data {Y 0 ,...,Y 127} to punch holes. For the first data {X 0 ,...,X 127}, the A...
Embodiment 3
[0190] The scenario and sending and receiving process are the same as those in Embodiment 1, the difference is:
[0191] Suppose the size of the data to be transmitted is 80 bits, denoted as {x 0 ,...,x 79}, and set the modulation and coding method of the sent data to QPSK 5 / 6.
[0192] On the AP side (transmitter), the AP first sends the data to be transmitted {x 0 ,...,x 79} Input a BCC encoder with a coding rate of 1 / 2 to perform BCC, and obtain encoded bits {X 0 ,...,X 159}, namely the first data; copy the first data to get the first data {Y 0 ,...,Y 159}, here, {X 0 ,...,X 159} and {y 0 ,...,Y 159} are the same, except that different letters are used for symbol representation; then, in order to obtain a sequence with a transmission code rate of 5 / 6, the AP uses different puncturing modes to process the first data {X 0 ,...,X 159} and first data {y 0 ,...,Y 159} to punch holes. For the first data {X 0 ,...,X 159}, AP adopts Figure 12 The existing 5 / 6 tra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com