Adaptive light compensation method based on projector-camera system
A projector and adaptive technology, applied in the field of adaptive optics, can solve problems such as unfavorable decision-making and execution, loss of detail information, etc., to achieve the effect of avoiding adverse effects and fast compensation processing speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and specific example the present invention will be further described;
[0022] In the adaptive light compensation of the present invention, the projector and the camera adopt a non-coaxial configuration, and for the convenience of subsequent calculation, the projector and the camera are placed on the same horizontal line. The distance between the projector and the camera is d, the distance from the projector to the reference plane is L, and the depth of the observation point O is h. Using the similarity principle of triangles, we have
[0023]
[0024] Represents the phase change, with
[0025]
[0026] Substituting formula (2) into formula (1), we get
[0027]
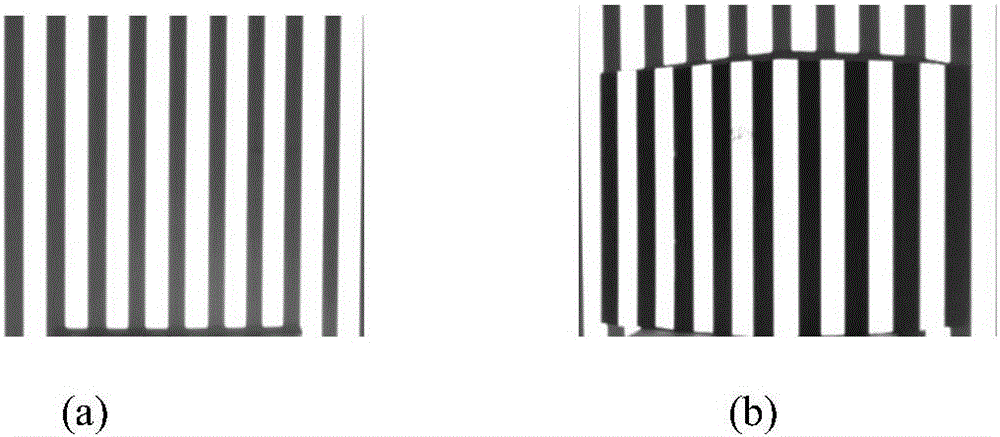
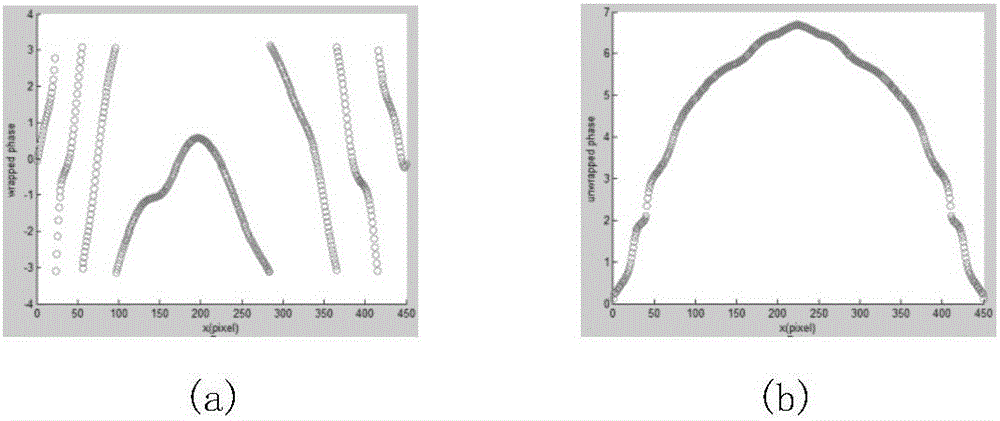
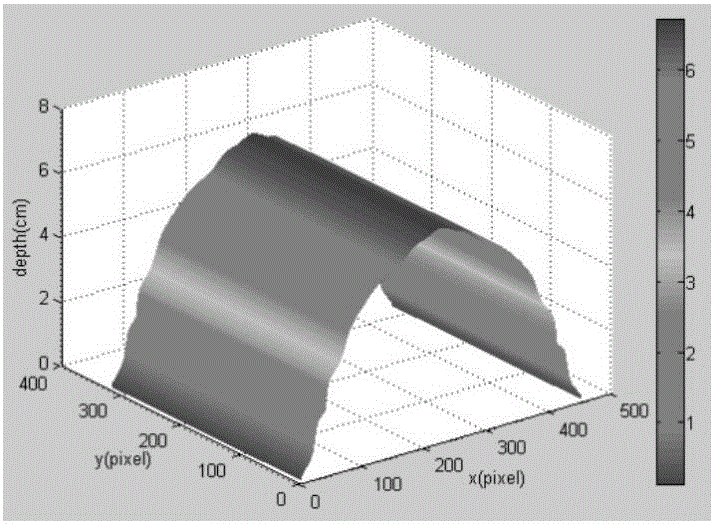
[0028] figure 1 Shown are the reference grating pattern and the distorted grating pattern in the present invention. The computer-generated sinusoidal grating stripes, such as figure 1 As shown in (a), when projected on the surface of a three-dimensi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com