Propping agent and method for placing same in a hydraulic fracture
A hydraulic fracturing and proppant technology, applied in the field of hydraulic fracturing and increasing flow through the formation, can solve the problems of fluid rheological properties deviating from optimal properties, long-term high-temperature stability damage, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
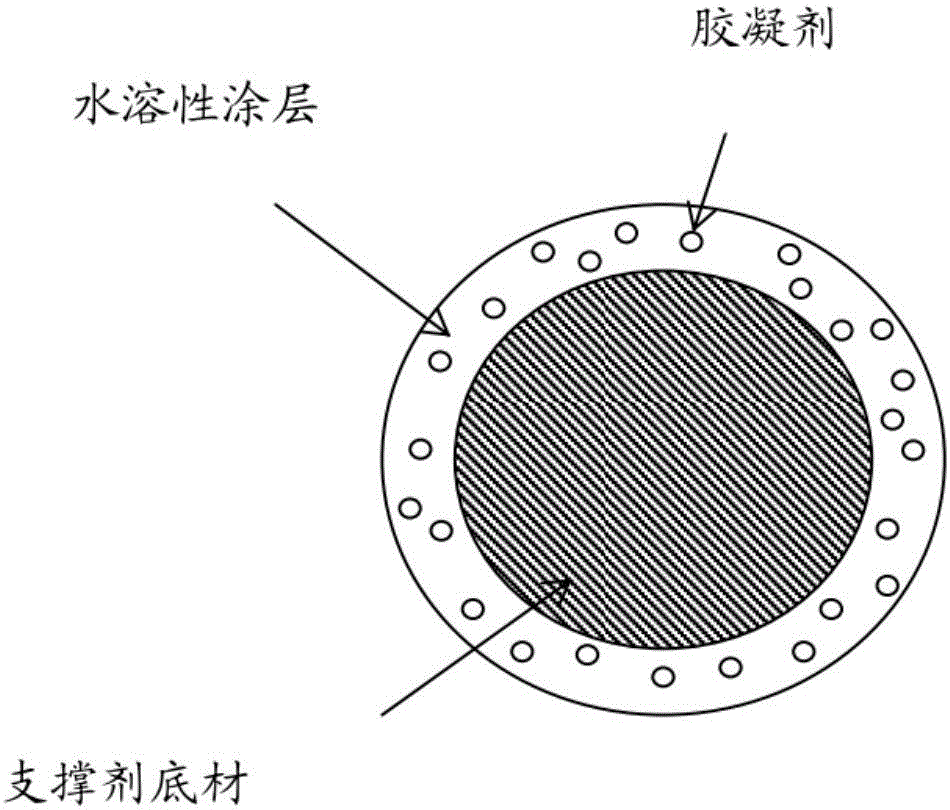
[0052] The following examples illustrate the feasibility of the proposed method of coating proppants with gelling agents embedded in a water-soluble polymer matrix.
[0053] Table 1. Composition of the coated proppants in Example 1.
[0054]
[0055]
[0056] Proppant CarboPROP The components and amounts listed in Table 1 were applied in the following manner.
[0057] 1. Dissolve polyvinyl alcohol in water.
[0058] 2. Then, the polysaccharide guar gum was slowly added to the polyvinyl alcohol aqueous solution. Shake the mixture well to ensure even distribution of the guar gum in the solution.
[0059] 3. Add the obtained solution to CarboPROP The fluid and proppant are then moderately agitated in the beaker until the coating on the proppant is dry.
[0060] The resulting proppant showed good coating adhesion to the surface and a very limited amount of particles sticking to each other, suggesting potentially good flowability of the coated proppant. The quality of...
Embodiment 2
[0062] The following examples illustrate the feasibility of using gelling agent-coated proppants when added to water.
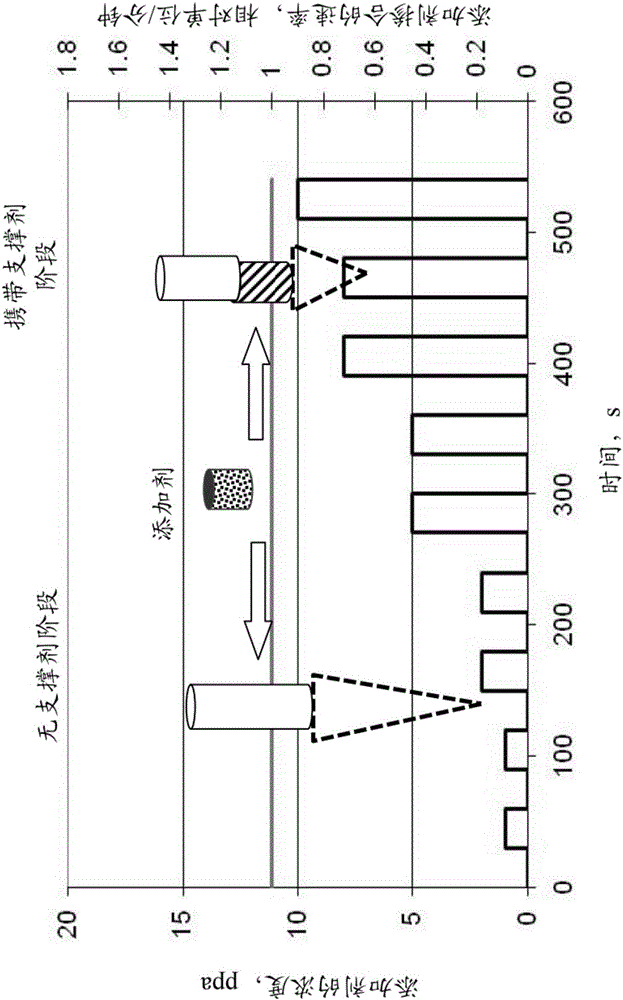
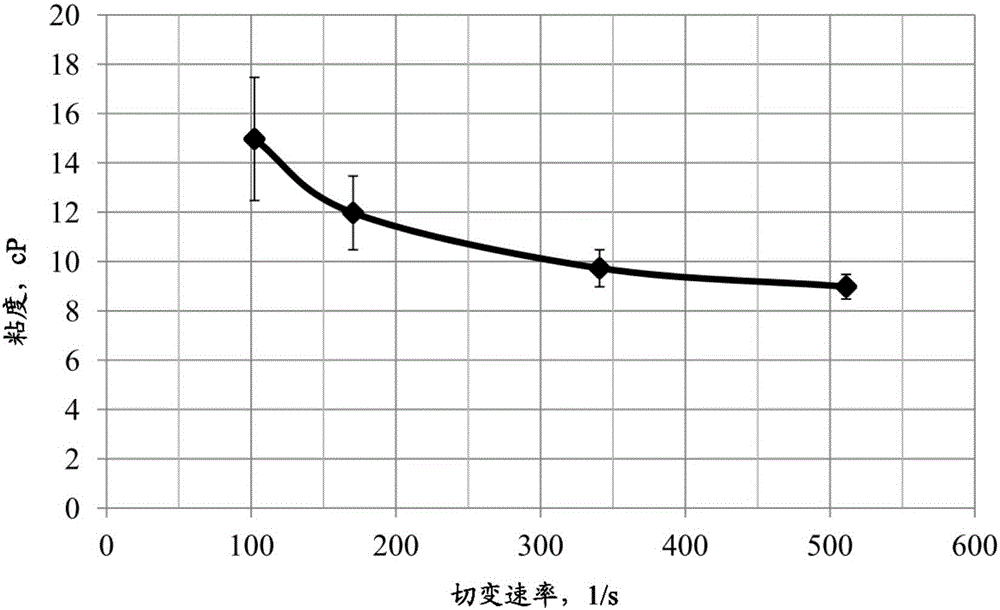
[0063] To evaluate how coated guar affects viscosity, the proppant from Example 1 was added to DI water. The coated proppant was added to the water at a concentration of 2.2 pounds of proppant per 1 gallon of fluid. The resulting fluid viscosities obtained after stirring for 5 minutes are shown in image 3 , and the results were close to a linear gel viscosity with a guar polymer loading of 17 lbs / 1,000 gallons.
[0064] It is worth mentioning that the amount of guar gum involved in the mixing can be increased or decreased in order to adjust the resulting viscosity.
Embodiment 3
[0066] The following examples illustrate the feasibility of using gelling agent-coated proppants when added to linear gels.
[0067] Proppant CarboPROP Coated in the manner described in Example 1 using the components and amounts listed in Table 2.
[0068] Table 2. Composition of proppants coated in Example 3
[0069]
[0070] After coating was complete, the resulting proppants were added to the linear gel in an amount of 30 pounds of polymer per 1,000 gallons of DI water in order to evaluate how the coated guar gum added to the fluid affected viscosity. The coated proppants were added to the water at concentrations of 3 pounds and 5 pounds of proppant per gallon of fluid. Compared to the original linear gel (WF130), 35, 40 and 50, 30 pounds of guar per 1,000 gallons of DI water, obtained from 3 and 5 pounds of proppant slurry per gallon of fluid after 5 minutes of agitation Viscosity is shown in Figure 4 middle.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com