Automated code lockdown to reduce attack surface for software
A negative, feature-specific technique used in the field of automatic code locking used to reduce the attack surface of software to address issues such as reduced capabilities and hindering the ability of cybersecurity products to identify attack behaviors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
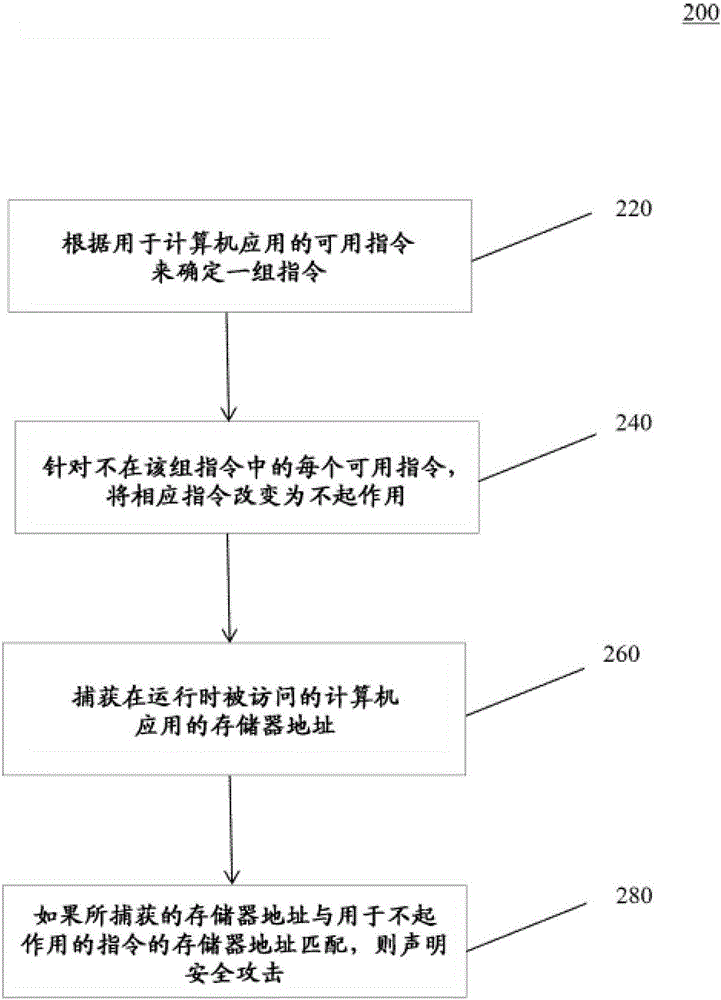
[0022] The following is a description of example embodiments of the present disclosure.
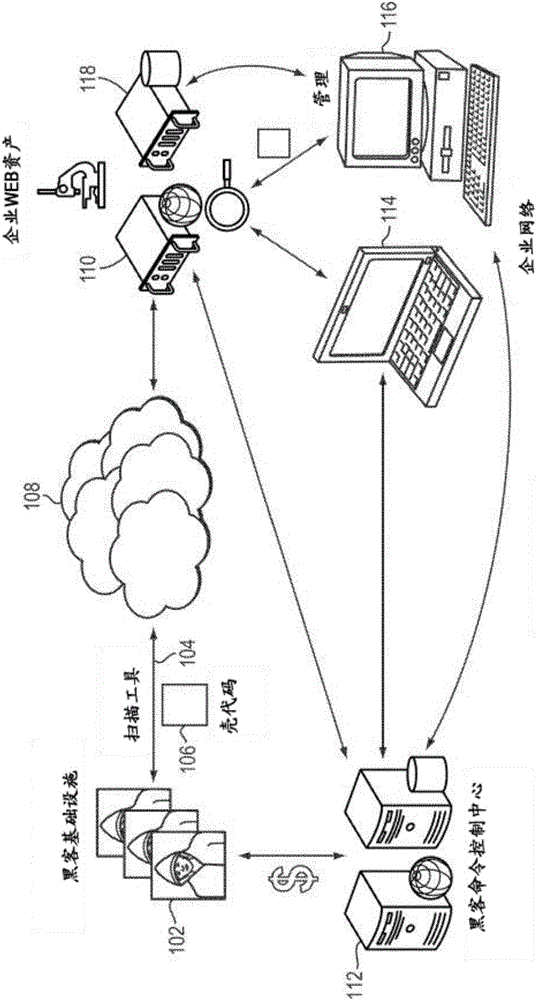
[0023] Overview of Malware Attacks
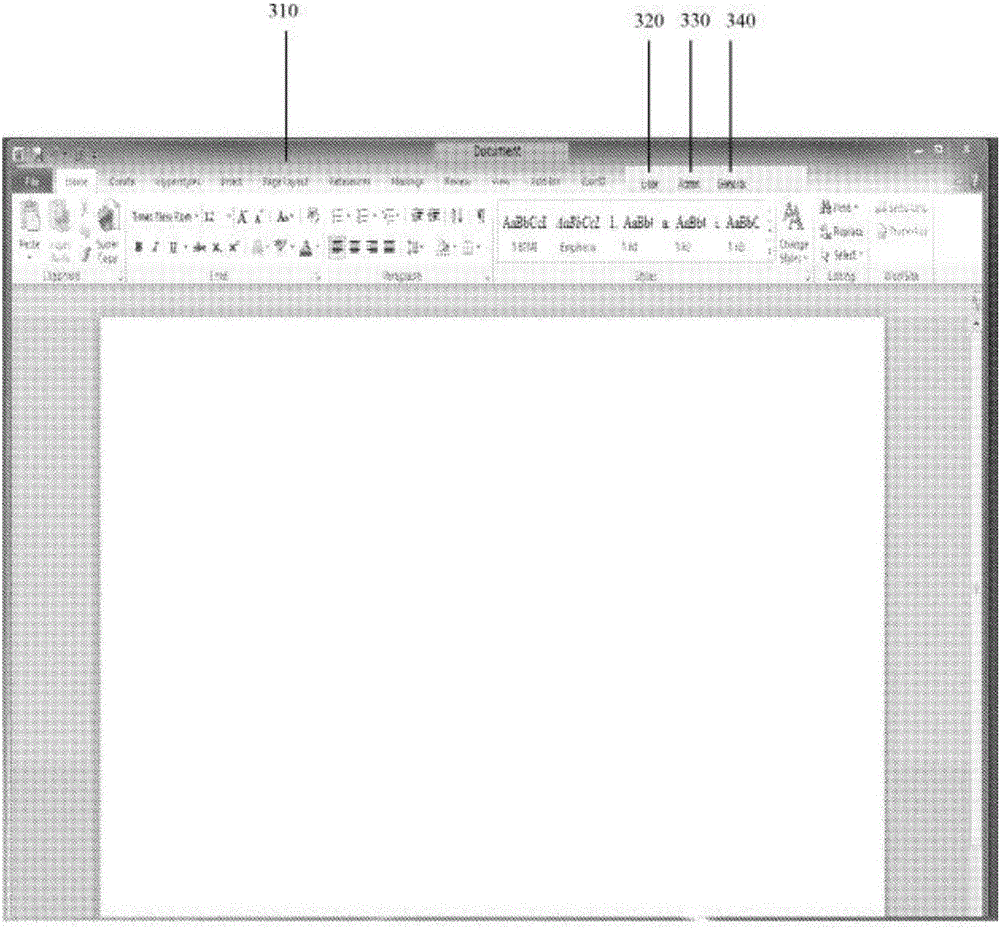
[0024] The National Vulnerability Database (NVD) listed approximately 4100 application vulnerabilities in 2011 and 5300 application vulnerabilities in 2012, which are classified into twenty-three attack categories. While several attack categories involve attacks resulting from negligence or misconfiguration, the largest number of attack categories involve malicious actors intentionally injecting malicious content into an organization's ongoing processes and subsequently causing the malicious content to execute. The process of injecting such malicious content involves identifying and exploiting some poorly designed code that performs inadequate input validation. For example, if code lacks size-related validation, the code may allow buffer-fault-style attacks included in the category of buffer-fault attacks. In these attacks, malicious actors inject ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com