Thermo-optic non-localized angle double-slit interference method and system
A technique of double-slit interference and localization, applied in the field of optics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
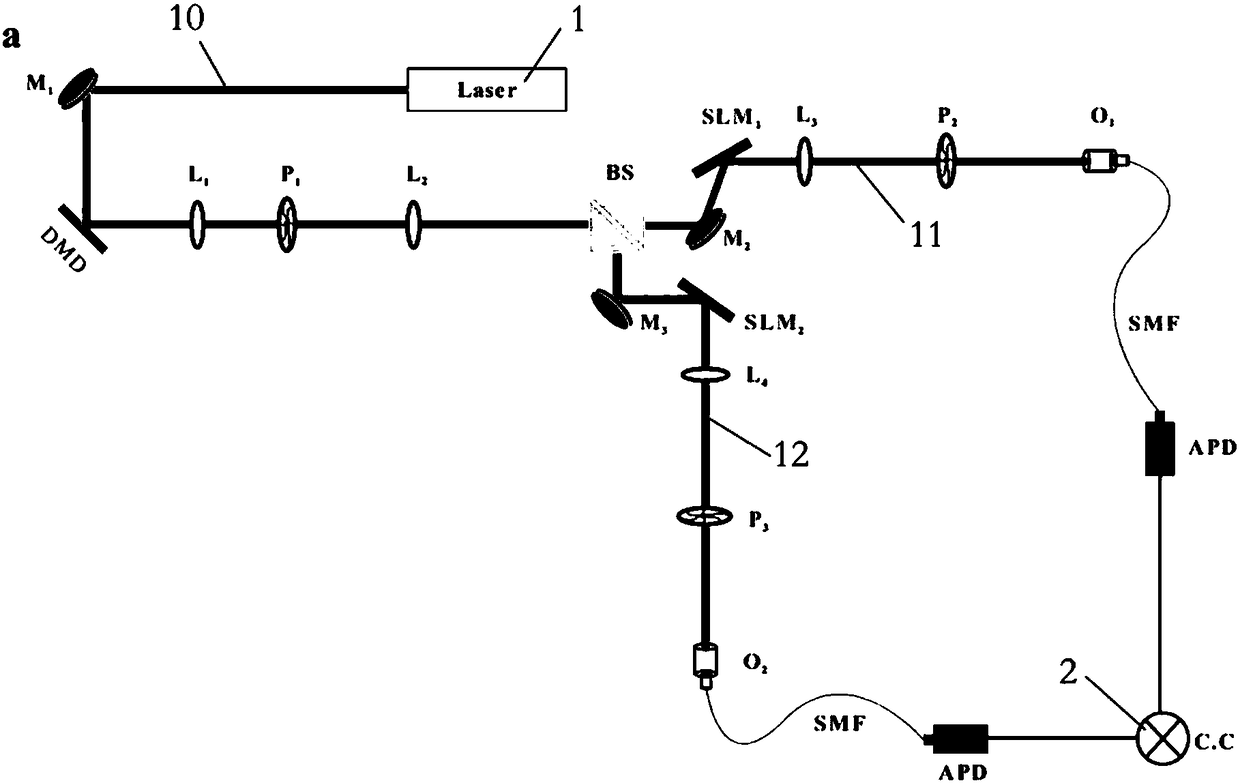
[0065] like Figure 1-2 As shown in the figure, the present embodiment provides a thermal-optical non-localized angle double-slit interference system, which includes a thermal light source, a non-polarizing beam splitter BS, a spatial light modulator, a single-photon detector, and a computer 2 arranged in sequence on the optical path. ;
[0066] a thermal light source for emitting an incoherent thermal beam 10;
[0067] The incoherent thermal light beam 10 is evenly divided into a first light beam 11 and a second light beam 12 according to the light intensity by the non-polarizing beam splitter BS;
[0068] The optical path of the first light beam 11 is the first optical path,
[0069] The optical path of the second light beam 12 is the second optical path;
[0070] The components on the first optical path and the second optical path are symmetrically arranged;
[0071] Spatial light modulators are used to change the orbital angular momentum of photons; single-photon detec...
Embodiment 2
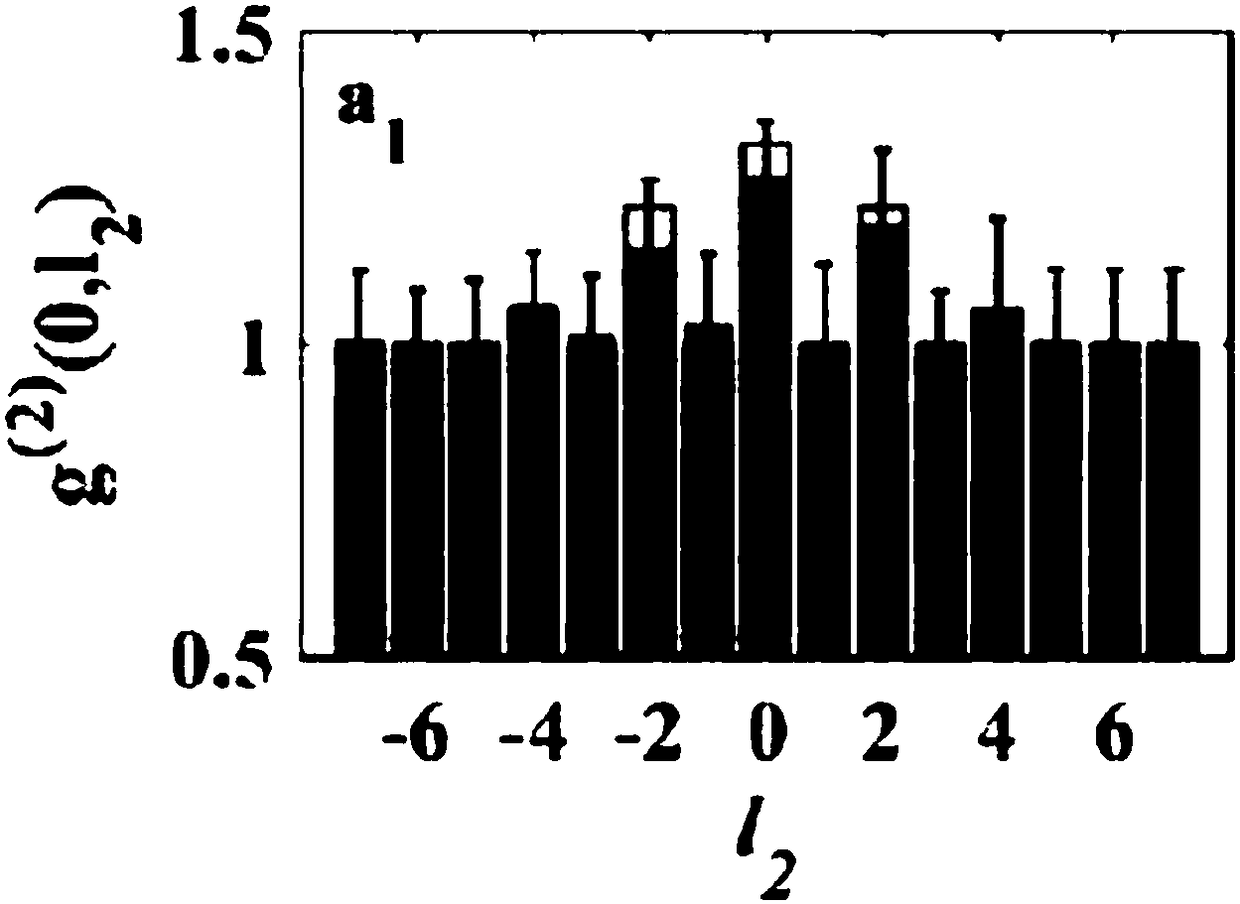
[0094] This embodiment provides a thermal-optical non-localized angle double-slit interference method using the above system, and the thermal-optical non-localized angle double-slit interference method includes the following steps:
[0095] S1. The incoherent thermal beam 10 is equally divided into a first beam 11 and a second beam 12;
[0096] S2. The first light beam 11 and the second light beam 12 respectively pass through the first light path and the second light path, wherein the first light path and the second light path are symmetrically arranged;
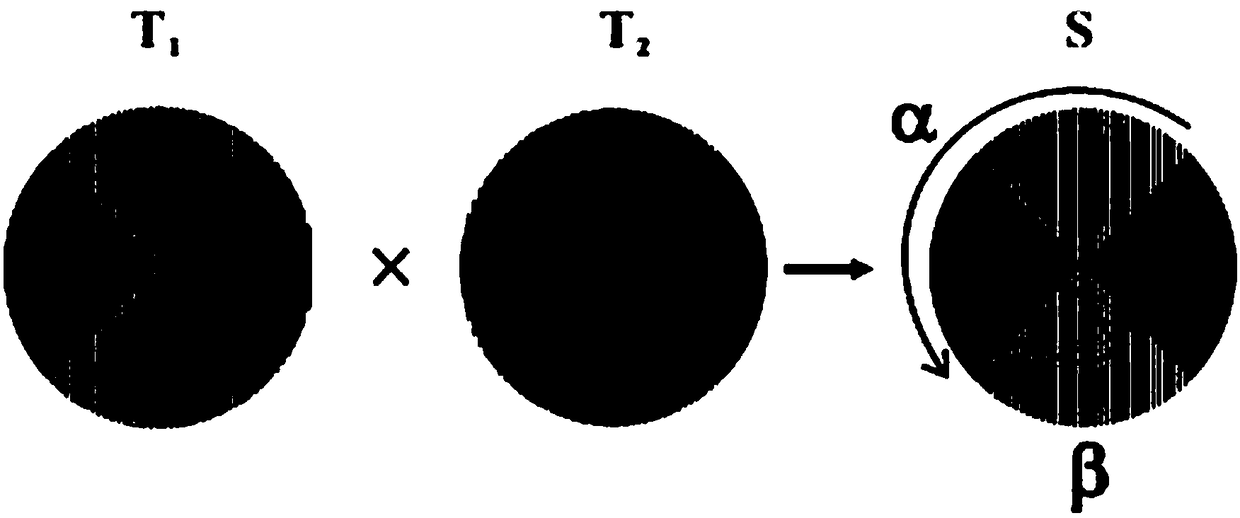
[0097] S3. Load different orbital angular momentum values to the first optical path and the second optical path by loading different fork patterns on the spatial light modulator SLM in the two optical paths;
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com