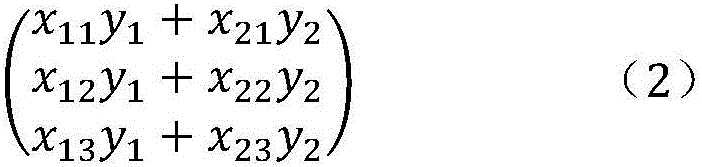FPGA-based real-time hyperspectral micrograph cell classification method
A hyperspectral image and microscopic image technology, applied in the field of biomedical images, can solve problems such as errors, lack of quantitative standards, misdiagnosis, missed diagnosis, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
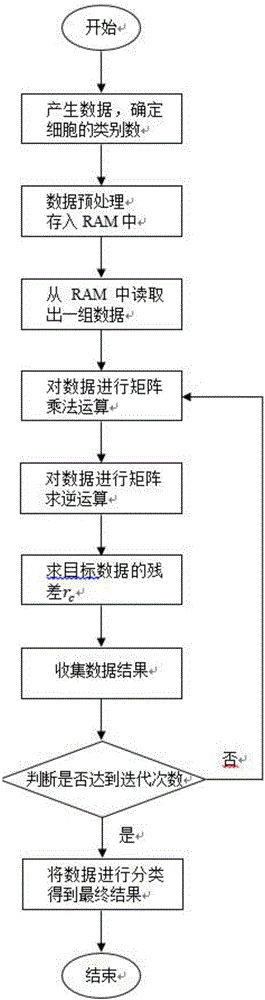
[0060] The basic flow of this method is as follows figure 1 As shown, a state machine is used on the FPGA, and the specific implementation will be introduced according to each state of the state machine.
[0061] 1) First convert the hyperspectral cell image data into a 16-bit binary unsigned number, input the first set of data in the hyperspectral cell image after this preprocessing into the FPGA chip, and convert all variables in the top-level file to Set to zero, this is the initial ready state.
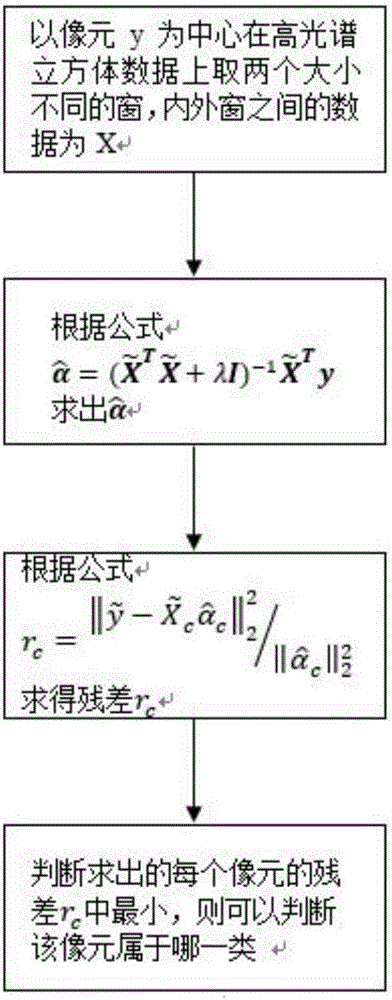
[0062] 2) Enter state=00 state, read data y and Through the multiplier IP core will as well as The part that needs to be multiplied in the operation is completed, because y and All are sixteen-bit data, after multiplication, and have become 32-bit data, and is thirty-two bits of data, so It is data of sixty-four bits.
[0063] 3) Enter state=01 state, will and Add up the multiplied components according to the formula, then complete and calculation, and too...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com