Method for predicting time sequence of number of people served by base stations based on space-time transfer probabilities of mobile phones
A technology of transition probability and mobile phone location, applied in the field of population forecasting, which can solve the problems of forecasting, the inability to guarantee the number of people in the study area, and the lack of consideration of the influence of spatial factors.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0015] In order to facilitate the understanding and implementation of the present invention by those of ordinary skill in the art, the present invention will be further described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the embodiments described herein are only used to illustrate and explain the present invention, but not to limit it. this invention.
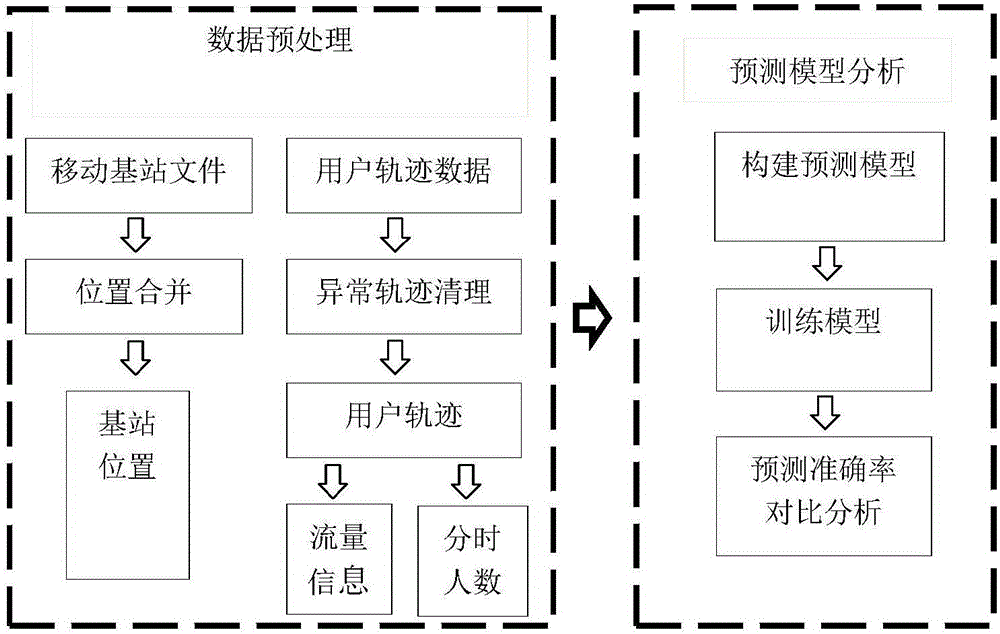
[0016] see figure 1 , the present invention provides a method for predicting the number of base station service numbers based on the time-space transition probability of mobile phone location, comprising the following steps:
[0017] Step 1: Calculate the total number of people in the service area of the mobile phone base station within the same time period by using the space-time trajectory data of the mobile phone;
[0018] Step 2: Use the time and space trajectory data of the mobile phone to divide the movement trajectory of the crowd, and calculate the numbe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com