LED wafer dead pixel picking sorting method
A technology of dead pixels and wafers, which is applied in the field of sorting LED wafers, can solve the problems of consuming sorting machine capacity, loss of qualified chips, large manpower and production time, etc., to improve the removal rate of dead pixels and The effect of success rate, capacity saving and manpower saving
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] In order to enable those skilled in the art to better understand the technical solutions of the present invention, the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with specific implementations shown in the accompanying drawings. However, these embodiments do not limit the present invention, and any structural, method, or functional changes made by those skilled in the art according to these embodiments are included in the protection scope of the present invention.
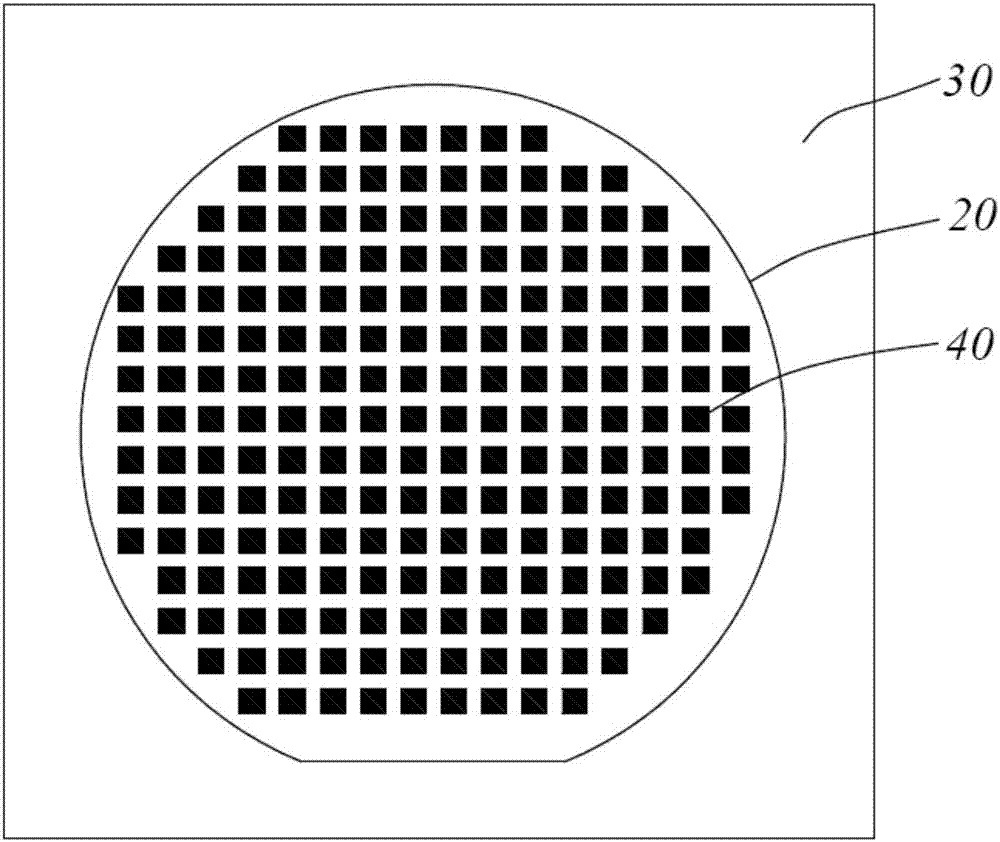
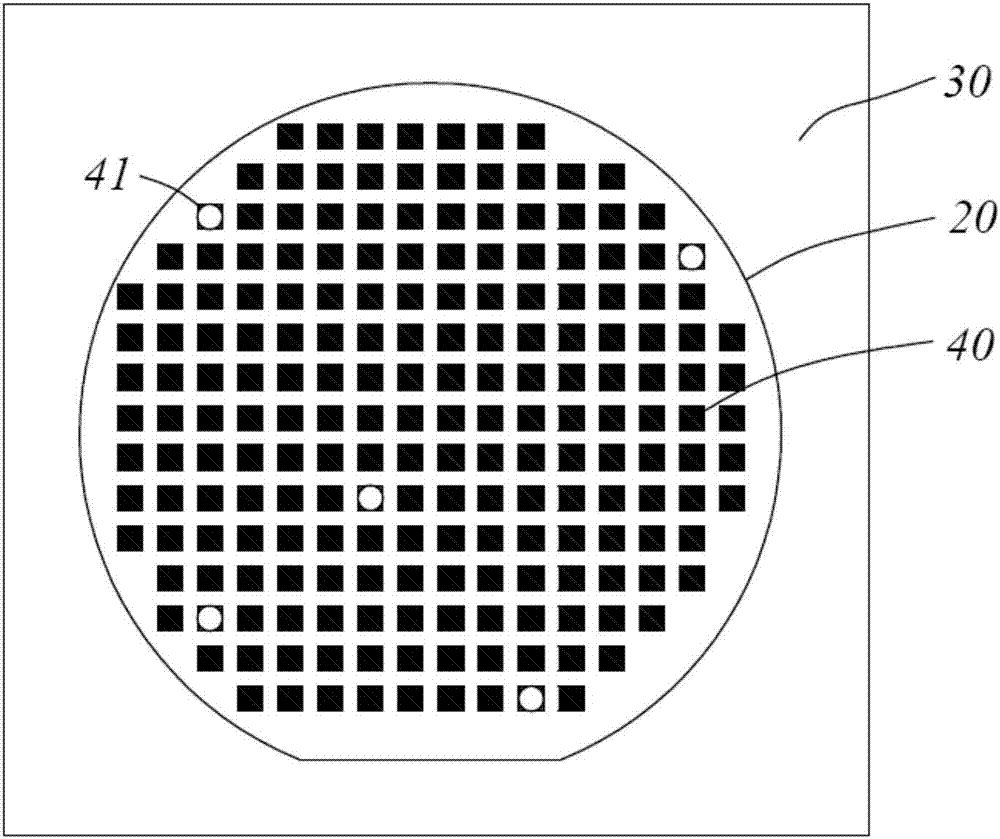
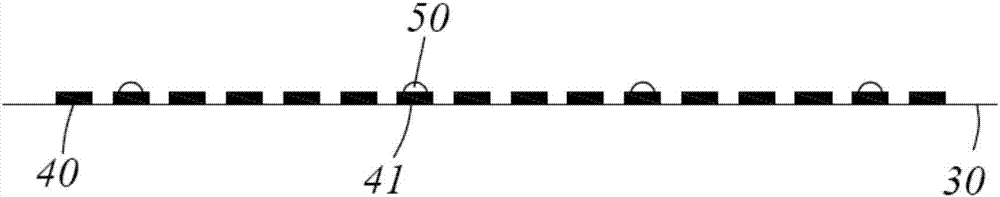
[0030] Preferred embodiments of the present invention, such as figure 1 As shown, a wafer 20 to be tested to pick out bad spots is provided. The wafer 20 here refers to a large wafer that has been cut, that is, a wafer (wafer). The wafer becomes a semiconductor grain after epitaxy and cutting. It is the most commonly used semiconductor material, divided into 4 inches, 5 inches, 6 inches, 8 inches, 12 inches, 14 inches, 15 inches, 16 inches, ... 20 inches and above according to its diam...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com