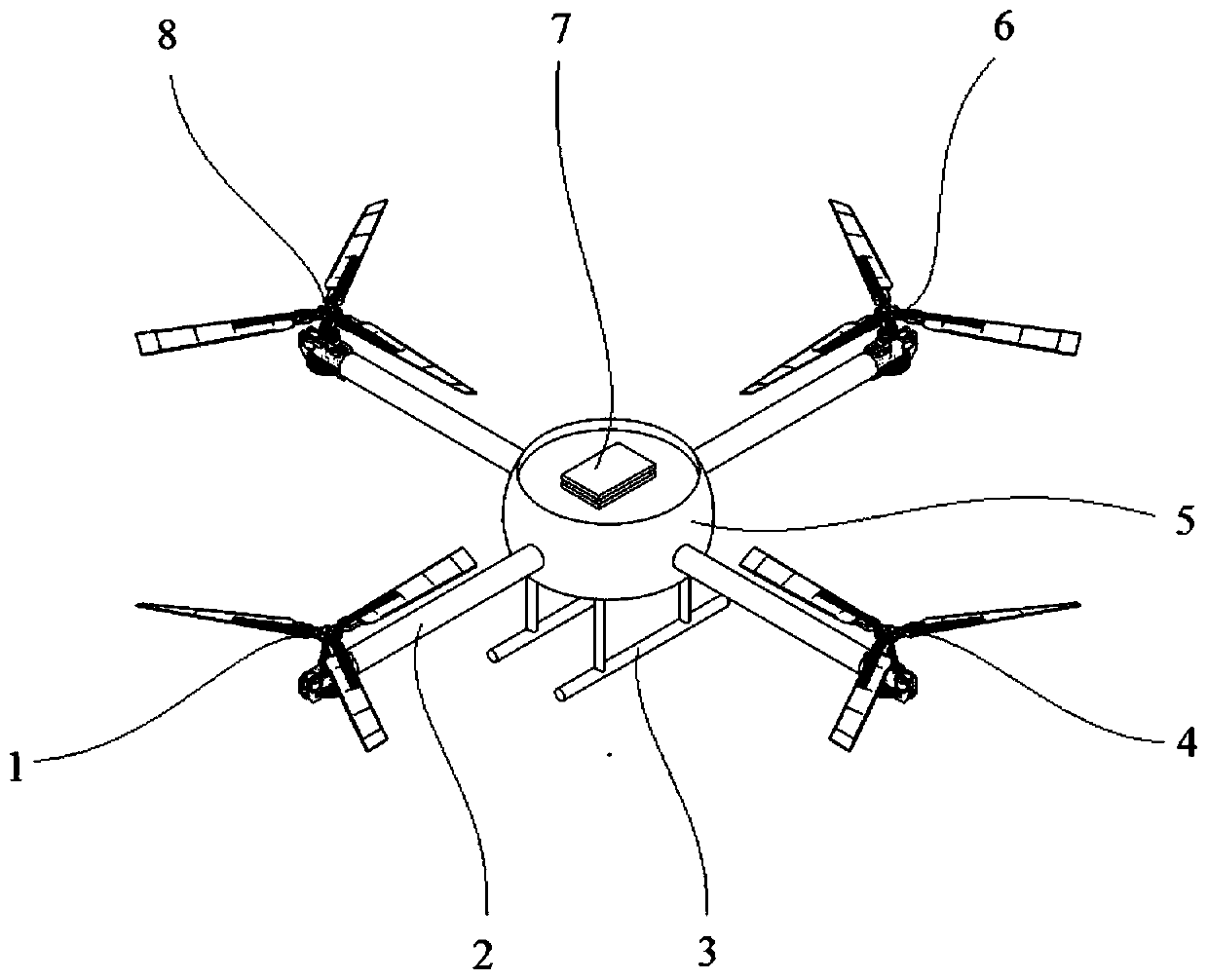
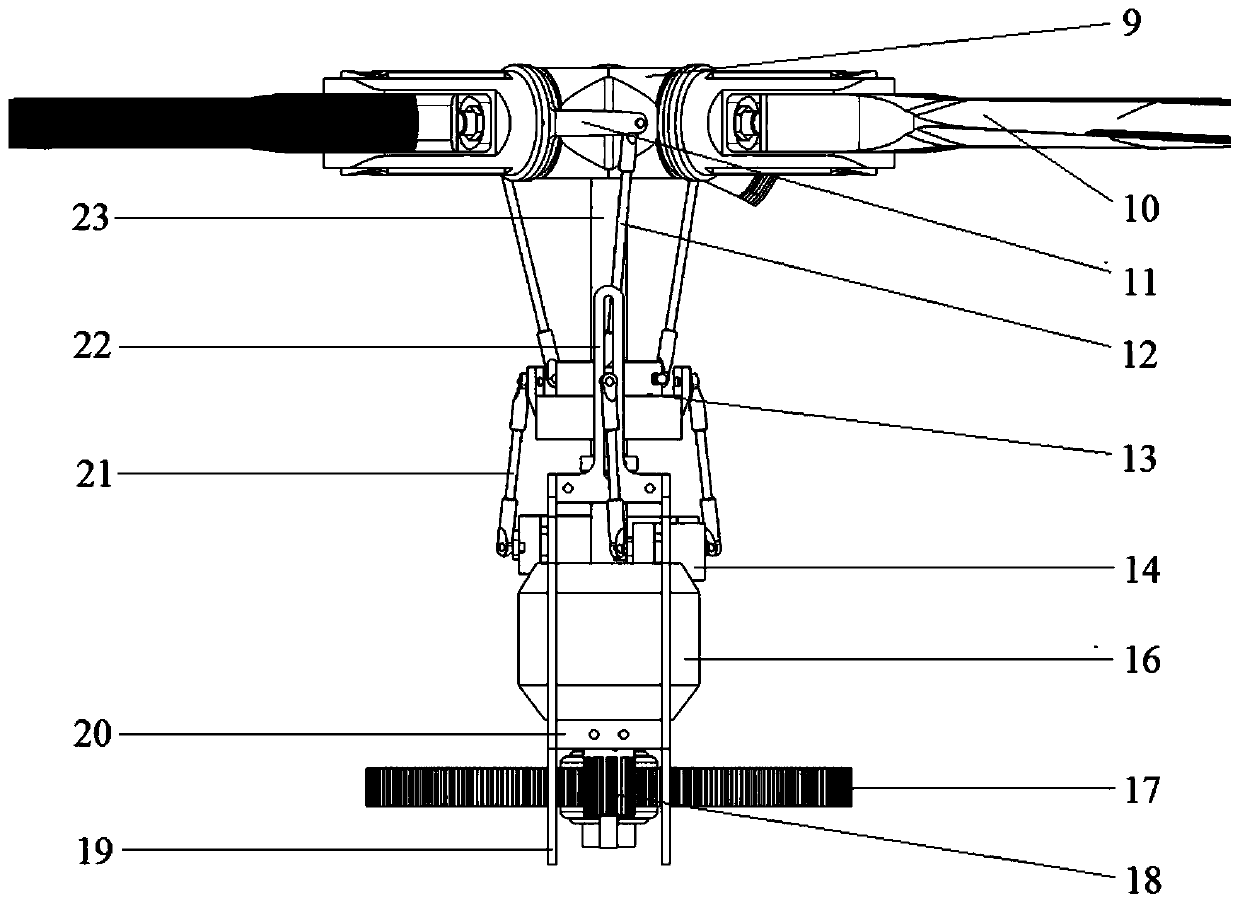
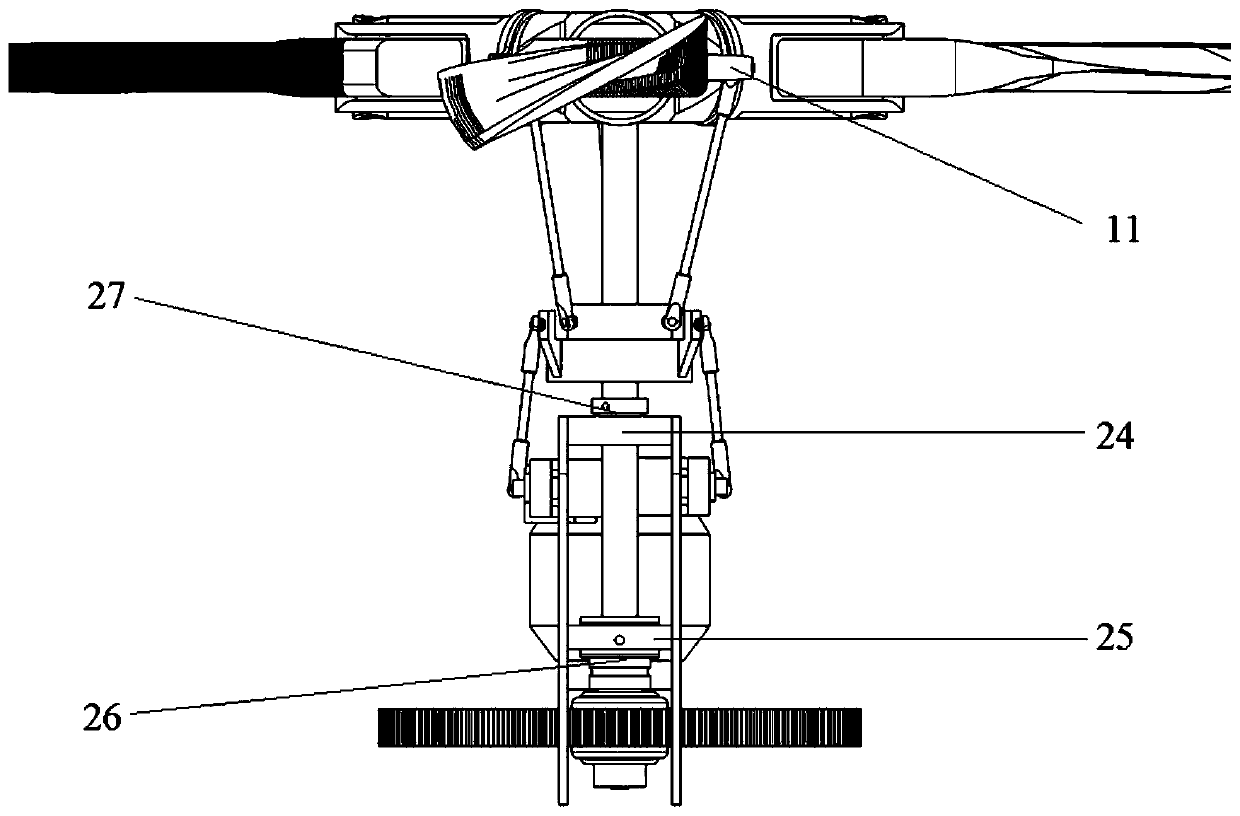
An independently controllable four-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle with six degrees of freedom in space and its control method
A technology of unmanned aerial vehicle and control method, which is applied in the field of six-degree-of-freedom decoupling control of multi-rotor aircraft, and can solve the problems of speed and attitude coupling, difficult to achieve effects, and increased structure.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0095] This embodiment introduces the implementation of vertical take-off, hovering at zero attitude angle, and vertical landing of the present invention.
[0096] Such as Image 6 As shown, the four rotors, including the front rotor, rear rotor, left rotor, and right rotor, can realize the vertical takeoff, zero attitude hovering and vertical landing of the aircraft through the synchronous control of the collective distance of the front and rear rotors and the synchronous control of the collective distance of the left and right rotors. , the specific process is: the aircraft is parked on the level ground or platform, and the motor 16 drives the four rotors to rotate after the power is turned on. The controller 7 receives the input of 6 channels of the aircraft, and the input of other channels is zero except for the up and down speed input. According to The multi-variable decoupling control algorithm with six degrees of freedom in space solves the control commands of 12 steeri...
Embodiment 2
[0099] This embodiment introduces the implementation of the present invention to fly forward at zero attitude angle.
[0100] On the basis of Embodiment 1, the aircraft reaches the zero-attitude hovering state, and the controller 7 receives 6 channel inputs of the aircraft. Except for the front and rear speed inputs, other channel inputs are all zero, and the 6-channel input is used as the flight state expectation value, according to The multi-variable decoupling control algorithm with six degrees of freedom in space calculates and obtains the control commands of all 12 steering gears and the speed commands of 4 motors under the expected value of the flight state, controls the rotation angle of the rocker arm 15 of the steering gear, and controls the rotation speed through the motor speed. The rotational speed of the rotor is to realize the desired control of the automatic tilter 13 on the rotor by the up and down pull rod, so as to realize the forward flight of the aircraft at...
Embodiment 3
[0102] This embodiment introduces the implementation of hovering at any attitude angle in the present invention.
[0103] On the basis of Embodiment 1, the aircraft reaches the zero-attitude hovering state, such as Figure 8 As shown, under the action of the controller 7, through the collective pitch differential control of the front and rear rotors and the collective pitch differential control of the left and right rotors, the pitching moment and rolling moment can be generated respectively for the center of gravity, and the fuselage 5 can realize the corresponding pitching, rolling, and rolling moments. Rolling action, at this time, cooperate with the synchronous control of the longitudinal periodical variable pitch of the front and rear rotors, and the synchronous control of the lateral periodical variable pitch of the left and right rotors, so that the pulling force of the rotor is always kept vertically upward, and the sum of the four pulling forces is equal to the gravity...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com