Scheduling information acquisition method, terminal and baseband chip
A technology for dispatching information and obtaining methods, which is applied in wireless communication, electrical components, network planning, etc., and can solve problems such as channel occupancy time not exceeding 10ms, data transmission interruption, and longer data sending and receiving time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
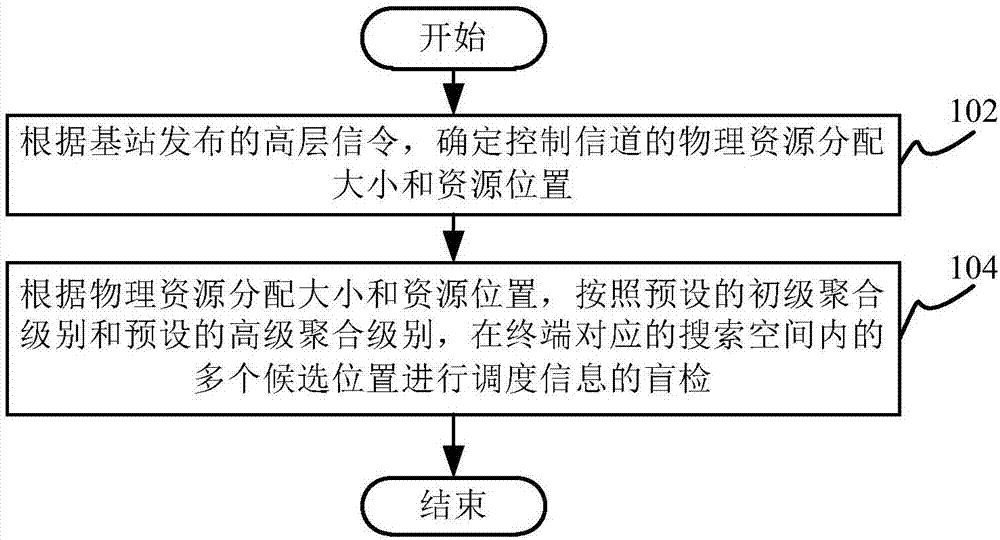
[0036] figure 1 A flow chart of a method for obtaining scheduling information according to an embodiment of the present invention is shown.
[0037] Such as figure 1 As shown, the methods for obtaining scheduling information include:
[0038] Step 102: Determine the physical resource allocation size and resource location of the control channel according to the high-level signaling issued by the base station.
[0039]On the basis of the original preset primary aggregation level, a new advanced aggregation level is added. Optionally, the preset primary aggregation level is {2, 4, 8, 16}, and the preset advanced aggregation level includes {24 , one or more of 32, 40, 48, 56, 64}. For example, the preset primary aggregation levels may be {2, 4, 8, 16}, and the preset advanced aggregation levels may be {24, 32, 40, 48, 56}.
[0040] Step 104, according to the physical resource allocation size and resource location, according to the preset primary aggregation level and the prese...
Embodiment 2
[0043] On the basis of the steps shown in Embodiment 1, the preset primary aggregation levels may also be {2, 4, 8, 16}, and the preset advanced aggregation levels may be {24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64}. When the acquired physical resource allocation size of the control channel is 2, 4, 8, or 16 PRBs (physical resource blocks, physical resource blocks), the number of possible candidate positions in the search space corresponding to the terminal is shown in Table 1 below.
[0044] Table 1
[0045] PRB L=2 L=4 L=8 L=16 L=32 L=24 L=48 L=56 L=64 2 4 2 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 8 4 2 1 0 0 0 0 0 8 6 4 2 1 1 0 0 0 0 16 0 0 6 4 2 3 1 1 1
[0046] Of course, the number of possible candidate positions in the search space corresponding to the terminal is not limited to the situation shown in Table 1, and the following Table 2 may also be implemented.
[0047] Table 2
[0048] PRB L=2 L=4 L=8 L=16 L=32 L=24 L=48...
Embodiment 3
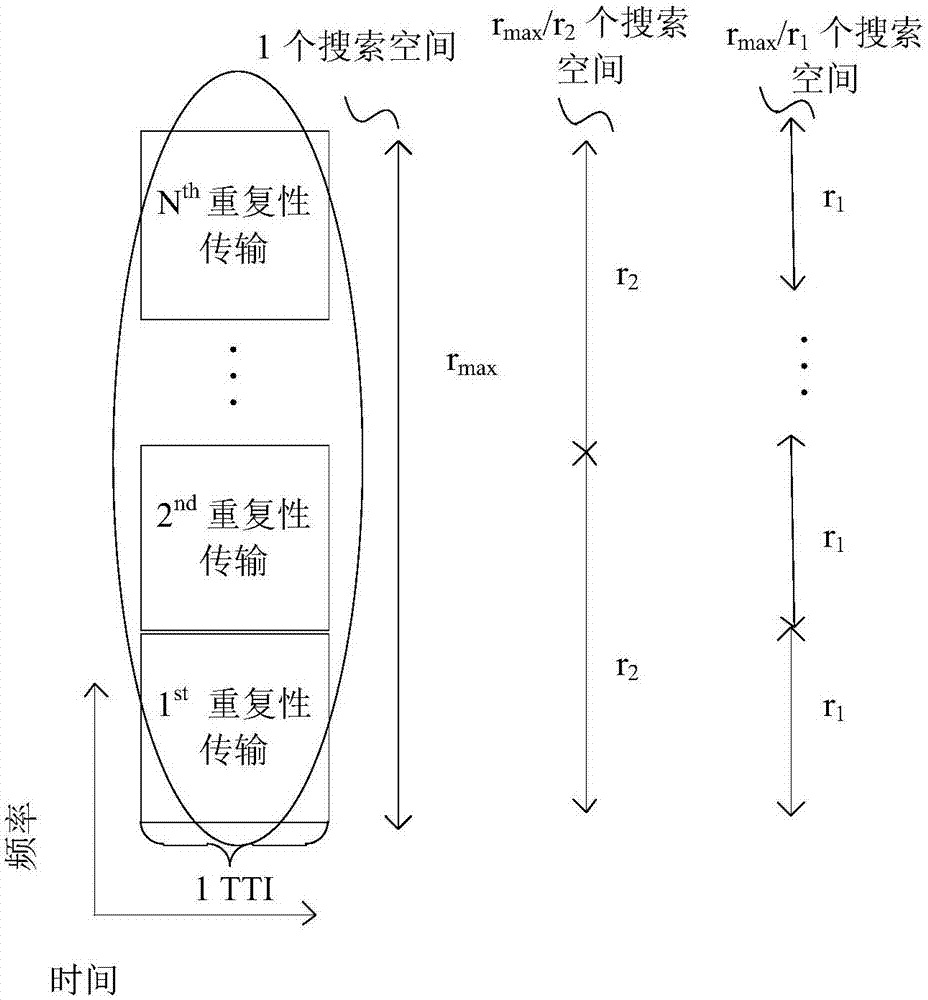
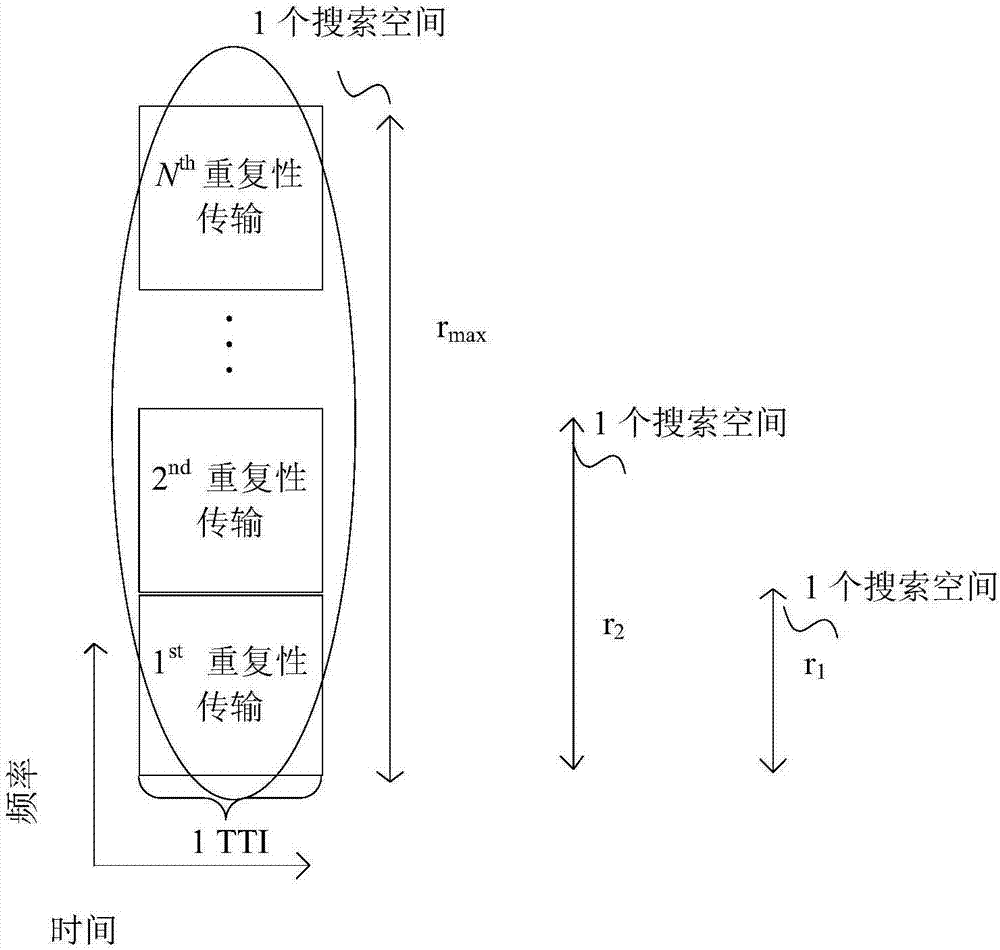
[0050] In an implementation manner of the present invention, all preset aggregation levels may be used to perform blind detection of scheduling information at each corresponding candidate position, so as to ensure effective detection of scheduling information and avoid missed detection. In one embodiment, the possible number of repeated transmissions {r 1 , r 2 ,...,r N}, where r 1 2 N , the base station can configure the maximum number of repeated transmissions r of the control channel in each TTI max , when the user blindly checks the scheduling information, select no greater than r max Blind detection is performed in different corresponding search spaces for all possible repeated transmission times.
[0051] Such as figure 2 As shown, for r 1 , corresponding to r max / r 1 search spaces, and each search space repeatedly transmits r 1 Second-rate. Here, r max With base station configuration, it can be {r 1 , r 2 ,...,r N} one of the values.
[0052] In the se...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com