Light-emitting diode chip having temperature compensation of the wavelength
一种芯片、温度变化的技术,应用在电气元件、电路、半导体器件等方向,能够解决温度影响改变色彩印象、亮度减小、敏感度降低等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
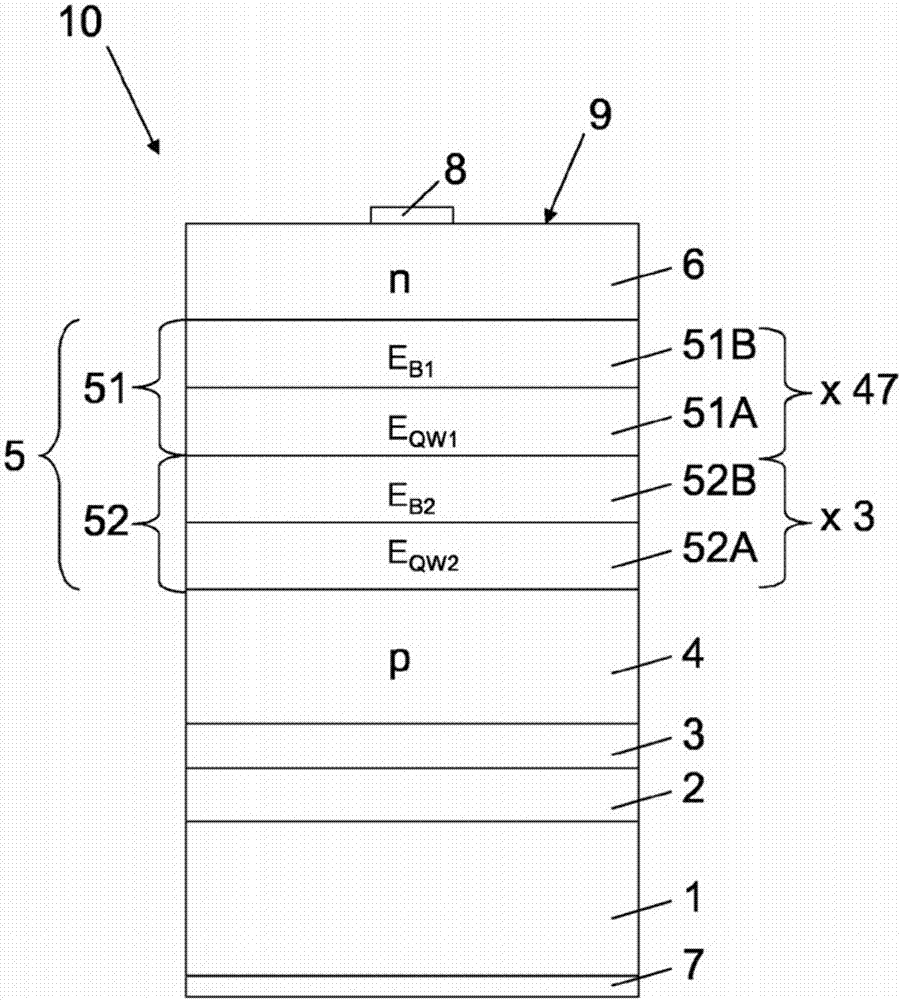
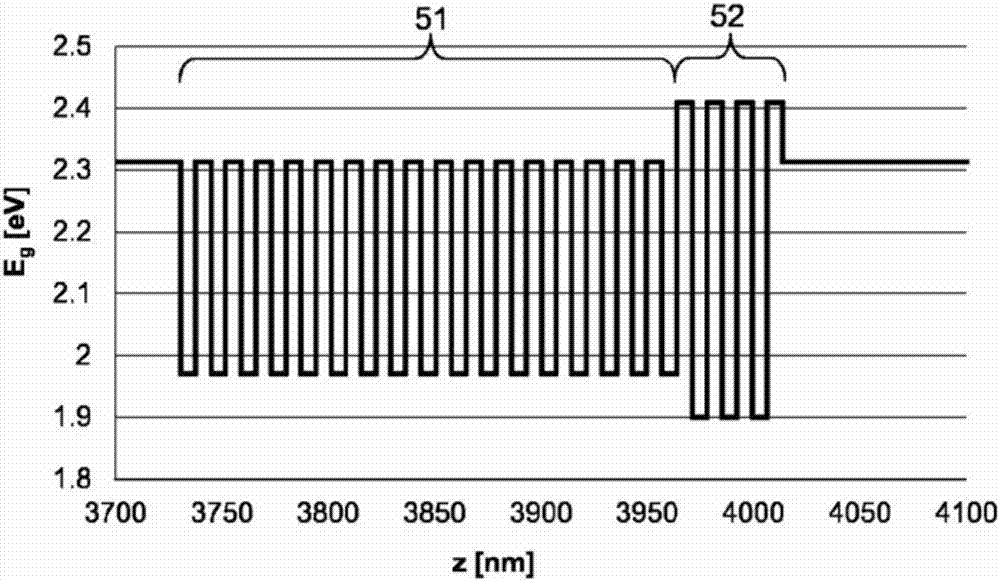
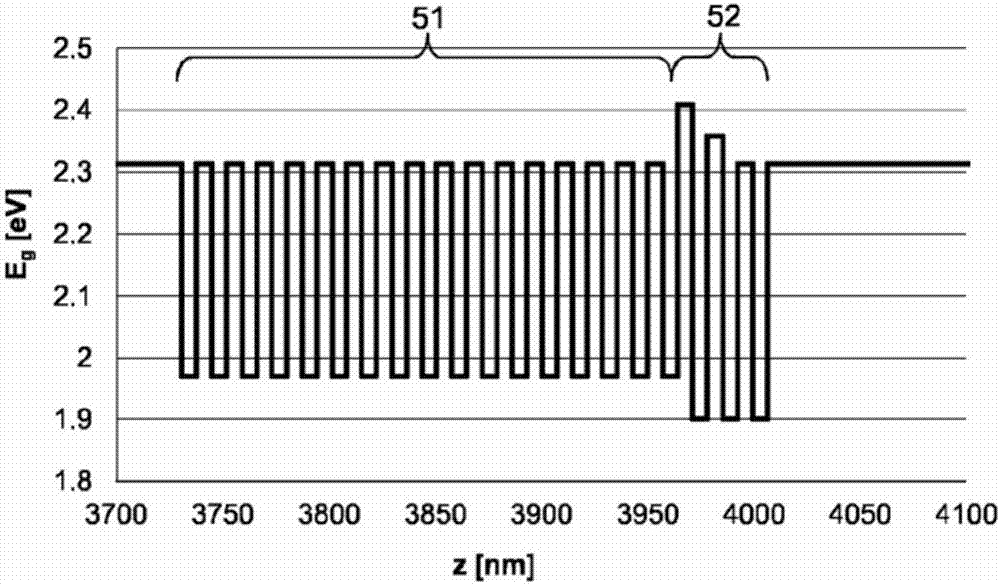
[0028] exist figure 1The optoelectronic semiconductor chip 10 according to one embodiment shown in is an LED chip with a p-type semiconductor region 4, an n-type semiconductor region 6 and a An active layer 5 suitable for emitting radiation. This embodiment of the optoelectronic semiconductor chip is a so-called thin-film semiconductor chip from which the growth substrate initially used for the epitaxial growth of the semiconductor layers 4 , 5 , 6 is peeled off and the semiconductor layer sequence is instead deposited by means of The connection layer 2 , in particular the solder layer, is connected to a carrier substrate 1 different from the growth substrate.
[0029] In such a thin-film light-emitting diode chip 10 , the p-type semiconductor region 4 generally faces the carrier substrate 1 . A mirror layer 3 is advantageously arranged between the p-type semiconductor region 4 and the carrier substrate 1 , which advantageously deflects radiation emitted in the direction of...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap