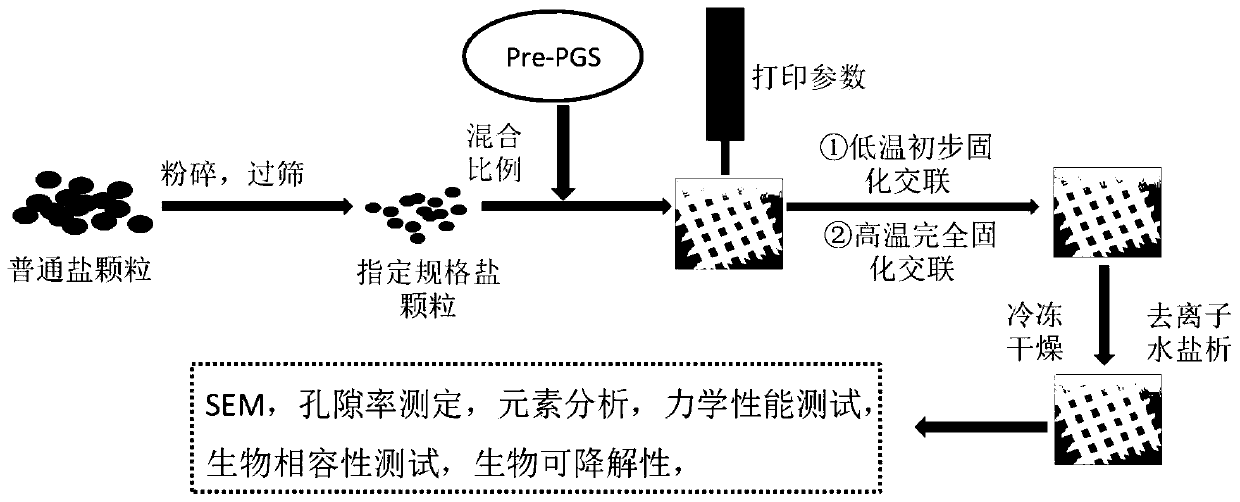
A preparation method of a thermosetting elastomer tissue engineering scaffold with a multi-level pore structure
A tissue engineering scaffold and pore structure technology, applied in tissue regeneration, prosthesis, additive processing, etc., can solve the problems of destroying the original structure, no FDM printing PGS elastomer scaffold, and inability to process PGS elastomer, etc., to achieve The effect of simple method and good application prospect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] 1. Printing material preparation
[0037] The mixing parameters of PGS prepolymer (Pre-PGS) and salt particles directly determine the extrudability, initial shape stability, high-temperature curing shape retention and pore structure of the scaffold during printing, which indirectly determine the performance of the scaffold. Including mechanical properties and biodegradability. The parameters that need to be studied in the mixing process include the mixing method, the mixing ratio and the diameter of the salt particles.
[0038] 1.1 Mixing method
[0039] Pre-PGS is viscous and has a high viscosity at room temperature. As the proportion of mixed salt increases, the viscosity of the mixture gradually increases, which is easy to cause uneven mixing. Therefore, it is necessary to consider reducing the viscosity of the mixture. There are two commonly used methods to reduce viscosity: solvent method and heating method. Therefore, two methods are used to mix materials, and ...
Embodiment 2
[0118] Prepare the PCLU stent, the method is the same as in Example 1. Using polycaprolactone diol and HDI trimer as raw materials, mixed with salt particles, printed and then solidified, the prepolymer synthesis step is omitted, and the raw material unit is reacted and solidified under heating conditions on the 3D formed structure.
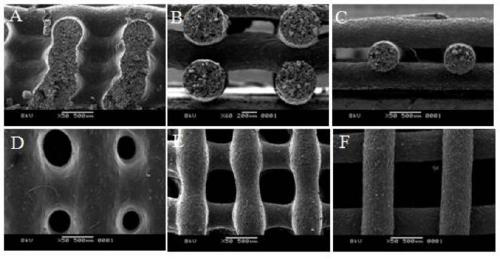
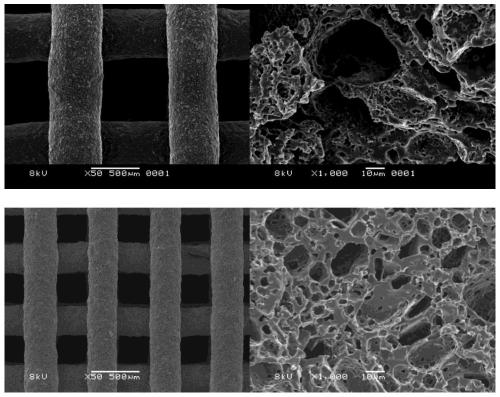
[0119] Such as Figure 11 As shown, this method is also suitable for the printing and molding of PCLU, which can prepare bioscaffolds and other irregular shapes. This thermosetting PCLU is also an elastic body, which can still recover quickly after repeated folding (a-d). The electron microscopy test of the scaffold shows that the fiber units are clearly and regularly arranged and stacked, the fiber cross-section is circular, no obvious fiber collapse is found, and it has good curing shape retention. At the same time, there are a large number of micropores distributed on the surface and inside of the fiber. The whole has a multi-level pore struc...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com