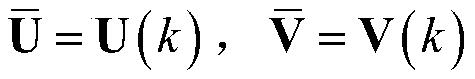A Low Complexity Robust Subspace Estimation Method
A space estimation, low-complexity technique, applied in the field of robust subspace estimation, capable of solving low-complexity problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
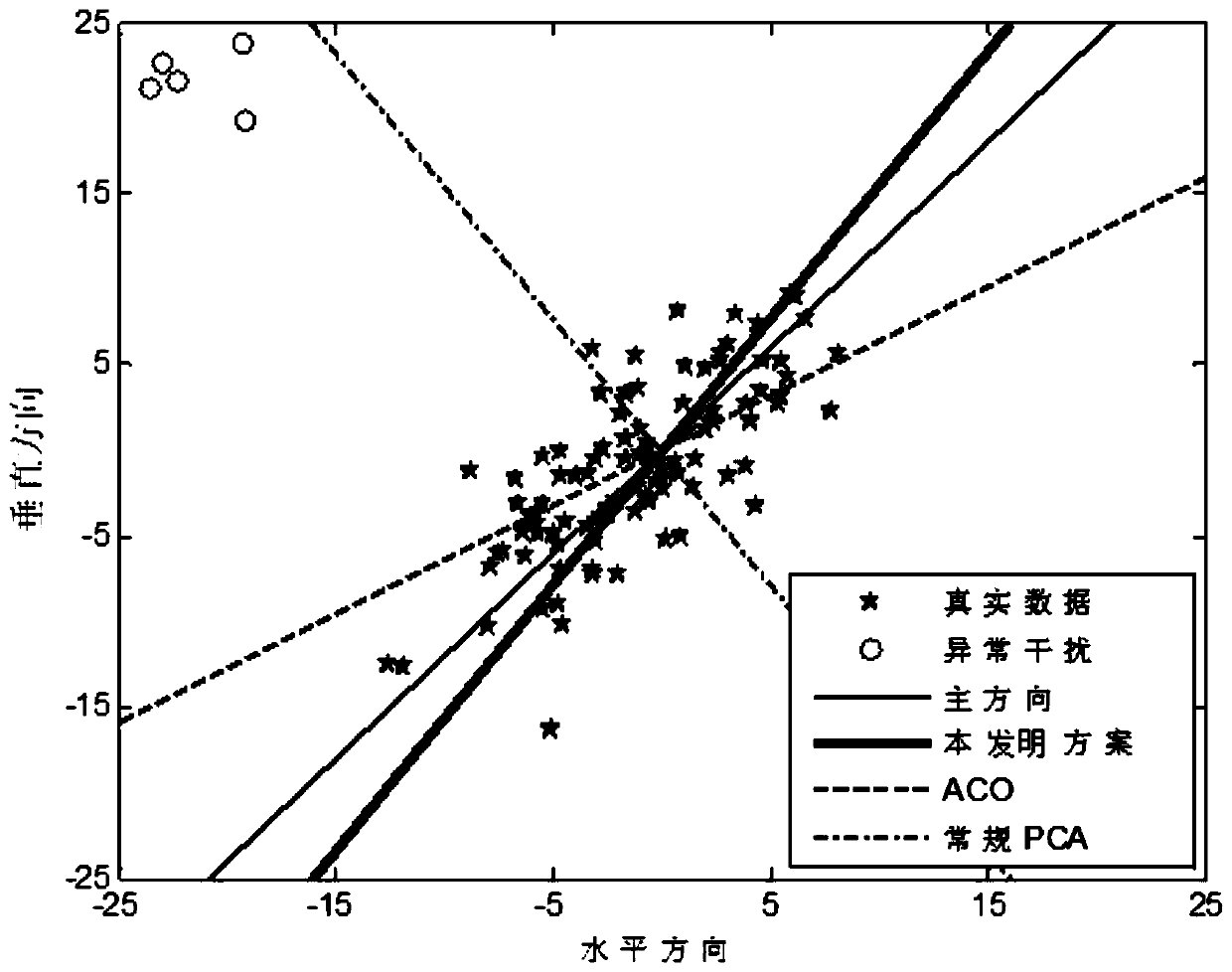
[0056] Example 1 The following uses robust (real number) data dimensionality reduction as an example to elaborate on the specific application of the robust subspace method proposed in the present invention. First, we generate 150 two-dimensional real data samples (Such as figure 1 The five-pointed star in), and obey the following Gaussian distribution:
[0057]
[0058] among them, Represents normal distribution, 0 2 (2-dimensional column vector) is the mean value, Indicates its variance. At the same time, 5 abnormal data points are generated, o 1 ,...,O 5 ,Such as figure 1 The circle point in the upper left corner. At the same time, 5 random abnormal data points obey the following Gaussian distribution:
[0059]
[0060] In this example, define Y in Algorithm 1 as At the same time, let ε=1, γ=0.5, and p=1. The initialization of U(0) and V(0) are the results obtained by conventional PCA (Singular Value Decomposition) respectively, and suppose the maximum number of iteration...
example 2
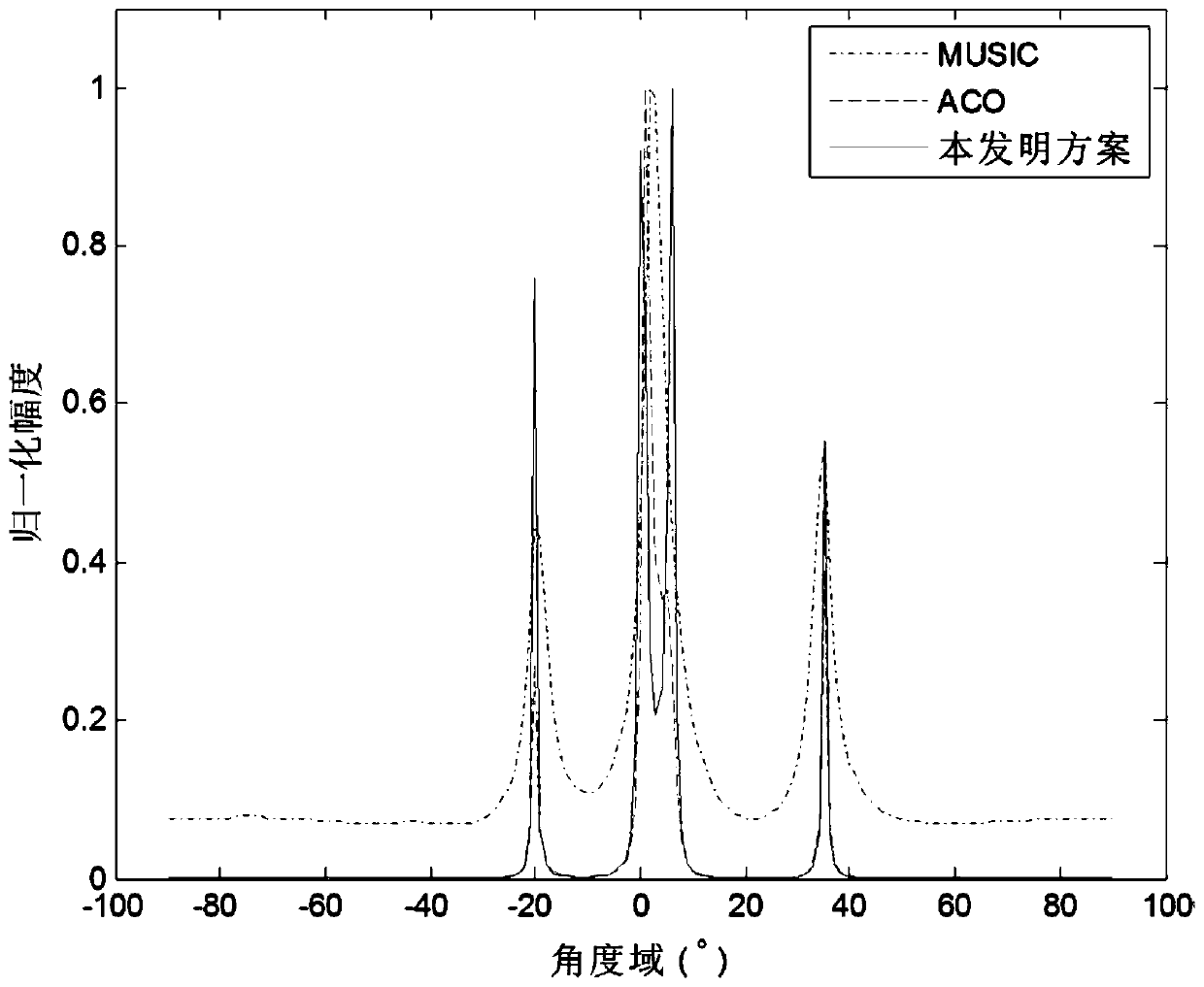
[0061] Example 2 The following describes the application of the solution of the present invention in the positioning of the source of the sensor array. Suppose K direction of arrival angles are θ=[θ 1 ,...,θ K ]'S narrowband source is located at M(M> K) far field of uniform linear array (ULA) structure, then the receiving signal model of N snapshot arrays is
[0062] x(t)=A(θ)s(t)+n(t), t=1,...,N
[0063] In the formula, s(t) is the zero mean signal vector, Is the array flow pattern vector, a(θ k ) Is an M-dimensional column vector and its elements are m=1,...,M,θ k Ε(-π / 2,π / 2), λ and d respectively represent the signal wavelength and the distance between array elements. In this case, set the number of antennas M=8, the number of sources K=4, the number of snapshots N=100, and the source position θ=[-20°,0°,6°,35°] T , And d=λ / 2; the superimposed noise is Gaussian mixed impulse noise, and the signal-to-noise ratio is -5dB. In order to make the solution of the present invention s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com