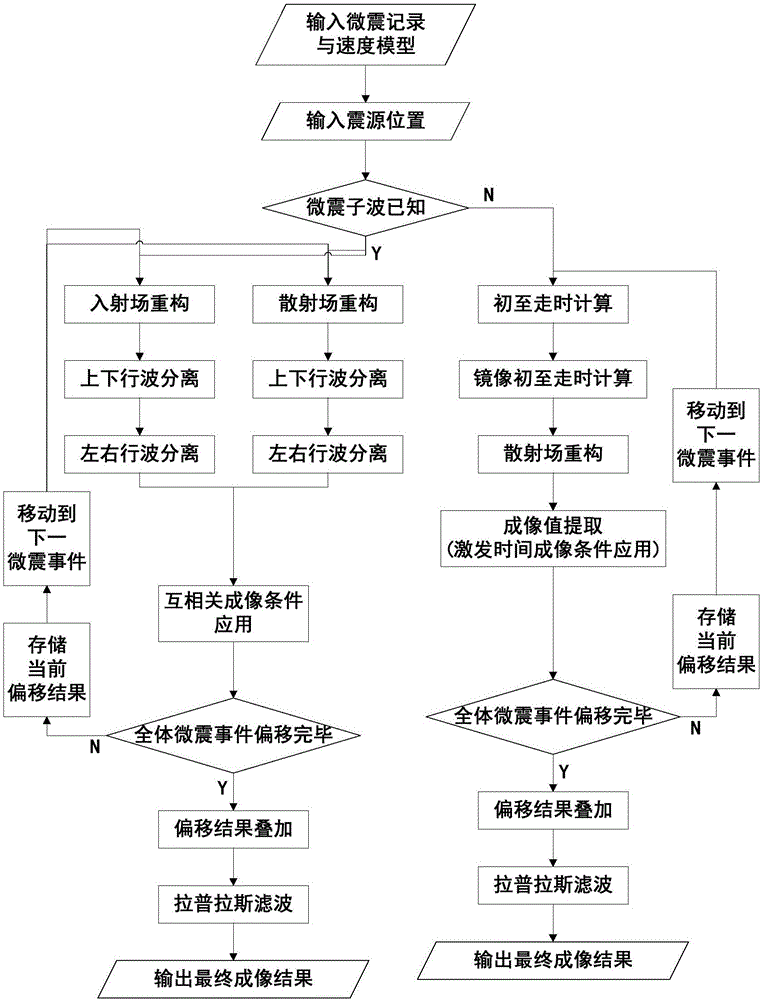
Method for recording subsurface structure and directly imaging by utilizing micro-earthquake
A technology of underground structure and recording pair, applied in seismology, geophysical measurement, seismic signal processing, etc., can solve the problem of poor deep imaging effect, and achieve the effect of improving imaging effect, accurate incident field, and saving computing time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0093] A. Input microseismic records and underground velocity models;
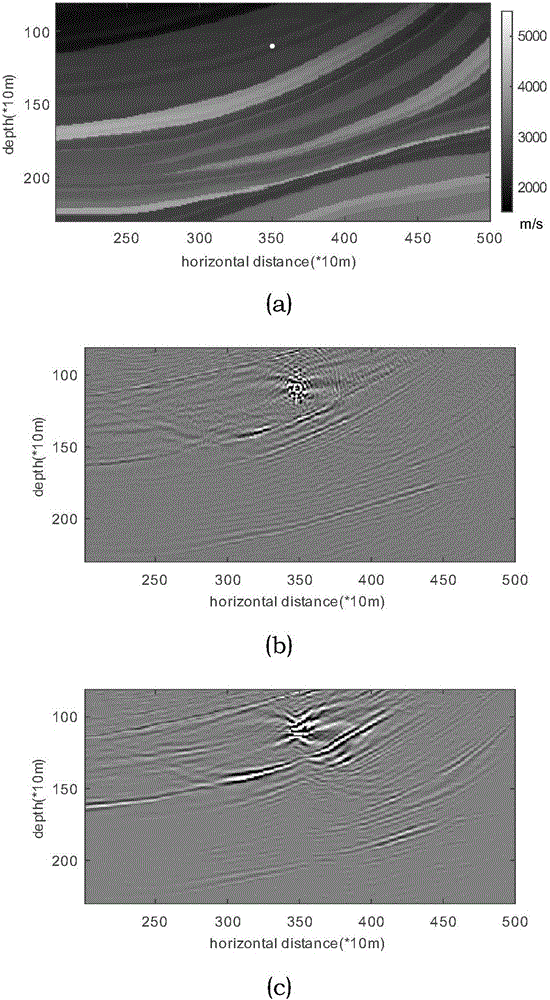
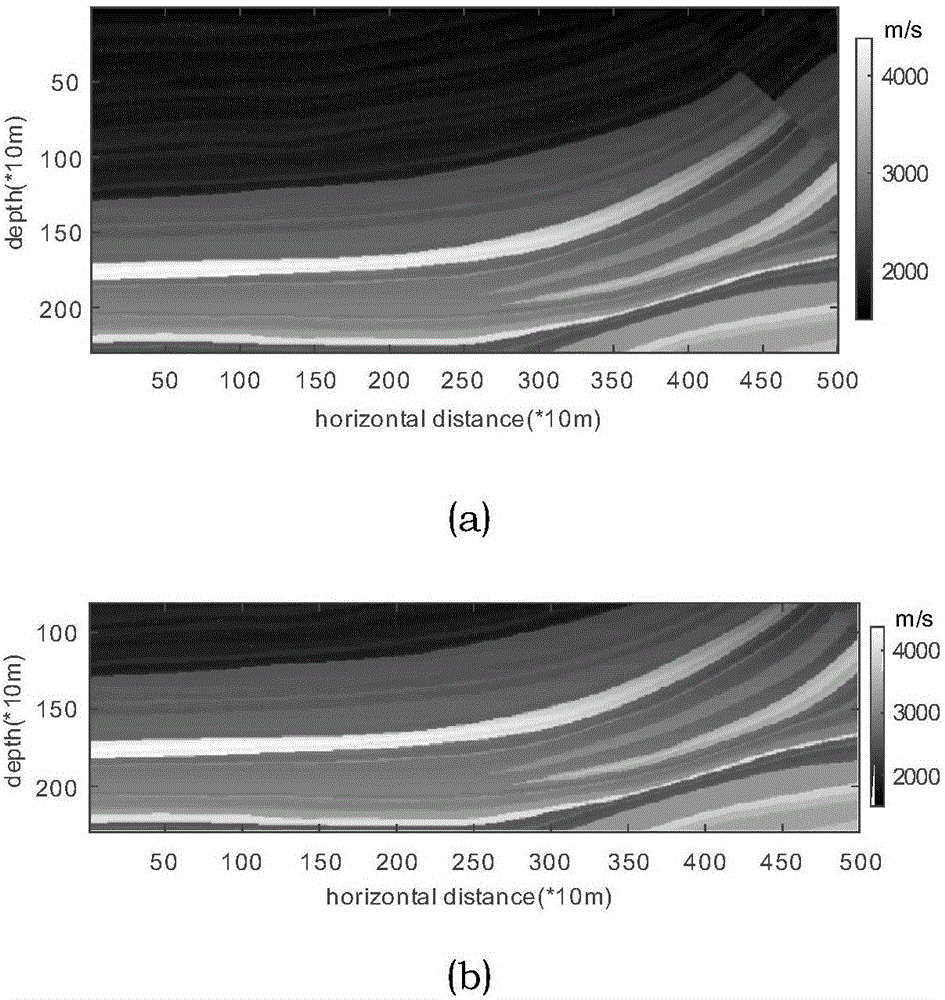
[0094] The method is verified by numerical experiments. Various parameters such as the model and observation system used are as follows: forward velocity model and migration velocity model such as image 3 As shown in (a), it is a relatively gentle part of the interface in the Marmousi model; the model size is 230*500, the grid spacing is 10m, 250 receiver points are evenly distributed on the surface at a spacing of 20m, and the time sampling interval is 1ms. The wavelets of the events all adopt the 30Hz Reck wavelet. Set the microseismic position, excitation time and wavelet as known quantities, that is, this example tests the cross-correlation imaging condition;
[0095] B. Input the source location;
[0096] Since this method only regards the imaging results below the seismic source as valid information, the seismic source location of the example is set in the shallow part of the ground, specifically...
Embodiment 2
[0109] a. Input microseismic records and underground velocity models;
[0110] The method is verified by numerical experiments. Various parameters such as the model and observation system used are as follows: forward velocity model and migration velocity model such as image 3 As shown in (a), it is a relatively gentle part of the interface in the Marmousi model; the model size is 230*500, the grid spacing is 10m, 250 receiver points are evenly distributed on the surface at a distance of 20m, and the time sampling interval is 1ms. The wavelets of the events all adopt the 30Hz Reck wavelet. The position and excitation time of microseisms are set as known quantities, while the wavelet is an unknown quantity, that is, the imaging conditions of excitation time are tested in this example;
[0111] b. Input the source location;
[0112] Since this method only regards the imaging results below the seismic source as valid information, the seismic source location of the example is s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com