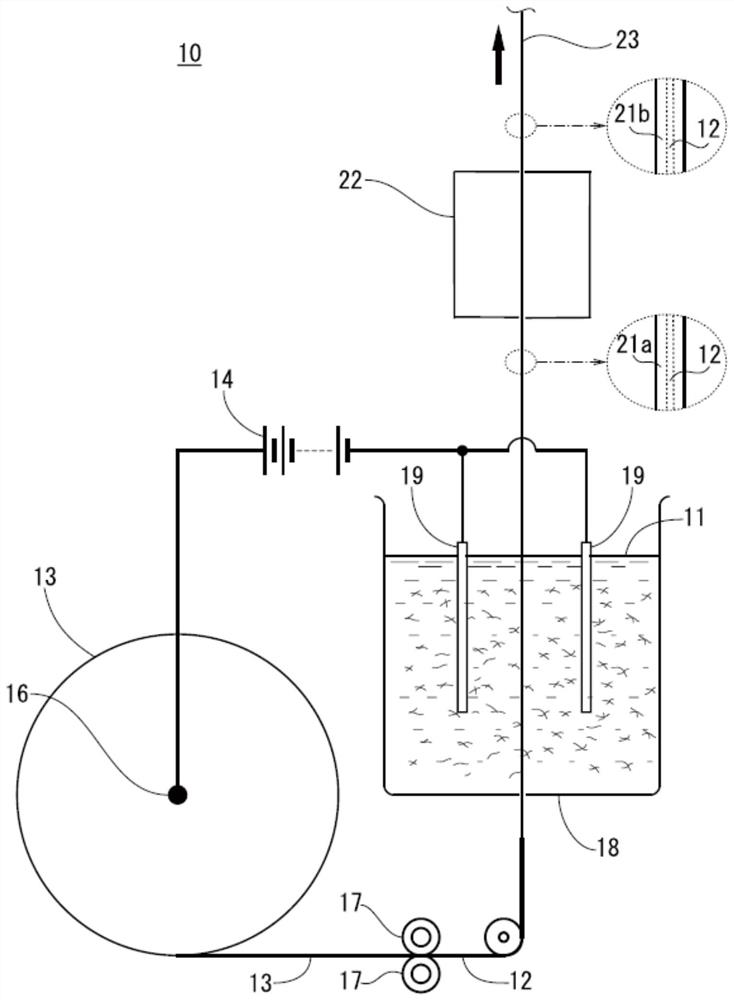
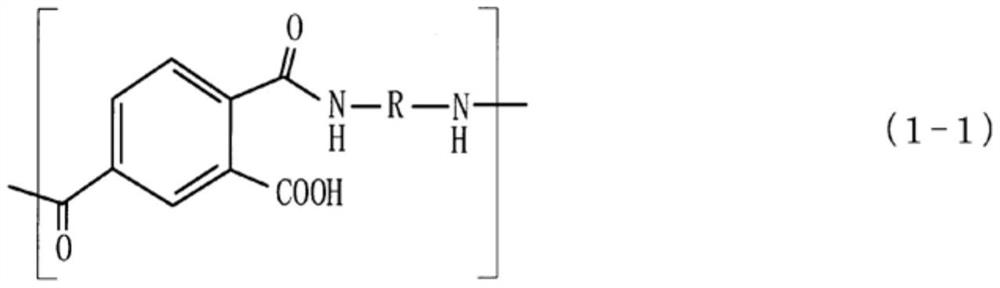
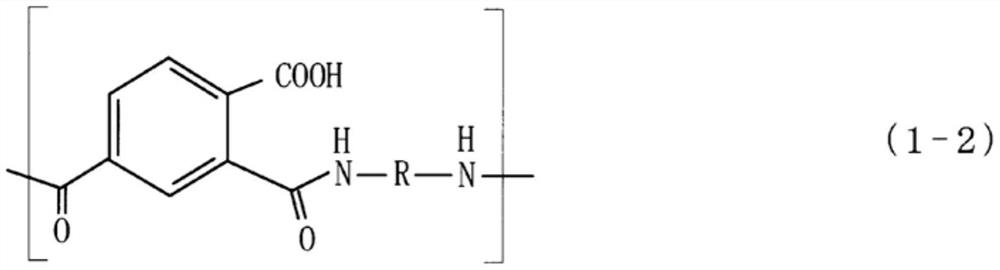
Electrodeposition solution for forming water-dispersed insulating film
An insulating coating and electrodeposition technology, applied in the direction of electrophoretic plating, electrophoretic coating, electrolytic coating, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient stability of dispersion, reduce the quality of electrodeposition resin, and deteriorate the productivity of insulating materials, etc., to achieve excellent dispersion performance, suppression of productivity decline, and improvement of dispersibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0111] Next, examples of the present invention will be described in detail together with comparative examples.
[0112]
[0113] First, 3.00 g (15 mmol) of 4,4'-diaminodiphenyl ether, 3.00 g (15 mmol) of N,N-dimethyl 45 g of acetamide (DMAc) was stirred and dissolved. Next, 3.16 g (15 mmol) of chlorinated trimellitic anhydride and 15 g of DMAc were added to the above-mentioned flask, and the contents of the above-mentioned flask were stirred at room temperature (25° C.) for 6 hours under an argon atmosphere to allow the reaction to proceed. Thus, a first reaction mixture liquid was prepared.
[0114] Then, 0.32 g (1.5 mmol) of chlorinated trimellitic anhydride was added to the first reaction liquid mixture in the above-mentioned flask, and the reaction was further stirred for 1 hour to prepare a second reaction liquid mixture.
[0115] Next, water and alcohol were put into a beaker at a mass ratio of 3:1, and vigorously stirred to prepare a mixed solution. In 800 ml of th...
Embodiment 2
[0120] An electrodeposition liquid was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the addition amount of 2-aminoethanol was 0.015 g. And, using this electrodeposition solution, an insulator was produced by the same method and conditions as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0122] An electrodeposition liquid was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the addition amount of 2-aminoethanol was 0.005 g. And, using this electrodeposition solution, an insulator was produced by the same method and conditions as in Example 1.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com