Intelligent electric meter
A smart meter and electricity technology, applied in payment circuits, measurement of electrical variables, data processing applications, etc., can solve the problems that transactions and records cannot be adapted, and cannot be divided into distributed wind power photovoltaic and battery power collection.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
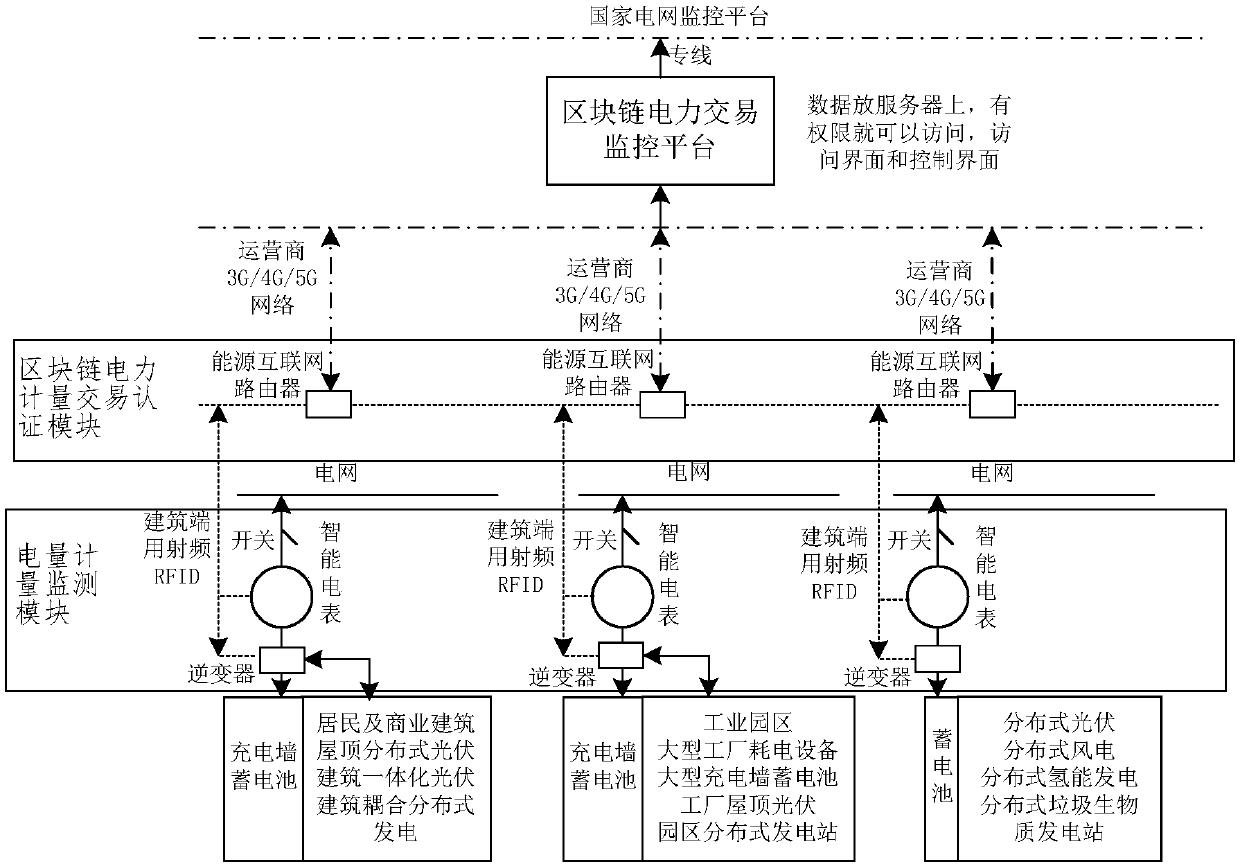
[0038] figure 1is the position of the smart meter provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention in the framework of the blockchain power transaction monitoring platform.
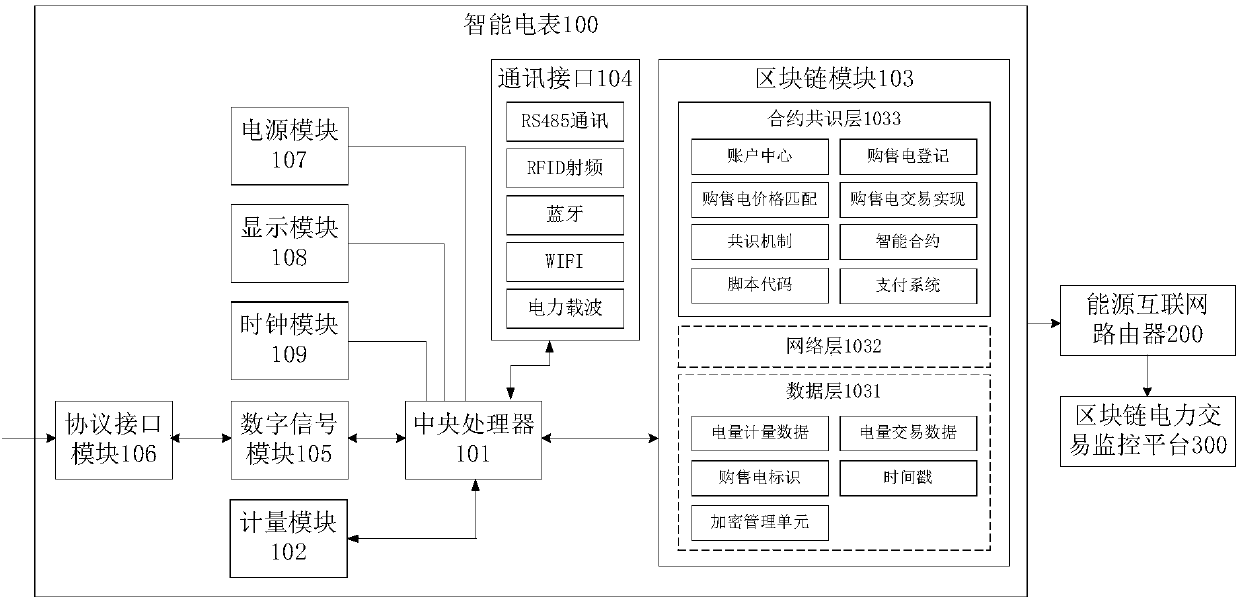
[0039] figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the composition of the smart meter provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention and its connection with the blockchain power transaction monitoring platform.
[0040] Please refer to figure 1 , figure 2 , the present invention provides a smart meter 100 , specifically an energy block chain meter, including: a central processing unit 101 , a metering module 102 and a block chain module 103 .
[0041] The central processing unit 101 is used for processing and computing data in the smart meter 100 and controlling data exchange.
[0042] The metering module 102 is connected with the central processing unit 101 and is used for two-way metering of electricity. The two-way metering here refers to the two-way metering of distributed power generation and st...
Embodiment 2
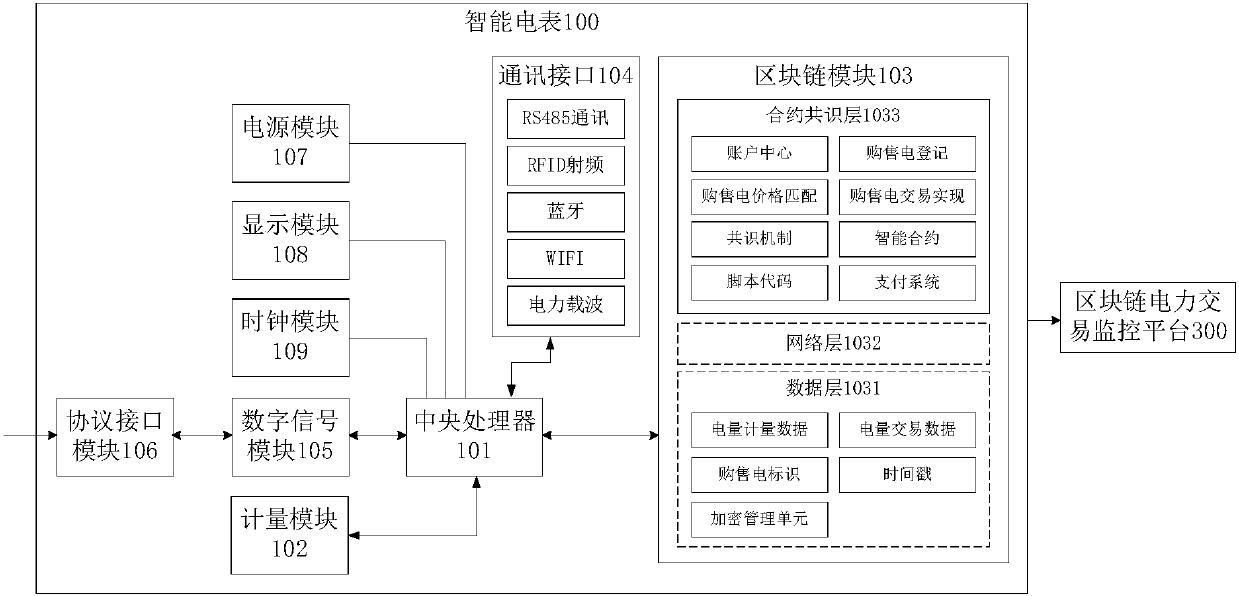
[0069] image 3 It is a schematic diagram of the composition of the smart meter provided by Embodiment 2 of the present invention and its connection with the blockchain power transaction monitoring platform.
[0070] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the smart meter 100 in this embodiment directly transmits data to the block chain power transaction monitoring platform 300 without relaying through the energy Internet router 200, which improves the transmission speed. Saves transaction time.
[0071] The structure, composition and connection relationship of the smart meter 100 in this embodiment are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
Embodiment 3
[0073] Figure 4 It is a composition diagram of the smart meter provided by Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
[0074] Please refer to Figure 4 The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 is that, in this embodiment, the smart meter 100 further includes a positioning module 110, which is connected to the central processing unit 101, and is used to perform geographical location of the smart meter 100. positioning.
[0075] The geographical location of the smart meter 100 is positioned by the positioning module 110 to obtain the geographical location information of the blockchain nodes, which realizes the geographic location informationization of the entire smart grid, thereby laying the foundation for the optimal rationalization of the blockchain point-to-point automatic power transaction. The basis, that is, in the blockchain smart contract, it can be stipulated that in the case of the same quotation, the power transaction between the two n...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com